- Виртуальная машина linux для vmware
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- How to Install Linux Mint 21 on VMware Workstation 17
- How to Install Linux Mint on a Virtual Machine in Windows 10 using VMware
- How to Create a New Virtual Machine for Linux Mint
- How to Install Linux Mint
- How to Install VMware Tools
- How to Configure Shared Folder
- How to Use USB Flash Memory
Виртуальная машина linux для vmware
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
You create a virtual machine in vCenter Server for each remote desktop that is deployed in a Horizon 8 environment. You must install your Linux distribution on the virtual machine.
Prerequisites
- Verify that your deployment meets the requirements for supporting Linux desktops. See System Requirements for Horizon Agent for Linux.
- Familiarize yourself with the steps for creating virtual machines in vCenter Server and installing guest operating systems. For more information see the Windows Desktops and Applications in Horizon document.
- Familiarize yourself with the video memory (vRAM) settings requirements for the monitors you plan to use with the virtual machine. See System Requirements for Horizon Agent for Linux.
Procedure
- In vSphere Client, create a virtual machine.
- Configure custom configuration options.
- Right-click the virtual machine and click Edit Settings .
- Specify the number of vCPUs and the vMemory size. For the required settings, refer to the following guidelines.
- If you are preparing the virtual machine for deployment as a single-session virtual desktop pool, follow the guidelines in the installation guide for your Linux distribution. For example, Ubuntu 18.04 specifies configuring 2048 MB for vMemory and 2 vCPUs.
- If you are preparing the virtual machine to serve as a multi-session host for a published desktop or application pool, specify at least 8 vCPUs and 40 GB of vMemory.
Important: A minimum of 8 vCPUs and 40 GB of vMemory is required to support up to 50 user sessions per published desktop or published application.
Only virtual machines running RHEL Workstation 7.8 or later, RHEL Workstation 8.1 or later, RHEL Workstation 9.0 or later, or Ubuntu 18.04/20.04/22.04 can support multi-session published desktop pools and single-session or multi-session application pools.
See the Desktop Environment section in System Requirements for Horizon Agent for Linux for additional information.
How to Install Linux Mint 21 on VMware Workstation 17
Last Updated: November 29, 2022 | VMware Workstation | Tolga Bagci
In this article, we will examine how to set up and configure Linux Mint 21 on a new virtual machine using the VMware Workstation 17 Pro virtualization program on Windows 10 64 Bit operating system.
How to Install Linux Mint on a Virtual Machine in Windows 10 using VMware
Faster and more stable than other Linux distributions, Linux Mint is an operating system that appeals to both home users and professionals. This system, which is basically derived from the Ubuntu package structure, aims to provide users with a more secure and stable distribution.
Linux Mint uses Cinnamon for its desktop environment by default but also has lighter and performance-oriented Mate and Xfce environments. Users can set up their system using one of these three desktop types.
You can run the Linux Mint system virtually without dual boot configuration on Windows 10 or other Microsoft systems by using the VMware Workstation virtualization software.
Workstation software, a paid program of VMware, allows users to configure more advanced settings on guest machines. However, users can also choose to use the free and non-commercial versions of the Player.
How to Create a New Virtual Machine for Linux Mint
After installing VMware Pro on your computer, you can create new virtual machines and install a Linux and Windows-based operating system.
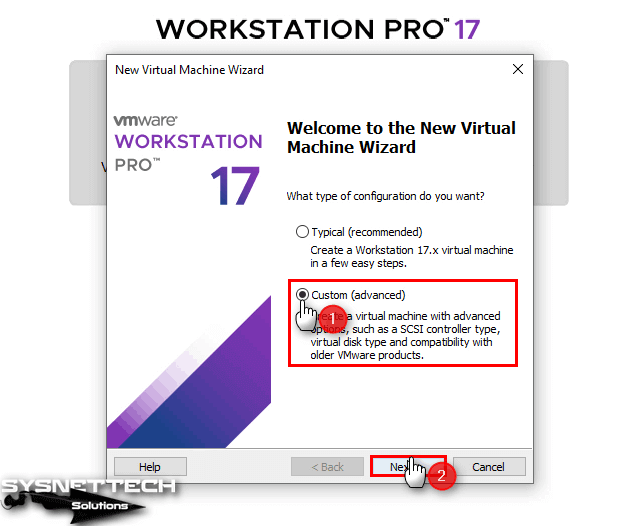
After running the Workstation 17 software, click on the Create a New Virtual Machine option from the options on the homepage, and select the Custom (Advanced) option to configure more advanced settings for the Linux system in the virtual machine wizard that opens and click Next.
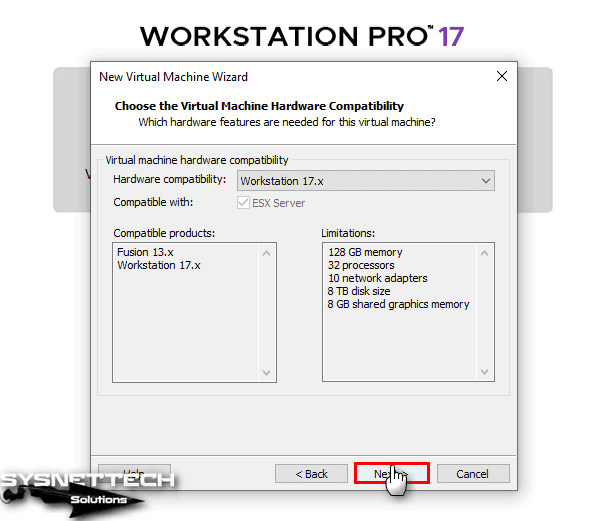
For Linux virtual machine compatibility, select the latest version of the Workstation software from the Hardware Compatibility section.
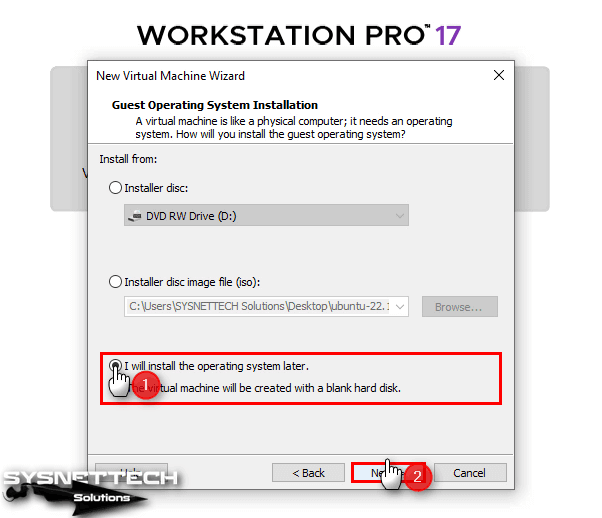
You can install the guest operating system using one of three methods. If you add the Linux Mint ISO file in this window, some settings of the virtual computer will be configured automatically.
Therefore, so that you can configure more advanced settings, check I will install the operating system later and continue.
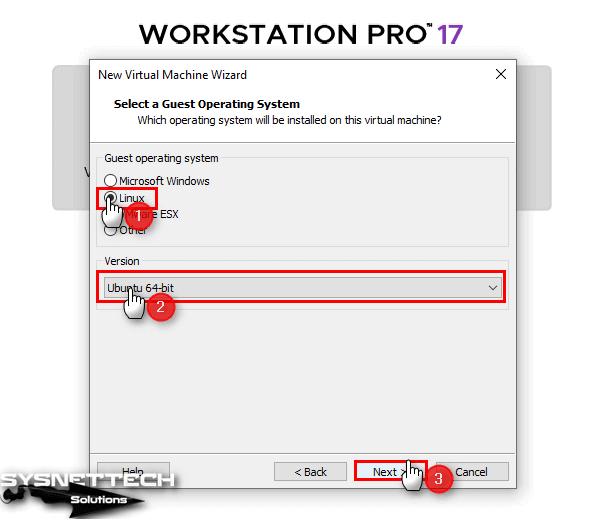
Select the Linux platform as the guest operating system and Ubuntu 64-bit from the version section.
After typing a name for your Linux Mint guest machine, specify the location where you will install it and continue.
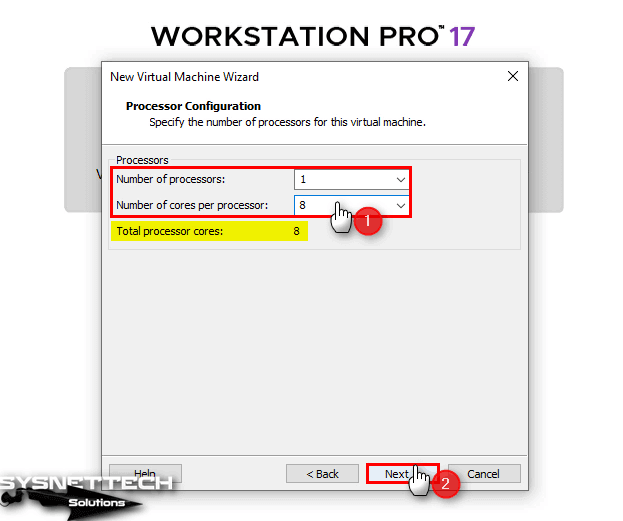
Configure the number of virtual processors and number of virtual cores for your virtual machine according to the processor characteristics of your host PC.
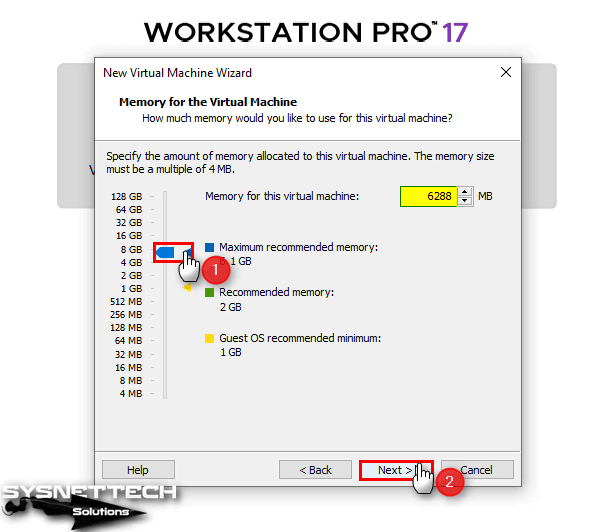
Select the maximum recommended memory size for the RAM size of the virtual machine. If you have a higher amount of memory in your computer, a larger size configuration will be beneficial for performance.
Select the NAT network adapter for your Linux Mint virtual machine.
Select the default LSI Logic as the I/O controller type and continue.
By configuring the type of virtual disk as NVMe, you will significantly increase the performance of your virtual computer. Therefore, select NVMe from the disk types and click Next.
Since you will install Linux Mint from scratch, select Create a new virtual disk and click Next. If you have previously installed this Linux distribution and backed up its virtual disk, you can add it using the Use an existing virtual disk option.
You can adjust the size of the virtual disk according to the recommended size, but you can specify a higher disk size according to the work you will do on your system. Also, if you choose to backup the virtual disk file as a single file, you can import your virtual machine more easily in the future.
Continue without changing the name and location of the Linux virtual disk file.
Click Customize Hardware to configure the advanced settings of the Linux Mint guest machine.
After clicking on the Processor virtual hardware, enable all the features in the Virtualization Engine section.
- Virtualize Intel VT-x/EPT or AMD-V/RVI
- Virtualize CPU Performance Counters
- Virtualize IOMMU (IO Memory Management Unit)
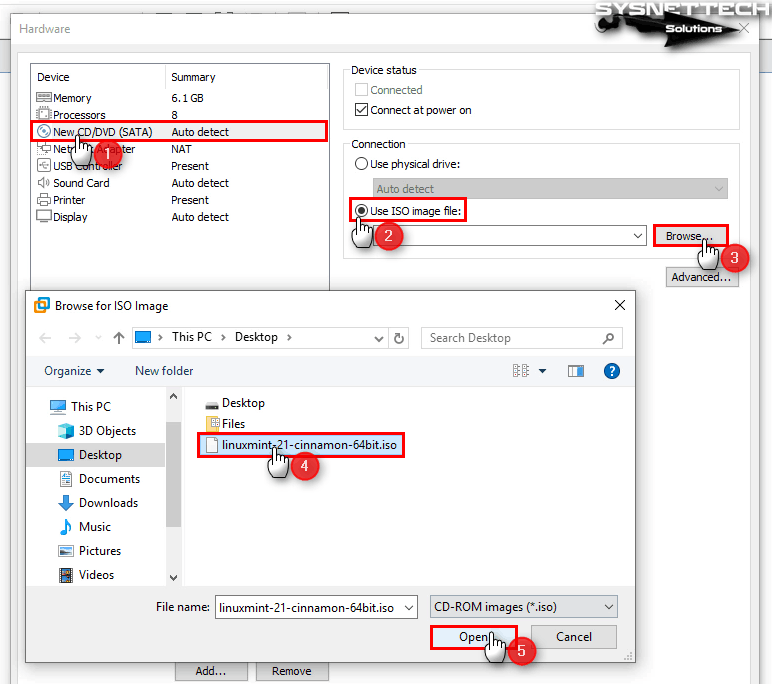
To download the Linux Mint ISO file, visit the official website and then click CD/DVD (SATA) / Use ISO Image File / Browse to add the ISO file to the virtual machine and select the downloaded image file.
Change the Compatibility setting to 3.1 in the USB Controller settings.
View the display hardware settings and enable Accelerate 3D Graphics and adjust the graphics memory size according to the capacity of your host GPU.
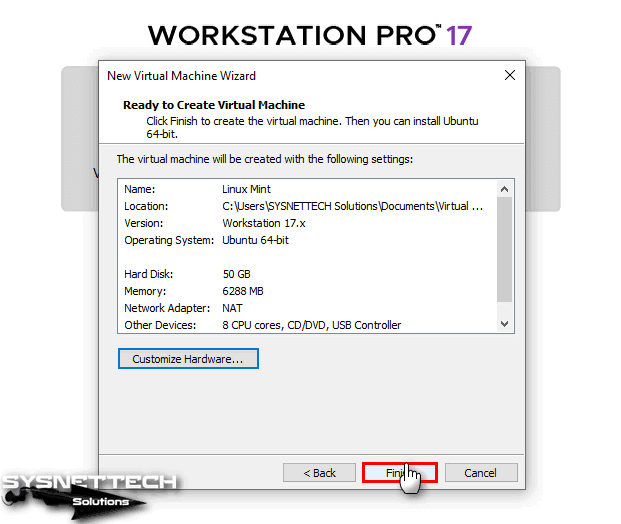
After configuring the hardware settings of your Linux Mint virtual computer, check the changes you have made in the summary window and close the wizard.
Click Power on this virtual machine to start installing the Linux system on the virtual machine you have prepared.
How to Install Linux Mint
After running the virtual computer, when it boots with the ISO file, you can set up your system as if you were installing it on a physical PC.
You can check system integrity, perform hardware tests, or do memory checks from Linux Mint 21 Cinnamon 64-bit options. Press Enter in the Start Linux Mint option to start installing the system.
When the system boots up, double-click Install Linux Mint on the desktop to start the installation wizard.
After opening the setup wizard, select the language you want to use your Linux system in and click Continue.
Select the keyboard layout of your virtual PC according to the hardware of your physical computer and click Continue.
Tick to install multimedia codecs so that you can play videos on your Linux Mint guest machine and click Continue.
Since you will be installing a system from scratch, select the Erase Disk and Install Linux Mint option, click Install Now, and then click Continue to confirm the changes on the virtual disk.
After choosing the location where you live, click Continue.
Configure the user account settings for your Linux system according to your personal information and create a characteristic password.
Wait while the files of the Linux Mint system are copied and the necessary applications are installed.
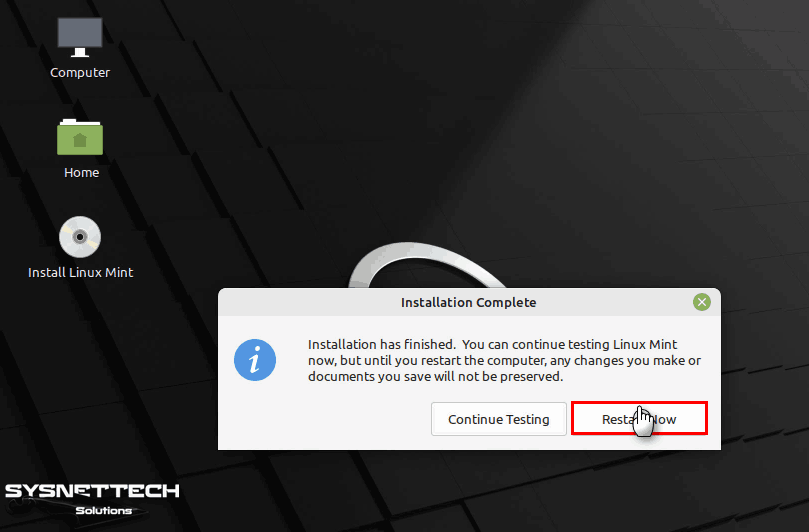
After installing Linux Mint, restart your virtual system.
Press Enter to remove the ISO installation media from the virtual machine.
Execute “lsb_release -a” command in terminal to check Linux system version.
How to Install VMware Tools
When installing Linux Mint on VMware Workstation, VMware Tools is automatically configured. However, VM tools will not be installed if your host computer is not connected to the Internet during installation.
After connecting the guest operating system to the Internet, open the terminal by pressing CTRL + Alt + T and execute the “sudo apt install open-vm-tools-desktop” command and confirm the additional disk space usage by pressing Y.
sudo apt install open-vm-tools-desktopAfter restarting your Linux machine, you can use the “vmware-toolbox-cmd –version” command in the terminal to check the VMware Tools version.
vmware-toolbox-cmd --versionWhen you try to copy a file from the desktop location of your host operating system by dragging and dropping it to the virtual machine, you can see that the operation is successful.
You can also use your Linux Mint virtual PC in full-screen resolution.
How to Configure Shared Folder
Another way to transfer files from your host computer to your VM is to use Shared Folder. Please note that VMware Tools must be installed in order to use this feature of VMware software.
Click VM / Settings from the VMware Pro tool menu and open the virtual machine settings. Click on Shared Folders on the Options tab and after marking Always Enabled, click the Add button to start the wizard.
Create a new folder named SharedFolder in a location you specify on your host system. To add the location of the folder you created, click Browse in the Host Path section, select the folder and click OK.
After adding the location of the shared folder, check that the Enable This Share option is selected in the next window, and click Finish.
Go to File System / mnt / hgfs on your Linux Mint virtual computer and check that the shared folder exists. For testing, create a new text document in the folder and check that the document has been created after opening the folder on your host.
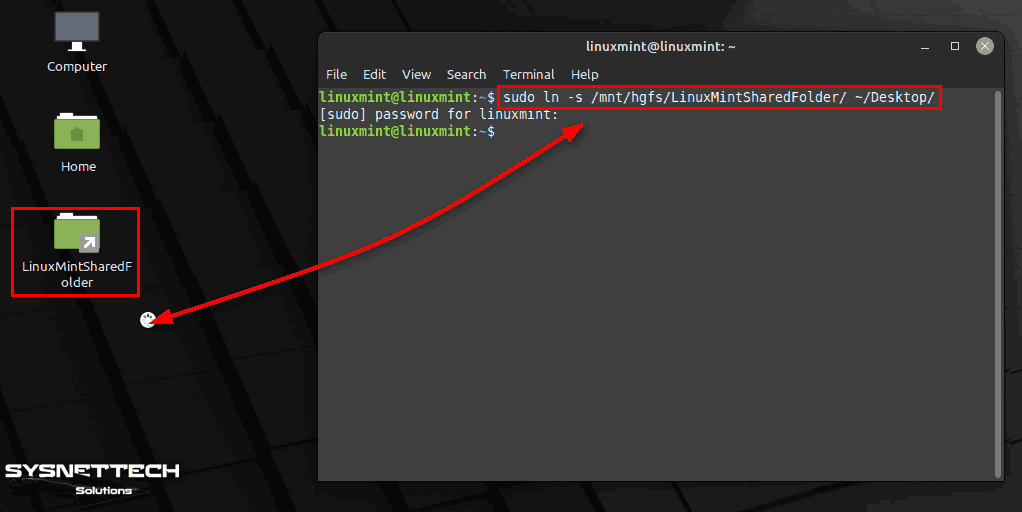
To create Shared Folder shortcut to desktop location, execute “sudo ln -s /mnt/hgfs/SharedFolder/ ~/Desktop/” command in terminal.
sudo ln -s /mnt/hgfs/SharedFolder/ ~/Desktop/When you restart your virtual computer, if you encounter the Shared Folder error as in the image below, you need to enable the folder again and set the automatic mount.
Execute the following command in the terminal to re-enable the shared folder.
sudo mount -t fuse.vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/hgfs/ -o allow_otherYou need to edit /etc/fstab to automatically mount the shared folder every time you reboot your system.
Add the following command to /etc/fstab and press CTRL + X, then Y and then Enter to save the file.
.host:/SharedFolder /mnt/hgfs/SharedFolder fuse.vmhgfs-fuse allow_otherRestart your Mint VM and you will no longer encounter the Shared Folder error.
How to Use USB Flash Memory
You can transfer files faster by connecting your USB flash drives or storage devices to your Linux virtual computer.
Plug a USB 3.0/3.1 supported flash memory into your host computer and create a folder named Backup in it.
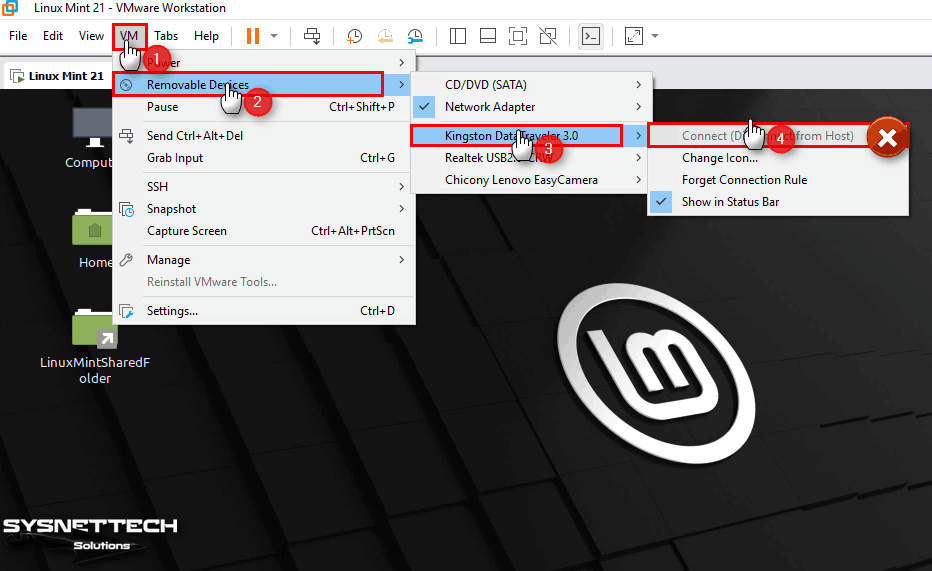
Plug your flash memory into the virtual machine by clicking VM / Removable Devices / Your USB / Connect from the tool menu. However, if you see the Connect option grayed out as in the image below, turn off your virtual computer.
Go to the location where you installed the VM and open the VMX file with notepad and change the value (usb.restrictions.defaultAllow = “FALSE”) to TRUE.
usb.restrictions.defaultAllow = "TRUE"After restarting your virtual computer, you can now connect your USB disk.
You can see the folder you created when you view the contents of your USB on your Linux Mint system.