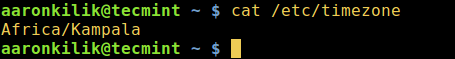- Как изменить часовой пояс Linux
- Как работает время в Linux?
- Настройка часового пояса в linux
- 1. Ссылка /etc/localtime
- 2. Настройка с помощью tzdata
- 3. Настройка с помощью systemd
- 4. Настройка часового пояса в GUI
- Выводы
- How to Check Timezone in Linux
- Related Posts
- 15 thoughts on “How to Check Timezone in Linux”
Как изменить часовой пояс Linux
Мы очень часто пользуемся временем в Linux, начиная от простой задачи узнать сколько сейчас времени, до более сложной — посмотреть логи или узнать когда произошло то или иное событие в системе. Все завязано на времени, поэтому очень важно, чтобы часы шли правильно.
Наша планета разделена на часовые пояса, это было сделано с одной простой целью, чтобы время в любой точке планеты соответствовало солнечному времени. Время между этими зонами отличается на час и всего таких поясов — 24, за эталон взято время по нулевому, Гринвичскому меридиану.
Поэтому в определенный момент время в разных участках планеты будет отличаться на час. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как изменить часовой пояс Linux, чтобы операционная система правильно работала со временем и могла правильно его синхронизировать через интернет.
Как работает время в Linux?
Операционная система Linux хранит и обрабатывает системное время в специальном Unix формате — количество секунд прошедших с полуночи первого января 1970 года. Эта дата считается началом эпохи Unix. И используется не ваше локальное время, а время по гринвичскому меридиану.
Для преобразования времени по Гринвичу в региональное время используется часовой пояс. Это преобразование выполняется для каждого пользователя. Это необходимо, чтобы каждый пользователь мог настроить для себя правильное по его временной зоне время. Такое поведение просто необходимо на серверах, когда на одной машине могут работать люди из разных частей мира.
По умолчанию в системе может быть установлен неправильный часовой пояс, это приведет к путанице в логах событий, да и другим трудностям. Но все это легко исправить. Дальше мы рассмотрим несколько способов изменить часовой пояс Linux.
Настройка часового пояса в linux
1. Ссылка /etc/localtime
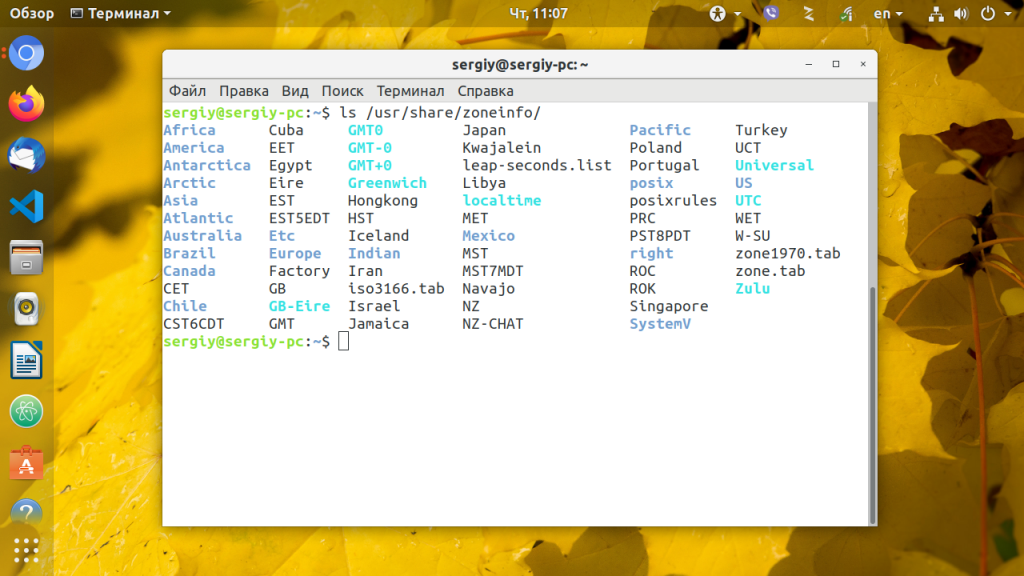
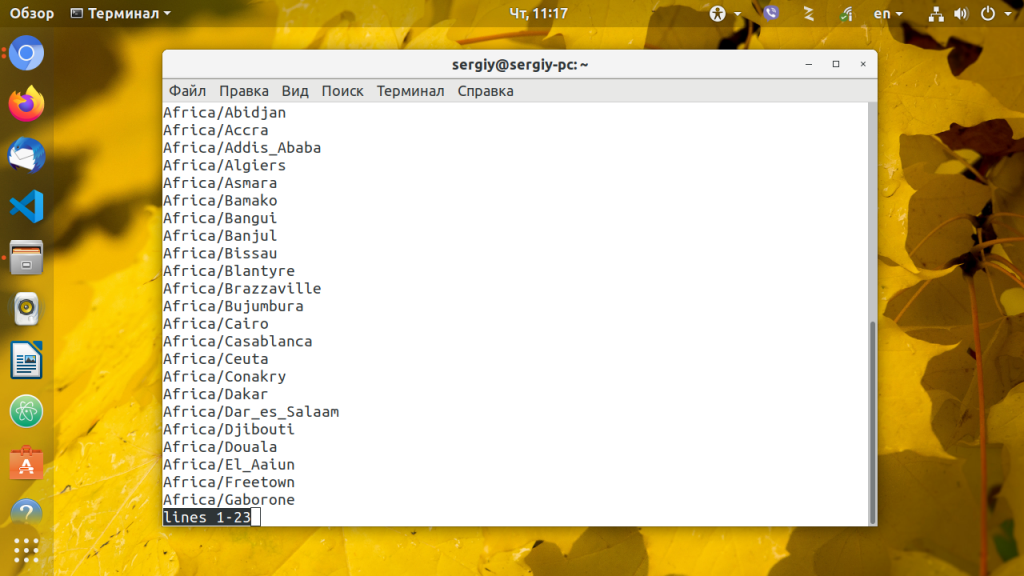
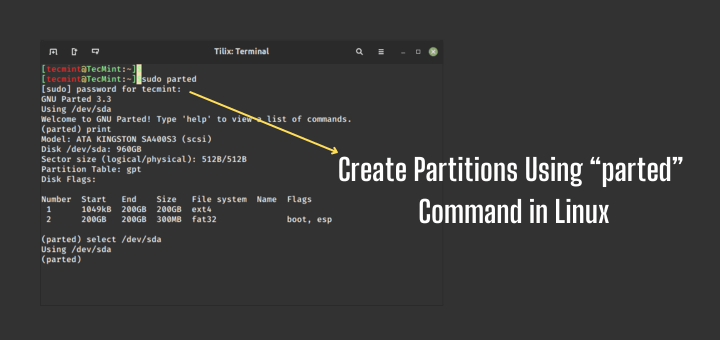
Наиболее популярный и поддерживаемый в большинстве дистрибутивов способ установки часового пояса для всех пользователей — с помощью символической ссылки /etc/localtime на файл нужного часового пояса. Список доступных часовых поясов можно посмотреть командой:
