- Как установить USB WiFi адаптер TP-Link в Debian
- Шаг 3: Установите предварительные пакеты
- How to Enable WiFi in Debian 11 Bullseye, Fix Missing wlan0
- Step 1: Identifying Wi-Fi Network Card Manufacturer on Debian
- Step 2: Installing firmware matching your network card manufacturer on Debian.
- For Atheros Card:
- For Intel Card:
- How to Install TP-Link USB WiFi Adapter on Debian 10
- Step 1: Open the Terminal
- Step 2: Update the Repository Index
- Step 3: Install the Prerequisites
- Step 4: Download the driver from git hub
- Search
- About This Site
- Latest Tutorials
- Broadcom BCM4311, BCM4312, BCM4313, BCM4321, BCM4322, BCM43224, BCM43225, BCM43227, BCM43228, BCM43142, BCM4331, BCM4352, BCM4360 devices (wl)
- Installation
- Switch between wl/OSS drivers
- Known Issues
- Supported Devices
- Version 6.30.223.271-5
- See Also
- External Links
Как установить USB WiFi адаптер TP-Link в Debian
После перехода на Debian 10 с Ubuntu и, к сожалению, Debian решил не распознать WiFi Устройство/USB WiFi адаптер. Пришлось приложить немало усилий, пытаясь настроить драйвер устройства, но всё свелось к тому, что в Debian отсутствовал соответствующий драйвер для устройства TP-Link WiFi. После установки драйвера и окончательного успеха в работе WiFi в Debian.
Пожалуйста, следуйте этим шагам один за другим, чтобы установить соответствующий драйвер TP-Link WiFi на ваш Debian:
Откройте приложение Терминал, нажав клавишу Super (Windows) и найдя его через Пуск приложений следующим образом:
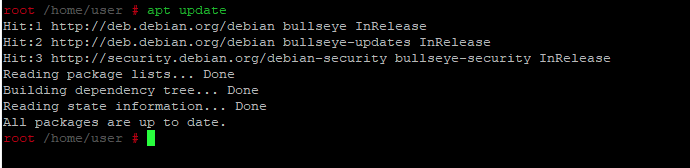
Шаг 2: Обновление индекса репозитория
Войдите в систему как root, введя su, а затем пароль root. Теперь вы авторизованы для добавления/удаления и настройки программного обеспечения в Debian. Теперь введите следующую команду, чтобы обновить индекс локального репозитория с индексом интернет-репозитория. Это поможет вам установить последнюю версию программного обеспечения, доступного в Интернете.
Шаг 3: Установите предварительные пакеты
Процесс установки драйвера WiFi адаптера включает в себя его загрузку из Интернета и последующую установку в вашей системе. Это требует установки Linux Headers, Build Essential и пакетов git в Debian. Выполните следующие команды от имени root, одну за другой, в Терминале:
apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)apt-get install build-essentialHow to Enable WiFi in Debian 11 Bullseye, Fix Missing wlan0
Are you looking for a way to fix no Wi-Fi problem on Debian? If yes, then you have landed on the right page. In this tutorial, I will share a straightforward method that you can apply to fix the missing Wi-Fi adapter issue on Debian.
If you just did a fresh Debian install on a PC, then you will most likely run into an issue where you can’t access Wi-Fi. Debian will not even show you wlan0 device if you run ip addr show the command.
This happens because the Debian ISO doesn’t include the Wi-Fi firmware by default. Thus, you have to manually install the firmware from a non-free repo in order to use the Wi-Fi facility.
Depending on the network card manufacturer of your computer, you have to install the correct firmware. If you are using a laptop of popular brands such as Lenovo, Acer, Samsung or Asus, which usually use Atheros network card, it could be a little daunting to find the right version of the firmware to install.
I ran into this issue a little while ago and couldn’t find a quick solution so I thought maybe share the fix, so others do not have to face what I went through. Let’s cut to the chase and see the steps involved:
- First, identify the manufacturer of your Wi-Fi network card.
- Install the firmware matching your network card manufacturer.
See how to complete these two steps below.
Step 1: Identifying Wi-Fi Network Card Manufacturer on Debian
There is a CLI utility called lshw which can help you identify all the hardware installed on your computer, including the network card. A very good chance is that it will be pre-installed. If not, then you will have to install it by connecting your PC to an Ethernet connection. You can use your Android phone as an Ethernet device via USB tethering.
Install lshw like this:
sudo apt install lshw
It is now time to use lshw to find out the network card vendor. Run the command below and wait for it to generate the HTML report.
lshw -html > lsh.html
Open the generated HTML report(lsh.html) in the browser and search for network or network controller. You will find the result something like this:
From this screenshot, it is now evident that the vendor of my network card is Atheros! But it can also be Intel. It all depends on the PC/laptop manufacturer. Never mind, it doesn’t matter because, firmware for both these cards available for Debian. See in next section, how to install it.
Step 2: Installing firmware matching your network card manufacturer on Debian.
In the last step, you will know what network card is installed on your system. So, based on what card it is, you need to install the correct firmware.
For Atheros Card:
On my Lenovo Ideapad 300-15ISK, it was Atheros card, as evident from the snapshots above.
So, to install the firmware for Atheros, you issue the following command.
sudo apt install firmware-atheros
After the firmware installs, you can try restarting your computer. You will now see that it will detect the available Wi-Fi networks nearby.
Alternatively, you can download the DEB file for the same firmware on some other device, transfer to the Debian PC, and manually install it.
After getting the DEB file, you open the terminal in the Downloads directory and issue this command.
sudo dpkg -i firmware-atheros*
After it completes, successfully, you will have both; wla0 will start showing along with the Wi-Fi network.
For Intel Card:
To install the firmware for Intel network controller, you issue the following command.
sudo apt install firmware-iwlwifi
After it installs successfully, restart your computer. You will now see that it will detect nearby Wi-Fi networks.
Alternatively, you also download the DEB file for the same firmware on some other device, transfer to the Debian PC, and install it manually.
Find and get Intel Wireless firmware here: firmware-iwlwifi (20210315-3) [non-free]
After getting the DEB file, you open the terminal in the Downloads directory and issue this command.
sudo dpkg -i firmware-iwlwifi*
After it completes, successfully, you will have both; wlan0 will start showing along with the Wi-Fi network.
These are the only two steps you have to perform. If you follow them correctly, I am sure you will get Wi-Fi access on Debian in easy way. Although, I hope that they make this process a bit smoother by restoring these back to the installation ISO.
How to Install TP-Link USB WiFi Adapter on Debian 10
So, a few days back I shifted to Debian 10 from Ubuntu and unfortunately, Debian decided to not recognize my WiFi Dongle/USB WiFi Adapter. It took a lot of effort at trying to configure the device driver but it boiled down to the fact that my Debian lacked the appropriate driver for my TP-Link WiFi device. After installing the driver and finally getting successful in getting my WiFi work on Debian, I jotted down the steps for whoever faces the same situation as me.
We have run the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on a Debian 10 Buster system.
Please follow these steps, one by one, in order to install the appropriate TP-Link WiFi driver on your Debian:
Step 1: Open the Terminal
Open the Terminal application by pressing the Super(Windows) key and searching for it through the Application Launcher as follows:
Step 2: Update the Repository Index
Login as root by entering su and then the password for root. You are now authorized to add/remove and configure software on Debian. Now, enter the following command in order to update the local repository index with that of the Internet. This helps you in installing the latest version of a software available online.
Step 3: Install the Prerequisites
The process of installing the WiFi Adapter’s driver includes downloading it from the Internet and then installing it on your system. This requires installing Linux Headers, Build Essential and the git packages on your Debian. Run the following commands as root, one by one, in your Terminal:
# apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
# apt-get install build-essential
Step 4: Download the driver from git hub
Search for the relevant driver on GitHub. I found the driver for my TP-Link device on:
https://github.com/lwfinger/rtl8188eu
Download the driver by cloning it on your system. This is how I cloned my driver:
$ git clone https://github.com/lwfinger/rtl8188eu
The cloned folder will now exist in your home drive. Simply switch to this folder through the cd command. And then install the driver through the make command. For example, I followed the following steps:
Finally, configure the driver through the following command and restart your system:
You can also blacklist an internal driver if it already existed on your system by adding it to the file: /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist
As you log in again, you will be able to see the WiFi adapter card listed in the WiFi tab of the Settings utility.
You are now ready to connect to the Internet through this adapter.
Search
About This Site
Vitux.com aims to become a Linux compendium with lots of unique and up to date tutorials.
Latest Tutorials
Broadcom BCM4311, BCM4312, BCM4313, BCM4321, BCM4322, BCM43224, BCM43225, BCM43227, BCM43228, BCM43142, BCM4331, BCM4352, BCM4360 devices (wl)
This page describes how to enable support for WiFi devices based on Broadcom wireless LAN chips, using the vendor driver on Debian systems.
The proprietary Broadcom wireless LAN driver (wl, aka broadcom-sta) provides support for some Broadcom-based PCI/PCIe hardware. It includes a binary-only component targeted for the x86 or x86-64 architecture. Supported devices are listed at the end of this page.
- Add a «non-free» component to /etc/apt/sources.list for your Debian version, for example:
# Debian 9 "Stretch" deb http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch-backports main contrib non-free
# Debian 10 "Buster" deb http://deb.debian.org/debian buster-backports main contrib non-free
# Debian 11 "Bullseye" deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye contrib non-free
# apt-get update # apt-get install linux-image-$(uname -r|sed 's,[^-]*-[^-]*-,,') linux-headers-$(uname -r|sed 's,[^-]*-[^-]*-,,') broadcom-sta-dkms
# apt-get install -f # dpkg-reconfigure broadcom-sta-dkms
# find /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/updates
# modprobe -r b44 b43 b43legacy ssb brcmsmac bcma
Switch between wl/OSS drivers
#!/bin/sh WIFI=$(find /sys/class/net -follow -maxdepth 2 -name wireless 2>/dev/null|cut -d / -f 5|head -1) echo ip link set $WIFI down ip link set $WIFI down >/dev/null 2>&1 modprobe -r wl brcmsmac modprobe -r cfg80211 brcmsmac cordic brcmutil bcma if [ "$1" = "wl" ]; then modprobe wl else modprobe brcmsmac fi sleep 0.1 WIFI=$(find /sys/class/net -follow -maxdepth 2 -name wireless 2>/dev/null|cut -d / -f 5|head -1) echo ip link set $WIFI up ip link set $WIFI up >/dev/null 2>&1
Known Issues
- The Sonics Silicon Backplane driver (ssb) conflicts with the wl driver (545388).
- b44, b43, b43legacy and ssb are blacklisted by default as of broadcom-sta 5.10.91.9.3-3 (brcm80211 and brcmsmac since 5.100.82.38-1, 5.100.82.38-2 respectively).
- This prevents use of any Ethernet device supported by b44.
- iwconfig(8) (e.g. iwconfig wlan0 power off)
- laptop-mode-tools: set WIRELESS_BATT_POWER_SAVING=0 within /etc/laptop-mode/conf.d/wireless-power.conf
See bugs reported on this package in the Debian Bug Tracking System.
Supported Devices
Version 6.30.223.271-5
This driver is packaged for the Debian 9 «Stretch» release as broadcom-sta-dkms.
- Broadcom BCM4311 (PCI IDs 14e4:4311, 14e4:4312)
- Broadcom BCM4312 (PCI ID 14e4:4315)
- Broadcom BCM4313 (PCI ID 14e4:4727)
- Broadcom BCM4321 (PCI IDs 14e4:4328, 14e4:4329, 14e4:432a)
- Broadcom BCM4322 (PCI IDs 14e4:432b, 14e4:432c, 14e4:432d)
- Broadcom BCM43224 (PCI IDs 14e4:0576, 14e4:4353)
- Broadcom BCM43225 (PCI ID 14e4:4357)
- Broadcom BCM43227 (PCI ID 14e4:4358)
- Broadcom BCM43228 (PCI ID 14e4:4359)
- Broadcom BCM43142 (PCI ID 14e4:4365)
- Broadcom BCM4331 (PCI ID 14e4:4331)
- Broadcom BCM4352 (PCI ID 14e4:43b1)
- Broadcom BCM4360 (PCI IDs 14e4:43a0, 14e4:4360)
See Also
- bcm43xx — Broadcom 43xx wireless devices
- brcm80211 — Broadcom BCM4313, BCM43224, BCM43225 devices
- How to use a WiFi interface
- NDISwrapper
External Links