- Установка Linux на Virtualbox
- Установка Linux на VirtualBox
- Выводы
- How to run an Ubuntu Desktop virtual machine using VirtualBox 7
- What you’ll learn
- What you’ll need
- Download an Ubuntu Image
- Download and install VirtualBox
- 2. Create a new virtual machine
- Create a user profile
- Define the Virtual Machine’s resources
- 3. Install your image
- 4. Explore Virtual Box
- 5. Tell us your thoughts!
- How will you use this tutorial?
Установка Linux на Virtualbox
Для тестирования новых дистрибутивов и операционных систем не всегда удобно использовать реальный компьютер. Если хочется посмотреть что изменилось в том или ином дистрибутиве, или вам нужно запустить несколько программ, которые не устанавливаются в вашей системе, вы можете установить нужный дистрибутив на виртуальную машину. Для новичков вообще обязательно сначала установить систему на виртуальную машину и разобраться с ней.
Установка Linux на VirtualBox достаточно проста и не требует много знаний. Нужно только выбрать подходящие параметры, настроить жесткий диск и пройти процесс установки, как и при установке обычной системы. В одной из предыдущих статей мы рассматривали как пользоваться VirtualBox в более общем смысле, в этой же поговорим как установить Linux на VirtualBox.
Установка Linux на VirtualBox
Для того чтобы установить Linux на VirtualBox нам понадобиться несколько вещей:
- Образ диска с Linux — определитесь какой дистрибутив вы собираетесь устанавливать и загрузите его образ на официальном сайте, например, Ubuntu или Fedora. Также обратите внимание на архитектуру образа, если у вас 32 битная основная система, то вряд ли у вас получиться запустить 64 бит гостевую;