Сначала создайте резервную копию текущего часового пояса:
cp /etc/localtime /etc/localtime.bak
Для создания символической ссылки используйте команду ln -sf. Файл зоны нужно выбрать из доступных в системе. Например, мой часовой пояс — Украина, Киев, для установки будет использоваться следующая команда:
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Kiev /etc/localtime
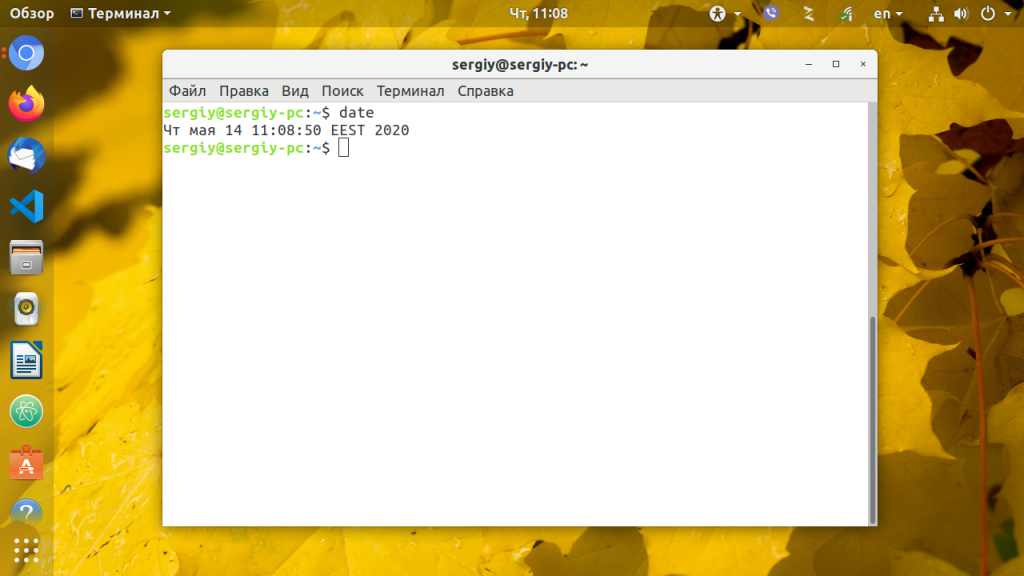
Теперь можете проверить текущее системное время с помощью утилиты date:
Если у вас установлена утилита rdate можно синхронизировать время с сетью:
sudo rdate -s time-a.nist.gov
Осталось только синхронизировать ваши аппаратные часы с новыми настройками, для этого выполните команду:
Если нужно изменить часовой пояс только для определенной программы или скрипта, просто измените для нее переменную окружения TZ, например:
Эта настройка сохраняется только для текущего сеанса командной оболочки. Чтобы сменить часовой пояс linux для определенного пользователя тоже нужно использовать переменную среды TZ. Только ее нужно добавить в файл ~/.environment. Этот файл читается по умолчанию при входе в систему, а значит переменная будет доступна всем программам:
