Vmware horizon client linux certificate
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
If a Horizon 7 server certificate is signed by a CA that is not trusted by client computers and client computers that access Horizon Administrator, you can configure all Windows client systems in a domain to trust the root and intermediate certificates. To do so, you must add the public key for the root certificate to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities group policy in Active Directory and add the root certificate to the Enterprise NTAuth store.
For example, you might have to take these steps if your organization uses an internal certificate service.
You do not have to take these steps if the Windows domain controller acts as the root CA, or if your certificates are signed by a well known CA. For well known CAs, the operating system venders preinstall the root certificate on client systems.
If your server certificates are signed by a little-known intermediate CA, you must add the intermediate certificate to the Intermediate Certification Authorities group policy in Active Directory.
For client devices that use other operating systems than Windows, see the following instructions for distributing root and intermediate certificates that users can install:
- For Horizon Client for Mac, see Configure Horizon Client for Mac to Trust Root and Intermediate Certificates.
- For Horizon Client for iOS, see Configure Horizon Client for iOS to Trust Root and Intermediate Certificates.
- For Horizon Client for Android, see documentation on the Google Web site, such as the Android 3.0 User’s Guide
- For Horizon Client for Linux, see the Ubuntu documentation
Prerequisites
Verify that the server certificate was generated with a KeyLength value of 1024 or larger. Client endpoints will not validate a certificate on a server that was generated with a KeyLength under 1024, and the clients will fail to connect to the server.
Procedure
- On your Active Directory server, use the certutil command to publish the certificate to the Enterprise NTAuth store.
- Select Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers .
- Right-click your domain and click Properties .
- On the Group Policy tab, click Open to open the Group Policy Management plug-in.
- Right-click Default Domain Policy , and click Edit .
- Select Start > Administrative Tools > Group Policy Management .
- Expand your domain, right-click Default Domain Policy , and click Edit .
- Select Start > Administrative Tools > Group Policy Management .
- Expand your domain, right-click Default Domain Policy , and click Edit .
- Select Start > Administrative Tools > Group Policy Management .
- Expand your domain, right-click Default Domain Policy , and click Edit .
- Right-click Trusted Root Certification Authorities and select Import .
- Follow the prompts in the wizard to import the root certificate (for example, rootCA.cer ) and click OK .
- Right-click Intermediate Certification Authorities and select Import .
- Follow the prompts in the wizard to import the intermediate certificate (for example, intermediateCA.cer ) and click OK .
Results
All systems in the domain now have certificate information in their trusted root certificate stores and intermediate certificate stores that allows them to trust the root and intermediate certificates.
Vmware horizon client linux certificate
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Server certificate checking occurs for connections between Horizon Client and a server. A certificate is a digital form of identification, similar to a passport or a driver’s license.
Server certificate checking includes the following checks:
- Is the certificate intended for a purpose other than verifying the identity of the sender and encrypting server communications? That is, is it the correct type of certificate?
- Has the certificate expired, or is it valid only in the future? That is, is the certificate valid according to the computer clock?
- Does the common name on the certificate match the host name of the server that sends it? A mismatch can occur if a load balancer redirects Horizon Client to a server that has a certificate that does not match the host name entered in Horizon Client . Another reason a mismatch can occur is if you enter an IP address rather than a host name in the client.
- Is the certificate signed by an unknown or untrusted certificate authority (CA)? Self-signed certificates are one type of untrusted CA. To pass this check, the certificate’s chain of trust must be rooted in the device’s local certificate store.
For information about distributing a self-signed root certificate that users can install on their Linux client systems, see the Ubuntu documentation.
Horizon Client uses the PEM-formatted certificates stored in the /etc/ssl/certs directory on the client system. For information about importing a root certificate stored in this location, see «Importing a Certificate into the System-Wide Certificate Authority Database» in the document at https://help.ubuntu.com/community/OpenSSL.
If a Horizon administrator has allowed it, you can set the certificate checking mode. To set the certificate checking mode, start Horizon Client and select File > Preferences from the menu bar. You can select one of the following options.
- Never connect to untrusted servers . This setting means that you cannot connect to the server if any of the certificate checks fail. An error message lists the checks that failed.
- Warn before connecting to untrusted servers . This setting means that you can click Continue to ignore the warning if a certificate check fails because the server uses a self-signed certificate. For self-signed certificates, the certificate name is not required to match the server name that you entered in Horizon Client . You can also receive a warning if the certificate has expired.
- Do not verify server identity certificates . This setting means that no certificate checking occurs.
You can configure the default certificate checking mode and prevent end users from changing it in Horizon Client . For more information, see Configuring the Certificate Checking Mode for End Users.
Using an SSL Proxy Server
If you use an SSL proxy server to inspect traffic sent from the client environment to the Internet, enable the Allow connection via an SSL Proxy setting. This setting allows certificate checking for secondary connections through an SSL proxy server and applies to both Blast Secure Gateway and secure tunnel connections. If you use an SSL proxy server and enable certificate checking, but you do not enable the Allow connection via an SSL Proxy setting, connections fail because of mismatched thumbprints. The Allow connection via an SSL Proxy setting is not available if you enable the Do not verify server identity certificates option. When the Do not verify server identity certificates option is enabled, Horizon Client does not verify the certificate or thumbprint and an SSL proxy is always allowed.
To allow VMware Blast connections through a proxy server, see Configure VMware Blast Options.
blog.vmpress.org
За последний год VMware активно дорабатывала VMware Horizon Client for Linux, добавляя в него все больше функций. Последняя актуальная версия клиента поддерживает проброс USB устройств и принтеров, RTAV (Real-Time Audio-Video) аутентификацию по смарт-картам, двухфакторную аутентификацию с помощью RSA SecurID или RADIUS, многомониторную конфигурацию, подключение локальных папок (в тестовом режиме).
Из функций, которые на текущий момент не поддерживаются в клиенте для Linux: MMR (Multimedia Redirection), проброс сканеров и serial портов, подключенных к клиентским устройствам.
В качестве примера рассмотрим установку клиента под 32-битной версией ОС Ubuntu 14.04.3 (64-битная версия Ubuntu 14.04 на текущий момент официально не поддерживается).
Установка клиента
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo ln -s /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libudev.so.1.3.5 /usr/lib/libudev.so.0
В Ubuntu Software Center доступна устаревшая версия клиента VMware View Client 2.2, поэтому загрузите с сайта VMware последнюю версию VMware Horizon Client 3.5 и запустите процедуру установки:
chmod +x VMware-Horizon-Client-3.5.0-2999900.x86.bundle
sudo ./VMware-Horizon-Client-3.5.0-2999900.x86.bundle
После завершения установки выберите автоматическую регистрацию сервисов (Register and start installed service(s) after the installation).
Клиент готов к работе и может быть запущен из консоли с помощью команды vmware-view, что довольно неудобно. В качестве альтернативного варианта можно создать ярлык и добавить его на панель Unity Launcher. Для этого создайте файл-описание:
cd ~/.local/share/applications/
nano vmware-view.desktop
[Desktop Entry]
Version=1.0
Type=Application
Name=VMware Horizon Client
Icon=/usr/share/pixmap/vmware-view.png
Path=/home/user
Exec=/usr/bin/vmware-view
StartupNotify=false
StartupWMClass=Vmware-view
#OnlyShowIn=Unity;
#X-UnityGenerated=true
sudo desktop-file-install vmware-view.desktop
Теперь приложение появится в списке доступных для запуска, и его можно будет вынести на панель launcher’а.
Настройка аутентификации по смарт-картам
Для аутентификации через клиент Horizon Client по смарт-картам требуется дополнительная настройка. В качестве примера приведено описание настройки для CCID карт-ридера и смарт-карт Aladdin eToken.
Для начала установите необходимые записимости:
sudo apt-get install pcsc-tools pcscd libccid libqt4-core libqt4-gui hal-info
Если вы используете CCID карт-ридер с драйвером libccid, то он автоматически определится ОС, для других моделей может потребоваться установка дополнительных драйверов (например, Athena ASEDrive IIIe). Список карт-ридеров и драйверов можно посмотреть на сайте wiki.debian.org/Smartcards.
Проверьте, что карт-ридер корректно работает, используя команду:
Смарт-карты Aladdin eToken
Для аутентификации с использованием eToken смарт-карт потребуется установить ПО SafeNet Authentication Client.
Перед установкой SAC загрузите и установите две библиотеки (libhal1 и libha1-storage1):
wget http://mirrors.kernel.org/ubuntu/pool/universe/h/hal/libhal1_0.5.14-8_i386.deb
sudo dpkg -i libhal1_0.5.14-8_i386.deb
wget http://mirrors.kernel.org/ubuntu/pool/universe/h/hal/libhal-storage1_0.5.14-8_i386.deb
sudo dpkg -i libhal-storage1_0.5.14-8_i386.deb
sudo dpkg -i SafenetAuthenticationClient-8.3.34-0_i386.deb
sudo mkdir /usr/lib/vmware/view/pkcs11/
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/libeTPkcs11.so /usr/lib/vmware/view/pkcs11/
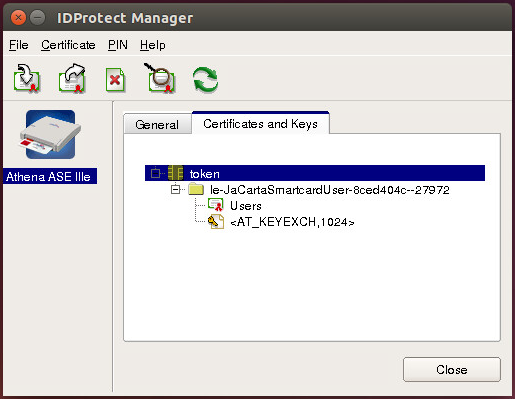
Смарт-карты Aladdin JaCarta
Для работы со смарт-картами Aladdin JaCarta вам потребуется загрузить ПО JaCarta PKI for Linux (http://www.aladdin-rd.ru/support/downloads/39875/).
После загрузки распакуйте архив и установите клиент JaCarta PKI:
sudo dpkg -i idprotectclient_637.03-0_i386.deb
sudo mkdir /usr/lib/vmware/view/pkcs11/
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86-athena/libASEP11.so /usr/lib/vmware/view/pkcs11/
Теперь аутентификация по смарт-картам должна заработать.
P.S. Для работы Single Sign-On при использовании смарт-карт на виртуальной машине вместе с VMware Horizon View Agent должен быть установлен компонент PCoIP Smartcard и SafeNet Authentication Client.