Introduction
Ubuntu can be installed from a USB flash drive. This may be necessary for most new portable computers without DVD drives and is handy for others because a USB flash drive is so convenient. Also, you can configure Ubuntu on the USB flash drive to save changes you make, unlike a read-only CD/DVD disk.
Booting from a USB flash drive created with usb-creator alias Startup Disk Creator and mkusb will behave just as if you had booted from the install CD. It will show the language selection and then the install menu, from which you can install Ubuntu onto the computer’s hard drive or launch the LiveCD environment. Other utilities, e.g. UNetbootin, may create slightly different boot drives or if on UEFI might not work at all with Debian iso files due to a bug
Note: This article uses the term «USB flash drive» alongside USB stick, USB drive, USB device, USB pendrive and thumb drive.
Prerequisites
- a 4 GB USB flash device/drive/stick. If the iso file is smaller than 2 GB, it is possible to use a 2 GB USB device, at least with some of the methods. Files on this USB device will be erased, so backup the files you want to keep before making the device bootable. Some of the tools require that this USB device is properly formatted and mounted while other tools will overwrite whatever is on the target device. Please follow the instructions for each tool.
- an Ubuntu flavour ISO file downloaded from an official web page, ubuntu.com/download or http://releases.ubuntu.com, stored in your running computer (for example in the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not in the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
- Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good. In Linux there is the tool ‘md5sum’. In Windows you can do it with Rufus: click on the circle with a tick mark (more about Rufus here.)
Dummy headlines
After a major remake of this help page the following headlines are kept here because they may be linked to from other web sites. Several other headlines further down in the page are also kept for this reason.
Install Linux from USB Device or Boot into Live Mode Using Unetbootin and dd Command
Installing Linux from a USB mass storage device or logging into Live Linux Environment is a cool Idea. Booting from a USB mass storage device is sometimes necessary, especially when the ROM media device is not working.
Booting Windows from a USB mass storage device is not difficult, and with the availability of various software, it has been just a few clicks away. Booting into a windows machine requires only three files, namely boot.ini, ntldr, and ntdetect.com.
But booting into a Linux machine is a complex process which requires a whole lot of files and process in a well-defined execution manner. The booting process is complex but creating a boot-able USB media is very interactive and fun.
We will be creating USB boot-able image in two different way
- Unetbootin – is an open-source tool for creating bootable Live USB drives for Ubuntu, Fedora, and other Linux distributions.
- dd – is a command-line tool for converting and copying files.
For creating a USB bootable image, certain basic requirements are:
- Usb Mass Storage Device (Pen Drive).
- Linux Image in CD/DVD/ISO or Internet connection (Not recommended for large images).
- Windows/Linux Platform.
Creating Bootable USB Device Using Unetbootin Tool
To install UNetbootin on Ubuntu and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, use the following apt command to add PPA and install it.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gezakovacs/ppa $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install unetbootin
Alternatively, you can download UNetbootin binaries and run them without installing on the Linux systems (supports all Linux distributions).
-------------- 64-bit System -------------- $ wget https://github.com/unetbootin/unetbootin/releases/download/681/unetbootin-linux64-681.bin $ chmod +x ./unetbootin-linux64-681.bin $ sudo ./unetbootin-linux64-681.bin -------------- 32-bit System -------------- $ wget https://github.com/unetbootin/unetbootin/releases/download/681/unetbootin-linux-681.bin $ chmod +x ./unetbootin-linux-681.bin $ sudo ./unetbootin-linux-681.bin
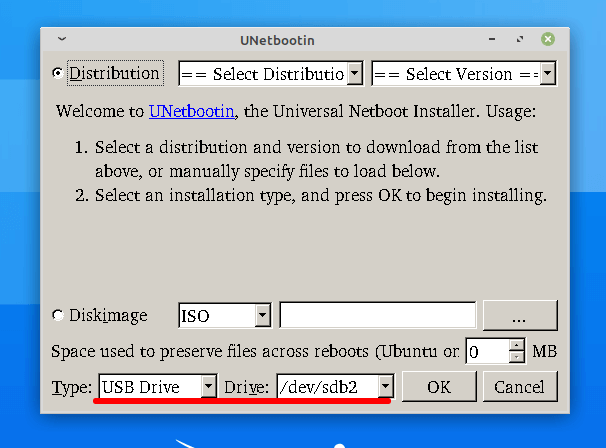
Insert Your USB pen-drive into the Windows/Linux machine and Launch Unetbootin, you will be greeted with a window similar to.
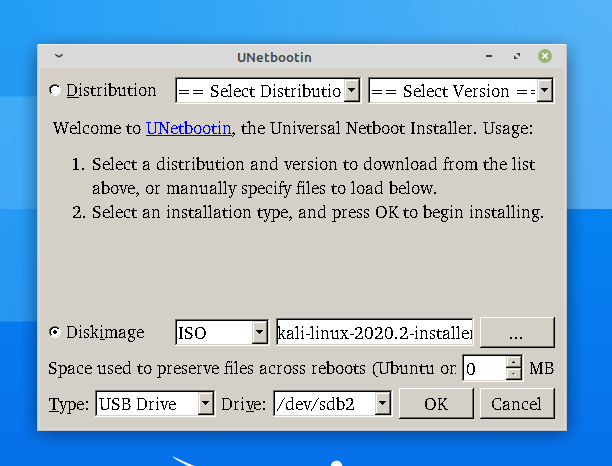
Check the content above the red line. The type should be Usb Device, strictly and if more than one usb device is plugged in you need to know the name of the exact Usb device you need to work upon. A wrong selection will lead to wiping your hard disk, so be aware. You can browse to the stored disk image on your hard drive, from the Unetbootin window.
Or alternatively download from the internet, in real-time. Although it is a time taking process and may result in an error when a larger image is downloaded.
Click OK, and the process of downloading and/or extracting the image will start. It will take time depending upon the size of the download and/or the file size of the ISO image. Once completed, click ‘exit‘.
Plug out the usb storage device safely and plug it into the machine you want to boot. Restart it and set that usb storage device to boot first from the BIOS menu which maybe F12, F8, F2, or Del depending upon your machine and build.
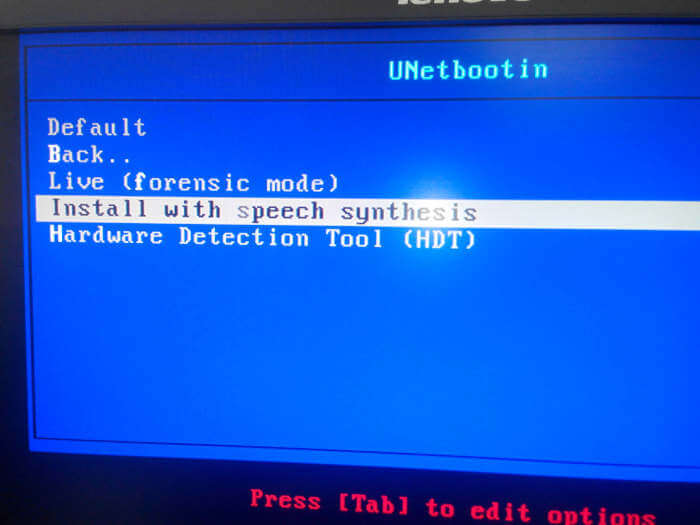
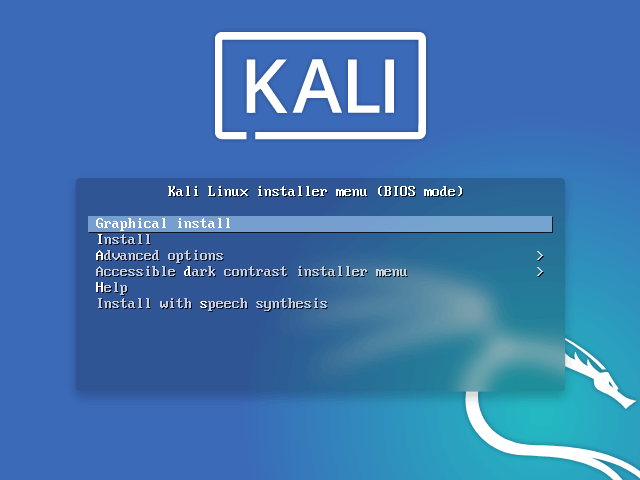
You will be greeted with a window as below, from where you can boot into Live Linux Mode and/or Install on Hard Disk from there, directly.
Pros of using Unetbootin
- Most of the processing is automated.
- Easy to use.
- Make it possible to create a boot-able stick from windows/Linux.
Cons of using Unetbootin
Creating a Bootable USB Device using dd Command
dd command originally was a part of UNIX, which is implemented in Linux. The dd command is capable of striping headers, extracting parts of binary files. It is used by the Linux kernel Makefiles to make boot images.
The basic syntax of dd command is
The bite Size is generally “some power of 2, and usually, not less than 512 bytes i.e., 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384, but can be any reasonable whole integer value.
sync option allows you to copy everything using synchronized I/O.
Run the below command with modification depending upon your source and destination.
# dd if=/home/server/Downloads/kali-linux-2020.2-installer-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdb1 bs=512M; sync
It will take time to create the boot-able disk depending upon the size of the ISO image and your RAM capacity.
Don’t interrupt the boot stick creation, once the process is completed, you will get something like this in your terminal.
4+1 records in 4+1 records out 2547646464 bytes (2.5 GB) copied, 252.723 s, 10.1 MB/s
Now safely eject the disk, plug it into the machine you want to boot with Linux, and Yup doesn’t forget to change the booting option in your BIOS, setting your flash stick to boot primarily.
When USB is booted, You will be greeted with a window similar to.
Pros of the above method:
Cons of the Above method:
- No room for error, an error, and everything is wiped.
- Non-interactive way.
- You should know, what you are doing, as you won’t get any manual/prompt/help at run time, you must be good in terminals.
Remember, All the distro don’t allow Live Environment, but most of today’s distro does. You will be able to log into a live Linux Environment only if supported.
The above article does not aim at comparing the two methods. Before writing anything we give hours in testing and executing the process to ensure you get a 100% working solution.
If you get stuck at somewhere, feel free to contact us in the comment section. For any damage to data/disk, as a result of the above method, neither the Author nor Tecmint is responsible.
That’s all for now. I will soon be here again, with another interesting article, you people will love to read. Till then stay healthy, safe, tuned, and connected to Tecmint.