Готово, теперь вы знаете как выполняется настройка часового пояса linux для определенного пользователя.
2. Настройка с помощью tzdata
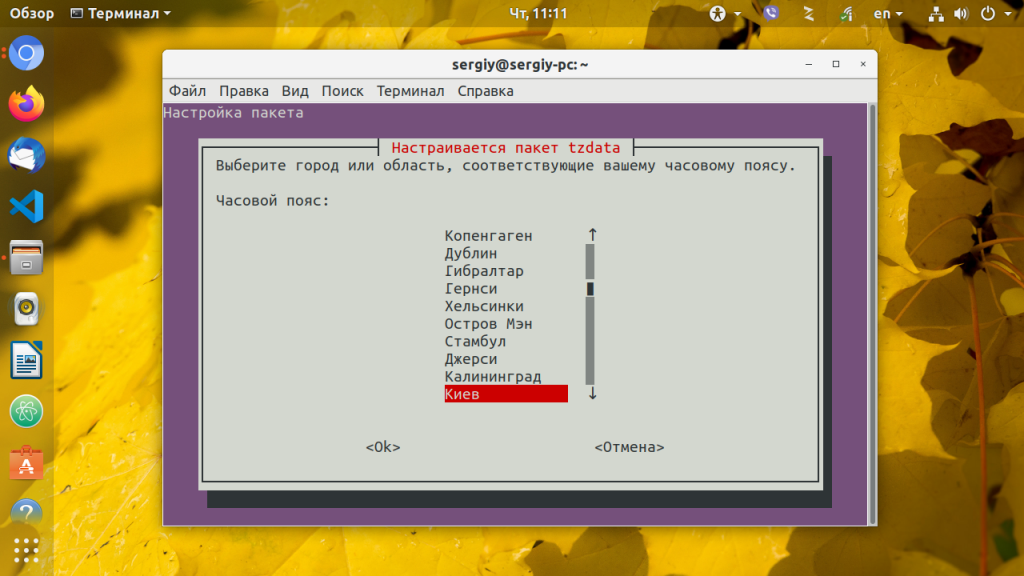
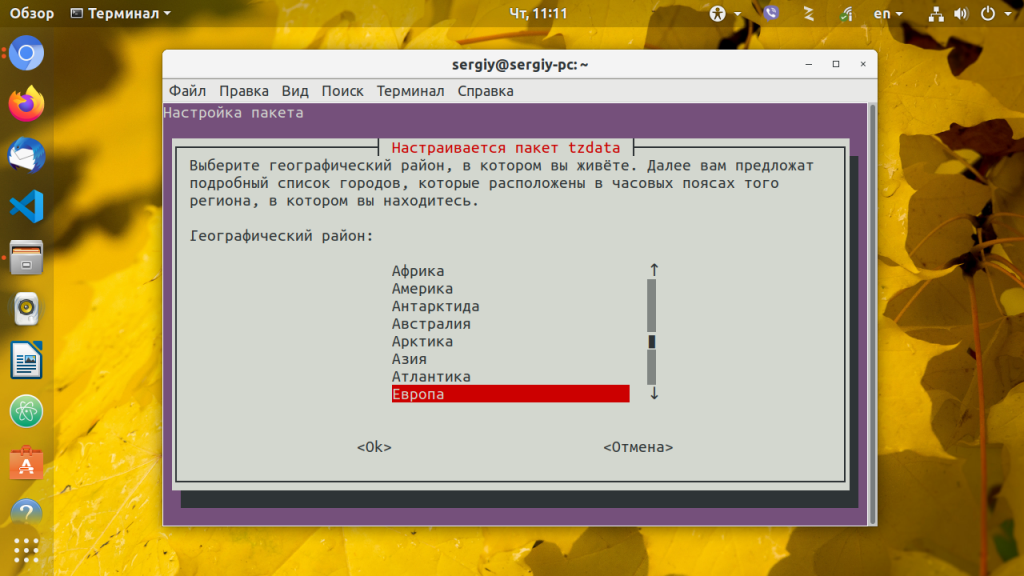
Если вы не хотите использовать описанный выше способ, можно воспользоваться специальными утилитами. Вот только в разных дистрибутивах используются свои утилиты. Рассмотрим варианты для самых популярных дистрибутивов.
В большинстве случаев вы увидите подобное диалоговое окно:
Здесь просто нужно выбрать нужный часовой пояс и нажать кнопку Enter. После этого для окончательного применения настроек нужно будет перезагрузить систему.
3. Настройка с помощью systemd
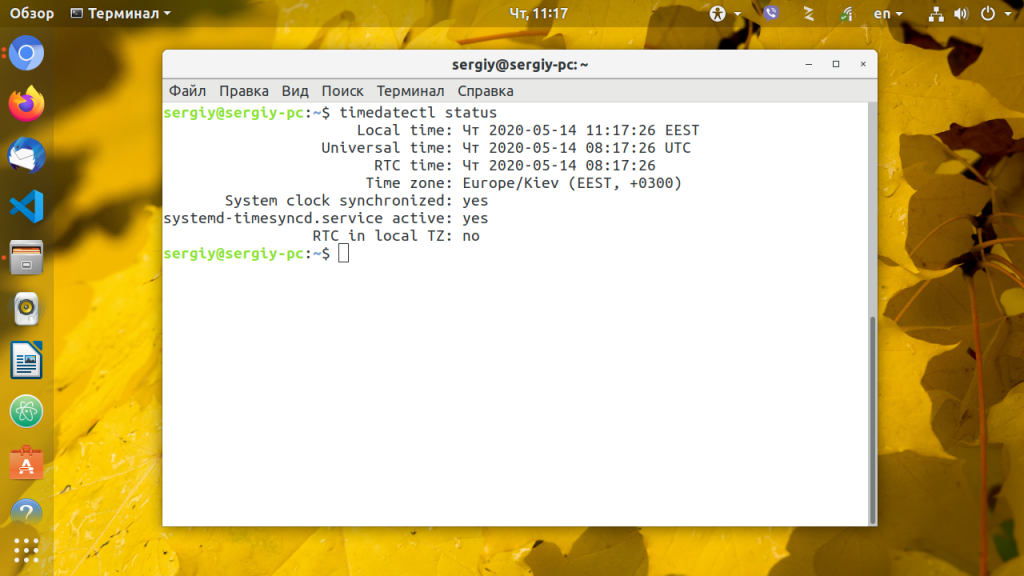
В systemd есть своя утилита для настройки даты и часового пояса. Чтобы узнать текущее состояние выполните:
Для просмотра всех доступных временных зон выполните такую команду:
А для установки нужного часового пояса используйте команду set-timezone, например, тот же Europe/Kiev:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Kiev
4. Настройка часового пояса в GUI
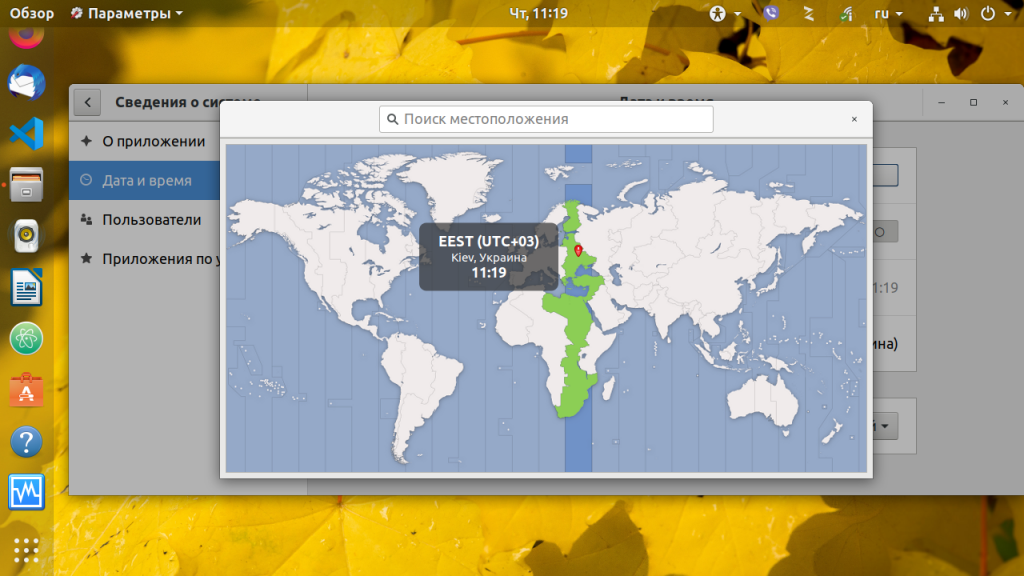
