- Устанавливаем Virtualbox в Fedora 36
- Подключаем RPM Fusion в Fedora 36
- Устанавливаем VirtualBox
- Заключение
- How to Install VirtualBox in Fedora Linux
- Downloading VirtualBox Repo on Fedora 31
- Installing Development Tools on Fedora 31
- Installing VirtualBox 6.1 on Fedora 31
- Related Posts
- 5 thoughts on “How to Install VirtualBox in Fedora Linux”
- How to Install VirtualBox on Fedora 36 / Fedora 35
- Add VirtualBox Repository
- Install VirtualBox on Fedora 36
- BIOS System
- EFI System
- Launch VirtualBox
- Conclusion
Устанавливаем Virtualbox в Fedora 36
VirtualBox является популярным продуктом для виртуализации, позволяющий запускать виртуальные машины с разным программным обеспечением. Для него существуют даже подготовленные сборки, например, тот же дистрибутив Kali Linux.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим рекомендуемый способ установки VirtualBox в дистрибутиве Fedora 36, из репозитория RPM Fusion. Репозиторий RPM Fusion содержит многое программное обеспечение, которое по тем или иным причинам не включено в официальный репозиторий Fedora, в том числе и проприетарные драйвера.
Подключаем RPM Fusion в Fedora 36
Если вы уже подключили данный репозиторий, то этот шаг можно пропустить, но для полноты картины так сказать, считаю, что стоит об этом упомянуть. Итак, открываем терминал и вводим команду для подключения репозитория RPM Fusion:
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpmПосле чего обновляем систему выполнив команду:
Устанавливаем VirtualBox
Теперь, когда репозиторий RPM Fusion подключен в Fedora 36, можно приступить к установке VirtualBox со всеми необходимыми зависимостями. Итак, возвращаемся в терминал и вводим команду на установку:
sudo dnf install gcc kernel-devel kernel-headers akmod-VirtualBox VirtualBox Когда все пакеты установятся, необходимо добавить вашего пользователя в группу vboxusers и vboxsf, для этого выполняем следующие команды:
sudo usermod -a -G vboxusers $(whoami) sudo usermod -a -G vboxsf $(whoami)На этом можно было бы закончить установку VirtualBox в Fedora 36, но, для полноценного использования необходимо установить расширение extension pack. Для этого можно перейти на официальный сайт VirtualBox и скачать данное расширение:
А можно воспользоваться консольной утилитой wget, тут стоит обратить внимание на то, какая версия VirtuelBox установилась в Fedora 36, это можно узнать из справки самой программы:
Как можно увидеть, у нас на данный момент установлен VirtualBox версии 6.1.34, а значит и расширение extension pack нам нужно скачивать именно под эту версию. Отправляемся в терминал и вводим команду на скачивания:
wget https://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/6.1.34/Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-6.1.34.vbox-extpackОбращаю ваше внимания на версию расширения, которое мы скачиваем, версия выделена жирным шрифтом, если у вас версия будет другая, то просто отредактируйте ссылку. Ну а мы продолжаем, скачиваем расширение:
Когда оно скачается, открываем VirtualBox и нажимаем на кнопку “Настройки”, затем переходим на вкладку “Плагины” и нажимаем на крестик, что бы добавить расширение:
По умолчанию расширение скачается в домашнюю директорию, по этому переходим в нее и добавляем его в VirtualBox:
Появится окно в котором нажимаем на кнопку “Установить”:
Принимаем лицензионное соглашения пролистав в самый низ, после чего активируется кнопка “Я согласен”, на которую собственно и необходимо нажать для установки extension pack :
Вводим пароль и нас радует сообщение об успешной установки расширения:
Заключение
Некоторые рекомендуют использовать в дистрибутиве Fedora вместо VirtualBox систему виртуализации KVM, в частности она уже предустановлена в виде приложения Boxes о котором написано тут. О том как конвертировать образы VirtualBox для KVM виртуализации, которые также можно загрузить в Boxes, читайте тут.
А на этом сегодня все, если статья оказалась вам полезна, подписывайтесь на рассылку журнала в pdf формате, а так же на социальные сети журнала Cyber-X:
Юморилка, Telegram канал с анекдотами:
Telegram
По вопросам работы сайта, сотрудничества, а так же по иным возникшим вопросам пишите на E-Mail. Если вам нравится журнал и вы хотите отблагодарить за труды, вы можете перечислить донат на развитие проекта.
С уважением, редакция журнала Cyber-X
How to Install VirtualBox in Fedora Linux
VirtualBox is a powerful, free, open-source, feature-rich, high performance and cross-platform x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization software for enterprise and home use. It runs on Linux, Windows, Macintosh, as well as Solaris hosts.
In this article, we will show how to install VirtualBox 6.1 on Fedora 31 distribution using the official yum repository.
