What is var log messages (/var/log/messages)
Operating system log data, and Linux in particular, contain a plethora of diagnostics regarding the machine. Linux logs everything from kernel operations to users’ operations, enabling you to view practically every activity taken on the servers. Whenever you administer any Linux computers, you must be aware of where the log files are usually stored and what they include. Several log files seem to be peculiar to deployment, and this folder can indeed hold programs like samba, apache, Lighttpd, and mail. We’ll go through what Linux log files are actually, in which directory you can locate them, as well as how to analyze them in this part. Take a while whenever your system is functioning properly to study and comprehend the contents of different log files. This will assist you whenever there is a catastrophe, and you need to dig through the log data to figure out what’s wrong.
Var/Log/Messages:
This folder contains overall system notifications and messages recorded at system boot. The folder /var/log/messages contain a variety of messages, such as mail, kern, auth, cron, daemon, and so on. Linux log data is a useful debugging utility whenever you run into problems with the Linux operating system, programs, or server. They give a chronology of the Linux system, apps, and framework actions.
Linux logs are simple documents that may be located in the /var/log folder and subdirectories. The “.conf” file that comes with it governs logging. When problems emerge, the very first thing an owner should do is examine log files. Log records are written to several destinations for difficulties with desktop apps. Whether or not the program enables customized log setup, the developer will determine which application software publishes logs.
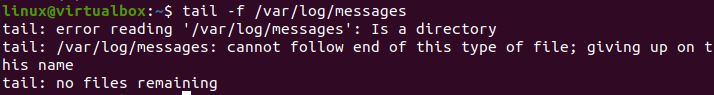
For instance, Crash reports are written to ‘/.chrome/Crash Reports’ in Chrome. All Linux has log data: the OS, core, package controllers, boot routines, Xorg, Apache, MySQL, etc. Unfortunately, the Ubuntu 20.04 system doesn’t record its log in /var/log/messages folder. However, it saves the record in the/var/log/Syslog directory. Therefore we will look to search for the logs in the /var/log/messages folder of Ubuntu 20.04 first. Firstly, you need to open the command-line shell via the shortcut key “Ctrl+Alt+T”. After opening it, we will be utilizing the “tail” command with the “-f” flag to check the logs in the “/var/log/messages”. In return, we have got the error that there is no such directory.
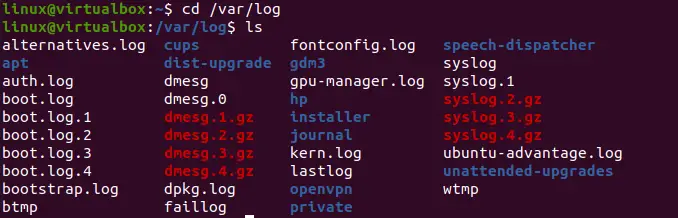
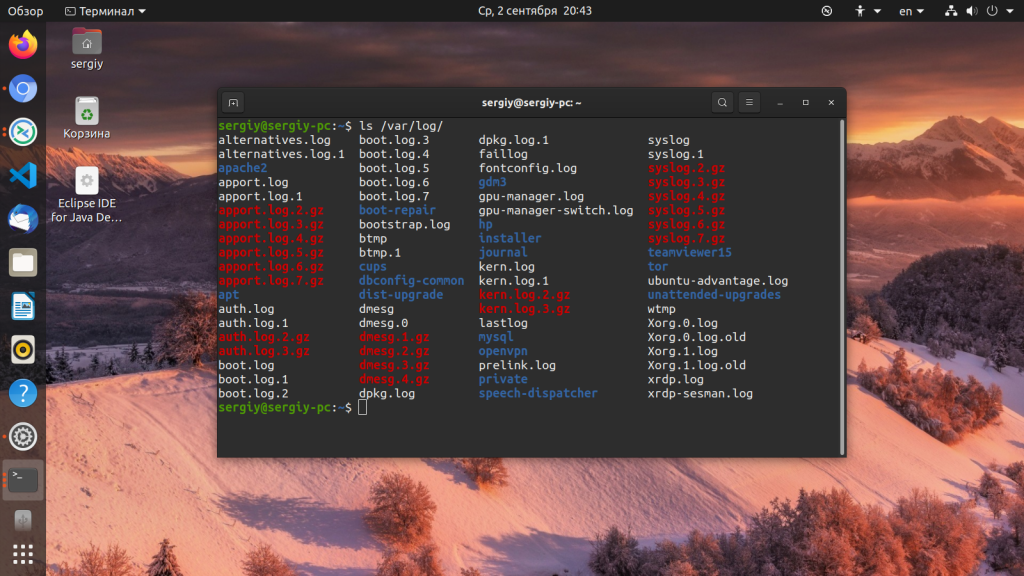
In this post, we’ll look at Linux system logs in particular. First and foremost, use the cd instruction to go to this directory “/var/log” as shown in the image. Then, list all its files and folders using the simple list “ls” command. In return, we can see the displayed files and folders residing in this folder. These files and folders contain log records of our system.