- Установленная виртуальная машина — VirtualBox, это кроссплатформенная программа, которая может работать не только в Linux, но и в Windows и MacOS. Поэтому вы можете запускать Linux в любой операционной системе. Для большинства из них можно скачать установщик VirtualBox на официальном сайте программы;
- Компьютер с поддержкой аппаратной виртуализации — конечно, вы можете запускать виртуальные машины и без поддержки аппаратной виртуализации, но они будут работать в разы медленнее. Большинство современных процессоров поддерживают AMD-V или Intel-VT-X. Посмотрите нельзя ли включить такую возможность в вашем BIOS.
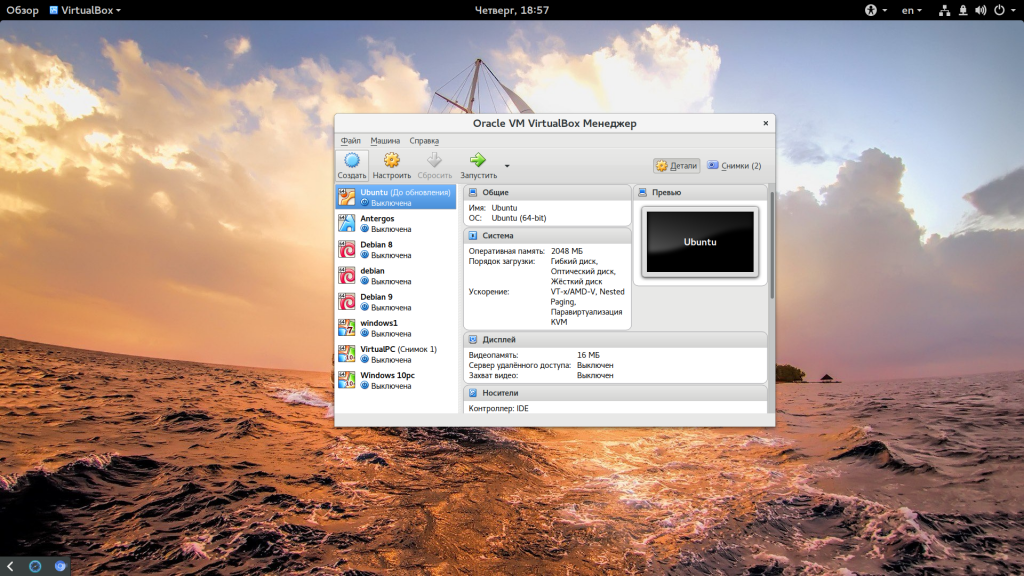
Если у вас все это поддерживается мы можем перейти к созданию виртуальной машины. Запустите VirtualBox и нажмите кнопку создать:
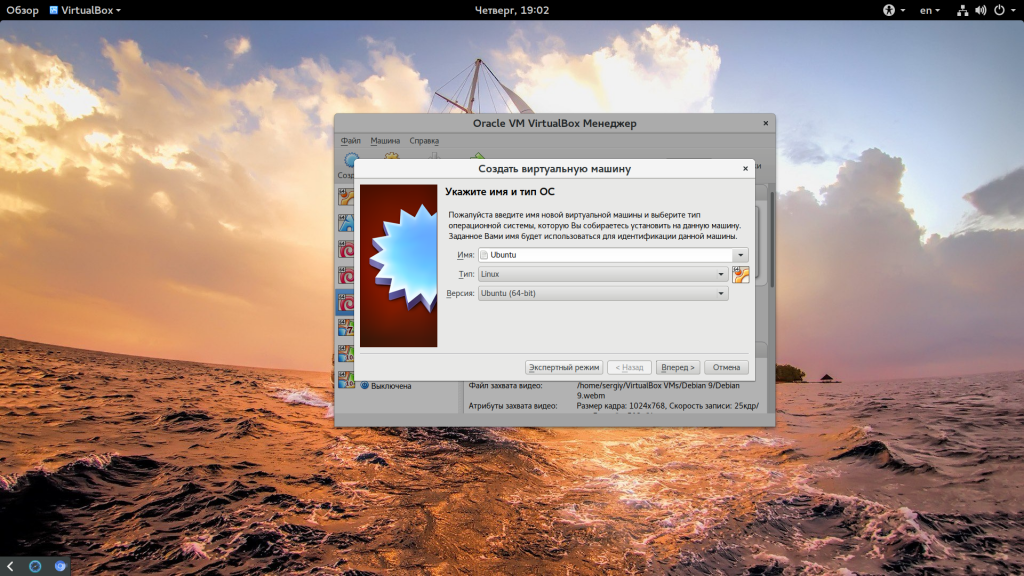
В первом окне мастера введите название вашей новой виртуальной машины, выберите тип (Linux) и дистрибутив, например, Ubuntu:
Следующий шаг — нужно выбрать количество оперативной памяти для вашей машины, но умолчанию VirtualBox предлагает количество памяти в зависимости от используемой машины, но для современных дистрибутивов будет достаточно 2 Гб, это нужно для более плавной и удобной работы, хотя система будет работать и при 1024 Мб и даже меньшем объеме.
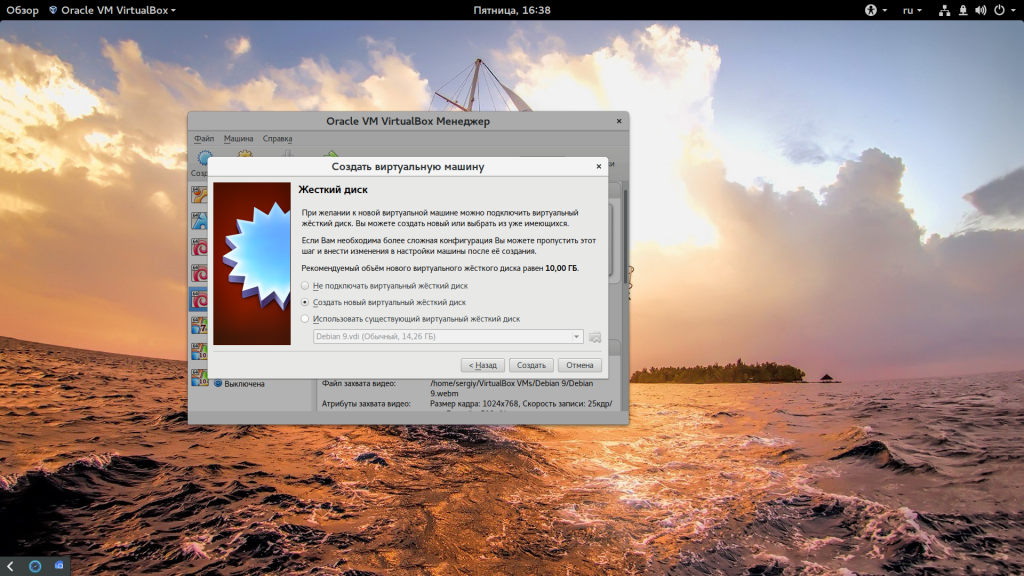
Дальше нам необходимо создать жесткий диск для установки системы, объем диска зависит от операционной системы, но поскольку вы можете создавать динамический диск, который будет изменять размер реального файла в файловой системе по мере наполнения, то можно указать 30 или даже 50 Гб чтобы было точно достаточно.
