- bluetooth в linuxmint
- Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
- Bluetooth¶
- Blueman¶
- Systemd-rfkill¶
- Bluez¶
- How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
- How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
- How to connect Bluetooth headset using the terminal in Linux Mint
- How to connect Bluetooth headset using Graphical Interface in Linux Mint
- Conclusion
bluetooth в linuxmint
Намедни взялся настроить на ноутбуке жены линукс взамен порядком подзабитой w7 всякими мейлгвардами и другими маргетингтулз.exe бякостями ну и чтобы обезопаситься первентивно. По опыту использования на работе выбор дистрибутива пал на Linuxmint Mate 64 bit. Ноутбук — Sony Vaio, модель «такой, розовенький».
Система встала успешно, всё оборудование увиделось «слёту», разве что потребовалось настроить звук: выставить у встроенного (Built-in Audio) профиль Analog Stereo Output и этот же Built-in указать во вкладке «Выход».
Не заработал же под Mate только Bluetooth. Борьба с ним весьма легка: заходим в менеджер пакетов и находим там mate-bluetooth, который безжалостно удаляем. После чего в терминале запускаем:
sudo -s
apt-get update
apt-get install gnome-bluetooth
bluetooth-wizard (последняя команда запустит мастер настройки подключения нового устройства)
Теперь у моей жены ее розовенькая сонька, как и на винде, успешно дружит с ее розовенькой же bluetooth мышкой (модель VGP-BMS20).
Если не помогло — пишите, разберемся.
Форум таких же мучеников — тут: http://forums.linuxmint.com/viewtopic.php?t=102417&f=206
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Для отправки комментария вам необходимо авторизоваться.
- AltLinux
- DevOps
- lvm create and resize
- Terraform configs
- Postgres backup & restore
- Gitlab восстановление из бэкапа
- Gitlab: настройка mattermost
- nginx и tomcat https для Jira
- Proxy settings nginx http2 installation
- Настройка Jira Software — подготовка к первому запуску
- Настройка почтового сервера на Jira Confluence
- Обновление Jira Confluence на CentOS
- Установка gitlab на Centos
- Установка Jira Confluence на CentOS
- Установка Jira Software на CentOS
- Установка и запуск PostgreSQL на CentOS
- SSL-объединенный сертификат
- Борьба со спам-ботами на сайте.
- Бэкап сайта — он же перенос WordPress на другой сайт
- Несколько сайтов на одном сервере
- Обновление вордпресс
- Обновление сертификата letsencrypt
- Отключение Selinux
- Отслеживание доступности сайта.
- Перенос WordPress — смена доменного имени
- Подключение к стороннему MySQL
- Защита консоли (ssh) — ручная настройка
- Защита консоли сервера (sshd)
- Защита консоли сервера: Fail2ban
- Как распознать вирус и вредонос во вложении
- Надёжность паролей — наглядная демонстрация
- connect to ubuntu desktop sharing from mac
- MacOs encrypt-decrypt disk
- Как подключить ntfs диск к маку на редактирование
- Настрока области просмотра в Mail
- Русская клавиатура на макбуке
- Уязвимость в Макбуке
- Про торговых ботов
- DNS привязка сайта.
- Автозагрузка в CentOS: добавление демона
- Выбор CMS платформы.
- Выбор доменного имени.
- Выбор хостинга.
- Настройка постоянных ссылок
- Размещение. Хостинг.
- Регистрация доменного имени. Выбор регистратора.
- Связь с Фейсбуком
- Установка CMS платформы WordPress.
- Установка mysql на Centos 7
- Установка счетчиков посещаемости.
- Evernote на Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Блокирование отображения рекламы
- Браузер по умолчанию
- Защита от отслеживания в Firefox
- Как посещать любые сайты
- Меняющиеся обои рабочего стола в линуксе
- Настройка eToken на Линукс
- Настройка браузера Chrome
- Настройка превьюшек в LinuxMint
- Открытие файлов без сохранения в хроме
- Подключение внешнего/сетевого диска
- Проверка контрольных сумм
- Установка Clear.OS с загрузочной флешки и настройка шлюза
- Установка сертификата для Цитрикса
- Хранение паролей
- Шифрованное облачное хранилище
Bluetooth¶
Bluetooth can be disabled by using a software kill switch.
On some laptops, a hardware kill switch is also provided either via a special function key or key combination or a dedicated physical button or mechanism.
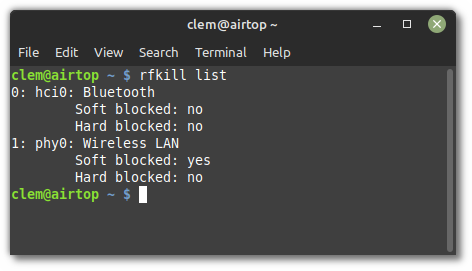
Using the rfkill command, you can see the state of these switches.
The output lists the state of software and hardware kill switches for all your wireless devices:
In the picture above you can see that Bluetooth is neither Soft blocked nor Hard blocked and is therefore enabled.
You can use rfkill to block (i.e. disable) or unblock (i.e. enable) bluetooth:
rfkill block bluetooth rfkill unblock bluetooth
Blueman¶
Blueman is the default Bluetooth Manager in Linux Mint.
It provides the little Bluetooth icon in your system tray.
To disable Bluetooth right-click the tray icon and select Turn Bluetooth Off .
To enable Bluetooth right-click the tray icon and select Turn Bluetooth On .
The very first time you open Blueman it asks if Bluetooth should be enabled automatically.
To check whether this feature is enabled open a terminal and type:
gsettings get org.blueman.plugins.powermanager auto-power-on
It auto-power-on is set to true , Blueman automatically unblocks Bluetooth at startup.
If you want to persistently disable Bluetooth you need to set auto-power-on to false :
gsettings set org.blueman.plugins.powermanager auto-power-on false
The auto-power-on option was recently removed in Blueman’s master branch. It’s still present in Blueman 2.3.2 but it’s likely to disappear in newer versions.
Systemd-rfkill¶
Systemd provides a service which saves the state of your kill switches during shutdown and restores them on the next boot.
This service is a core part of systemd and is installed in Linux Mint by default.
Blueman runs after systemd-rfkill, so if Blueman’s auto-power-on setting is enabled it overrides systemd-rfkill.
Bluez¶
Bluez is the Bluetooth stack used by Blueman.
Bluez has a setting called AutoEnable in the file /etc/bluetooth/main.conf .
If you don’t want Bluez to automatically enable Bluetooth during boot set this option to false.
© Copyright 2020, Linux Mint Revision 92937742 .
Versions latest Downloads pdf html epub On Read the Docs Project Home Builds Free document hosting provided by Read the Docs.
How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology that is meant to connect electronic devices to share data or connect for media-related purposes. The major application domain of Bluetooth technology is to use it for media-related tasks or sharing data. Bluetooth allows two devices to connect without requiring any modem, network, or any third medium. Therefore, it is the prior choice of users to share files/data (within a short-range). Users may connect the speakers with any computing device or smartphone to play music/movies, or to have a handset calling and texting access.
Following the importance of this technology, this guide provides a demonstration to connect Bluetooth headset to the Linux Mint system.
How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
This section contains the procedural guide to connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint using the Command Line Interface, and Graphical User Interface methods:
How to connect Bluetooth headset using the terminal in Linux Mint
To connect Bluetooth to your Linux Mint, you must follow the steps provided below.
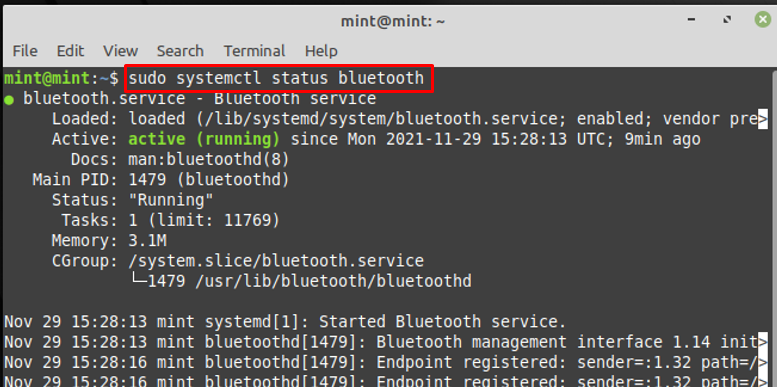
Step 1 : Before getting into details, check the status of Bluetooth service with the help of the command written below:
If the service is disabled or not working; you may provide the following commands to start and enable the Bluetooth service.
$ sudo systemctl start bluetooth
$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth
Step 2 : Ensure that your system’s Bluetooth is discoverable to all nearby devices. For this, use the discoverable option of bluetoothctl as shown in the below-mentioned command.
Note : The bluetoothctl is a Linux-based utility to manage Bluetooth devices on the system
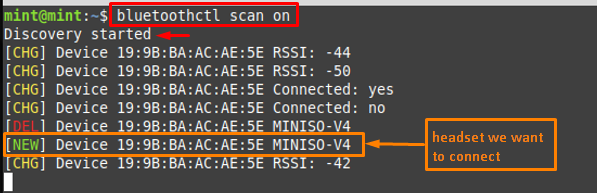
Now, scan for the devices by issuing the below-stated command.
The above command lists down the available devices with their MAC (Media Access Control Address) addresses as well. As in our case, the device is “MINISO-V4“, so we have noted its MAC address.
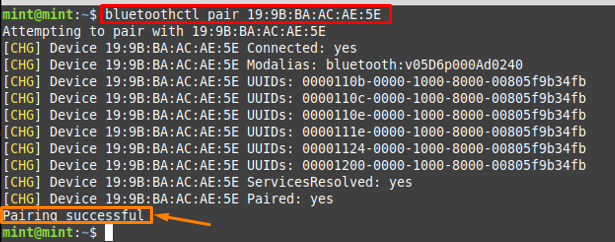
Step 3 : Pair the specific device using the following syntax. For instance, the command provided below will pair the “MINISO-V4” headset using its MAC address.
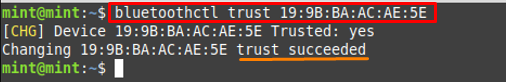
After pairing, it is recommended that you must trust the paired device with the help of the command written below.
After pairing, check for the list of paired devices by using the command written below. And you will get your paired devices list in the output.
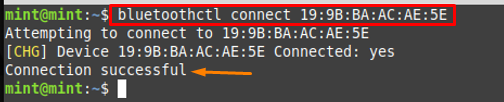
Step 4 : And after pairing, connect that Bluetooth headset device with the help of the command provided below. Upon successful connection, the “Connection successful” message is returned.
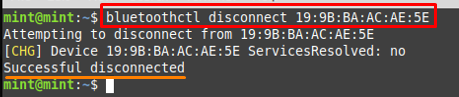
Step 5 : Unpair or Disconnect
However, if you want to disconnect any device then you would execute the bluetoothctl command in the following way.
You can unpair any device by using the remove keyword as shown in the command below.
How to connect Bluetooth headset using Graphical Interface in Linux Mint
If your Bluetooth manager is working fine, then you will find the Bluetooth symbol on the desktop taskbar as seen in the image below.
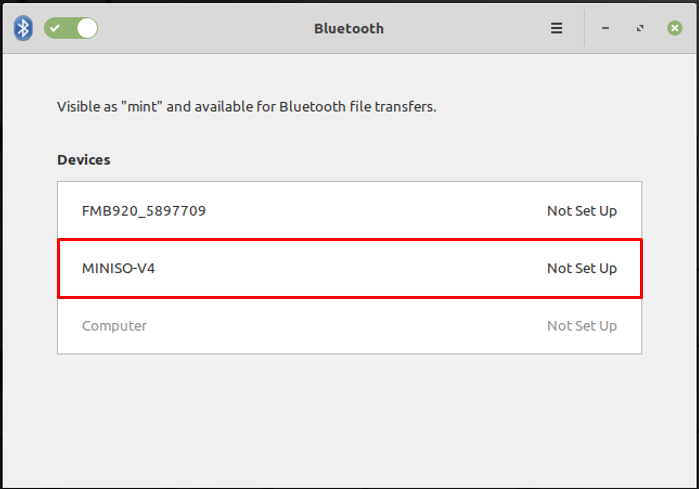
Upon clicking, all the devices will be displayed as can be seen in the image below and here the name of the headset device is “MINISO-V4”.
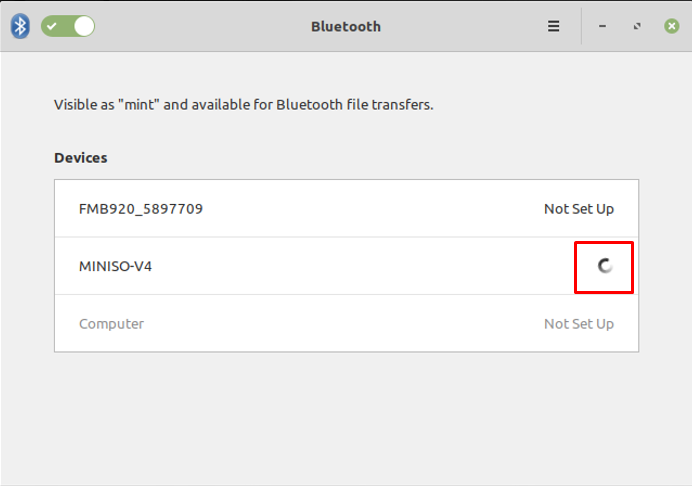
After clicking on the Bluetooth headset name, the connection will be made instantaneously.
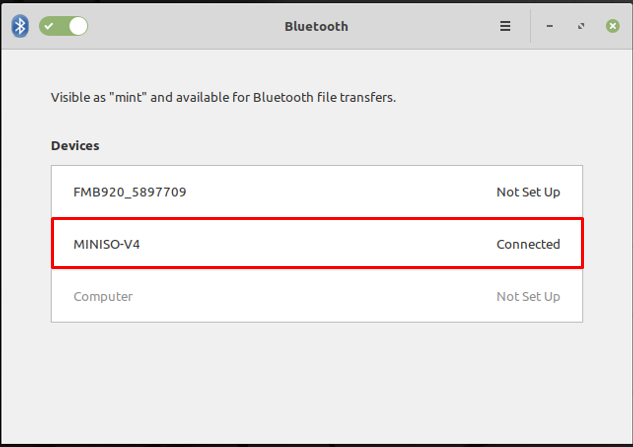
And the status will be changed to “Connected” as displayed below.
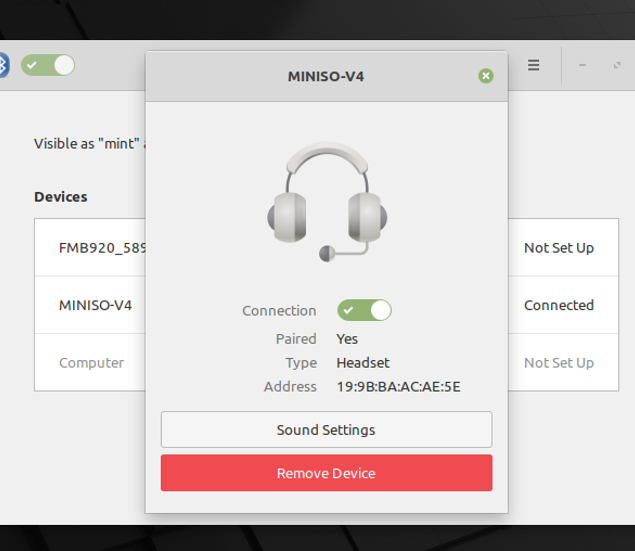
You can get further details by clicking on it and after doing so the interface obtained is displayed below.
From the image shown above:
– You can disconnect your headset by clicking on the “Remove Device” button
– To get detailed sound settings, you can click “Sound Settings”
Conclusion
Wireless technology has improved the accessibility of several devices in a network. Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology being used to connect electronic devices, share data or play any music. This guide provides a detailed demonstration to use Bluetooth to connect your headset to the Linux Mint system. We have also provided the installation and configuration of the Bluetooth manager on Linux Mint; this configuration is required as in many cases users are not able to get the nearby devices.