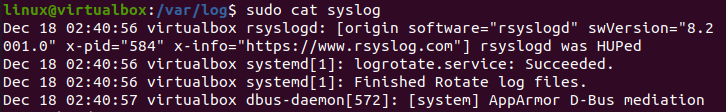
As mentioned earlier, most of our system logs are saved to the “Syslog” file of the “/var/log” directory. So, we will first begin with displaying all the log records in the “Syslog” folder. For this, we must have sudo privileges at our end. The command is started with the keyword “sudo” followed by the keyword “cat” to open the directory “Syslog” as shown in the attached image. The output displays all the system logs from start to end in your shell terminal. We have only displayed a few logs in our photos to save space.
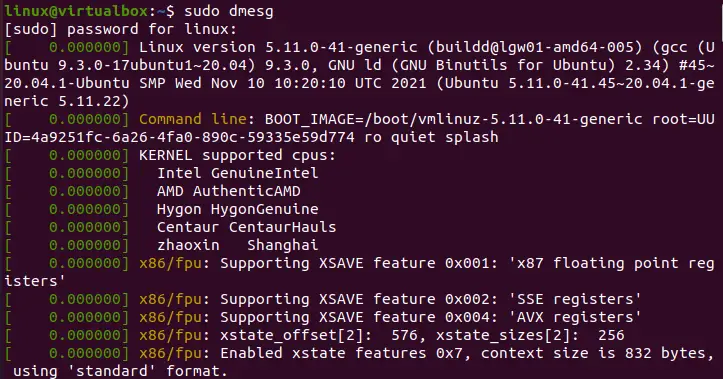
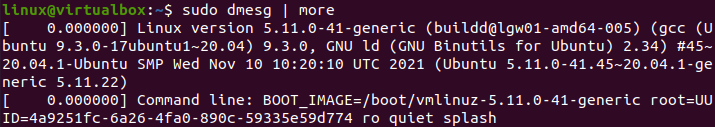
Let’s see another file containing logs for our system in the “/var/log” folder. This time we have chosen the “dmesg” files of this folder. It shows simple logs and system records in it as below.
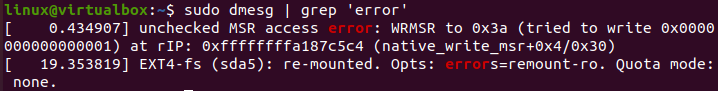
Each record in the log files is of a specific type, i.e., error failed, warn, etc. Let’s specify our sudo command a little with the “dmesg” keyword. We have utilized the “grep” package here to list the records of this log file, specifically of the “error” type. You can see the instruction and its output below. The command has listed and highlighted the logs of only the “error” type.
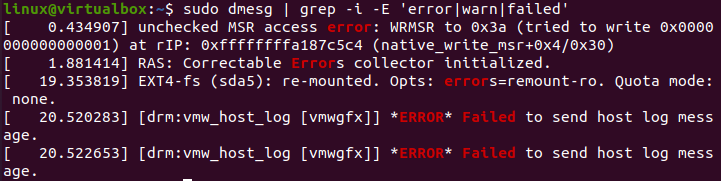
You can also mention more than one specification for a log record to display on the shell. So, within the same “dmesg” command, we have been using the “error”, “warn”, and “failed” parameters with grep to display all three types of log records. In return, we have got many records for it, as shown in the attached picture.
To do a generic search, you can just utilize the keyword “more” instead of “grep” as below.
One can clean the log when the machine is in a testing regime or maybe if you do not bother what was in it. However, if one of your applications generates a failure, the failure logs seem to be the only location where you can get a detailed explanation. If you’re positive that neither of the records is of any value to you, you may always delete them.
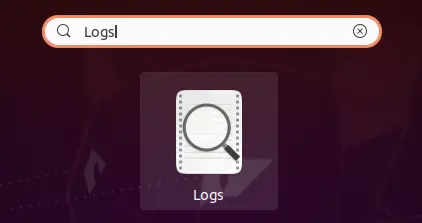
There is another way to see the system logs if you don’t want to use the shell console of Ubuntu 20.04. There is an application named “Logs” in Ubuntu 20.04 that can allow you to see different types of logs. You have to open it through the search bar of your Ubuntu system’s activity area. Search for it as shown and tap on it to open.
Here you have all the types of logs in your Ubuntu 20.04 system Logs application. You can get the information regarding important logs, all logs at one place, application logs, system logs, security and hardware logs
Conclusion:
This article has covered the explanation of answering: what is var/log/messages in Ubuntu 20.04 system. We have discussed different types of commands to list all the generic logs, specific logs, i.e., warn, failed, error. We have done it for specific folders in var/log/ folder. We have also discussed the way to check logs through the Logs application of Ubuntu 20.04.
About the author
Omar Farooq
Hello Readers, I am Omar and I have been writing technical articles from last decade. You can check out my writing pieces.
Как посмотреть логи в Linux
Системные администраторы, да и обычные пользователи Linux, часто должны смотреть лог файлы для устранения неполадок. На самом деле, это первое, что должен сделать любой сисадмин при возникновении любой ошибки в системе.
Сама операционная система Linux и работающие приложения генерируют различные типы сообщений, которые регистрируются в различных файлах журналов. В Linux используются специальное программное обеспечение, файлы и директории для хранения лог файлов. Знание в каких файлах находятся логи каких программ поможет вам сэкономить время и быстрее решить проблему. В этой статье мы рассмотрим основные части системы логирования в Linux, файлы логов, а также утилиты, с помощью которых можно посмотреть логи Linux.
Расположение логов по умолчанию
Большинство файлов логов Linux находятся в папке /var/log/ вы можете список файлов логов для вашей системы с помощью команды ls:
Ниже мы рассмотрим 20 различных файлов логов Linux, размещенных в каталоге /var/log/. Некоторые из этих логов встречаются только в определенных дистрибутивах, например, dpkg.log встречается только в системах, основанных на Debian.
- /var/log/messages — содержит глобальные системные логи Linux, в том числе те, которые регистрируются при запуске системы. В этот лог записываются несколько типов сообщений: это почта, cron, различные сервисы, ядро, аутентификация и другие.
- /var/log/dmesg — содержит сообщения, полученные от ядра. Регистрирует много сообщений еще на этапе загрузки, в них отображается информация об аппаратных устройствах, которые инициализируются в процессе загрузки. Можно сказать это еще один лог системы Linux. Количество сообщений в логе ограничено, и когда файл будет переполнен, с каждым новым сообщением старые будут перезаписаны. Вы также можете посмотреть сообщения из этого лога с помощью команды dmseg.
- /var/log/auth.log — содержит информацию об авторизации пользователей в системе, включая пользовательские логины и механизмы аутентификации, которые были использованы.
- /var/log/boot.log — Содержит информацию, которая регистрируется при загрузке системы.
- /var/log/daemon.log — Включает сообщения от различных фоновых демонов
- /var/log/kern.log — Тоже содержит сообщения от ядра, полезны при устранении ошибок пользовательских модулей, встроенных в ядро.
- /var/log/lastlog — Отображает информацию о последней сессии всех пользователей. Это нетекстовый файл, для его просмотра необходимо использовать команду lastlog.
- /var/log/maillog /var/log/mail.log — журналы сервера электронной почты, запущенного в системе.
- /var/log/user.log — Информация из всех журналов на уровне пользователей.
- /var/log/Xorg.x.log — Лог сообщений Х сервера.
- /var/log/alternatives.log — Информация о работе программы update-alternatives. Это символические ссылки на команды или библиотеки по умолчанию.
- /var/log/btmp — лог файл Linux содержит информацию о неудачных попытках входа. Для просмотра файла удобно использовать команду last -f /var/log/btmp
- /var/log/cups — Все сообщения, связанные с печатью и принтерами.
- /var/log/anaconda.log — все сообщения, зарегистрированные при установке сохраняются в этом файле
- /var/log/yum.log — регистрирует всю информацию об установке пакетов с помощью Yum.
- /var/log/cron — Всякий раз когда демон Cron запускает выполнения программы, он записывает отчет и сообщения самой программы в этом файле.
- /var/log/secure — содержит информацию, относящуюся к аутентификации и авторизации. Например, SSHd регистрирует здесь все, в том числе неудачные попытки входа в систему.
- /var/log/wtmp или /var/log/utmp — системные логи Linux, содержат журнал входов пользователей в систему. С помощью команды wtmp вы можете узнать кто и когда вошел в систему.
- /var/log/faillog — лог системы linux, содержит неудачные попытки входа в систему. Используйте команду faillog, чтобы отобразить содержимое этого файла.
- /var/log/mysqld.log — файлы логов Linux от сервера баз данных MySQL.
- /var/log/httpd/ или /var/log/apache2 — лог файлы linux11 веб-сервера Apache. Логи доступа находятся в файле access_log, а ошибок в error_log
- /var/log/lighttpd/ — логи linux веб-сервера lighttpd
- /var/log/conman/ — файлы логов клиента ConMan,
- /var/log/mail/ — в этом каталоге содержатся дополнительные логи почтового сервера
- /var/log/prelink/ — Программа Prelink связывает библиотеки и исполняемые файлы, чтобы ускорить процесс их загрузки. /var/log/prelink/prelink.log содержит информацию о .so файлах, которые были изменены программой.
- /var/log/audit/— Содержит информацию, созданную демоном аудита auditd.
- /var/log/setroubleshoot/ — SE Linux использует демон setroubleshootd (SE Trouble Shoot Daemon) для уведомления о проблемах с безопасностью. В этом журнале находятся сообщения этой программы.
- /var/log/samba/ — содержит информацию и журналы файлового сервера Samba, который используется для подключения к общим папкам Windows.
- /var/log/sa/ — Содержит .cap файлы, собранные пакетом Sysstat.
- /var/log/sssd/ — Используется системным демоном безопасности, который управляет удаленным доступом к каталогам и механизмами аутентификации.
Просмотр логов в Linux
Чтобы посмотреть логи на Linux удобно использовать несколько утилит командной строки Linux. Это может быть любой текстовый редактор, или специальная утилита. Скорее всего, вам понадобятся права суперпользователя для того чтобы посмотреть логи в Linux. Вот команды, которые чаще всего используются для этих целей:
Я не буду останавливаться подробно на каждой из этих команд, поскольку большинство из них уже подробно рассмотрены на нашем сайте. Но приведу несколько примеров. Просмотр логов Linux выполняется очень просто:
Смотрим лог /var/log/dmesg, с возможностью прокрутки: