- How do I mount shared folders in Ubuntu using VMware tools?
- 14 Answers 14
- Requirements
- Official Article
- Virtual Machine settings
- On the Ubuntu Guest
- OUTDATED FOR UBUNTU > 15.10 (Wiley)
- Mounting VMware Shares from the Command Line on Linux VM
- Adding a Share to the VMware VM:
- Installing Open VM Tools:
- Mounting VMware Shares on Linux VM:
- Automatically Mount VMware Shares:
- About the author
- Shahriar Shovon
- Vmware общие папки linux mint
How do I mount shared folders in Ubuntu using VMware tools?
Experts. I’ve successfully installed VMware tools for Ubuntu. Everything seems to work fine, but shared folders were not mounted automatically.
How do I get them to work? If I run vmware-hgfsclient in terminal, I get the list of shared folders, but ls -l /mnt/hgfs is empty. Actually there’s no hgfs dir in /mnt . I know I should probably use the vmware-hgfsclient tool, but I realy don’t know how. P.S. I wouldn’t ask if I could understand the vmware-hgfsclient help I’ve read. Any suggestions?
with open-vm-tools installed, you should use vmhgfs-fuse for that, see #1 answer in this question: askubuntu.com/questions/580319/…
14 Answers 14
Most other answers are outdated. For Ubuntu 18.04 (or recent Debian distros), try:
sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/hgfs/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000 If the hgfs directory doesn’t exist, try:
sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000 You may have use a specific folder instead of .host:/ . In that case you can find out the share’s name with vmware-hgfsclient . For example:
$ vmware-hgfsclient my-shared-folder $ sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/my-shared-folder /mnt/hgfs/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000 If you want them mounted on startup, update /etc/fstab with the following:
# Use shared folders between VMWare guest and host .host:/ /mnt/hgfs/ fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other,uid=1000 0 0 I choose to mount them on demand and have them ignored by sudo mount -a and the such with the noauto option, because I noticed the shares have an impact on VM performance.
Requirements
Software requirements may require installing the following tools beforehand:
sudo apt-get install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktop Others have claimed the following are required:
sudo apt-get install build-essential module-assistant \ linux-headers-virtual linux-image-virtual && dpkg-reconfigure open-vm-tools Official Article
How to configure VMware Tools Shared Folders Linux mounts (60262)
Can confirm, on Ubuntu 19.10 virtual machine running on Windows 10 Pro host, this worked. Specifically, sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000
I have set up on Windows 7 host with Ubuntu 11.04 Desktop with VMware Tools installed on.
Virtual Machine settings
- Folder sharing = Always Enabled
- Make sure you have at least one Folder shared between the host and guest
On the Ubuntu Guest
- check /mnt/hgfs that you can access your shared folder. If you don’t see your shared folders (automounted) inside /mnt/hgfs , run VMware configuration tools: sudo vmware-config-tools.pl
- update your fstab using the details below: gksu gedit /etc/fstab (I am using ubuntu desktop so use other text editor to enter the next line at the end of the file) .host:/ / vmhgfs defaults,ttl=5,uid=1000,gid=1000 0 0
- Restart your vm (You may need to restart few times or get error message saying unable to mount just skip the error and restart)
with
@V-Light if you cd /mnt/hgfs/ then ls -a you’ll see that share folders are auto mounted there. When you do sudo mount -t vmhgfs .host:/hst_ebooks ~/hst_ebooks this will mount hst_ebooks into your home directory. What you might be wanting to do is making is easy for you to use shared folders for that try above.
run vmware-config-tools.pl, AGAIN!
vmware-config-tools.pl is not available if using open-vm-tools from Ubuntu-Software-Center or compiled from source from sourceforge. In that case user must use vmware-hgfsmounter as @snth describes in his answer. It may be possible to use open-vm-toolbox , tools and components for VMware guest systems (GUI tools) package from the Ubuntu software repository
this fixed it for me, if anyone doesn’t know it’s located under the VMWare tools after you untar.gz it in: `vmware-tools-distrib/bin/vmware-config-tools.pl’
[UPDATE 2017-05-18] This answer is outdated for Ubuntu newer than 15.10 (Wiley). The executable vmware-hgfsmounter has not been available in Ubuntu since 16.04LTS (xenial). Although, hgfsmounter may still be available on other Linux distributions, since the hgfsmounter function is still currently available in the upstream source code on GitHub. If anyone has updated information, please comment or edit this answer, instead of down-voting, as I believe this answer may still be valid for older Ubuntu releases.
This answer also assumes that you are not using VMWare Tools from VMWare but instead using open-vm-tools from your Linux distribution. VMWare decided to support this switch in 2015. See KB2073803. Therefore this answer also assumes that your version of Ubuntu can install the open-vm-tools from it’s software repository.
OUTDATED FOR UBUNTU > 15.10 (Wiley)
cd /mnt sudo mkdir hgfs sudo vmware-hgfsmounter .host:/`vmware-hgfsclient` /mnt/hgfs assuming of course that I had already enabled a shared folder from the host machine in VMware Player settings.
Note that vmware-hgfsclient returns the list of shared folders that are enabled in the VMware Player settings. This function is available for both open-vm-tools and vmware-tools.
Also note that vmware-hgfsmounter is equivalent to
mount -t vmhgfs .host:/win7share /mnt/hgfs or to adding to your /etc/fstab file
.host:/win7share /mnt/hgfs vmhgfs defaults 0 0 But the vmware-hgfsmounter function is not available using the official vmware-tools from VMware that ships with the current VMware player. Therefore, as the currently accepted answer suggests, running the vmware-config-tools.pl -d fixes the problem.
Mounting VMware Shares from the Command Line on Linux VM
In this article, I am going to show you how to share a directory/folder to a VMware Virtual Machine (VM) and how to mount the VMware share from the command line on a Linux VMware Virtual Machine (VM). So, let’s get started.
Adding a Share to the VMware VM:
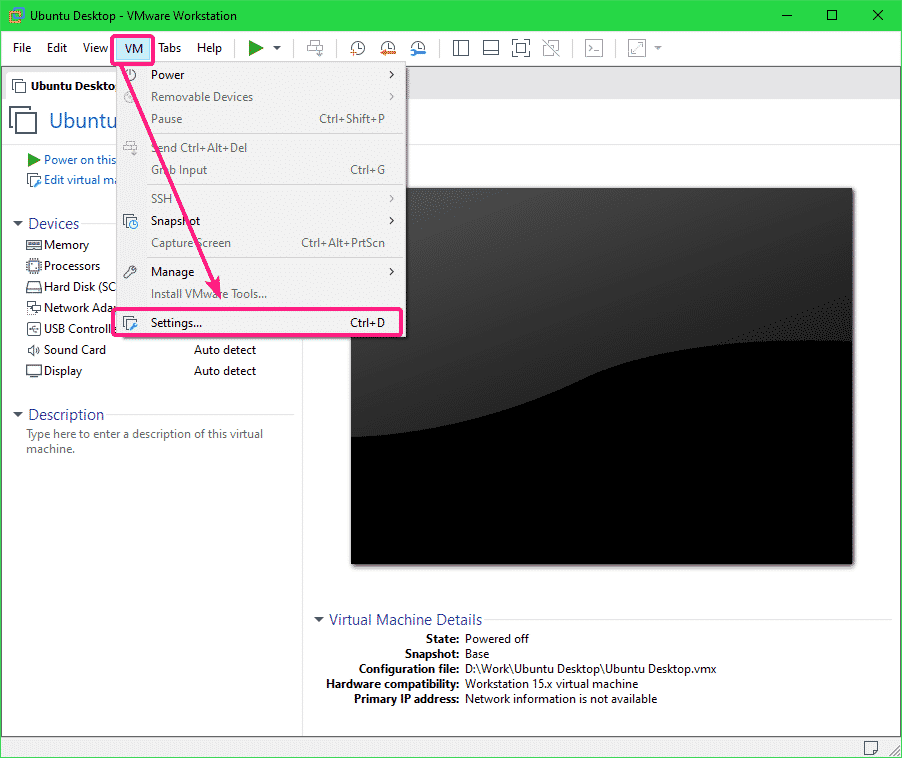
To share a directory/folder from the host to a VMware VM, open the VM, make sure the VM is not powered on and go to VM > Settings.
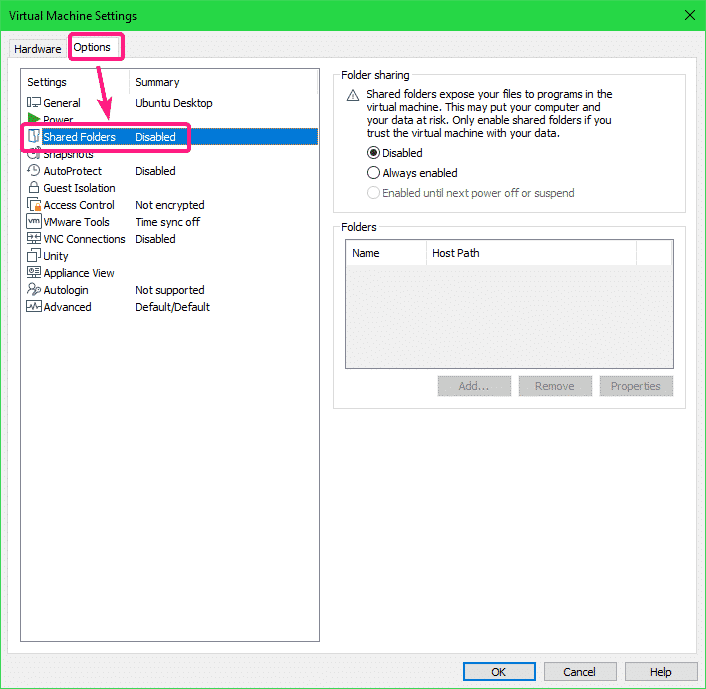
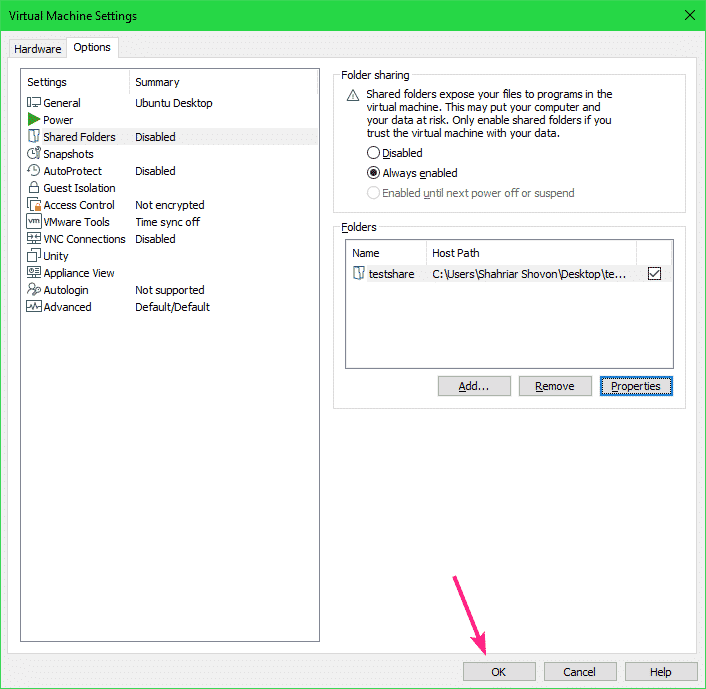
Then, go to the Options tab and click on Shared Folders.
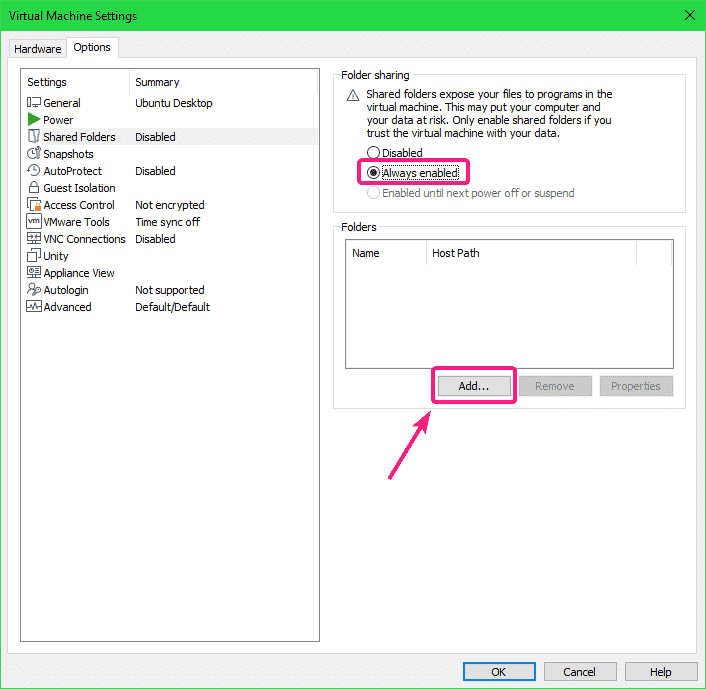
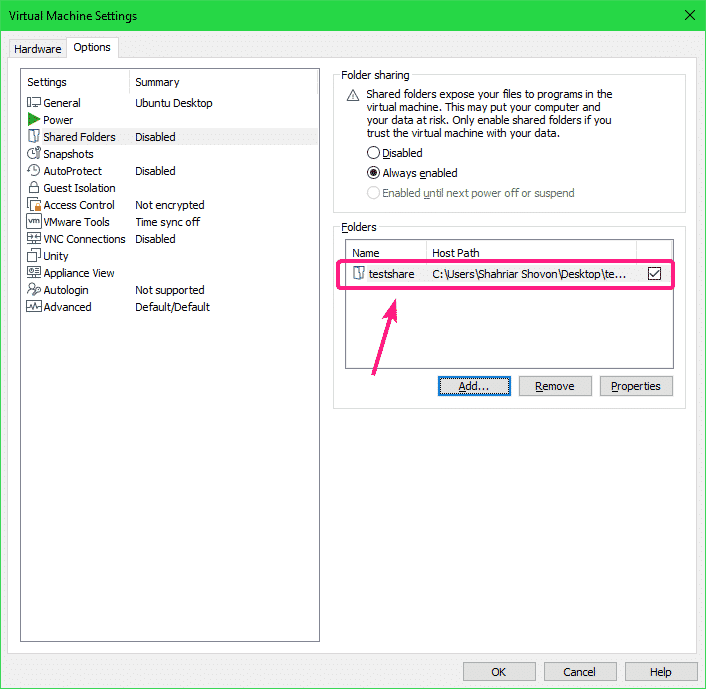
By default, Shared Folders is Disabled. To enable Shared Folders, select Always enabled.
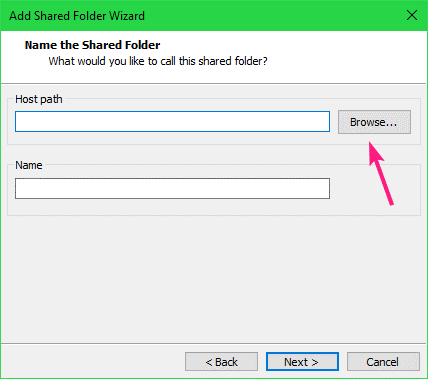
Now, you can add shared folders. To add a shared folder, click on Add…
Now, click on Next.
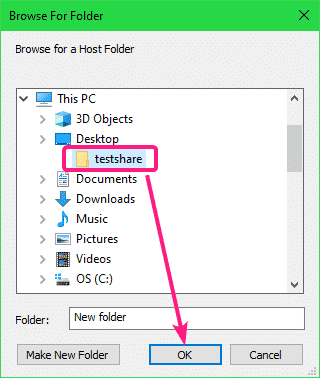
Now, click on Browse to select a directory/folder from your host computer.
Select a directory/folder that you want to share to the VMware VM and click on OK.
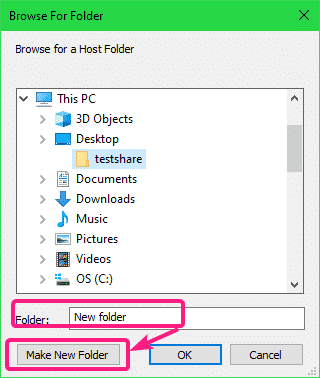
If you want to create a new directory, select a directory (parent) where you want to create a new directory, type in a Folder name and click on Make New Folder. Once the directory/folder is created, you should be able to select it for sharing.
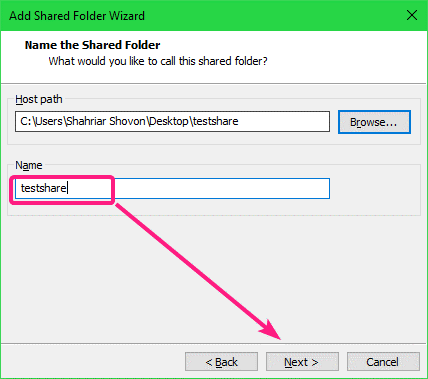
By default, the Name of the shared folder should be the name of the directory you’ve selected. If you want, you can change it. I recommend you not to add spaces in the share Name.
Once you’re done, click on Next.
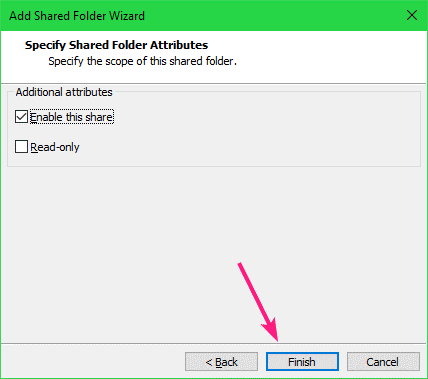
Make sure Enable this share checkbox is checked.
If you want this share to be read only, check the Read-only checkbox.
Once you’re done, click on Finish.
The share should be added to the VM.
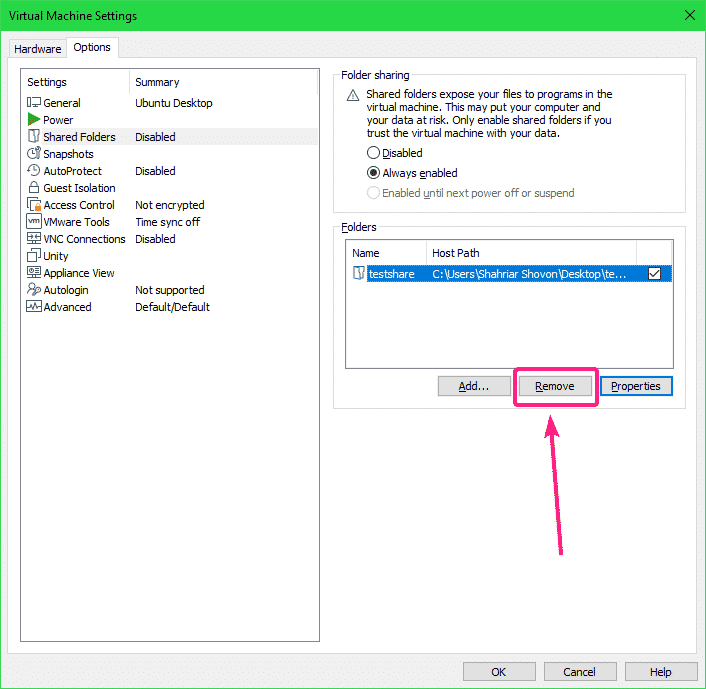
If you want to remove a share, select it and click on Remove.
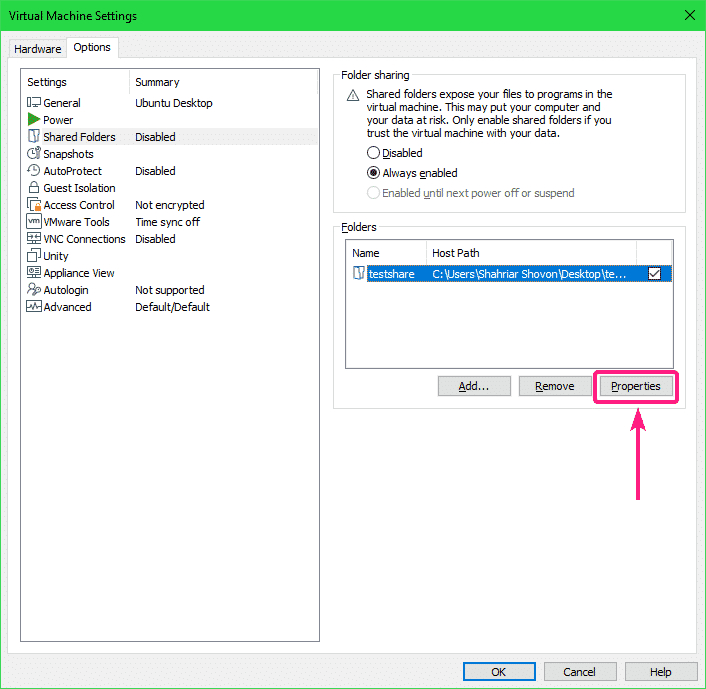
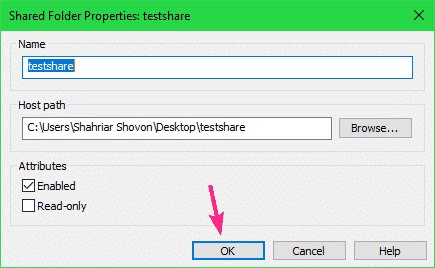
If you want to change any property of the share, select the share and click on Properties.
You can modify the Name, the Host path, share attributes from here. Once you’re done, click on OK for the changes to take effect.
Now, click on OK.
Now, power on the virtual machine.
The virtual machine should start.
Installing Open VM Tools:
In order to mount VMware shares on Linux, you must have Open VM Tools or VMware Tools installed on your Linux VM.
If you’re using a Ubuntu/Debian or any Ubuntu/Debian based operating system in the VMware VM, then check How to Install VMware Tools on Ubuntu/Debian VMware Virtual Machine.
Mounting VMware Shares on Linux VM:
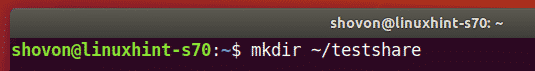
First, make a directory (let’s say ~/testshare) on the Linux VM where you want to mount the VMware share with the following command:
The command to mount a VMware share on a Linux VM is:
To mount the VMware share testshare on the ~/testshare directory, run the following command:
The VMware share testshare should be mounted on the ~/testshare directory.
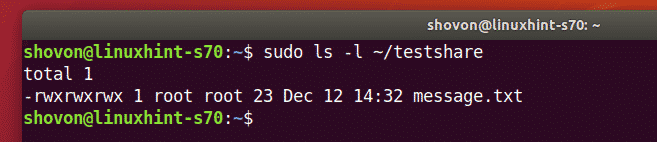
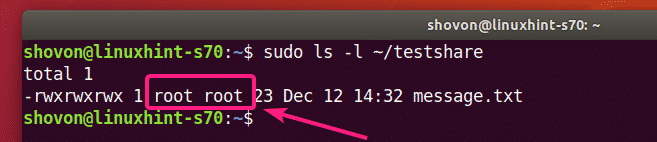
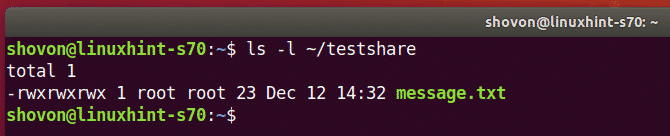
By default, the VMware shares mounted on the Linux VM is only accessible to the root user as you can see in the screenshot below. I will show you how to solve this problem. So, don’t worry.
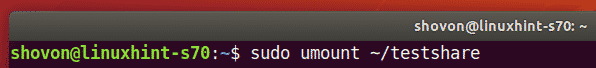
You can unmount the VMware share mounted in the ~/testshare directory with the following command:
To allow any user on the Linux VM to access the mounted VMware share, use the allow_other mount option while mounting the VMware share.
Now, you should be able to access the mounted VMware share without sudo or superuser privileges.
But, the files and directories on the share are still owned by root.
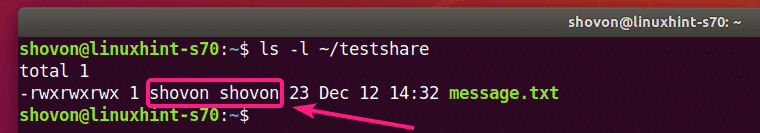
If you want the VMware share files to be accessible to your login user and also be owned by your login user, then mount the VMware share with the uid and gid mount options as follows:
$ sudo mount -t fuse.vmhgfs-fuse -o allow_other, uid =$ ( id -u ) , gid =$ ( id -g )
.host: / testshare ~ / testshare
As you can see, the VMware share files and directories are now accessible to my login user and also owned by my login user.
Automatically Mount VMware Shares:
If you want the VMware Linux VM to automatically mount the VMware share on boot, then you have to add a new line to the /etc/fstab file.
First, open the /etc/fstab file with the following command:
You may want to use vi text editor for editing the /etc/fstab file. In that case, run the following command:
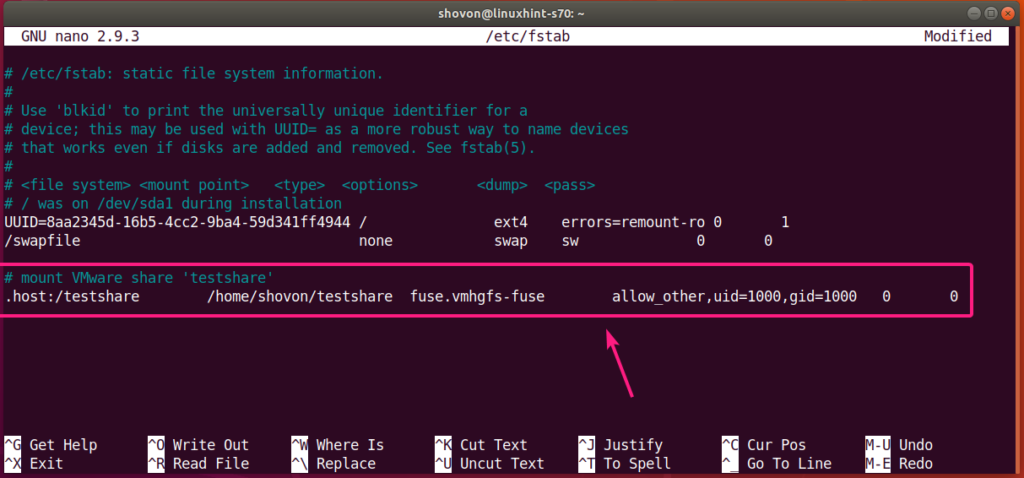
Now, add the following line at the end of the /etc/fstab file:
Note: Make sure to replace , , and .
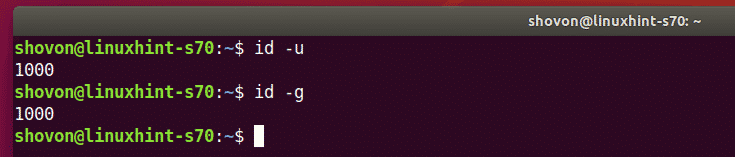
You can find with the id -u command and with the id -g command.
In my case, I added to the following line to the /etc/fstab file:
.host: / testshare / home / shovon / testshare fuse.vmhgfs-fuse
allow_other, uid = 1000 , gid = 1000 0 0
Once you’re done, save the /etc/fstab file.
Now, reboot your Linux VM with the following command:
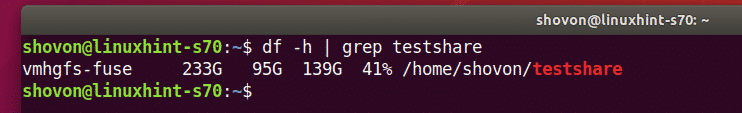
Once your Linux VM starts, run the following command to verify whether the VMware share is mounted on the Linux VM:
As you can see, the VMware share testshare is mounted correctly in the ~/testshare directory.
I can access the VMware share as usual.
So, that’s how you share a directory/folder from the host to your Linux VMware VM and mount it from the command line on your Linux VM. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.
Vmware общие папки linux mint
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
After you enable a shared folder, you can mount one or more directories or subdirectories in the shared folder to any location in the file system in addition to the default location of /mnt/hgfs .
Depending on the kernel version of the Linux guest operating system, VMware Tools uses different components to provide shared-folder functionality. In Linux kernels prior to version 4.0, the VMware Tools services script loads a driver that performs the mount. Linux kernels 4.0 and later use a FUSE file system component.
You can use different mount commands to mount all shares, one share, or a subdirectory within a share to any location in the file system. The commands also vary depending on the Linux-kernel version of the guest.
Table 1. Mount Command Syntax| Linux Kernel Prior to 4.0 | Linux Kernel 4.0 and Later | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/ /home/user1/shares | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /home/user1/shares -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts all shares to /home/user1/shares |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo /tmp/foo | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo /tmp/foo -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the share named foo to /tmp/foo |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the subdirectory bar within the share foo to /var/lib/bar |
For Linux kernel prior to version 4.0, you can use VMware-specific options in addition to the standard mount syntax. Enter the command /sbin/mount.vmhgfs -h to list the options.
For Linux kernel version 4.0 or later, enter the command /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse -h to list the available options.
Note: The mount can fail if shared folders are not enabled or if the share does not exist. You are not prompted to run the VMware Tools vmware-config-tools.pl configuration program again.