В дистрибутиве Ubuntu и других, использующих Gnome, настройка часового пояса Linux может быть выполнена прямо в параметрах системы. Для этого выберите пункт Сведения о системе, затем Дата и время, выберите свое местоположение на карте, или наберите название для поиска в поле ввода:
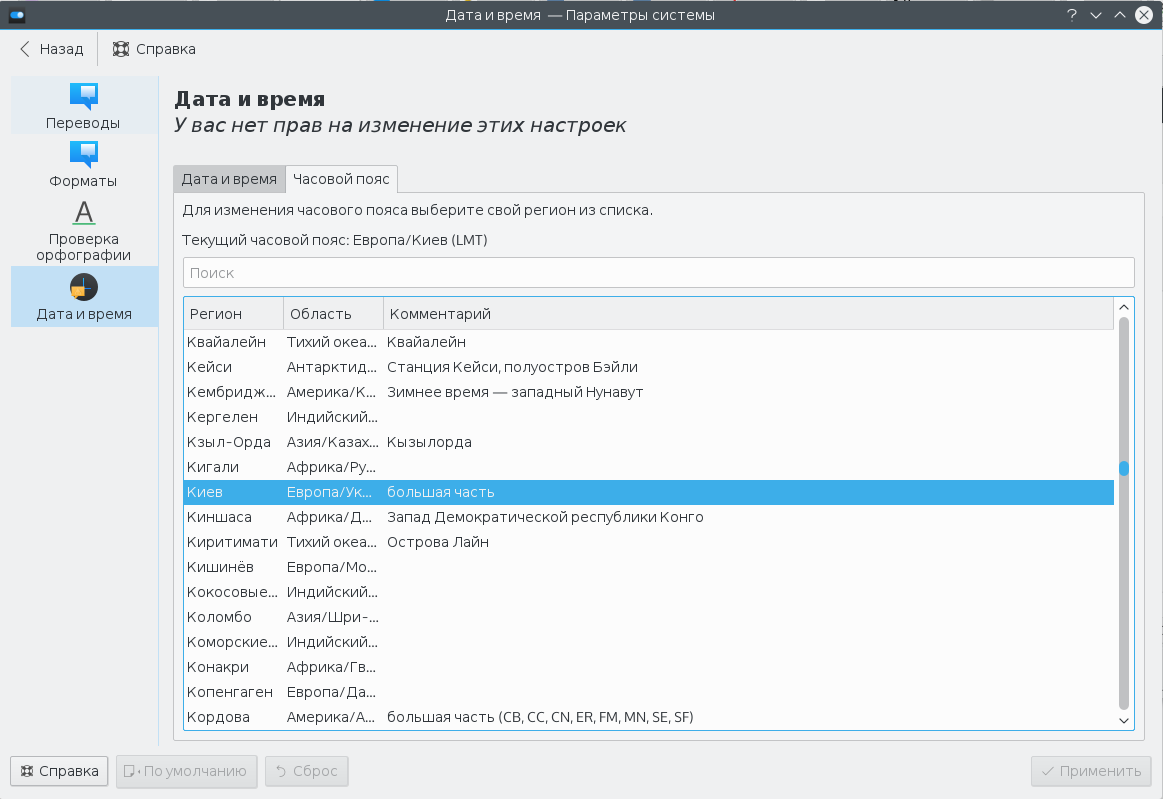
В KDE аналогично можно установить часовой пояс в настройках системы. Запустите утилиту настроек, откройте пункт Локализация, перейдите в раздел Дата и время, а затем откройте вкладку Часовой пояс:
Остается выбрать часовой пояс в списке и нажать кнопку Применить. Здесь уже изменения должны проявиться моментально.
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете как выполняется установка часового пояса в linux и сможете настроить не только свой домашний компьютер но и сервер с множеством пользователей, которым нужен отдельный часовой пояс для правильного местного времени. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение видео, в котором подробно рассказано, что такое часовые пояса и зачем они нужны:
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Check Timezone in Linux
In this short article, we will walk newbies through the various simple ways of checking system timezone in Linux. Time management on a Linux machine especially a production server is always an important aspect of system administration.
There are a number of time management utilities available on Linux such as date and timedatectl commands to get the current timezone of system and synchronize with a remote NTP server to enable an automatic and more accurate system time handling.
Well, let us dive into the different ways of finding out our Linux system timezone.
1. We will start by using the traditional date command to find out present timezone as follows:
Alternatively, type the command below, where %Z format prints the alphabetic timezone and %z prints the numeric timezone:
Note: There are many formats in the date man page that you can make use of, to alter the output of the date command:
2. Next, you can likewise use timedatectl, when you run it without any options, the command displays an overview of the system including the timezone like so:
More so, try to employ a pipeline and grep command to only filter the timezone as below:
$ timedatectl | grep “Time zone”
3. In addition, users of Debian and its derivatives can display the content of the file /etc/timezone using cat utility to check your timezone:
Important: For REHL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 25-22 users, the file /etc/localtime is a symbolic link to the timezone file under the directory /usr/share/zoneinfo/.
However, you can use date or timedatectl command to display the current time and timezone as well.
To change the timezone, create the symbolic link /etc/localtime to the appropriate timezone under /usr/share/zoneinfo/:
$ sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/zoneinfo /etc/localtime
The flag -s enables creation of a symbolic link, otherwise a hard link is created by default and -f removes an existing destination file, which in this case is /etc/localtime.
For example, to change the timezone to Africa/Nairobi, issue the command below:
$ sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Africa/Nairobi /etc/localtime
That’s all! Do not forget to share you thoughts about the article by means of the feedback form below. Importantly, you should look through this time management guide for Linux to get more insight into handling time on your system, it has simple and easy-to-follow examples.
Lastly, always remember to stay tunned to Tecmint for the latest and interesting Linux stuff.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
15 thoughts on “How to Check Timezone in Linux”
Any suggestion where should I check further? All settings seem correct? It looks like there is an extra character at the end of America/Chicago. ERROR:
tzone_read_system: no match found for America/Chicago^? Here are my current settings
[[email protected] etc]# timedatectl Local time: Thu 2020-04-23 11:28:51 CDT Universal time: Thu 2020-04-23 16:28:51 UTC RTC time: Thu 2020-04-23 16:28:51 Time zone: America/Chicago (CDT, -0500) NTP enabled: no NTP synchronized: yes RTC in local TZ: no DST active: yes Last DST change: DST began at Sun 2020-03-08 01:59:59 CST Sun 2020-03-08 03:00:00 CDT Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at Sun 2020-11-01 01:59:59 CDT Sun 2020-11-01 01:00:00 CST [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# ls -ltr /etc/localtime lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 37 Mar 26 12:20 /etc/localtime -> ../usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Chicago [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# timedatectl | grep local RTC in local TZ: no [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# timedatectl list-timezones | grep Chicago America/Chicago [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# date Thu Apr 23 11:34:36 CDT 2020 [[email protected] etc]#
CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core). We just fixed the issue by “rerunning” the timezone. The log showed bad characters at the end, America/Chicago^? (^?) . We ran tzselect and then chose options 2, 49, 11 for Chicago. Gracefully rebooted the server “shutdown -r now” Thank you, Aaron, for your reply. Reply
@Ketan Great! Many thanks for sharing the solution. This will be of benefit to readers in the future. Reply
The formatting on your «%Z %z» example is a bit off. When your text is displayed, the usual, plain double quotes («) are replaced with “pretty” ones (”) . When I pasted your example into my terminal, I only received errors. You should format your example as:
(Here’s hoping that when I post this comment, the website doesn’t replace my simple quotes with pretty ones!) Reply
Yes, my simple quotes were replaced with pretty ones. That’s not good for displaying things on a technical website. You should see about disabling that feature. Reply
On Centos 7 there’s no “clock” under /etc/sysconfig. And neither is there a /etc/timezone, which, from what you’re saying, should exist on most or all linux distributions. Reply
@lethargo Yap, you can use /etc/localtime instead of /etc/timezone. Thanks for mentioning that. Reply
Indeed, but /etc/localtime is not plain text, it is a binary file. To be more specific, it is a symbolic link to a binary file found in /usr/share/zoneinfo. So you couldn’t simply grep it in Centos 🙂 You simply create a symbolic link to whatever timezone you want and then you can use date or timedatectl to see the current clock. Reply
@lethargos Once again, many thanks for the vital insight into checking and managing timezone on RHEL/CentOS 7, this will be very helpful to users out there. Reply
You’re welcome, but shouldn’t you update the article accordingly, so that other users actually know? There’s a higher chance that they’ll read the article than the comments.
@lethargos As you usefully suggested, we have updated the article to include the correct way of setting and checking timezone in REHL 7/CentOS 7/Fedora 25-22 systems. Many thanks for always following us and offering constructive thoughts.
Hello, How can I change the timezone and how can i set the time period of 12 hrs instead of 24hrs? Reply