- Using VNC
- Installing a VNC Viewer
- Performing a VNC Installation
- Installing in VNC Direct Mode
- Installing in VNC Connect Mode
- Kickstart Considerations
- How to install and use VNC on Ubuntu 20.04
- BitLaunch
- BitLaunch
- How to install VNC Server on Ubuntu
- How to start and configure VNC server
- Creating an SSH tunnel
- Connect to your VNC server with a VNC client
- How to Disable Internet Explorer Enhanced Security on Your Windows RDP Server
- How to install Mailcow and Delta chat on a VPS
Using VNC
The graphical installation interface is the recommended method of installing CentOS. However, in some cases, accessing the graphical interface directly is difficult or impossible. Many enterprise systems, notably servers (IBM Power Systems), lack the capability to connect a display and a keyboard, making VNC a necessity for manual (non-Kickstart) installations.
To allow manual installations on headless systems (systems without a directly connected display, keyboard and mouse), the Anaconda installation program includes a Virtual Network Computing (VNC) installation which allows the graphical mode of the installation program to run locally, but display on a system connected to the network. The VNC installation provides you with the full range of installation options, even in situations where the system lacks a display or input devices.
This chapter provides instructions on activating VNC mode on the installation system and connecting to it using a VNC viewer.
Installing a VNC Viewer
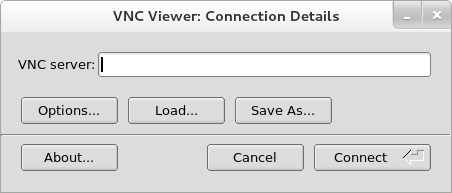
Performing a VNC installation requires a VNC viewer running on your workstation or another terminal computer. VNC viewers are available in the repositories of most Linux distributions; free VNC viewers are also available for other operating systems such as Windows. On Linux systems, use your package manager to search for a viewer for your distribution.
The following VNC viewers are available in CentOS:
- TigerVNC — A basic viewer independent of your desktop environment. Installed as the tigervnc package.
- Vinagre — A viewer for the GNOME desktop environment. Installed as the vinagre package.
- KRDC — A viewer integrated with the KDE desktop environment. Installed as the kdenetwork-krdc package.
To install any of the viewers listed above, execute the following command as root :
Replace package with the package name of the viewer you want to use (for example, tigervnc).
Procedures in this chapter assume you are using TigerVNC as your VNC viewer. Specific instructions for other viewers can differ, but the general principles still apply.
Performing a VNC Installation
The Anaconda installation program offers two modes for VNC installation. The modes are Direct Mode and Connect Mode. Direct Mode requires the VNC viewer to initiate the connection to the system being installed. Connect Mode requires the system being installed to initiate the connection to the VNC viewer. Once the connection is established, the two modes do not differ. The mode you select depends on the configuration in your environment.
In this mode, Anaconda is configured to start the installation and wait for a VNC viewer before proceeding. The IP address and port are displayed on the system being installed. Using this information, you can connect to the installation system from a different computer. For this reason you must have visual and interactive access to the system being installed.
In this mode, the VNC viewer is started on the remote system in listening mode. The VNC viewer waits for an incoming connection on a specified port. Then, Anaconda is started and the host name and port number are provided using a boot option or a Kickstart command. When the installation begins, the installation program establishes a connection with the listening VNC viewer using the specified host name and port number. For this reason, your remote system must be able to accept incoming network connections.
- If visual and interactive access to the system being installed is not available, then you must use Connect Mode.
- If the system being installed is not allowed inbound connections by a firewall, then you must use Connect Mode or disable the firewall. Disabling a firewall can have security implications.
- If the remote system running the VNC viewer is not allowed incoming connections by a firewall, then you must use Direct Mode, or disable the firewall. Disabling a firewall can have security implications. See the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Security Guide for information about configuring the firewall.
You must specify custom boot options to start a VNC installation. The exact way to do this differs depending on the system architecture. For architecture-specific instructions about editing boot options, see:
Installing in VNC Direct Mode
The Direct Mode expects the VNC viewer to initiate a connection to the system being installed. Anaconda asks you to initiate this connection.
- Run the VNC viewer of your choice on the workstation you are using to connect to the system being installed. For example, if you use TigerVNC:
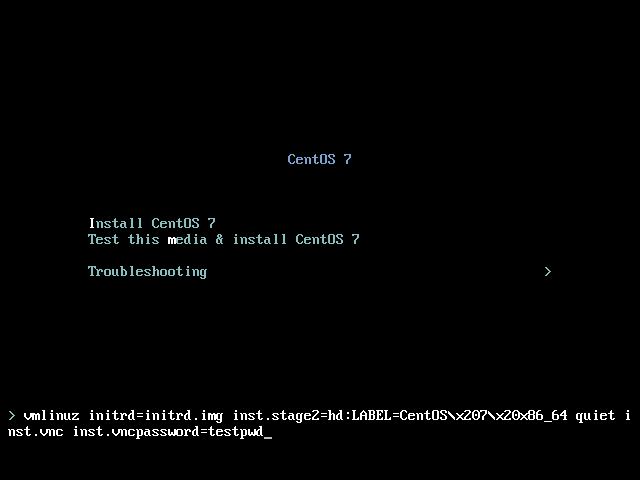
Optionally, if you want to restrict VNC access to the installation system, add the inst.vncpassword=PASSWORD boot option as well. Replace PASSWORD with the password you want to use for the installation. The VNC password must be between 6 and 8 characters long.
Use a temporary password for the inst.vncpassword= option. It should not be a real or root password you use on any system.
13:14:47 Please manually connect your VNC viewer to 192.168.100.131:1 to begin the install.For further details about using a VNC client, see the corresponding section in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 System Administrator’s Guide.
After you finish the procedure, a new window opens with the VNC connection established, displaying the installation menu. In this window, you can use the Anaconda graphical interface the same way you would use it when installing directly on the system.
Installing in VNC Connect Mode
In Connect Mode, the system being installed initiates a connection to the VNC viewer running on a remote system. Before you start, make sure the remote system is configured to accept an incoming connection on the port you want to use for VNC. The exact way to make sure the connection is not blocked depends on your network and on your workstation’s configuration. Information about configuring the firewall is available in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Security Guide.
- Start the VNC viewer on the client system in listening mode. For example, on CentOS using TigerVNC, execute the following command:
TigerVNC Viewer 64-bit v1.3.0 (20130924) Built on Sep 24 2013 at 16:32:56 Copyright (C) 1999-2011 TigerVNC Team and many others (see README.txt) See http://www.tigervnc.org for information on TigerVNC. Thu Feb 20 15:23:54 2014 main: Listening on port 5901
inst.vnc inst.vncconnect=HOST:PORTReplace HOST with the IP address of the system running the listening VNC viewer, and PORT with the port number that the VNC viewer is listening on.
When the connection is successfully established, a new window opens on the system running the VNC viewer, displaying the installation menu. In this window, you can use the Anaconda graphical interface the same way you would use it when installing directly on the system.
Afer you finish the procedure, you can proceed with:
Kickstart Considerations
Commands for using VNC are also available in Kickstart installations. Using only the vnc command results in an installation using Direct Mode. Additional options are available to set up an installation using Connect Mode. For more information about the vnc command and options used in Kickstart files, see Kickstart Commands and Options.
All CentOS Documentation content available under CC-BY-SA 3.0.
This page was built using a modified version of the Antora default UI. The source code for this UI is licensed under the terms of the MPL-2.0 license.
How to install and use VNC on Ubuntu 20.04
Struggling with command-line interfaces? Here’s how to install and use VNC on your Ubuntu 20.04 VPS for a UI-based experience.
BitLaunch
BitLaunch
VNC, aka Virtual Network Computing, is a useful tool for users who aren’t quite used to the terminal-based interfaces of most servers. With the pairing of a VNC server and VNC viewer, you can use your local keyboard and mouse to interact with your server via a graphical user interface (GUI).
Setting up, installing, and configuring VNC is relatively easy. Though you’ll have to run quite a few commands to get going, the advantage is that you won’t have to use the command-line-based interface after that point.
Today, we’re going to show you how to install VNC on Ubuntu 20.04 and then how to use a VNC viewer on a Windows 10 client PC to connect to it. First, though, you should be aware of some pre-requisites:
- An Ubuntu 20.04 server with a non-root admin user and configured firewall (need one quickly? Sign up to BitLaunch).
- A local PC from which you can install a VNC client (we’ll cover options for Windows 10/11, macOs, and Linux below)
How to install VNC Server on Ubuntu
When you boot your Ubuntu server for the first time, you’ll notice there’s no GUI. Naturally, we’re going to need to change that if we want to use it with a UI via VNC.
There are a few options when it comes to VNC servers and desktops environments, but the main lightweight ones are Xfce and TightVNC. These are what we’re going to use today.
First, make sure your list of packages are up to date:
Install Xfce and its goodies enhancements package:
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies You’ll be given the option to choose between gdm3 and lightdm as your display manager. gdm3 tends to be more lightweight, but you may also find it uglier. As we’re running on a lower-spec VPS, we’re going to choose gdm3 by pressing Enter with it selected.
Now it’s time to install TightVNC server:
sudo apt install tightvncserverHow to start and configure VNC server
You can start a VNC server instance at any point with the following command:
TightVNCServer will ask you to enter a username and password. This is what you’ll use later to connect to the VNC instance, so note it down. You’ll also be asked to if you want to create a view-only password. This password will let users log in to view a VNC instance, but will disable any of their inputs.
So, with that VNC is running, but it’s not much use to us at this point. We need to tell it which desktop environment we want to use, in this case Xfce. This will require a bit of fiddling with config files.
Unfortunately, we can’t edit those config files until VNC is stopped. You can quickly kill it with vncserver -kill :1 .
Now we can edit the /.vnc/startup file and point it to xfce4:
Add the following to the bottom of the config and press Ctrl + O and Ctrl + X to save the changes:
xrdb $HOME/.Xresources startxfce4 & If there’s nothing in your xstartup file already, make sure you add #!/bin/bash at the top. You’ll also need to make it executable with chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup .
Let’s restart our VNC server with the localhost option to ensure only connections that start on our server are allowed.
Creating an SSH tunnel
At this point you may be wondering how you’re supposed to connect to your VNC server if all connects outside of your remote host are disabled. For this, we can create an SSH tunnel. You’ll want to use your local PC for this part.
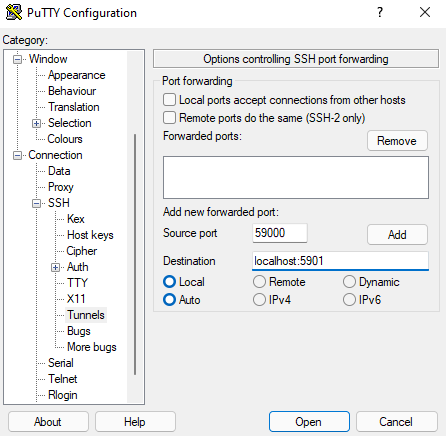
Let’s create the SSH connection by opening CMD on our local Windows PC and entering the following command:
ssh -L 59000:localhost:5901 -C -N -l nonrootuser your_server_ipIf you use PuTTy, you can also add the relevant port to your settings. You can find the Tunnels options under the SSH section and add your details like so:
When you connect to your server with PuTTy it will automatically open the tunnel. If you only want to open the tunnel, you can tick «Don’t start a Shell or Command at all» under SSH settings.
Connect to your VNC server with a VNC client
With your SSH tunnel open, you should be able to connect to the VNC server with the VNC client on your local PC.
If you don’t yet have a client, there are a few options, which vary depending on your OS.
We’ll be using TigerVNC for this tutorial as it has wide compatibility, good picture quality, and various options and features.
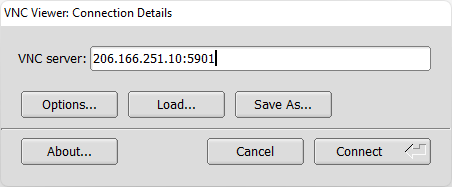
Enter the IP address of your VPS server followed by 5901 and press Connect.
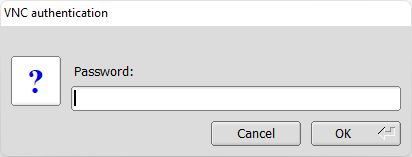
Enter the VNC server password you chose earlier. Note: this should be different to your user password. Press OK.
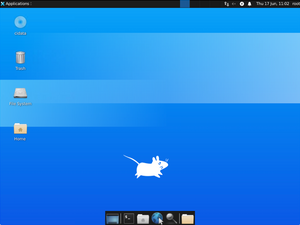
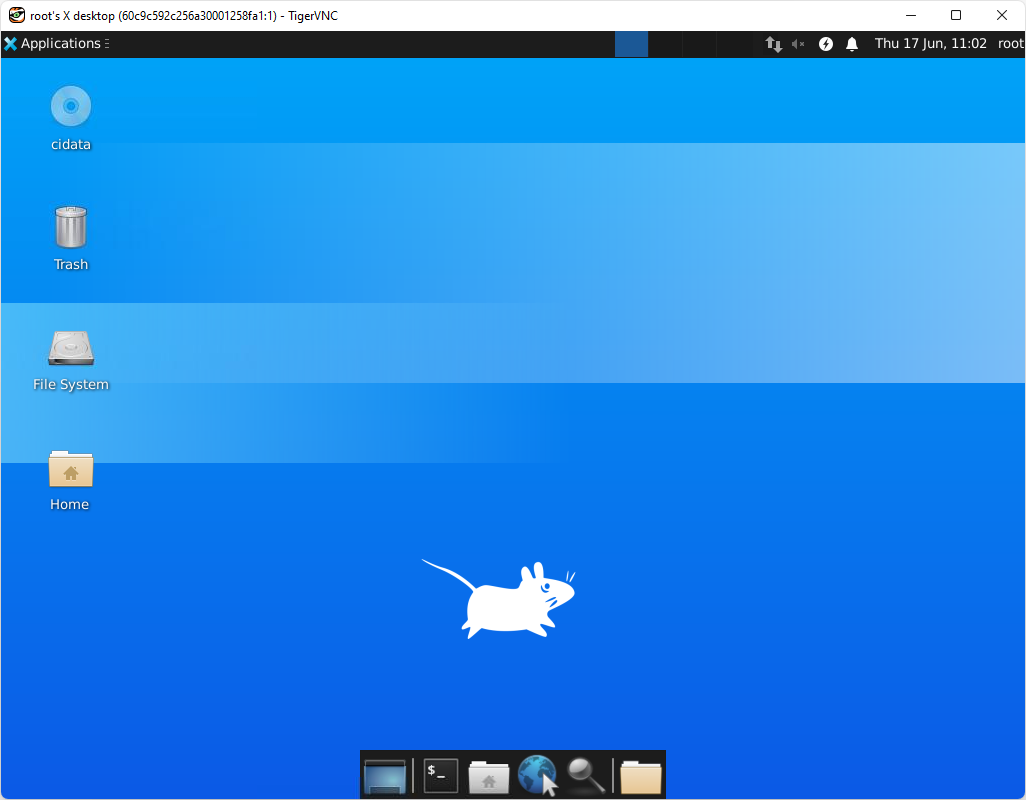
You’ll now be taken the desktop of the Xfce (or other) desktop environment and will be able to browse and edit files via the UI. You can also browse the internet, run commands from the terminal, view images, take screenshots, and more.
How to Disable Internet Explorer Enhanced Security on Your Windows RDP Server
Disabling Internet Explorer Enhanced Security on your Windows RDP server takes just a few minutes.
How to install Mailcow and Delta chat on a VPS
Today, we’re going to show you how to install Mailcow on a VPS, utilizing BitLaunch’s new DNS support to simplify things further. As a bonus, we’ll also show you how to set up Delta Chat on that server for full messaging services.