- Install Linux Inside Windows Using VirtualBox [Step by Step Guide]
- Installing Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox
- Requirements
- Troubleshooting: AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS
- Any questions?
- 10 Reasons to Run Linux in Virtual Machines
- Things to Keep in Mind Before Running Linux as a Virtual Machine
- Here Are 10 Benefits of Running Linux on Virtual Machines
- 1. Easy Setup
- 2. Does Not Affect the Host OS
- 3. Resource Sharing
- 4. Multi-Tasking
- 5. Facilitates Software Testing
- 6. Great for Development
- 7. Learning or Research
- 8. Easy to Clone or Migrate
- 9. Try Variety of Distros
- 10. Debugging
- Wrapping Up
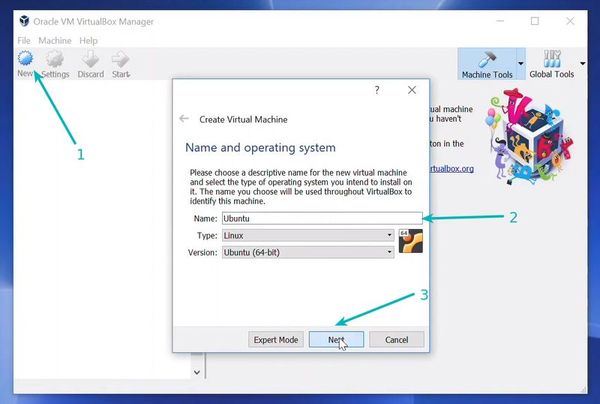
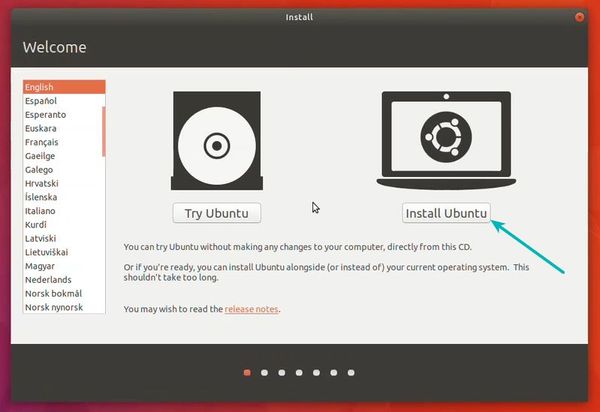
Install Linux Inside Windows Using VirtualBox [Step by Step Guide]
Using Linux in a virtual machine allows you to try Linux within Windows. This step-by-step guide shows you how to install Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox.
- You can clean everything from your system and install Linux.
- You can dual boot Linux with Windows and choose one of the operating systems at the boot time.
- You can even install Linux within Windows from Microsoft Store (though this only provides you with the command line version of Linux).
But if you want to use Linux without making any changes to your Windows system, you can go the virtual machine route.
Basically, you install and use Linux like any regular Windows application. When you just want to try Linux for limited use, virtual machines provide the most comfortable option.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to install Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox.
Installing Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox
VirtualBox is free and open source virtualization software from Oracle. It enables you to install other operating systems in virtual machines. It is recommended that your system should have at least 4GB of RAM to get decent performance from the virtual operating system.
Requirements
- Good internet connection to download software and Linux ISO. (You can also use some other computer with an internet connection to download these files.)
- Windows system with at least 12 GB of free space.
- Windows system with 4GB of RAM. (It can work with less RAM as well, but your system will start to lag while using Linux in the virtual machine.)
- Make sure to enable virtualization in the BIOS (some system need it)
I am installing Ubuntu 17.10 in this tutorial, but the same steps apply to any other Linux distribution. If you prefer videos, you can watch the one below from our YouTube channel:
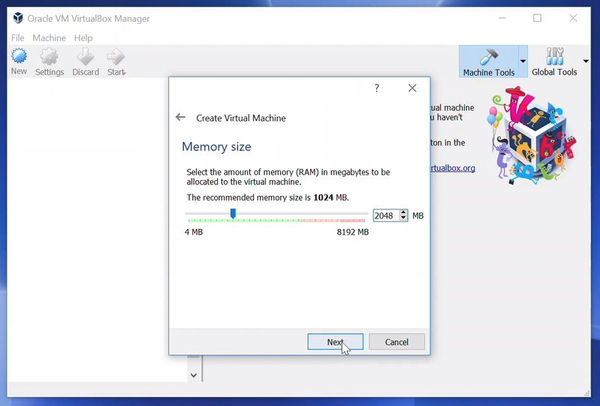
Allocate RAM to the virtual OS. My system has 8GB of RAM and I decided to allocate 2GB of it. You can use more RAM if your system has enough extra.
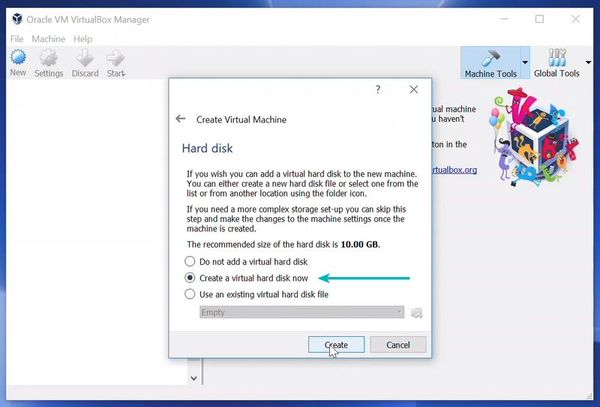
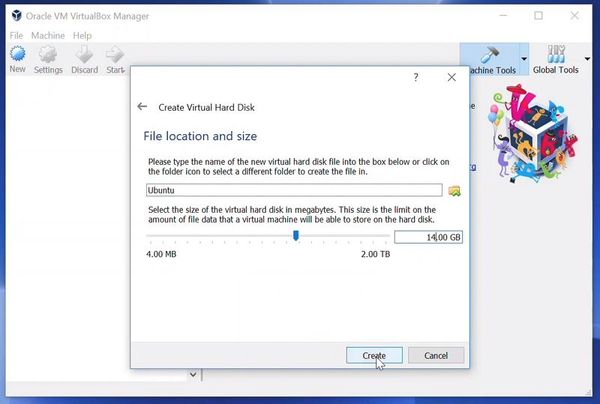
Create a virtual disk. This serves as the hard disk of the virtual Linux system. It is where the virtual system will store its files.
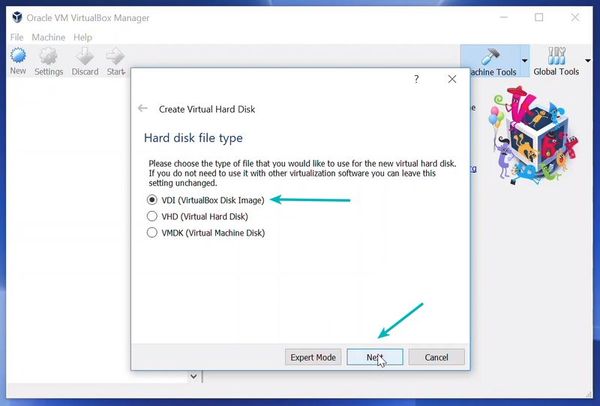
I recommend using the VDI file type here.
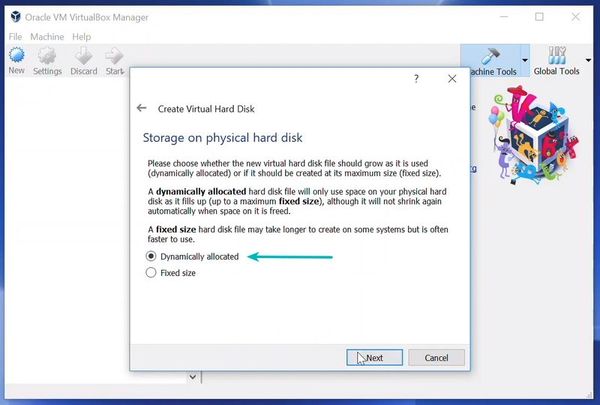
You can choose either the “Dynamically allocated” or the “Fixed size” option for creating the virtual hard disk.
The recommended size is 10 GB. However, I suggest giving it more space if possible. 15-20 GB is preferable.
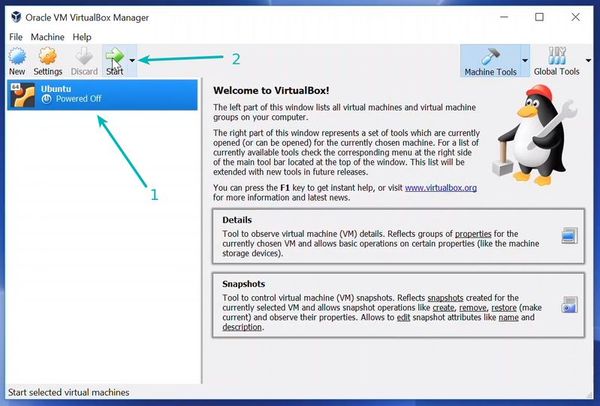
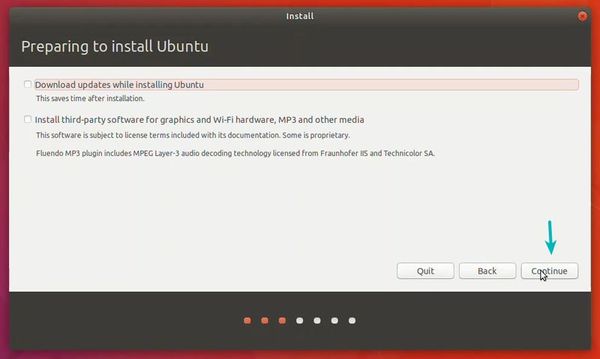
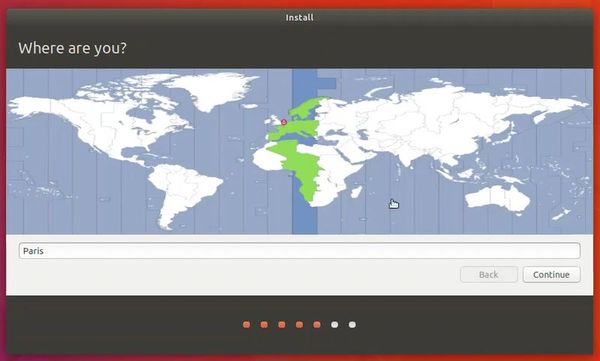
Once everything is in place, it’s time to boot that ISO and install Linux as a virtual operating system.
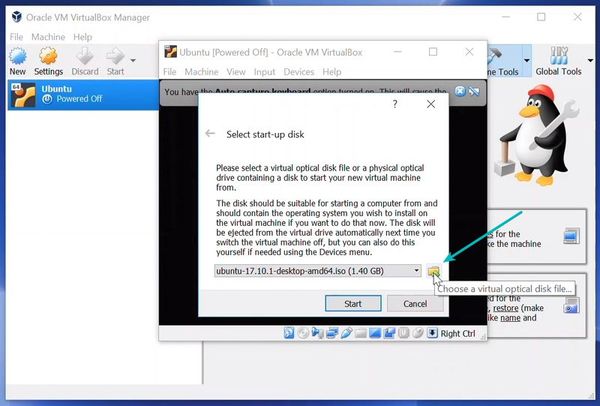
If VirtualBox doesn’t detect the Linux ISO, browse to its location by clicking the folder icon as shown in the picture below:
Soon you’ll find yourself inside Linux. You should be presented with the option to install it.
Things from here are Ubuntu-specific. Other Linux distributions may have slightly different looking steps, but it won’t be complicated at all.
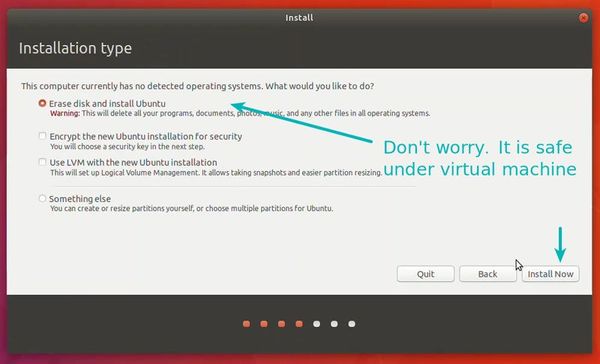
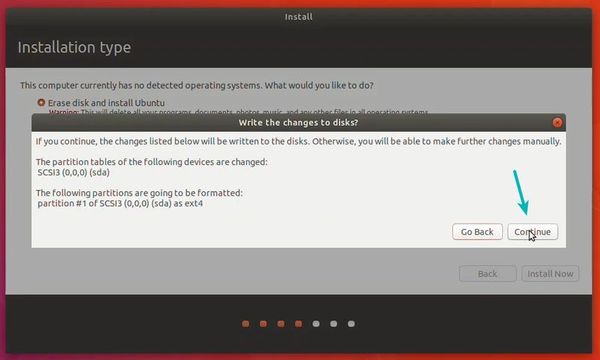
Select ‘Erase disk and install Ubuntu’. Don’t worry. It won’t delete anything on your Windows operating system. You are using the virtual disk space of 15-20GB that we created in previous steps. It won’t impact the real operating system.
Things are pretty straightforward from here.
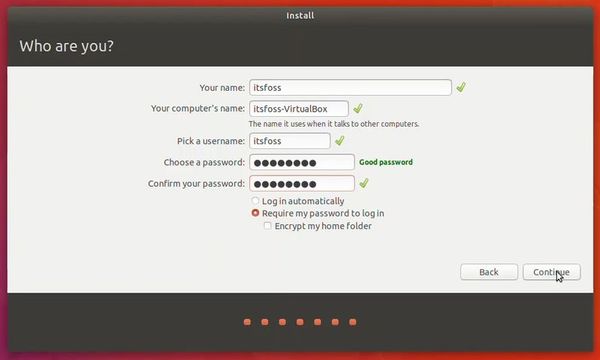
Try to choose a password that you can remember. You can also reset the password in Ubuntu if you forget it.
You are almost done. It may take 10-15 minutes to complete the installation.
Once the installation finishes, restart the virtual system.
If it gets stuck on the screen below, you may close the VirtualBox.
And that’s all. From now on, just click on the installed Linux virtual machine. You’ll be able to use it directly. The installation is a one time only process. You can even delete the Linux ISO that you downloaded earlier.
I strongly recommend using VirtualBox Guest Additions on Ubuntu for it provides better compatibility and you would be able to use copy-paste and drag-drop between Linux and Windows.
Troubleshooting: AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS
If you face this error while using the virtual machine:
Not in a hypervisor partition (HVP=0) (VERR_NEM_NOT_AVAILABLE).
AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS (or by the host OS) (VERR_SVM_DISABLED).
Result Code:
E_FAIL (0x80004005)
Component:
ConsoleWrap
Interface:
IConsole
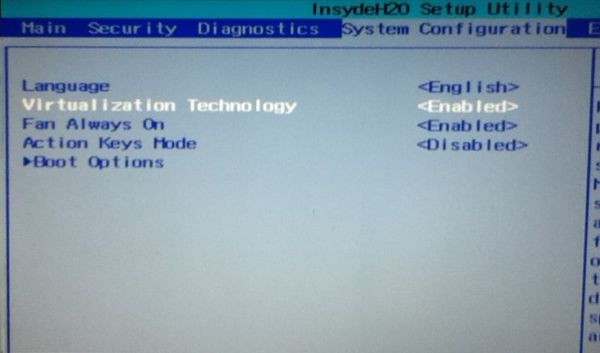
This means that virtualization is blocked on your system. You’ll have to activate it in your BIOS settings first.
Reboot your system and as soon as it powers up, press F2/F10/F12 to access BIOS settings. You have to look for the virtualization option in the BIOS and enable it.
Any questions?
That’s all you need to do to install Linux in VirtualBox on Windows.
If you have any doubts, or if you encounter any issues, please feel free to ask your questions in the comment box below.
10 Reasons to Run Linux in Virtual Machines
You can run any operating system as a virtual machine to test things out or for a particular use case.
When it comes to Linux, it is usually a better performer as a virtual machine when compared to other operating systems. Even if you hesitate to install Linux on bare metal, you can try setting up a virtual machine that could run as you would expect on a physical machine.
Of course, we don’t rule out the possibility of running Linux distros in VM even when using Linux as your host OS.
Moreover, you get numerous benefits when trying to run Linux on virtual machines. Here, I shall mention all about that.
Things to Keep in Mind Before Running Linux as a Virtual Machine
It is worth noting that running Linux on a virtual machine may not be a daunting task, but there are a few pointers that you should keep in mind.
- The virtual machine performance will depend on your host system. If you do not have enough system resources to allocate, the virtual machine experience will not be pleasant.
- Certain features only work well with bare metal (hardware acceleration, graphics drivers, etc.)
- You should not expect intensive disk I/O tasks to work well, like testing games.
- The user experience with Linux virtual machines varies with the program you use. For instance, you can try VMware, VirtualBox, GNOME Boxes, and Hyper-V.
In addition to all these tips, you should also make a list of your requirements before choosing a virtual machine program to run Linux.
Here Are 10 Benefits of Running Linux on Virtual Machines
While there are perks to using a Linux VM, you should consider the current opportunities available on your host OS. For instance, you may want to install Linux using WSL on Windows if you do not require a GUI desktop.
Once you are sure that you need a VM, here’s why you should proceed with it:
1. Easy Setup
Compared to the traditional installation process on bare metal, setting up a virtual machine is often easier.
For Ubuntu-based distros, programs like VMware offer an Easy Install option where you have to type in the required fields for username and password; the rest will proceed without needing additional inputs. You do not need to select a partition, bootloader, or advanced configurations.
In some cases, you can also use prebuilt images offered by Linux distributions for a specific virtual program, where you need to open it to access the system. Think of it as a portable VM image ready to launch wherever you need it.
For example, you can check out how you can use VirtualBox to install Arch Linux.
You may still need to configure things when installing other distros, but there are options where you need minimal effort.
2. Does Not Affect the Host OS
With a virtual machine, you get the freedom to do anything you want, and it is because you get an isolated system.
Usually, if you do not know what you’re doing with a Linux system, you could easily end up with a messed-up configuration.
So, if you set up a VM, you can quickly try whatever you want without worrying about affecting the host OS. In other words, your system will not be impacted by any changes to the VM because it’s entirely isolated.
Hence, a VM is the best way to test any of your ambitious or destructive changes that you may want to perform on bare metal.
3. Resource Sharing
If you have ample free system resources, you can utilize the rest using a Virtual Machine for any other tasks. For instance, if you want a private browsing experience without leaving any traces on your host, a VM can help.
It can be a far-fetched example, but it is just one of the ideas. In that way, you get to use the resources fully without much hassle.
Also, as opposed to a dual-boot scenario, where you need to install Linux alongside Windows on separate disks or install Windows after Linux, you need dedicated resources locked on to your tasks.
However, with a VM, you can always use Linux without locking up your resources, rather than temporarily sharing them to get your tasks done, which can be more convenient.
4. Multi-Tasking
With the help of resource-sharing, you can easily multi-task.
For instance, you need to switch back and forth between a dual-boot setup to access Windows and Linux.
But, with a virtual machine, you can almost eliminate the need for dual-booting Linux and multi-task with two operating systems seamlessly.
Of course, you need to ensure that you have the required amount of system resources and external hardware (like dual monitors) to effectively use it. Nevertheless, the potential to multi-task increases with a Linux VM in place.
5. Facilitates Software Testing
With virtualization, you get the freedom to test software on Linux distros by instantly creating various situations.
For instance, you can test different software versions simultaneously on multiple Linux VMs. There can be more use-cases, such as testing a software development build, early build of a Linux distro, etc.
6. Great for Development
When you want to learn to code or just get involved in developing something, you want an environment free from any conflicts and errors.
So, a Linux VM is the perfect place to install new packages from scratch without worrying about conflicts with existing ones. For instance, you can install and set up Flutter to test things on Ubuntu.
If you mess up the system, you can quickly delete the VM and spin up a new one to learn from your mistakes.
You get a perfect isolated environment for development work and testing with a Linux VM.
7. Learning or Research
Linux is something to explore. While you could use it for basic computing tasks, there’s so much more that you can do with it.
You can learn how to customize the user interface, try some popular desktop environments, install various essential apps, and take control of your system without worrying about it.
If anything goes wrong, you create a new Linux VM. Of course, it is not just for general-purpose usage, but aspiring system administrators can also take this opportunity to test what they learn.
8. Easy to Clone or Migrate
Virtual machines, in general, are easy to clone and migrate. With a Linux VM, as long as the virtual program is supported on another system or host OS, you can easily migrate it without any special requirements.
If you need to clone an existing virtual machine for any reason, that is pretty easy too, and it should take a couple of clicks to get it done.
9. Try Variety of Distros
Of course, with hundreds of Linux distros available, you can try all kinds of distros by creating a Linux virtual machine.
You may consider this a part of learning/research, but I believe trying out different distros is a massive task if you want to test things out before installing them on your system.
10. Debugging
Whether it is for fun or serious research, debugging is relatively more straightforward in an isolated environment provided by the Linux VM.
You get the freedom to try various troubleshooting methods without thinking about the outcome. Also, you do not need root access to your host OS (if it’s Linux) to access the system configuration/files in the VM.
Wrapping Up
If you are not an experienced user or depend on a different host OS, you can benefit from installing Linux using a virtual machine.
A Linux VM should be beneficial for development, learning, experimenting, or any other special use cases.
Have you used Linux on a virtual machine? What do you use it for? Let me know in the comments below.