Как получить быструю виртуальную macOS Ventura в линуксе
Ничего сильно нового или необычного в процессе нет, тема старая и рабочая. Руководств, наборов скриптов и всяких гайдов в интернете также уже куча, я остановился вот на этом. Все манипуляции производились на ноутбуке Dell G3,с 32Гб памяти и SSD.
Настоятельно рекомендую также использовать что-то производительное, поскольку macOS (тем более последняя) чрезвычайно прожорливая.
Еще вам будет нужно ~50Гб свободного места на диске. Я использовал Mageia Linux, официальный гайд от авторов руководства — для Ubuntu. Но коль уж вы залезли так далеко, что собираетесь разворачивать виртуальный мак на линуксе — полагаю вам уже глубоко похер на дистрибутив.
Подготовка
Устанавливаем вот этот параметр:
echo 1 | sudo tee /sys/module/kvm/parameters/ignore_msrs В репозитории проекта есть готовая настройка modprobe для постоянной настройки:
sudo cp kvm.conf /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf # for intel boxes only, after cloning the repo below Устанавливаем пакеты. Для убунты:
sudo apt-get install qemu uml-utilities virt-manager git \ wget libguestfs-tools p7zip-full make dmg2img -y urpmi qemu git wget virt-manager libguestfs-tools libgu p7zip make dmg2img Добавляем своего пользователя в группы, для использования KVM:
sudo usermod -aG kvm $(whoami) sudo usermod -aG libvirt $(whoami) sudo usermod -aG input $(whoami) Нужно будет выйти из сессии для применения этих изменений. Клонируем репозиторий со скриптами:
git clone --depth 1 --recursive https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM.git cd OSX-KVM Тут будет текстовое меню выбора версии:
1. High Sierra (10.13) 2. Mojave (10.14) 3. Catalina (10.15) 4. Big Sur (11.7) - RECOMMENDED 5. Monterey (12.6) 6. Ventura (13) Choose a product to download (1-6): 4 Нужно будет выбрать Ventura.
Конвертируем в RAW-образ, который может читать Qemu:
dmg2img -i BaseSystem.dmg BaseSystem.img Создаем виртуальный диск, на который виртуальная MacOS будет установлена:
qemu-img create -f qcow2 mac_hdd_ng.img 128G Установка
Дальше запускается уже графический инсталлятор, пошаговые картинки из которого есть в оригинальной статье. Тут привожу лишь текстовое описание.
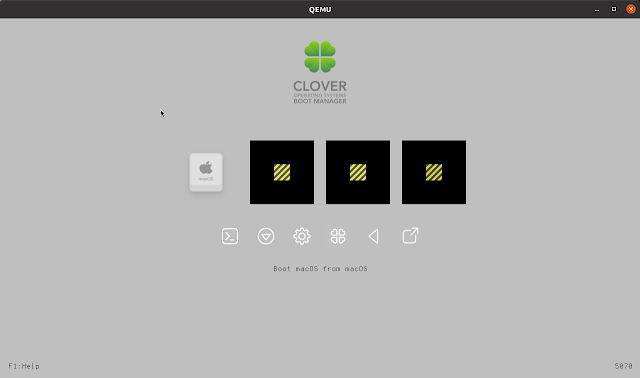
Выбираем иконку с диском и нажимаем «Enter». Выбираем «Disk Utility».
Выбираем созданный выше образ диска и форматируем.
Поскольку MacOS поставляется с оборудованием Apple, чистой пользовательской установки не существует, поэтому в меню оно называется «Reinstall», т. е. «Переустановка».
Соглашаемся и клянемся соблюдать лицензионное соглашение, во славу Луны .
Выбираем отформатированный диск.
Пропускаем Apple ID, его можно установить позже.
Настройка сети
Вот таким скриптом создается виртуальный адаптер:
#!/usr/bin/env bash sudo ip tuntap add dev tap0 mode tap sudo ip link set tap0 up promisc on sudo ip link set dev virbr0 up sudo ip link set dev tap0 master virbr0 Который подцепляется Qemu при запуске.