Сначала выберите «Создать новый виртуальный жесткий диск», затем выберите тип диска:
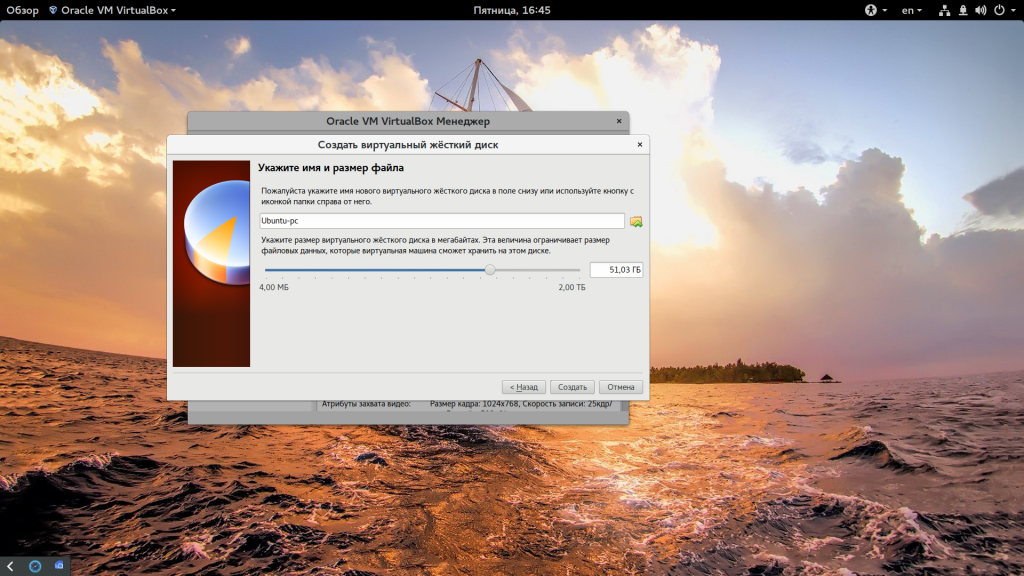
Наиболее часто для виртуальных машин используется диск типа VDI. Затем выберите размер диска и имя для его файла. Хотя и есть возможность использовать место по мере необходимости, лучше так не делать на HDD, лучше выделяйте все место сразу, это увеличит производительность до 10%:
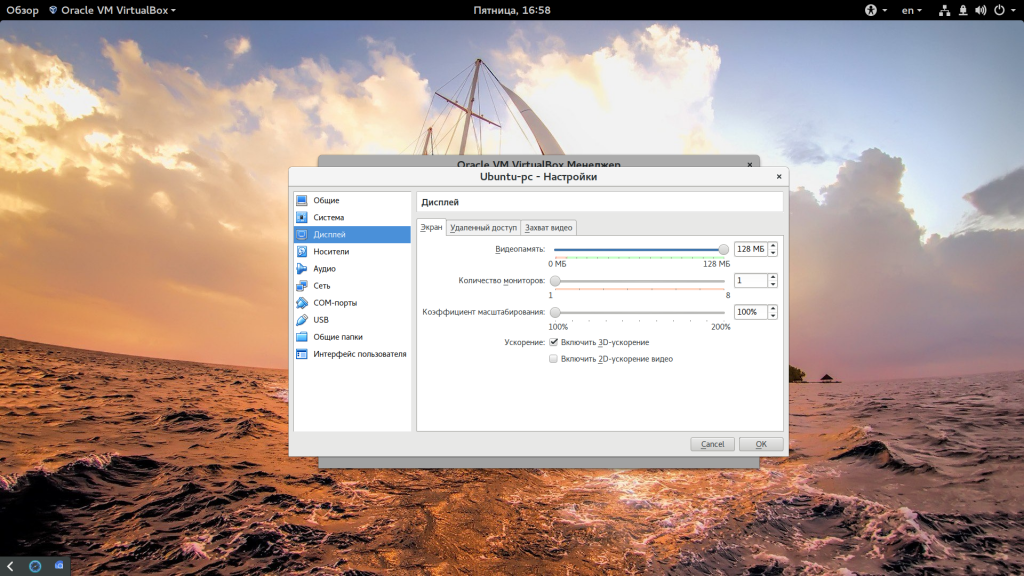
Виртуальная машина почти готова, но нужно еще кое-что настроить. По умолчанию VirtualBox выделяет 16 мегабайт оперативной памяти для машин, но современным дистрибутивам этого мало, поэтому нажмите «Настройки», а затем на вкладке «Дисплей» установите значение видеопамяти в 128 мегабайт. Этого уже должно хватить. Кроме того, отметьте галочку 3D ускорения:
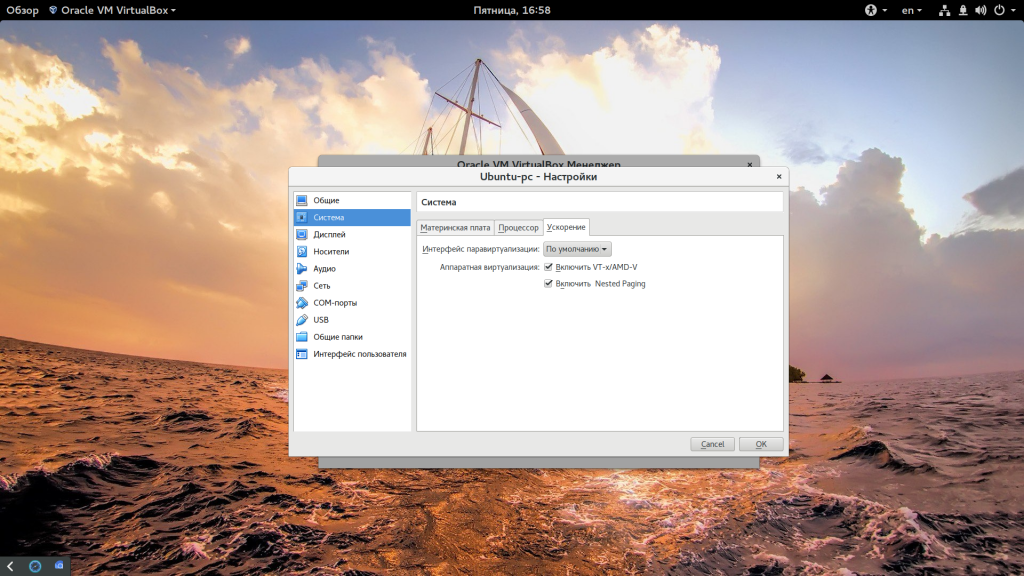
Еще нас будет интересовать раздел «Система», вкладка «Материнская плата», здесь нужно выбрать чипсет » ICH9″, Linux работает с ним лучше, также отметьте галочки часов в UTC.
