- Set up CUPS printer server on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to install CUPS on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to set up CUPS on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to use CUPS printer server on Ubuntu 22.04
- Conclusion
- Linux cups tutorial for beginners
- CUPS web interface
- Add a printer in CUPS
- CUPS commands
- Controlling the CUPS service
- Conclusion
- Related Linux Tutorials:
- NEWSLETTER
- WRITE FOR US
- TAGS
- FEATURED TUTORIALS
- LATEST TUTORIALS
Set up CUPS printer server on Ubuntu 22.04
A printer server acts as a bridge between the end-users and the printers. A printer server software is installed on the network server and the printing facility can be available on the whole network.
CUPS (Common UNIX Printing System) is a widely used printing system for Linux-based operating systems. The Linux system equipped with CUPS acts as a printing server and multiple clients can put their requests to that server.
Keeping in view the importance of CUPS, this post provides the following learning outcomes.
How to install CUPS on Ubuntu 22.04
CUPS printer server is available on the official Ubuntu repository. By default, the Ubuntu 22.04 is equipped with the latest version of CUPS. Moreover, if you run the install command as we did here. You would come to know that the CUPS is already installed and is the latest version.
The output shows that the CUPS is already installed on Ubuntu 22.04.
How to set up CUPS on Ubuntu 22.04
As CUPS is available on Ubuntu 22.04. You are now set to configure the CUPS to start using it. This section enlists the recommended steps to configure the CUPS on Ubuntu 22.04.
Step 1: Firstly, you need to start and enable the CUPS service. This would help you to keep using the CUPS service after reboot. To do so, make use of the following commands to start and enable the CUPS service.
To start the cups service
To enable the cups service
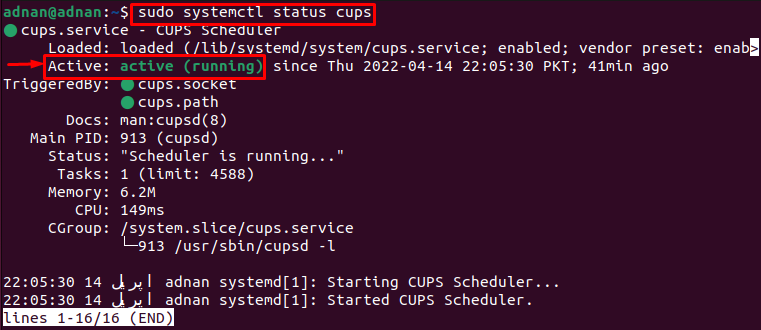
You need to check the status of the CUPS service to verify the service is running in an active mode.
The output shows that the service is enabled and running actively.
Step 2: Now, edit the configuration file of CUPS to make some changes. The following command will help you to access the cups configuration file.
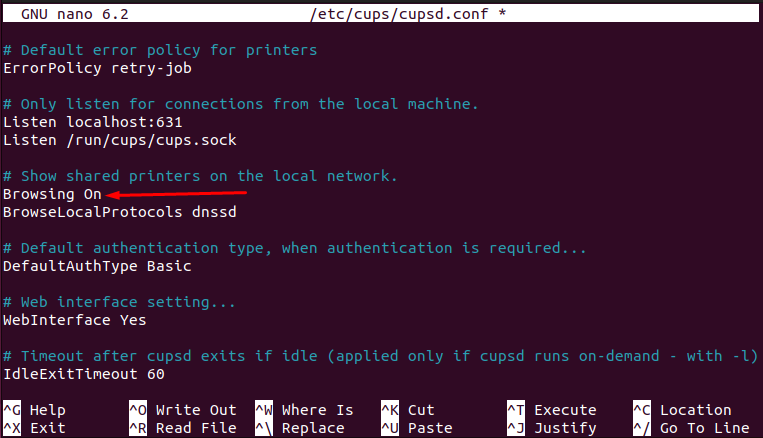
Here you need to do the following changes.
– Track the “Browsing No” line and change it to “Browsing On“.
– Trace the line where you find the “Listen localhost:631” line. Replace it with “Port 631” as we did here.
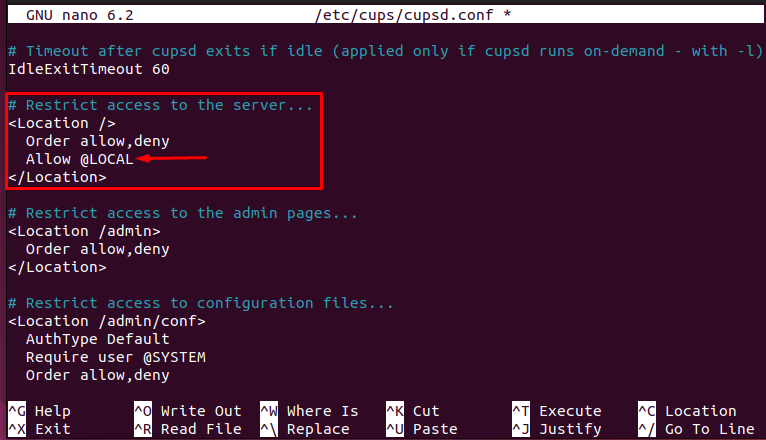
– Look for the line named “# Restrict access to the server” and add the line “Allow @LOCAL” to ensure the cups must listen to all interfaces.
– You would find another line “# Restrict access to the admin pages” and modify it as shown in the following image.
Once all the changes are performed, press “CTRL+S” and “CTRL+X” to save and exit the editor.
Step 3: Lastly, restart the cups service by issuing the following command.
Once all the three steps are executed properly, you can now use the CUPS printer server on Ubuntu 22.04.
How to use CUPS printer server on Ubuntu 22.04
The functionality of the CUPS printer server depends on its configuration. If the configuration file is updated accordingly, then you can use it as follows.
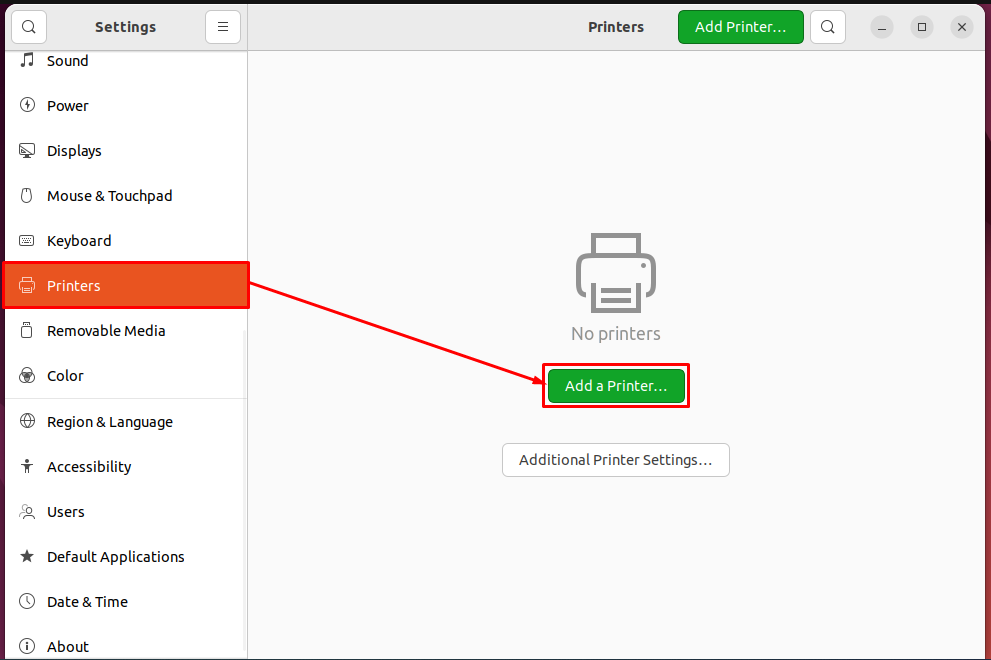
Step 1: Firstly, the CUPS printer server is not added to your printers list. To add it, open the “Settings“.
Scroll down the left pane and choose “Printers” and you will find a green button “Add a Printer“.
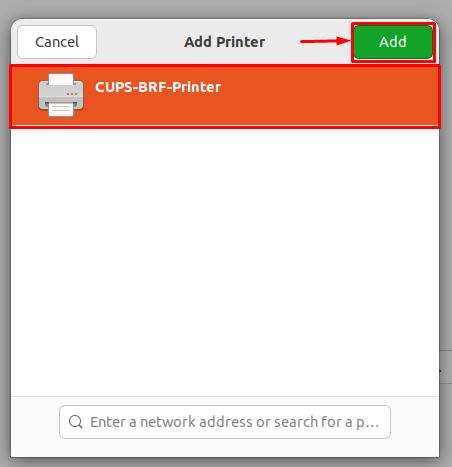
Once you click on the “Add a Printer” button, you will get the CUPS printer in the list as shown below. Select it and click on “Add” to add CUPS to the printers list.
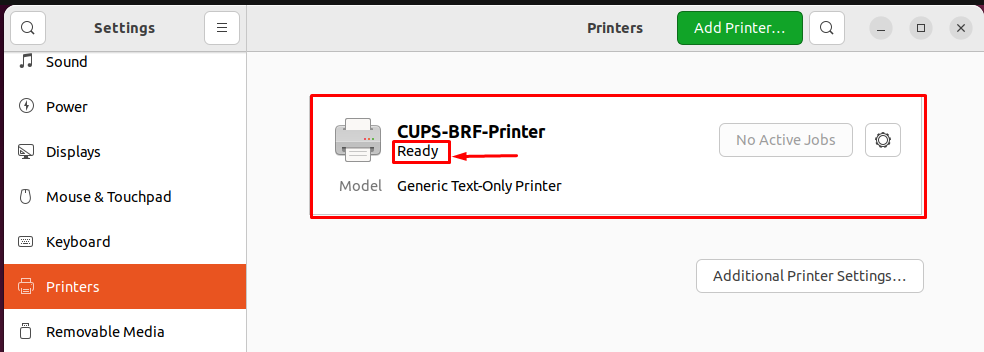
After doing so, it is observed that the CUPS will be added to your printer list and is ready to serve you as can be seen from the following image.
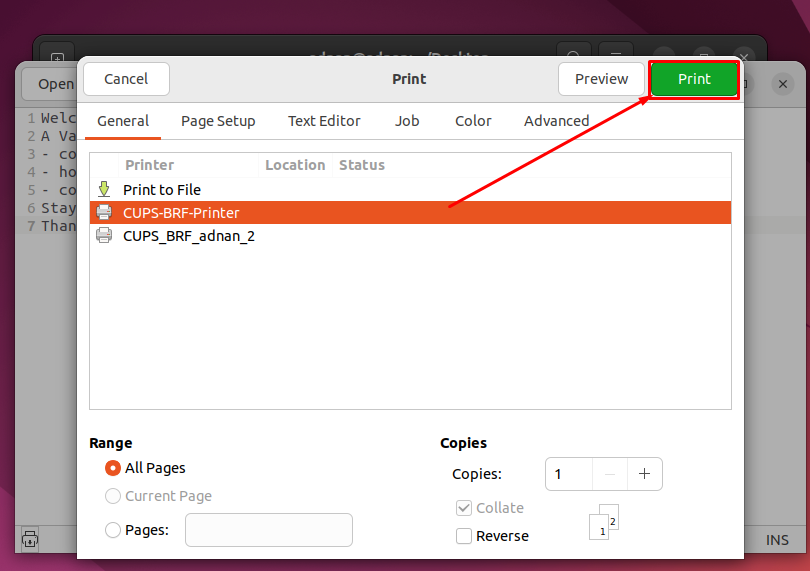
Step 2: Once the printer is added to the list, you can print any file using the CUPS printer server. Head over to the file you want to get printed. Open it and press “CTRL+P“.
You would get the list of printers. Choose the relevant CUPS printer and hit “Print” to get the print of the file.
Here you go with the CUPS printer server!
Conclusion
CUPS is a well-known printer server for Linux-based operating systems. CUPS acts as a server and multiple requests can be made to CUPS for printing. Ubuntu 22.04 is equipped with the latest version of the CUPS printer server. This post acts as a masterpiece of CUPS for Ubuntu 22.04. You would have learned to install, configure and use the CUPS printer server on Ubuntu 22.04.
Linux cups tutorial for beginners
CUPS is a printing system used on many different Linux distributions. Its use is very widespread, as it has become the standard print manager on the majority of popular Linux distros. It acts as a print spooler, scheduler, print job manager, and can store information for numerous local or network printers.
In this guide, we’ll introduce you to CUPS on Linux, with basic information like commands, accessing its web interface, default port, how to add a printer, testing, and starting and stopping the service. Various systems may implement CUPS differently or put their own spin on it, but CUPS works mostly the same on any distro and these instructions will likely apply to any system that utilizes CUPS.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to use the CUPS web interface
- How to add a printer in CUPS
- Various CUPS commands
- How to control the CUPS service
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Any Linux distro with CUPS |
| Software | CUPS |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
CUPS web interface
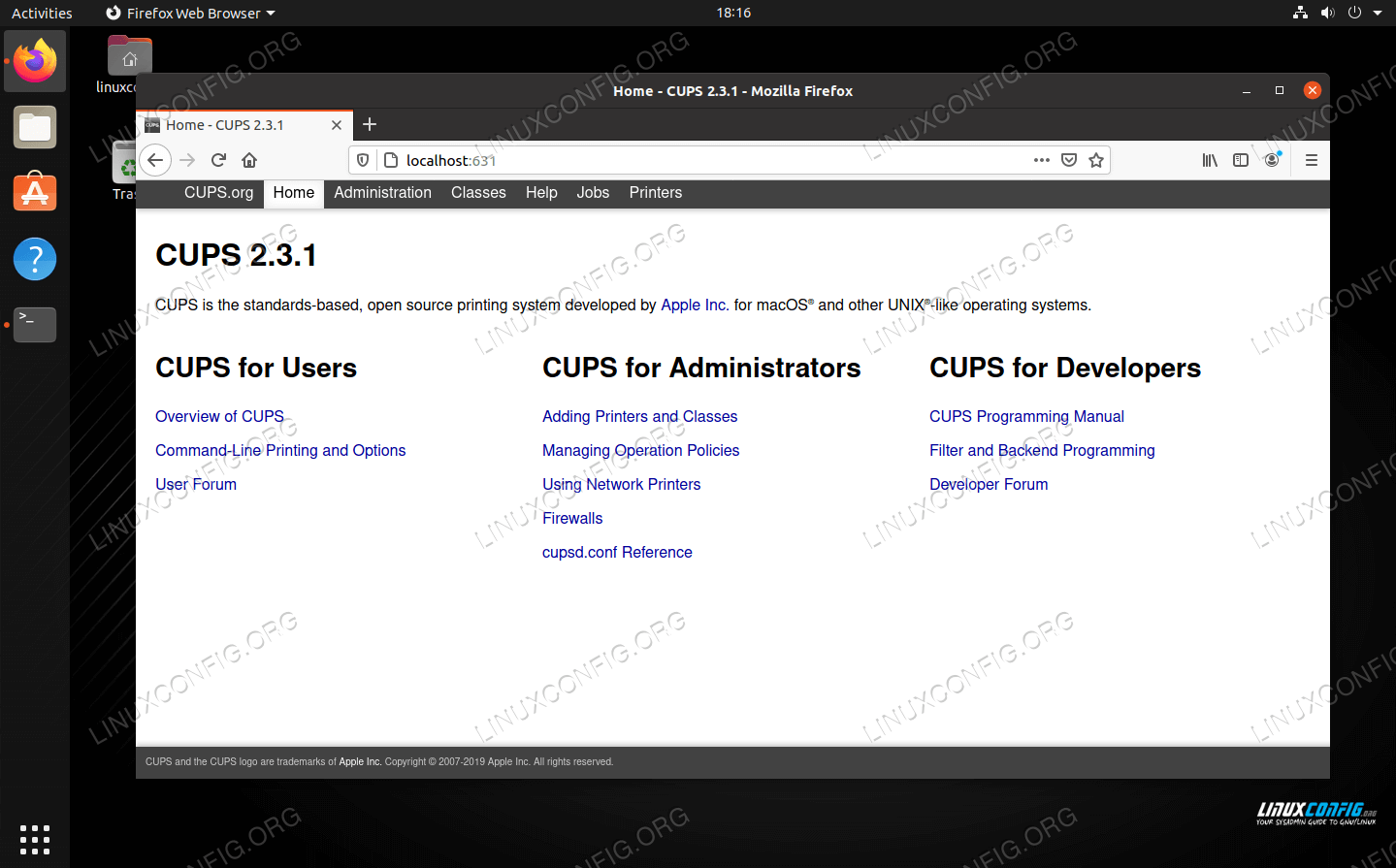
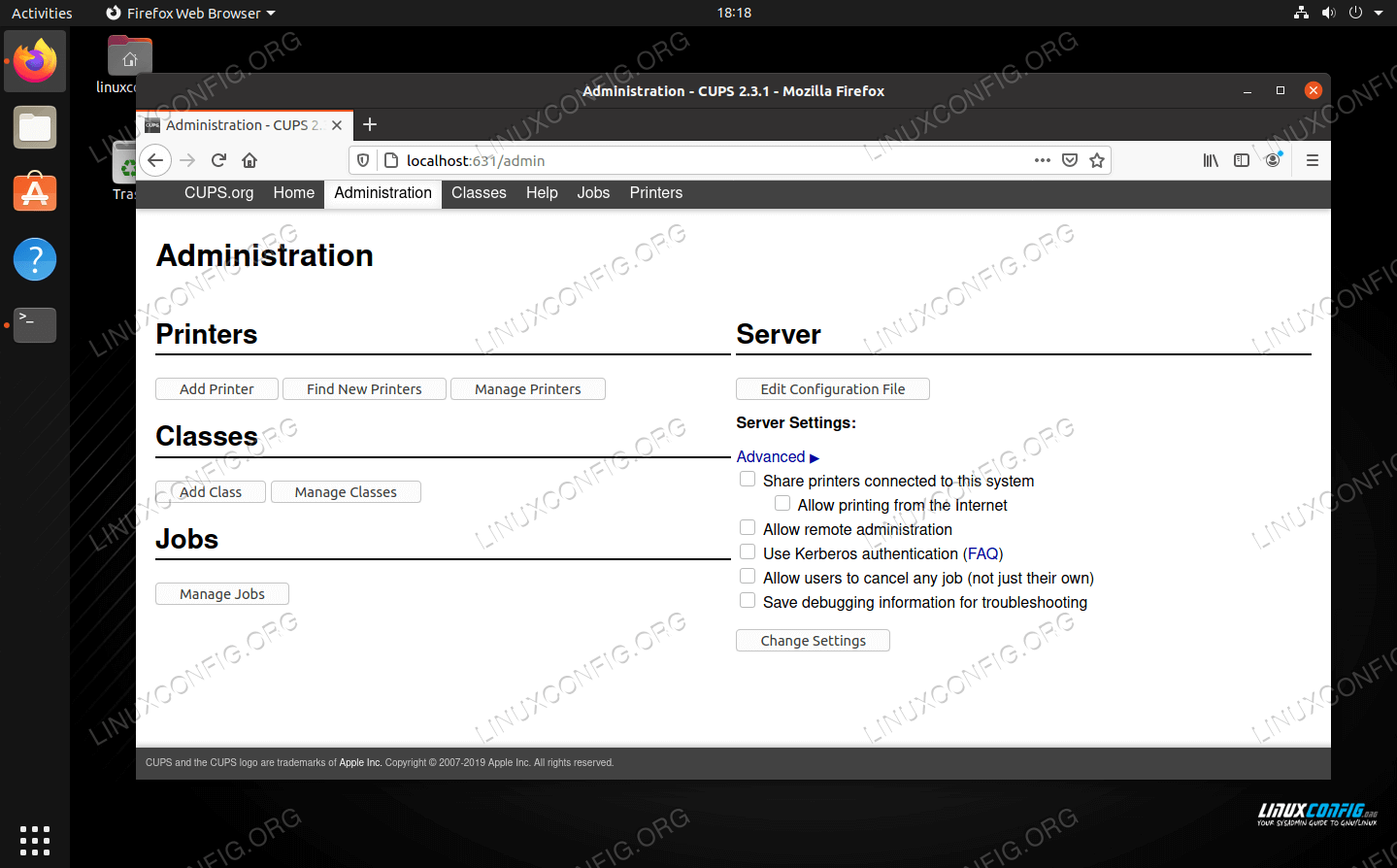
Most users will wish to interact with CUPS through its provided web interface. The web interface runs on port 631, thus it can be accessed through any browser by navigating to http://localhost:631 .
In the web control panel, you can add or delete printers, install drivers, access the print spooler, and configure various settings for all the printers accessible from your PC. Most or all of the options you’ll need to interact with can be found in the “Administration” section.
Add a printer in CUPS
You can add a printer through CUPS by going to the “Administration” section as described above, then clicking “Add printer.” If there are any network printers discovered, they’ll be listed here. Otherwise, you can choose to add an “HP printer” which is more of a catch-all for any type of hardwired printer, and not specifically HP manufactured printers.
If you’re sure there is a printer on the network that hasn’t been automatically discovered and listed here, just choose the appropriate network protocol and click through to the next menu to add it via its network address.
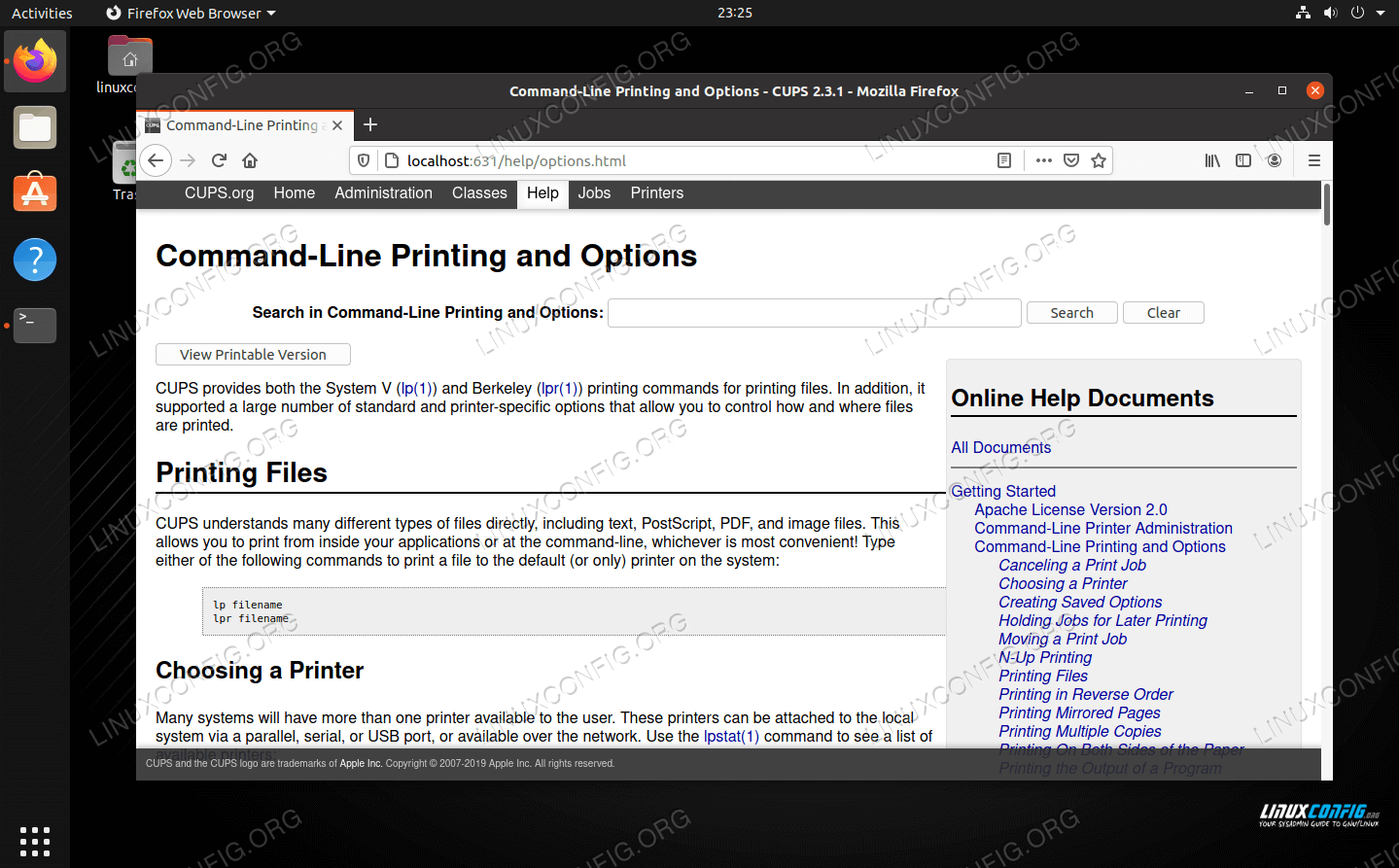
CUPS commands
CUPS can be used from the Linux command line to print files, see available printers, and even configure lots of different printing options. The following is not an exhaustive list of commands, but they’re enough to get an idea for how CUPS works on the command line.
To print a file, use the lp command followed by the file you wish to print. CUPS can interpret most types of files, including text, PDF, images, etc.
CUPS will attempt to send this print job to your default printer. You can specify a particular printer with -P :
Or, to change your default printer, use the lpoptions command:
You can specify various options for your print job with the -o option. Pass as many options as you’d like.
$ lp -o landscape -o fit-to-page -o media=A4 filename.jpg
A full list of options and other commands can be found in the help section of the web control panel.
Controlling the CUPS service
If you’re experiencing problems with CUPS, it can be helpful to restart the service. Controlling the process can be done with systemctl commands on Linux distros with systemd.
To start, stop, or restart CUPS:
$ sudo systemctl start cups $ sudo systemctl stop cups $ sudo systemctl restart cups
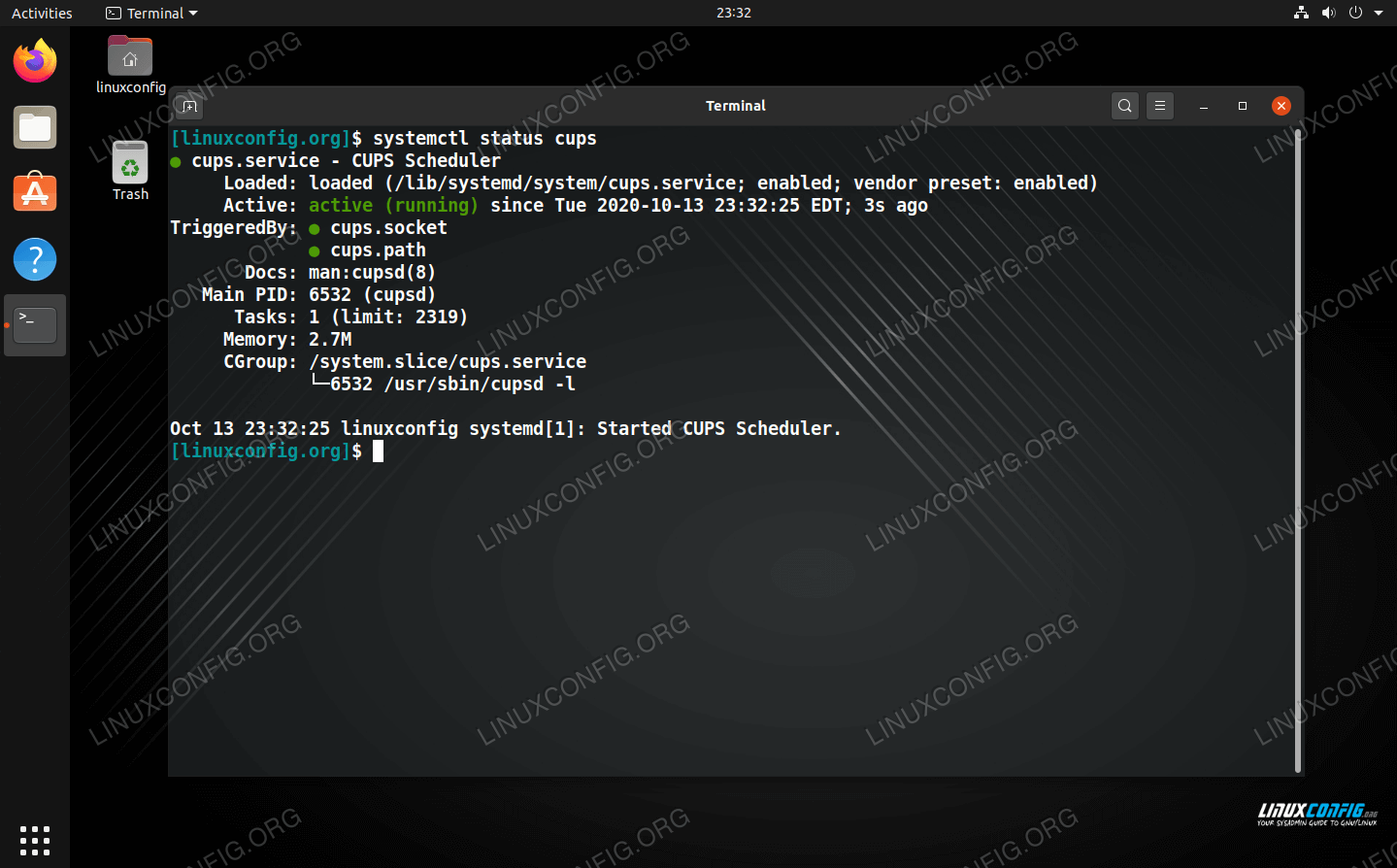
To check on the status of CUPS, and enable or disable it from starting automatically upon system boot:
$ systemctl status cups $ sudo systemctl enable cups $ sudo systemctl disable cups
Conclusion
In this guide, we learned about CUPS, the Linux print manager. We saw how to use it to add printers to our system and control the print spooler. We also saw how to access CUPS from the command line, and systemctl commands which provide us with basic troubleshooting options.
Related Linux Tutorials:
Comments and Discussions
NEWSLETTER
Subscribe to Linux Career Newsletter to receive latest news, jobs, career advice and featured configuration tutorials.
WRITE FOR US
LinuxConfig is looking for a technical writer(s) geared towards GNU/Linux and FLOSS technologies. Your articles will feature various GNU/Linux configuration tutorials and FLOSS technologies used in combination with GNU/Linux operating system.
When writing your articles you will be expected to be able to keep up with a technological advancement regarding the above mentioned technical area of expertise. You will work independently and be able to produce at minimum 2 technical articles a month.
TAGS
FEATURED TUTORIALS
- VIM tutorial for beginners
- How to install the NVIDIA drivers on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- Bash Scripting Tutorial for Beginners
- How to check CentOS version
- How to find my IP address on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- Ubuntu 20.04 Remote Desktop Access from Windows 10
- Howto mount USB drive in Linux
- How to install missing ifconfig command on Debian Linux
- AMD Radeon Ubuntu 20.04 Driver Installation
- Ubuntu Static IP configuration
- How to use bash array in a shell script
- Linux IP forwarding – How to Disable/Enable
- How to install Tweak Tool on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa Linux
- How to enable/disable firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux
- Netplan static IP on Ubuntu configuration
- How to change from default to alternative Python version on Debian Linux
- Set Kali root password and enable root login
- How to Install Adobe Acrobat Reader on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- How to install the NVIDIA drivers on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux
- How to check NVIDIA driver version on your Linux system
- Nvidia RTX 3080 Ethereum Hashrate and Mining Overclock settings on HiveOS Linux
LATEST TUTORIALS
- Enabling SSH on Raspberry Pi: A Comprehensive Guide
- Boot Your Raspberry Pi from a USB: A Tutorial
- Checking Your Raspberry Pi’s OS Version
- Install an OS on Your Raspberry Pi: Step-by-Step
- Finding Your Raspberry Pi’s IP Address: A Quick Guide
- Easy Steps to Update Your Raspberry Pi
- Connecting Your Raspberry Pi to Wi-Fi: A How-To
- How to install RealVNC viewer on Linux
- How to check Raspberry Pi RAM size and usage
- How to check Raspberry Pi model
- Understanding UEFI and BIOS in Relation to Linux Nvidia Driver Installation
- How to orchestrate Borg backups with Borgmatic
- How to monitor filesystem events on files and directories on Linux
- Debian USB Firmware Loader Script
- How to install and self host an Ntfy server on Linux
- How to backup your git repositories with gickup
- How to bind an SSH public key to a specific command
- Creating a Bootable USB for Windows 10 and 11 on Linux
- How to list all displays on Linux
- List of QR code generators on Linux