Для Ventura будет необходимо модифицировать скрипты запуска OpenCore-Boot* :
# -netdev tap,id=net0,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no -device vmxnet3,netdev=net0,id=net0,mac=52:54:00:c9:18:27 -netdev user,id=net0 -device vmxnet3,netdev=net0,id=net0,mac=52:54:00:c9:18:27 Там же я добавил пару параметров для решения проблем с размером экрана:
-monitor stdio -device VGA,vgamem_mb=128 Только в следующий раз обрати внимание, что теги разделяются запятыми. Если поставить пробелы, движок ЛОРа попытается эту конструкцию воспринять как один тег (разумеется, несуществующий).
Ок, я буду тогда текстовые версии выкладывать дальше, как в свежем скрине про сборку дотнета.
Ничего про проброс видео( Баловство.
sudo cp kvm.conf /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf # for intel boxes only, after cloning the repo below
А есть инструкция для AMD? Или если у тебя AMD ты просто не запускаешь эту инструкцию?
Unixson ★ ( 22.03.23 14:13:47 MSK )
Последнее исправление: Unixson 22.03.23 14:14:11 MSK (всего исправлений: 1)
эмм, такой вопрос.
то что скачивается BaseSystem.dmg ~650mb это нормально?
просто со времен пика популярности hackintosh»ей, ванильная весила как минимум ~5гб, а уж всякие iAtkos’ы и того более.
вероятно, оно в процессе докачает что необходимо?-.-
Да, это настройка специфичная для процессоров Intel.
то что скачивается BaseSystem.dmg ~650mb это нормально?
Да, после конвертации dmg2img будет больше.
оно в процессе докачает что необходимо?
За наводку спасибо, но оно внутри на том же самом OSX-KVM:
quickemu will automatically download the required OpenCore bootloader and OVMF firmware from OSX-KVM.
Optimised by default, but no GPU acceleration is available. Host CPU vendor is detected and guest CPU is optimised >accordingly. VirtIO Block Media is used for the system disk where supported. VirtIO usb-tablet is used for the mouse. VirtIO Network (virtio-net) is supported and enabled on macOS >Big Sur and newer but previous releases use vmxnet3. VirtIO Memory Ballooning is supported and enabled on macOS Big >Sur and newer but disabled for other support macOS releases. USB host and SPICE pass-through is: UHCI (USB 2.0) on macOS Catalina and earlier. XHCI (USB 3.0) on macOS Big Sur and newer. Display resolution can only be changed via macOS System >Preferences. Full Duplex audio requires VoodooHDA OC or pass-through a USB >audio-device to the macOS guest VM. NOTE! Gatekeeper and System Integrity Protection (SIP) need to be disabled to install VoodooHDA OC File sharing between guest and host is available via virtio-9p >and SPICE webdavd. Copy/paste via SPICE agent is not available on macOS.
If you see «Your device or computer could not be verified» when you try to login to the App Store, make sure that your wired ethernet device is en0. Use ifconfig in a terminal to verify this.
If the wired ethernet device is not en0, then then go to System Preferences -> Network, delete all the network devices and apply the changes. Next, open a terminal and run the following:
sudo rm /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/NetworkInterfaces.plist Now reboot, and the App Store should work.
Про аппстор видимо надо добавить в статью.
How To Install macOS In A Virtual Machine On Linux Using Sosumi (Snap Package)
Sosumi is a snap package based on macOS-Simple-KVM that makes it easy to download and install macOS in a virtual machine (it comes bundled with qemu-virgil, which includes virtio-vga, a paravirtual 3D graphics driver). It does not ship with macOS, but downloads an installer image for macOS Catalina.
[[Edit]] This package has been abandoned, and is no longer updated. Use this instead: Install macOS Big Sur Or Catalina In A Virtual Machine Using Docker-OSX
————————————————————————————————
It’s worth noting from the start that Apple doesn’t allow installing macOS on non-Apple hardware, so to use this legally you must have Linux installed on Apple hardware.
After using Sosumi for a few hours on my Ubuntu 20.04 desktop, I can tell you that the installation takes quite a while (about 50 minutes on my system), and the macOS system may be a bit slow, but it’s usable. So this may not be suitable to be used for heavy tasks, but it’s perfect for testing.
This snap package, created by Alan Pope of Canonical / Ubuntu, makes it easy to install and run macOS in a virtual machine on Debian / Ubuntu, Fedora and other Linux distributions (after installing snapd), shipping with basically everything you need to get it running. You can find the snap package source on GitHub. If you don’t want to use the snap package though, you have the alternative of using macOS-Simple-KVM, a set of tools to set up a quick macOS virtual machine in QEMU (accelerated by KVM).
Before installing this there are a few important things I want to note:
- After installing macOS in the virtual machine, the total size of the Sosumi folder ( ~/snap/sosumi ) on my system is about 31,5 GB, but this can get larger as you install extra applications in the macOS virtual machine
- Your computer CPU needs to support hardware virtualization. See the KVM checklist from here to find out if your CPU supports this
- Both Intel and AMD CPUs are supported, but the recommendations are Ivy Bridge (or later) Core and Xeon processors, or Ryzen and Threadripper processors (from the macOS-Simple-KVM FAQ)
- You can get the QEMU virtual machine to release your mouse focus by pressing CTRL + Alt + G
- The launch script, which contains various parameters (like the available VM memory, CPU count, etc.) that you can tweak, can be found in ~/snap/sosumi/common/launch
How to install macOS in a virtual machine (QEMU) on Linux using Sosumi snap package
To install Sosumi you’ll need to be able to install Snap packages on your system. This is enabled by default in Ubuntu, and on other Linux distributions follow the instructions from the Snapcraft docs.
sudo snap install sosumi --edgeWhy edge? In my test, the macOS virtual machine did not start after using the Sosumi stable package, but it does work with the edge version. You can skip —edge from the command to install the stable version if you wish.
2. Run Sosumi for the first time by typing sosumi in a terminal. This is only required the first time; an applications menu shortcut is created for future launches.
[[Edit]] In case you run into an issue saying it failed to run Sosumi / qemu because it can’t start X11, add your user to the kvm group:
Issue mentioned by Bob White in the comments below.
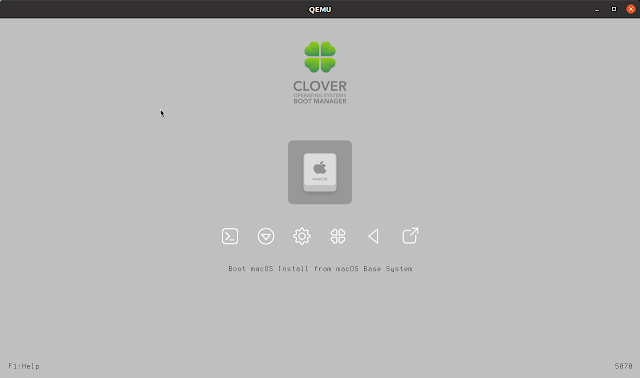
3. After the virtual machine boots, press Enter to Boot macOS Install from macOS Base System :
4. Format the macOS virtual machine HDD.
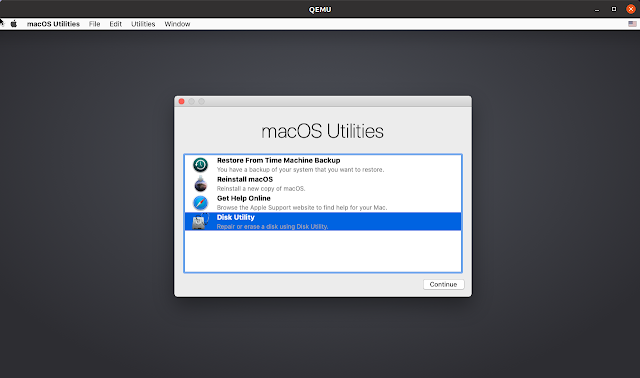
You’ll get to a screen with a dialog called macOS Utilities — from there click on Disk Utility :
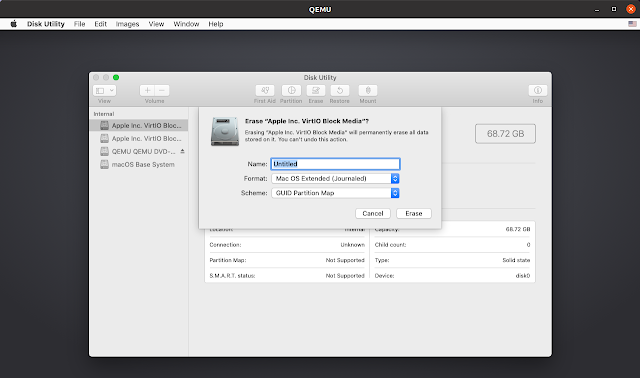
In the Disk Utility dialog choose the first Apple HDD on the left-hand sidebar (the one with a capacity of 68,72 GB), then click Erase , enter a name for the HDD (like macOS), and leave the rest of options as they are (mac OS Extended (Journaled) filesystem with GUID Partition Map):
Now click the Erase button to format the partition.
5. Install macOS in the virtual machine.
When you’re done close Disk Utility , and you’ll get to the macOS Utility dialog again. From this dialog choose Reinstall macOS . Click Continue a couple of times and you’ll get to a screen where you must choose the HDD formatted in step 4:
Next, click Install and the installation will begin:
The virtual machine will reboot automatically at some point, continuing with the installation after that, and reboot again when it’s done.
After the installation is completed, the macOS virtual machine will reboot, and in the boot menu you’ll see some extra options. Use the left/right arrow keys to select Boot macOS from. , like this (in Boot macOS from macOS , the second macOS is the name of the HDD set in step 4):
You will need to select this option each time you start the virtual machine, when you want to boot into macOS.
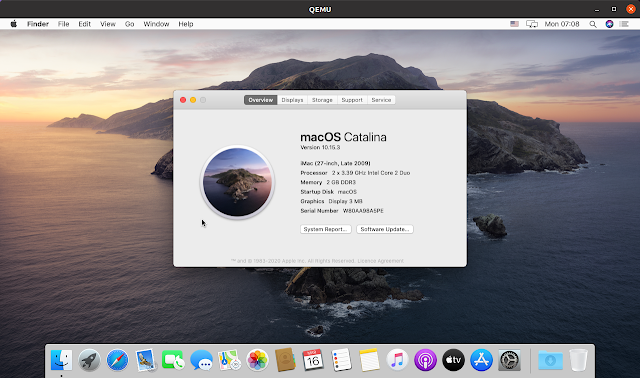
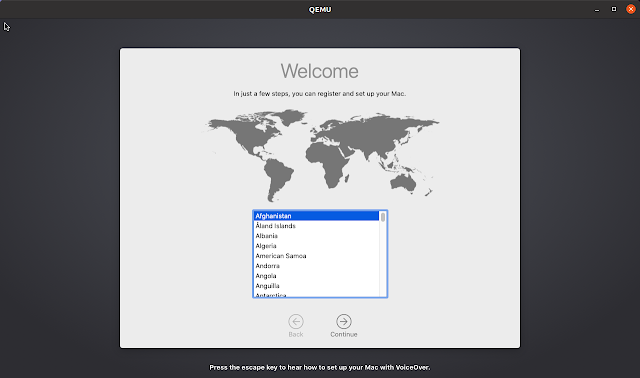
The first time you boot into macOS you’ll need to perform the initial setup (screenshot above), choosing your location, preferred languages, optionally sign in with your Apple ID, agree to the terms and conditions etc., as well as create your computer account (username and password). Once you’re done, the macOS Catalina desktop should load.