На вкладке «Процессор» нужно отметить использовать «PAE/NX», и не выбирайте много процессоров, одного ядра будет достаточно. В разделе «Ускорение» отметить все галочки и выбрать ваш гипервизор, в Linux лучше всего использовать KVM:
Дальше запускайте виртуальную машину:
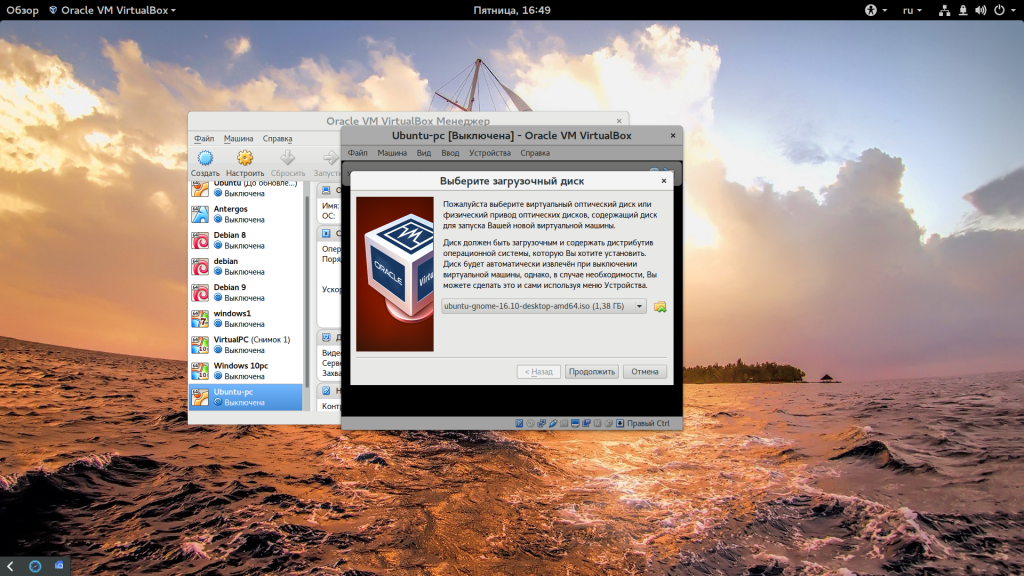
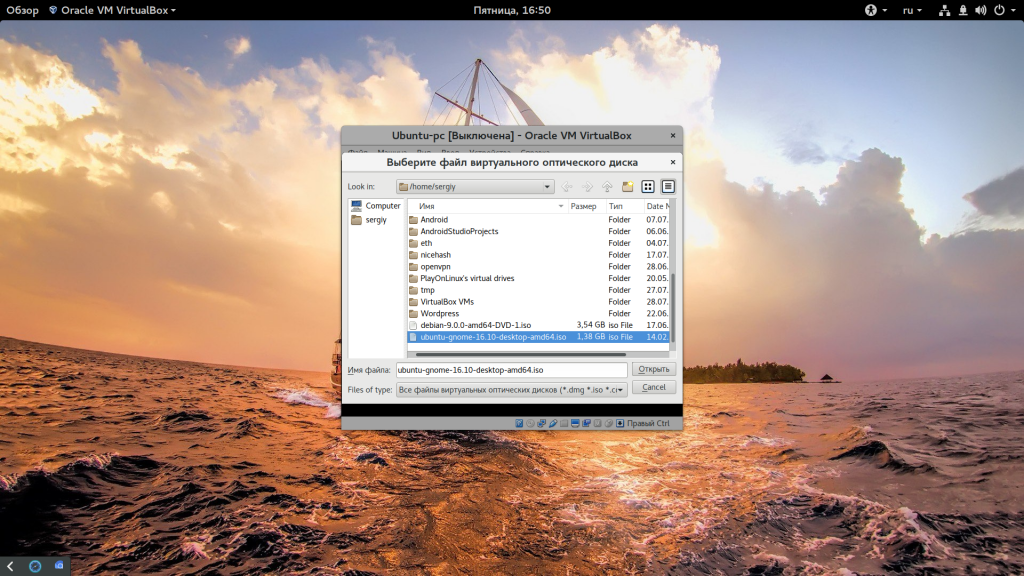
При первом запуске вам будет предложено выбрать установочный носитель, с которого будет проводиться установка, это может быть реальный CD привод или же просто образ в файловой системе:
Дальше будет запущена виртуальная машина и операционная система, которую вы выбрали и вам необходимо выполнить все действия для установки:
Мы не будем рассматривать установку Ubuntu, поскольку это уже подробно описано в одной из предыдущих статей.

Но после завершения установки есть еще несколько настроек. Во-первых — вам нужно установить дополнения гостевой ОС Ubuntu или для другого выбранного вами дистрибутива. Процесс везде одинаковый. Также, если вы используете Ubuntu, нужно включить облегченный режим Unity, чтобы все работало быстрее. Для этого выполните:
gsettings set com.canonical.Unity lowgfx true
На всякий случай, команда для отключения этого режима:
gsettings set com.canonical.Unity lowgfx false
Эти команды работают в Ubuntu 17.04, в более ранних версиях такой режим можно включить только через CompizConfig. Теперь установка Linux на VirtualBox полностью завешена и система готова к использованию.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как установить Linux на VirtualBox, как видите, это совсем не сложно и будет очень полезным для новичков, которые хотят протестировать новую операционную систему или же для пользователей, которые часто устанавливают новые дистрибутивы. А вы используете VirtualBox? Для чего? Часто тестируете системы в виртуальных машинах? Напишите в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to run an Ubuntu Desktop virtual machine using VirtualBox 7
In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through one of the easiest ways to try out Ubuntu Desktop on a virtual machine. VirtualBox is a general purpose virtualiser that is available across Linux, Mac OS and Windows. It’s a great way to experience Ubuntu regardless of your current operating system.