Note: If you are using the system as a normal or administrative user, employ the sudo command to gain root privileges to run most if not all the commands in this article.
Downloading VirtualBox Repo on Fedora 31
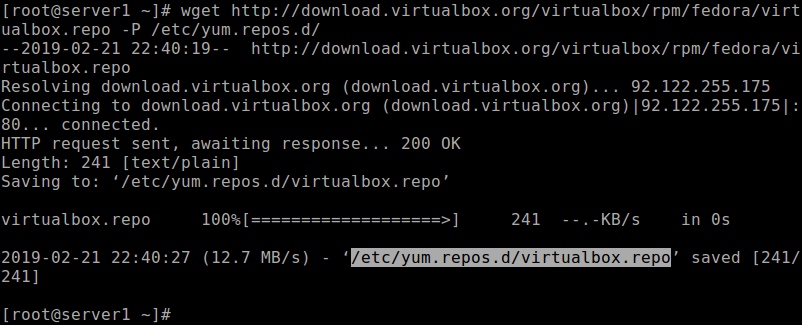
To install VirtualBox on Fedora Linux 30, you first need to download the virtualbox.repo configuration file using the following wget command.
# wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/rpm/fedora/virtualbox.repo -P /etc/yum.repos.d/
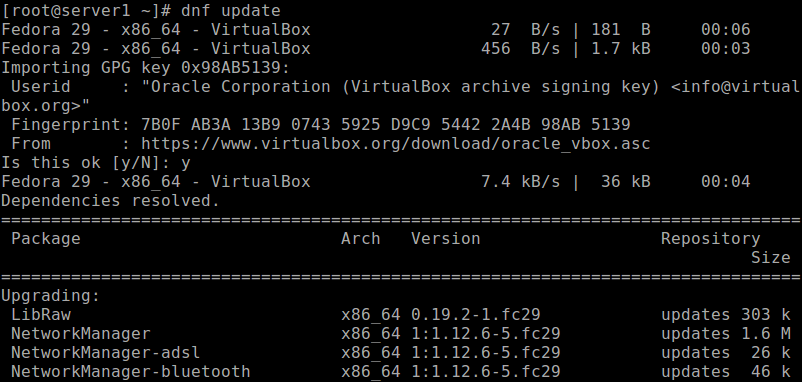
Next, update the installed packages on the system and import the VirtualBox public key by running the following dnf command. This ensures that all system updates are installed and that the system is running the most up-to-date kernel included in the distribution.
Installing Development Tools on Fedora 31
If you want to run the Oracle VM VirtualBox graphical user interfaces (VirtualBox), you need to install Qt and SDL packages. However, if you only want to run VBoxHeadless, the aforementioned packages aren’t required.
In addition, the installer will create kernel modules on the system, therefore you need to install development tools (GNU compiler (GCC), GNU Make (make)) and packages containing header files for your kernel for the build process as well.
# dnf install @development-tools # dnf install kernel-devel kernel-headers dkms qt5-qtx11extras elfutils-libelf-devel zlib-devel
Installing VirtualBox 6.1 on Fedora 31
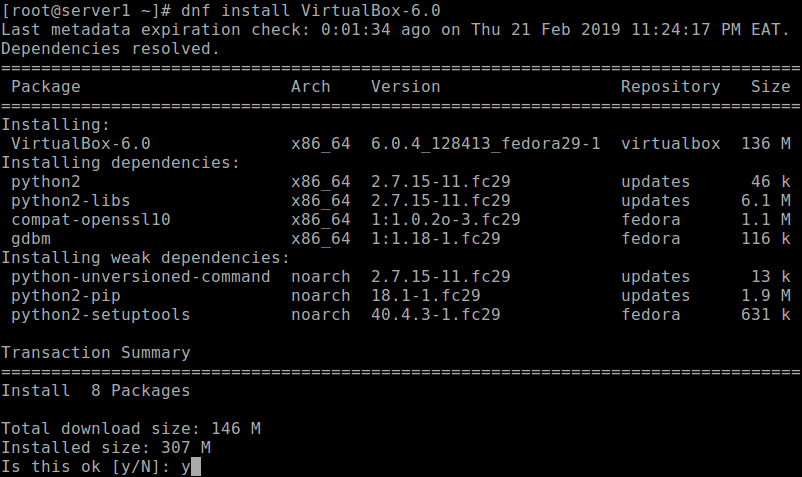
Once the required packages and development tools installed, you can now install VirtualBox 6.0 with the following dnf command.
During the VirtualBox package installation, the installer created a group called vboxusers, all system users who are going to use USB devices from Oracle VM VirtualBox guests must be a member of that group.
To add a user to that group, use the following usermod command.
# usermod -a -G vboxusers tecmint
At this point, you are ready to start using VirtualBox on your Fedora 31. Search for VirtualBox in the Activities search feature and click on it to launch it.
Alternatively, execute the following command to start VirtualBox from the terminal.
Congratulations! You just installed VirtualBox 6.0 on Fedora 31. If you have any questions or thoughts to share with us, use the feedback form below.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
5 thoughts on “How to Install VirtualBox in Fedora Linux”
HI, No need to publish this, but the first line reads: “VirtualBox is a powerful, free, open-source, feature-rich, high performance and cross-platform x86 and AMD64/Intel64 visualization software for enterprise and home use.” One can argue that it VISUALIZES as well, but I guess you mean Virtualize. Thanks for the post. d. Reply
@degski Many thanks for pointing this out. True, it should be virtualization instead of a visualization. We will correct this as soon as possible. Reply
You’ll have to turn USB off, there’s an [new] entry for Fedora 31 in the Wiki, no ifs, buts or maybes. This is new in Fedora 31 and my feeling is, it won’t make Fedora 32, basically, your system is now military-grade secure and military-grade usable at the same time. If you don’t carry 4 stars on your shoulder, it’s overshoot. Reply
/sbin/vboxconfig
vboxdrv.sh: Stopping VirtualBox services.
depmod: WARNING: could not open /lib/modules/4.20.3-200.fc29.x86_64/modules.order: No such file or directory
depmod: WARNING: could not open /lib/modules/4.20.3-200.fc29.x86_64/modules.builtin: No such file or directory
vboxdrv.sh: Starting VirtualBox services.
vboxdrv.sh: Building VirtualBox kernel modules.
vboxdrv.sh: failed: modprobe vboxdrv failed. Please use ‘dmesg’ to find out why. There were problems setting up VirtualBox. To re-start the set-up process, run
/sbin/vboxconfig
as root. If your system is using EFI Secure Boot you may need to sign the
kernel modules (vboxdrv, vboxnetflt, vboxnetadp, vboxpci) before you can load
them. Please see your Linux system’s documentation for more information. Reply
How to Install VirtualBox on Fedora 36 / Fedora 35
VirtualBox is a widely known open-source virtualization software that lets you run multiple guest operating systems (virtual machines) on a single host machine.
It supports the guest virtual machines running Windows, Linux, BSD, OS/2, Solaris, Haiku, and OSx86 operating systems.
Here, we will see how to install VirtualBox on Fedora 36 / Fedora 35.
Add VirtualBox Repository
First, switch to the root user.
Then, install kernel headers and DKMS packages
dnf install -y kernel-devel-$(uname -r) kernel-headers
Next, import Oracle public key to the system.
rpm --import https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox.asc
Then, add the VirtualBox repository to the system with the below command.
dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/rpm/fedora/virtualbox.repo
Install VirtualBox on Fedora 36
BIOS System
First, install VirtualBox using the dnf command.
dnf install -y VirtualBox-6.1
Then, add your user account to the vboxuser group.
EFI System
First, install VirtualBox using the dnf command.
dnf install -y VirtualBox-6.1
Then, add your user account to the vboxuser group.
On EFI secure boot systems, you need to sign VirtualBox modules (vboxdrv, vboxnetflt, vboxnetadp, vboxpci) before loading them. So, to sign the modules, you will need to have a machine owner key that is trusted by EFI firmware.
Follow the below steps to sign all the VirtualBox modules.
First, generate the MOK (Machine Owner Key).
dnf install -y openssl mkdir /root/module-signing cd /root/module-signing openssl req -new -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout MOK.priv -outform DER -out MOK.der -nodes -days 36500 -subj "/CN=MSI/" chmod 600 MOK.priv
Then, import the generated key to the system. This command will prompt you to set the password, which you will later while enrolling the key.
mokutil --import /root/module-signing/MOK.der
Reboot the system and then press any key to start the MOK management utility
1. Choose Enroll MOK
2. Choose View Key 0 to check the Machine Owner Key. If the key is OK, press enter and then select Continue
3. Choose Yes to enroll the key(s) and then enter the password you supplied during the import
4. Finally, choose Reboot to reboot the system
Create a script called /root/module-signing/sign-vbox-modules to sign all the VirtualBox modules using the generated MOK key.
#!/bin/bash for modfile in $(dirname $(modinfo -n vboxdrv))/*.ko; do echo "Signing $modfile" /usr/src/kernels/$(uname -r)/scripts/sign-file sha256 \ /root/module-signing/MOK.priv \ /root/module-signing/MOK.der "$modfile" done
Then, change the ownership of the script and run it. You can run this script whenever you update the system.
chmod 700 /root/module-signing/sign-vbox-modules /root/module-signing/sign-vbox-modules
Finally, start the VirtualBox Linux kernel module service.
Launch VirtualBox
After the installation, you can launch VirtualBox by going to Activities >> Search for VirtualBox or running the virtualbox command in the terminal.
Conclusion
That’s All. I hope you have learned how to install VirtualBox on Fedora 36 / Fedora 35.