- Vmware workstation linux shared folder
- Общая папка VMware в Linux
- Настройка общей папки VMware в Linux
- Vmware workstation linux shared folder
- How do I mount shared folders in Ubuntu using VMware tools?
- 14 Answers 14
- Requirements
- Official Article
- Virtual Machine settings
- On the Ubuntu Guest
- OUTDATED FOR UBUNTU > 15.10 (Wiley)
Vmware workstation linux shared folder
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
After you enable a shared folder, you can mount one or more directories or subdirectories in the shared folder to any location in the file system in addition to the default location of /mnt/hgfs .
Depending on the kernel version of the Linux guest operating system, VMware Tools uses different components to provide shared-folder functionality. In Linux kernels prior to version 4.0, the VMware Tools services script loads a driver that performs the mount. Linux kernels 4.0 and later use a FUSE file system component.
You can use different mount commands to mount all shares, one share, or a subdirectory within a share to any location in the file system. The commands also vary depending on the Linux-kernel version of the guest.
Table 1. Mount Command Syntax| Linux Kernel Prior to 4.0 | Linux Kernel 4.0 and Later | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/ /home/user1/shares | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /home/user1/shares -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts all shares to /home/user1/shares |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo /tmp/foo | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo /tmp/foo -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the share named foo to /tmp/foo |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the subdirectory bar within the share foo to /var/lib/bar |
For Linux kernel prior to version 4.0, you can use VMware-specific options in addition to the standard mount syntax. Enter the command /sbin/mount.vmhgfs -h to list the options.
For Linux kernel version 4.0 or later, enter the command /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse -h to list the available options.
Note: The mount can fail if shared folders are disabled or if the share does not exist. You are not prompted to run the VMware Tools vmware-config-tools.pl configuration program again.
Общая папка VMware в Linux
Общая папка для виртуальной машины и основной системы очень часто необходима для обмена файлами между хостовой и гостевой операционной системой. В одной из прошлых статей мы говорили о том как настроить общую папку VirtualBox. Но VMware — это тоже очень популярная виртуальная машина.
Поэтому в сегодняшней статье мы рассмотрим как сделать общую папку VMware Player в вашей системе. Я буду подразумевать, что обе операционные системы, хост и гость — это какой-либо дистрибутив Linux. В данном случае это Ubuntu.
Настройка общей папки VMware в Linux
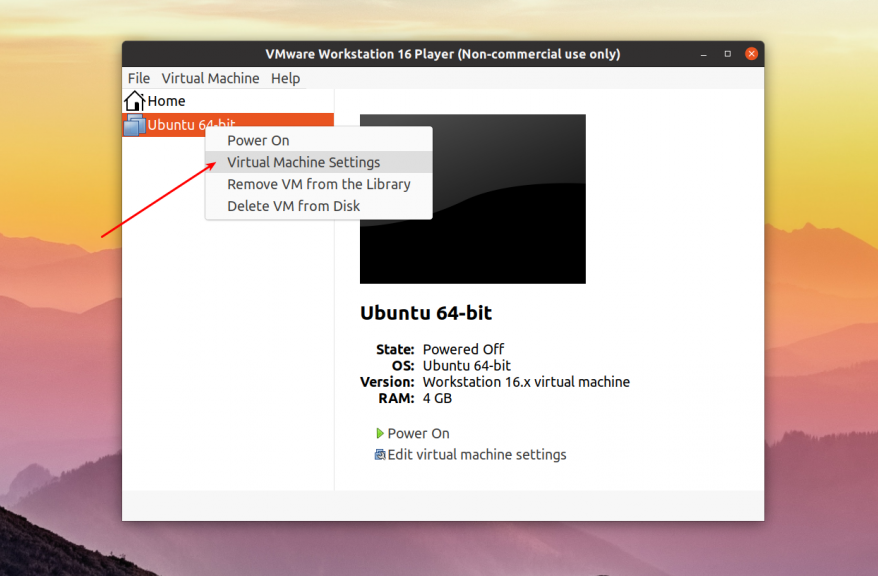
Начать надо с настройки самой виртуальной машины. Запустите VMware и откройте контекстное меню для нужной машины. В нём выберите Virtual Machine Settings:
В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку Options:
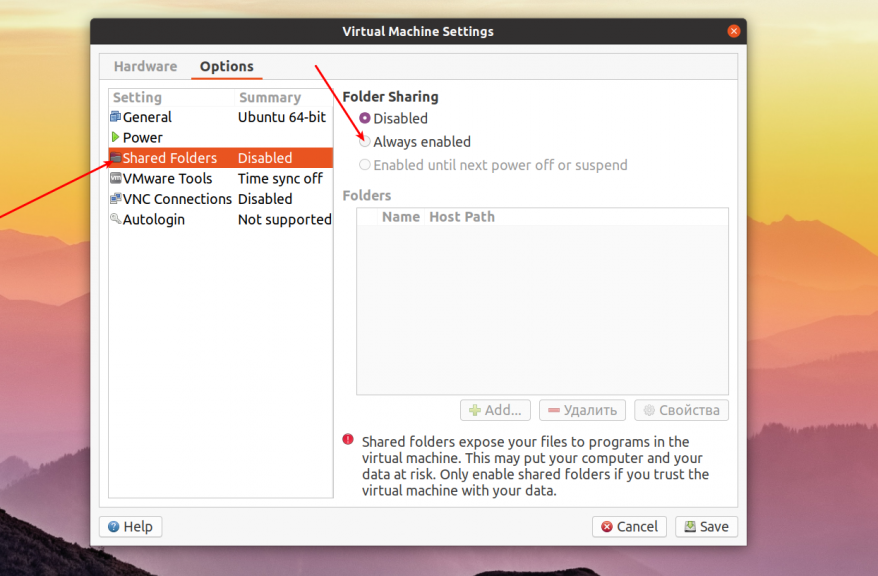
На этой вкладке откройте пункт Shared Folders, а значение переключателя Folder Sharing установите в положение Always enabled:
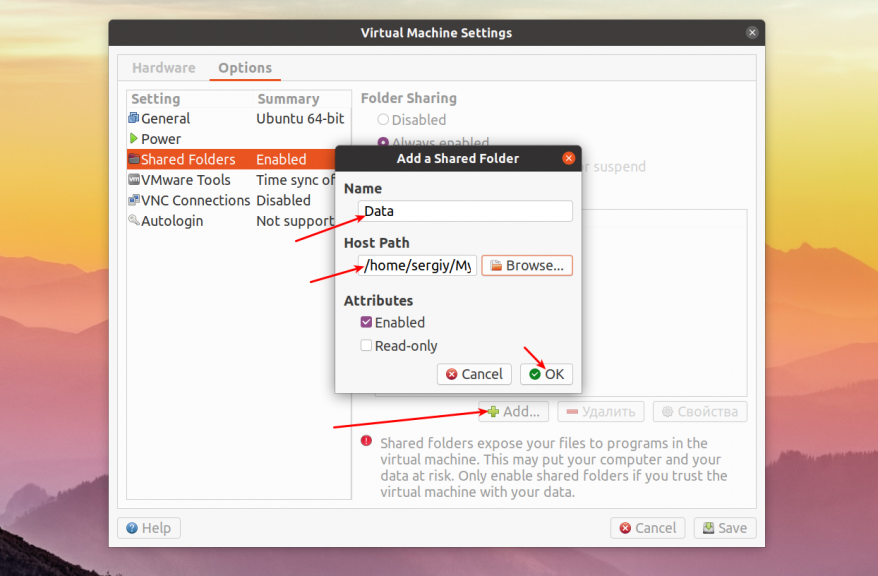
Затем надо добавить общую папку. Для этого кликните по кнопке Add. , в открывшемся окне введите название общей папки, а затем введите или выберите путь к нужной папке в основной системе. Затем нажмите кнопку OK и Save внизу окна чтобы всё сохранить.
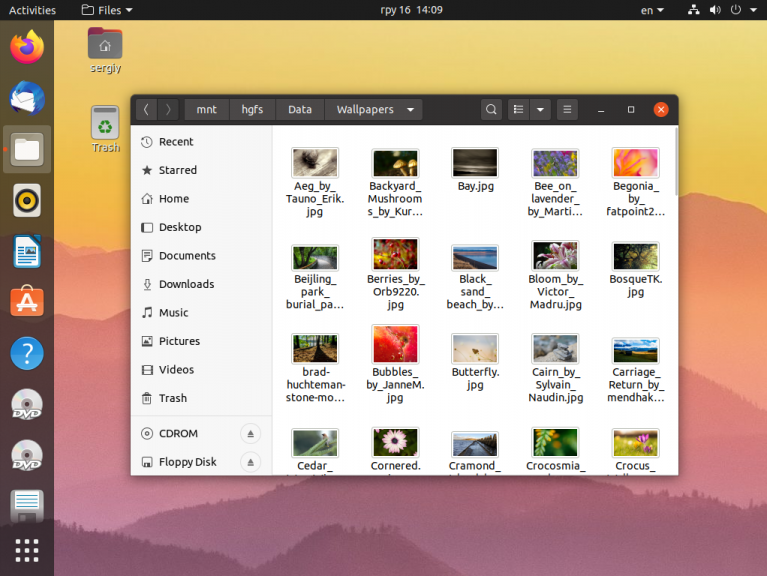
После этого можно запускать виртуальную машину. В самой виртуальной машине общая папка должна монтироваться в /mnt/hgfs. Если такой папки нет проверьте установлены ли пакеты open-vm-tools и open-vm-tools-desktop:
sudo apt install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktop
Затем с помощью такой команды, вы можете проверить видна ли ваша общая папка в гостевой системе:
Затем можно смонтировать попытаться смонтировать все общие папки в /mnt. Для этого сначала создайте папку /mnt/hgfs, если она не существует:
Затем осталось выполнить монтирование с помощью утилиты vmhgfs-fuse:
sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host: /mnt/hgfs -o allow_other -o uid=1000
Кроме, непосредственно, пути к точке монтирования надо передать опцию allow_other чтобы все пользователи могли получить доступ к папке, а владельцем папки сделать пользователя с идентификатором 1000, обычно это идентификатор первого зарегистрированного в системе пользователя, если у вас другой идентификатор замените на свой. Это позволит этому пользователю записывать файлы в эту папку.
Теперь можно посмотреть её содержимое:
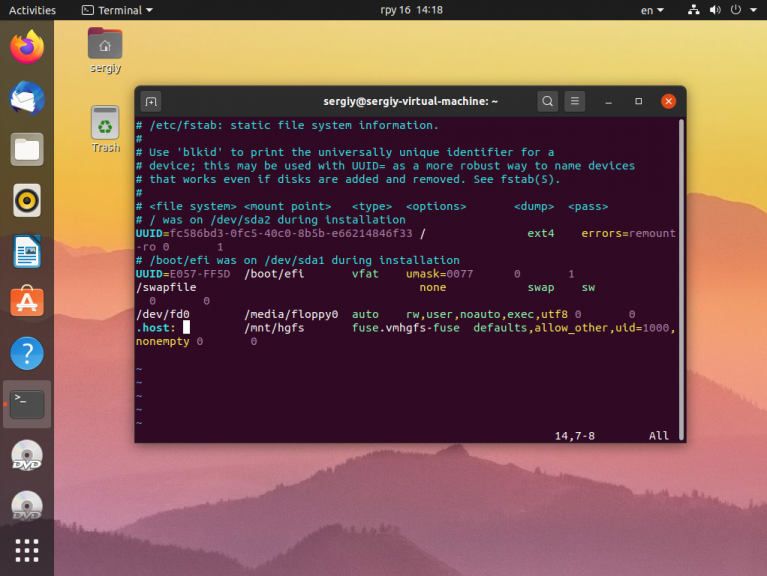
Теперь, чтобы эта папка монтировалась всегда при запуске системы надо добавить такую строчку в /etc/fstab:
.host: /mnt/hgfs fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other,uid=1000,nonempty 0 0
Или если вы хотите монтировать только определённую общую папку, например, Data, то надо указать её имя после адреса .host:
.host:/Data /mnt/hgfs fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other,uid=1000,nonempty 0 0
Вот и всё. Теперь вы знаете как настраивается общая папка VMware в Linux, а также как смонтировать её, если автоматическое монтирование не работает. Как видите, всё довольно просто.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Vmware workstation linux shared folder
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
After you enable a shared folder, you can mount one or more directories or subdirectories in the shared folder to any location in the file system in addition to the default location of /mnt/hgfs .
Depending on the kernel version of the Linux guest operating system, VMware Tools uses different components to provide shared-folder functionality. In Linux kernels prior to version 4.0, the VMware Tools services script loads a driver that performs the mount. Linux kernels 4.0 and later use a FUSE file system component.
You can use different mount commands to mount all shares, one share, or a subdirectory within a share to any location in the file system. The commands also vary depending on the Linux-kernel version of the guest.
Table 1. Mount Command Syntax| Linux Kernel Prior to 4.0 | Linux Kernel 4.0 and Later | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/ /home/user1/shares | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /home/user1/shares -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts all shares to /home/user1/shares |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo /tmp/foo | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo /tmp/foo -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the share named foo to /tmp/foo |
| mount -t vmhgfs .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar | /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/foo/bar /var/lib/bar -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse,allow_other | Mounts the subdirectory bar within the share foo to /var/lib/bar |
For Linux kernel prior to version 4.0, you can use VMware-specific options in addition to the standard mount syntax. Enter the command /sbin/mount.vmhgfs -h to list the options.
For Linux kernel version 4.0 or later, enter the command /usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse -h to list the available options.
Note: The mount can fail if shared folders are not enabled or if the share does not exist. You are not prompted to run the VMware Tools vmware-config-tools.pl configuration program again.
How do I mount shared folders in Ubuntu using VMware tools?
Experts. I’ve successfully installed VMware tools for Ubuntu. Everything seems to work fine, but shared folders were not mounted automatically.
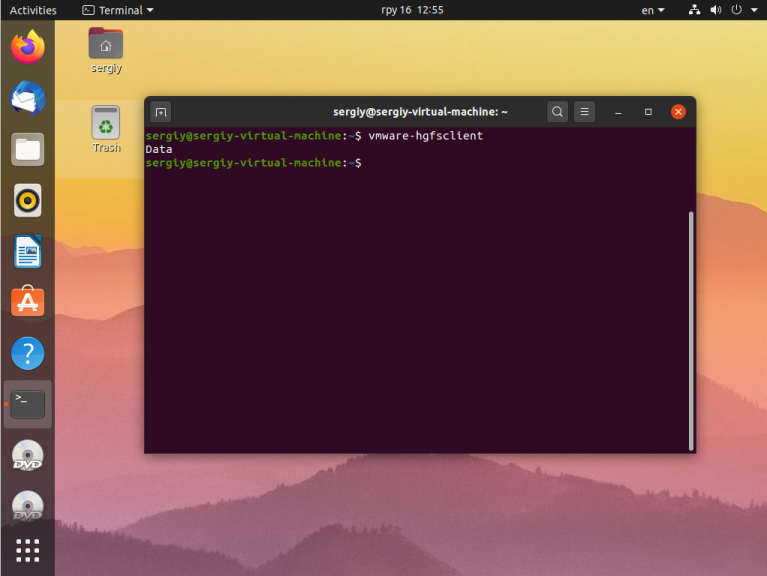
How do I get them to work? If I run vmware-hgfsclient in terminal, I get the list of shared folders, but ls -l /mnt/hgfs is empty. Actually there’s no hgfs dir in /mnt . I know I should probably use the vmware-hgfsclient tool, but I realy don’t know how. P.S. I wouldn’t ask if I could understand the vmware-hgfsclient help I’ve read. Any suggestions?
with open-vm-tools installed, you should use vmhgfs-fuse for that, see #1 answer in this question: askubuntu.com/questions/580319/…
14 Answers 14
Most other answers are outdated. For Ubuntu 18.04 (or recent Debian distros), try:
sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/hgfs/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000 If the hgfs directory doesn’t exist, try:
sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000 You may have use a specific folder instead of .host:/ . In that case you can find out the share’s name with vmware-hgfsclient . For example:
$ vmware-hgfsclient my-shared-folder $ sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/my-shared-folder /mnt/hgfs/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000 If you want them mounted on startup, update /etc/fstab with the following:
# Use shared folders between VMWare guest and host .host:/ /mnt/hgfs/ fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other,uid=1000 0 0 I choose to mount them on demand and have them ignored by sudo mount -a and the such with the noauto option, because I noticed the shares have an impact on VM performance.
Requirements
Software requirements may require installing the following tools beforehand:
sudo apt-get install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktop Others have claimed the following are required:
sudo apt-get install build-essential module-assistant \ linux-headers-virtual linux-image-virtual && dpkg-reconfigure open-vm-tools Official Article
How to configure VMware Tools Shared Folders Linux mounts (60262)
Can confirm, on Ubuntu 19.10 virtual machine running on Windows 10 Pro host, this worked. Specifically, sudo vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/ -o allow_other -o uid=1000
I have set up on Windows 7 host with Ubuntu 11.04 Desktop with VMware Tools installed on.
Virtual Machine settings
- Folder sharing = Always Enabled
- Make sure you have at least one Folder shared between the host and guest
On the Ubuntu Guest
- check /mnt/hgfs that you can access your shared folder. If you don’t see your shared folders (automounted) inside /mnt/hgfs , run VMware configuration tools: sudo vmware-config-tools.pl
- update your fstab using the details below: gksu gedit /etc/fstab (I am using ubuntu desktop so use other text editor to enter the next line at the end of the file) .host:/ / vmhgfs defaults,ttl=5,uid=1000,gid=1000 0 0
- Restart your vm (You may need to restart few times or get error message saying unable to mount just skip the error and restart)
with
@V-Light if you cd /mnt/hgfs/ then ls -a you’ll see that share folders are auto mounted there. When you do sudo mount -t vmhgfs .host:/hst_ebooks ~/hst_ebooks this will mount hst_ebooks into your home directory. What you might be wanting to do is making is easy for you to use shared folders for that try above.
run vmware-config-tools.pl, AGAIN!
vmware-config-tools.pl is not available if using open-vm-tools from Ubuntu-Software-Center or compiled from source from sourceforge. In that case user must use vmware-hgfsmounter as @snth describes in his answer. It may be possible to use open-vm-toolbox , tools and components for VMware guest systems (GUI tools) package from the Ubuntu software repository
this fixed it for me, if anyone doesn’t know it’s located under the VMWare tools after you untar.gz it in: `vmware-tools-distrib/bin/vmware-config-tools.pl’
[UPDATE 2017-05-18] This answer is outdated for Ubuntu newer than 15.10 (Wiley). The executable vmware-hgfsmounter has not been available in Ubuntu since 16.04LTS (xenial). Although, hgfsmounter may still be available on other Linux distributions, since the hgfsmounter function is still currently available in the upstream source code on GitHub. If anyone has updated information, please comment or edit this answer, instead of down-voting, as I believe this answer may still be valid for older Ubuntu releases.
This answer also assumes that you are not using VMWare Tools from VMWare but instead using open-vm-tools from your Linux distribution. VMWare decided to support this switch in 2015. See KB2073803. Therefore this answer also assumes that your version of Ubuntu can install the open-vm-tools from it’s software repository.
OUTDATED FOR UBUNTU > 15.10 (Wiley)
cd /mnt sudo mkdir hgfs sudo vmware-hgfsmounter .host:/`vmware-hgfsclient` /mnt/hgfs assuming of course that I had already enabled a shared folder from the host machine in VMware Player settings.
Note that vmware-hgfsclient returns the list of shared folders that are enabled in the VMware Player settings. This function is available for both open-vm-tools and vmware-tools.
Also note that vmware-hgfsmounter is equivalent to
mount -t vmhgfs .host:/win7share /mnt/hgfs or to adding to your /etc/fstab file
.host:/win7share /mnt/hgfs vmhgfs defaults 0 0 But the vmware-hgfsmounter function is not available using the official vmware-tools from VMware that ships with the current VMware player. Therefore, as the currently accepted answer suggests, running the vmware-config-tools.pl -d fixes the problem.