VirtualBox 7 and above includes a new feature called Unattended Guest OS Install which significantly streamlines the setup experience for common operating systems like Ubuntu, making it easier than ever to get started.
Note: This tutorial will also work for other distributions, so try it out with some of the Ubuntu flavours as well!
What you’ll learn
- How to install and configure VirtualBox
- How to import an Ubuntu image
- How to run a virtual instance of Ubuntu Desktop
- Further configuration options
What you’ll need
Download an Ubuntu Image
You can download an Ubuntu image here. Make sure to save it to a memorable location on your PC! For this tutorial, we will use the latest Ubuntu 22.10 release.
Download and install VirtualBox
You can download VirtualBox from the downloads page here. This page includes instructions on how to install VirtualBox for your specific OS so we won’t repeat those here.
Once you have completed the installation, go ahead and run VirtualBox.
2. Create a new virtual machine
Click New to create a new virtual machine. Fill in the appropriate details:
- Name: If you include the word Ubuntu in your name the Type and Version will auto-update.
- Machine Folder: This is where your virtual machines will be stored so you can resume working on them whenever you like.
- ISO Image: Here you need to add a link to the ISO you downloaded from the Ubuntu website.
We want to install Ubuntu unattendedly so we can leave the checkbox to skip unchecked.
Create a user profile
To enable the automatic install we need to prepopulate our username and password here in addition to our machine name so that it can be configured automatically during first boot.
The default credentials are:
It is important to change these values since the defaults will create a user without sudo access.
Ensure your Hostname has no spaces to proceed!
It is also recommended to check the Guest Additions box to install the default Guest Additions ISO that is downloaded as part of VirtualBox. Guest additions enables a number of quality of life features such as changing resolution and dynamic screen resizing so it is highly recommended!
Note: If you choose not to use unattended install then this step will be skipped and you will go straight to the following screen. Once your machine has been created you will be able to create a username and password by proceeding through the standard Ubuntu Desktop installation flow on first boot.
Define the Virtual Machine’s resources
In the next section we can specifiy how much of our host machine’s memory and processors the virtual machine can use. For good performance it’s recommended to provide your VM with around 8GB of RAM (althought 4GB will still be usable) and 4 CPUs. Try to remain in the green areas of each slider to prevent issues with your machine running both the VM and the host OS.
Then we need to specify the size of the hard disc for the virtual machine. For Ubuntu we recommend around 25 GB as a minimum. By default the hard disk will scale dynamically as more memory is required up to the defined limit. If you want to pre-allocate the full amount, check the ‘Pre-allocate Full Size’ check box. This will improve performance but may take up unnecessary space.
Click Next to continue and view a summary of your machine setting.
After this click Finish to initialize the machine!
3. Install your image
Click Start to launch the virtual machine.
You will see a message saying ‘Powering VM up …’ and your desktop window will appear.
On first boot the unattended installation will kick in so do not interact with the prompt to ‘Try and Install Ubuntu’ and let it progress automatically to the splash screen and into the installer.
Note: If you chose not to use unattended install then you will need to progress through the Ubuntu install manually. Check out our Ubuntu Desktop installation tutorial for more details.
You will notice at this stage that the resolution of the window is fixed at 800×600. This is because the Guest Additions features are not installed until after the Ubuntu installation has completed.
Once the installation completes, the machine will automatically reboot to complete the installation.
Finally you will be greeted with the Ubuntu log-in screen where you can enter your username and password defined during the initial setup (don’t forget that the default password is ‘changeme’ if you left everything as the default).
4. Explore Virtual Box
Enjoy your shiny new Ubuntu Desktop!
As always we recommend opening a terminal and running sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y and then sudo snap refresh to get everything updated to the latest versions.
Once you’ve finished your session you can close your machine by clicking the X in the top right of the window and choosing whether to keep your machine frozen in its current state or shut it down completely.
As you can probably tell, there are tonnes of further configuration options available in VirtualBox and we’ve only scratched the surface.
VirtualBox allows you to create and configure multiple virtual machines, so don’t be afraid to create new instances of Ubuntu to try out different system and storage configurations to fine tune your performance.
Why not try following the tutorial above with one of the Ubuntu flavours!
5. Tell us your thoughts!
Thank you for following this tutorial, we’d love to hear how you got on.
Give us feedback in the Ubuntu Discourse if you have any issues.
To help us improve our tutorials, we’d love to hear more about you: