- How to Use telnet Command in Linux?
- Installing Telnet in Different Linux Distributions
- CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL
- Ubuntu and Debian-Based Distributions
- How to Use telnet in Linux
- Check for Open Ports
- Download Web Page to File
- Test SMTP Communication
- Connect to Remote System
- How To Install and Use Telnet Client In Linux and Windows
- Install
- Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali
- Fedora, CentOS, RHEL
- Windows
- Security
- Connect Telnet Server
- Connect Different Telnet Port
- Specify Login Name
- Interactive Shell
- Установка Putty под Astra Linux
- Установка Putty
- Изменяем шрифт
- Заключение
How to Use telnet Command in Linux?
Home » Networking » How to Use telnet Command in Linux?
The telnet command (short for teletype network) utilizes the telnet network protocol to connect to remote machines and manage them through a TCP/IP network. The protocol uses port 23 to establish a connection and provides a way to manage remote systems using the CLI.
Although telnet is similar to SSH, the two are different because SSH is a much more secure option as it uses encryption. telnet , on the other hand, sends data without encryption, making it an easy target for hackers.
In this tutorial, you will learn to use the telnet command in Linux.
- A system running Linux (for Windows users, learn about telnet on Windows).
- An account with root privileges.
- Access to the terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T).
Installing Telnet in Different Linux Distributions
Depending on the Linux distribution you are using, follow the steps below to download and install telnet .
CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL
CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL use yum (Yellowdog Update Manager) as the primary package manager. Follow the steps below:
1. Update the system package repository to make sure the latest version is installed:
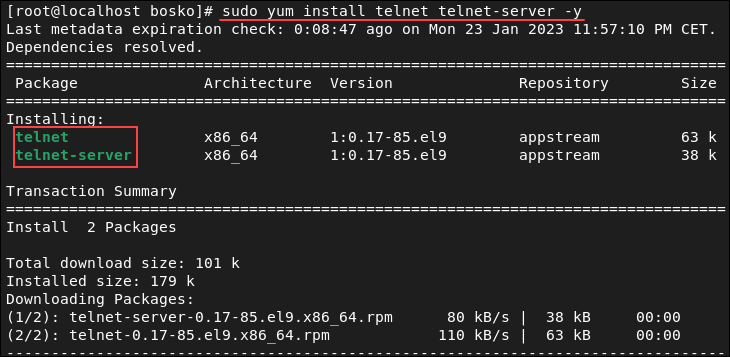
2. Run the following commands to install telnet and the telnet server packages required for it to function properly:
sudo yum install telnet telnet-server -yThe command installs the two packages. The -y flag automatically answers Yes to any prompts during the installation.
3. After the installation completes, start and enable the telnet service by running:
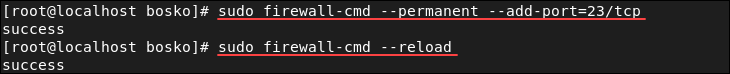
systemctl start telnet.socket systemctl enable telnet.socket4. Allow the telnet port (the default port is 23) through the firewall on the remote machine. Run the following command:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=23/tcp5. Reload the firewall to apply the changes:
The telnet port is now allowed through the firewall.
Ubuntu and Debian-Based Distributions
Ubuntu and other Debian-based distributions use the apt package manager by default. Follow the steps below to install telnet :
1. Update the system package repository:
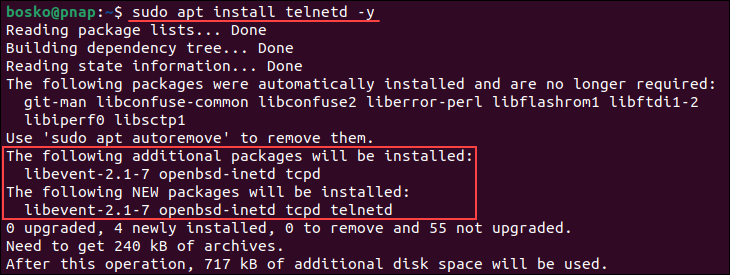
2. Run the following command to install telnet :
sudo apt install telnetd -yWait for the installation to complete. The service should start automatically.
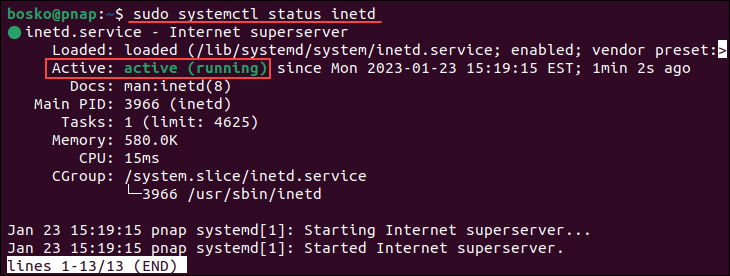
3. Check if telnet is properly installed by running:
sudo systemctl status inetdThe output shows that the daemon is up and running.
4. Allow port 23 through the firewall on the remote machine by running:
The telnet port is now allowed through the firewall.
Note: The command above is for the ufw firewall. If you are using a different firewall, follow the instructions for that specific program.
How to Use telnet in Linux
A vital prerequisite for using telnet is to have it installed on both the local and remote machine, and that the default port 23 is allowed through the firewall on the remote machine.
The syntax for the telnet command is:
telnet [options] [remote_server_address] [port]The [options] and [port] parameters are optional. For [remote_server_address] , telnet accepts symbolic and numeric addresses.
Running the command without options or without specifying an address opens the telnet interactive mode:
Use the interactive shell to connect to remote servers, print the connection status, etc.
To end a session and exit telnet , run:
The sections below provide practical telnet use case examples.
Check for Open Ports
Although it is not a secure option for establishing a remote connection, telnet is a great way to check if a specific port is open on a server. Check if a certain port is answering any calls by specifying the port number in the command. Doing so allows you to see what’s going on in a network and if a port is responsive or not.
1. Use the following syntax:
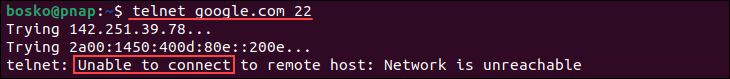
telnet [server_address] [port]2. Not specifying a port number defaults to port 23. For example, to check if port 22 is open on a server, run:
The connection breaks, which means that the specified port is not open.
3. However, trying port 80 yields a different result:
The output shows that the port is open since the connection was established.
Download Web Page to File
telnet allows users to connect to port 80 of a website and download the HTML source code to the terminal. This allows you to save and inspect the source code, check it for errors, etc.
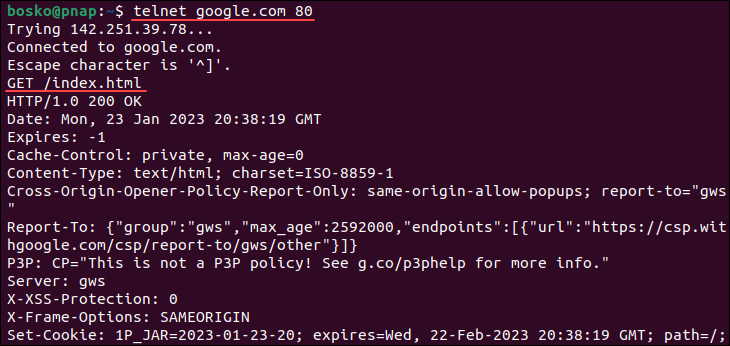
1. For example, the following command connects to port 80 on google.com:
2. After establishing the connection, download the HTML web page by running:
The screenshot above shows that the command has downloaded the homepage source code.
3. Save the code to a file or inspect it in the terminal.
Test SMTP Communication
Another useful feature of telnet is that it allows users to test the SMTP port by sending emails directly from the command line. To do so, you need an email server that doesn’t require authentication. It is a great way to troubleshoot problems in an email client.
Note: Want to send and read email using the CLI? See how to use the Linux mail command.
Follow the steps below to send an email using telnet :
1. Connect to the server via the SMTP port:
telnet [server_address] [port]For [server_address] , specify the SMTP server address. For example, for Gmail it is smtp.gmail.com, while the SMTP [port] can be 25, 465, 587, etc., depending on the provider.
Important: Since May 2022, Google has prohibited access to Google accounts for less secure apps and won’t accept connections from telnet .
2. Greet the server with HELO or EHLO :
5. Specify the subject and email body, separated by a blank line:
SUBJECT: This is the email subject. "" This is the email body.Note: Most mail servers flag unsolicited anonymous mail, which means that it will likely end up in the spam folder.
Connect to Remote System
If you decide to use telnet for remote connections despite its lack of security, do it by specifying the remote machine’s IP address.
Make sure that telnet is installed on both machines and port 23 is allowed through the firewall on the remote machine.
When prompted, enter the account username and password to log in to the system. After logging in, you can operate the other machine remotely.
After the connection is established, you are in control of the remote machine.
This tutorial showed how to use the telnet command in Linux. Although it has poor security features and isn’t recommended for remote connections, the command has other uses that make it beneficial.
Next, see how SSH works and why it is more secure than telnet .
How To Install and Use Telnet Client In Linux and Windows
Telnet is easiest remote management protocol used in Computer networks. It remains popular even today because of its simplicity. Telnet is a client server protocol where clients uses telnet tool which to connect remote telnet server. This telnet server may be switch, router, windows operating system, linux server or a printer. In this tutorial we will look how to install and enable telnet with some usage examples.
Install
Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali
We can install telnet package with the following command in deb based Linux distributions.
Fedora, CentOS, RHEL
We can install telnet package with yum command for rpm based distributions like Fedora, centOS and RHEL.
Windows
As windows operating system do not have online package manager telnet is provided by inline. By defualt telnet server and client applications are not enabled. We will enable the client where server can be enabled too. Follow these instructions.
- Click Start >Control Panel.
- Click Programs and Features.
- Click Turn Windows features on or off.
- In the Windows Features dialog box, check the Telnet Client check box.
Security
As telnet is old fashion protocol it provides some defects. One of the most important negative issue with telnet is its security features. Telnet do not have any encryption support as builtin. So telnet traffic can be easily eavesdropped during transmission. So do not rely telnet on insecure networks.
Connect Telnet Server
We will start by simply connecting a telnet server. The simplest form is just providing the host name or IP address of the telnet server. The syntax is like below. In this example telnet server is a Ubuntu 17.10 .
Connect Different Telnet Port
The default port for telnet is TCP 23 . By default it is not specified during connection. But in some cases telnet server may use different then 23. We can specify the port number by adding after the host name or IP address. In this example we will connect port number 2323 .
Specify Login Name
Most cases telnet servers requires authentication. In order to authenticate ourself we need to provide some user name and password. The regular usage is providing username and then put password interactively. We will use -l which stands for login.
$ telnet -l ismail 192.168.115.143
Interactive Shell
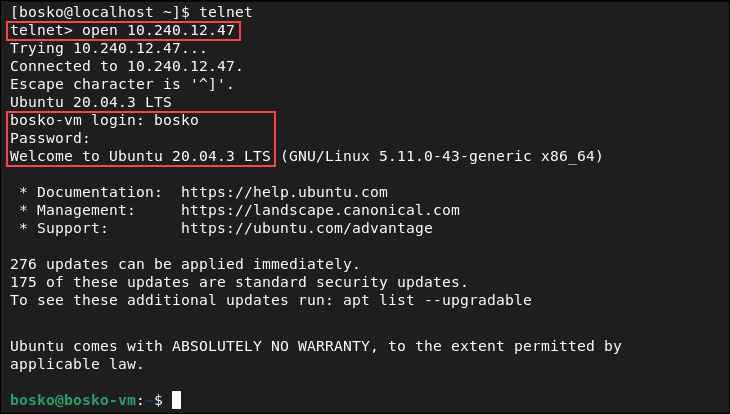
Telnet provides interactive shell where it provides its own environment. We can enter interactive shell just putting telnet command.
We can get help for interactive shell with help command. We can see that we will use open command and the hostname or IP address to connect telnet server.
We will connect to the localhost telnet server.
Установка Putty под Astra Linux
Сегодня мы рассмотрим установку популярного консольного клиента для работы по протоколам SSH, Telnet и через COM-порты (Serial) — Putty. В Astra Linux и есть Remmina, но для подключения по протоколу Telnet и через Com-порт (Serial) вам понадобится другой клиент. Вот тут на помощь и придет Putty.
Установка Putty
К сожалению Putty нет в репозитории Astra Linux, поэтому нам придется ставить его вручную. Скачаем необходимые пакеты:
wget http://ftp.ru.debian.org/debian/pool/main/p/putty/putty_0.67-3+deb9u1_amd64.deb wget http://ftp.ru.debian.org/debian/pool/main/p/putty/putty-tools_0.67-3+deb9u1_amd64.debdpkg -i putty-tools_0.67-3+deb9u1_amd64.deb putty_0.67-3+deb9u1_amd64.debИли через меню Пуск –> Сеть -> Putty SSH Client 

Изменяем шрифт
Возможно вас не устроит используемый Putty шрифт. Давайте поменяем шрифт на более приятный, например terminus-14 . Запустим Putty и выберем Default Settings Нажмем Load 


Заключение
Сегодня мы рассмотрели установку Putty в Astra Linux. Скачали и установили необходимые пакеты. Запустили и соединились по SSH с нашим ПК Узнали как поменять шрифт, используемый в консоли.