- How to Setup an L2TP/IPsec VPN Client on Linux
- How to Setup L2TP VPN Connection in Linux
- How to Create Your Own IPsec VPN Server in Linux
- Prerequisites:
- Setting Up IPsec/L2TP VPN Server in Linux
- How to Add or Remove a VPN User in Linux
- How to Upgrade Libreswan Installation in Linux
- How to Uninstall the VPN Server in Linux
- On RHEL/CentOS
- On Debian/Ubuntu
How to Setup an L2TP/IPsec VPN Client on Linux
L2TP (which stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) is a tunneling protocol designed to support virtual private networks (VPN connections) over the internet. It is implemented in most if not all modern operating systems including Linux and VPN-capable devices.
The L2TP does not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms directly to traffic that passes through it, it is usually implemented with the IPsec authentication suite (L2TP/IPsec) to provide encryption within the L2TP tunnel.
In this article, we will show how to set up an L2TP/IPSec VPN connection in Ubuntu and its derivatives and Fedora Linux.
This guide assumes that the L2TP/IPsec VPN server has been set up and that you have received the following VPN connection details from your organization’s or company’s system administrator.
Gateway IP address or hostname Username and Password Pre-shared Key (Secret)
How to Setup L2TP VPN Connection in Linux
To add an L2TP/IPsec option to the NetworkManager, you need to install the NetworkManager-l2tp VPN plugin which supports NetworkManager 1.8 and later. It provides support for L2TP and L2TP/IPsec.
To install the L2TP module on Ubuntu and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, use the following PPA.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nm-l2tp/network-manager-l2tp $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install network-manager-l2tp network-manager-l2tp-gnome
On RHEL/CentOS and Fedora Linux, use the following dnf command to install L2TP module.
# dnf install xl2tpd # dnf install NetworkManager-l2tp # dnf install NetworkManager-l2tp-gnome OR # yum install xl2tpd # yum install NetworkManager-l2tp # yum install NetworkManager-l2tp-gnome
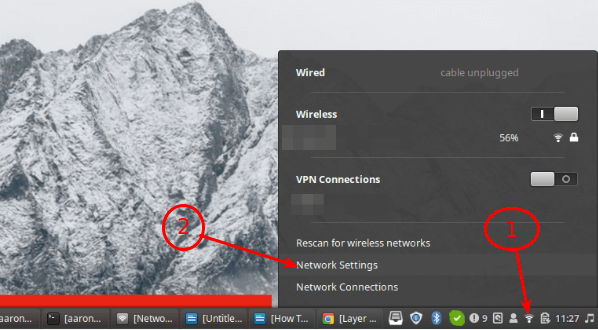
Once the package installation is complete, click on your Network Manager icon, then go to Network Settings.
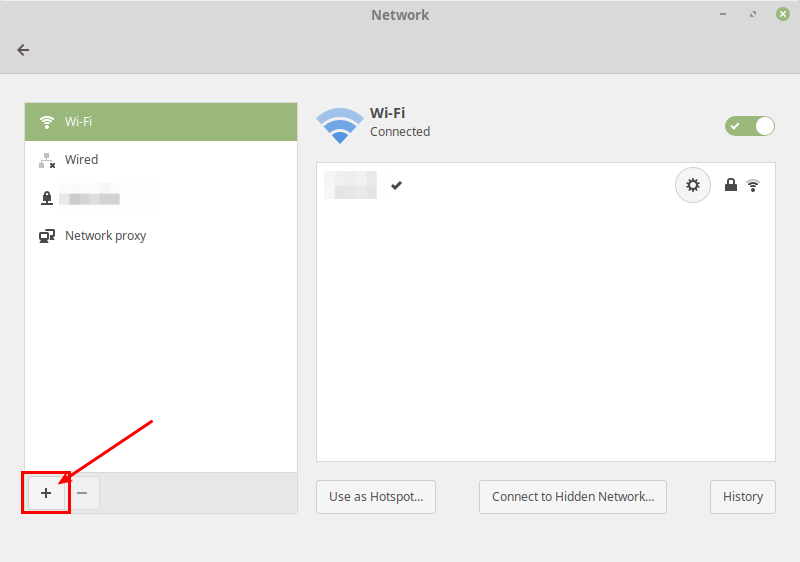
Next, add a new VPN connection by clicking on the (+) sign.
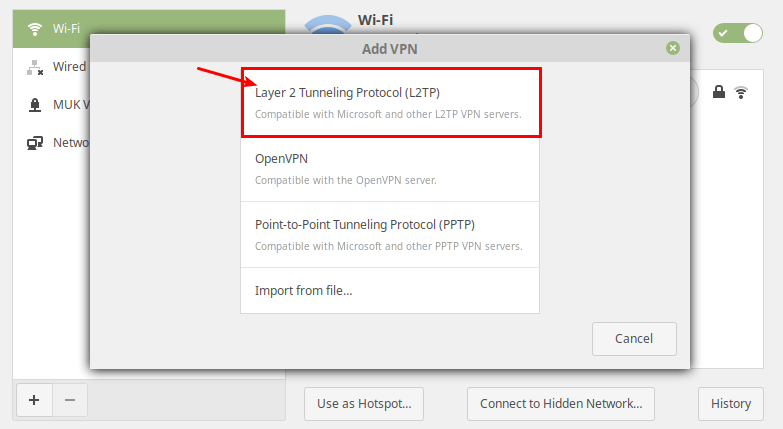
Then select Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) option from the pop-up window.
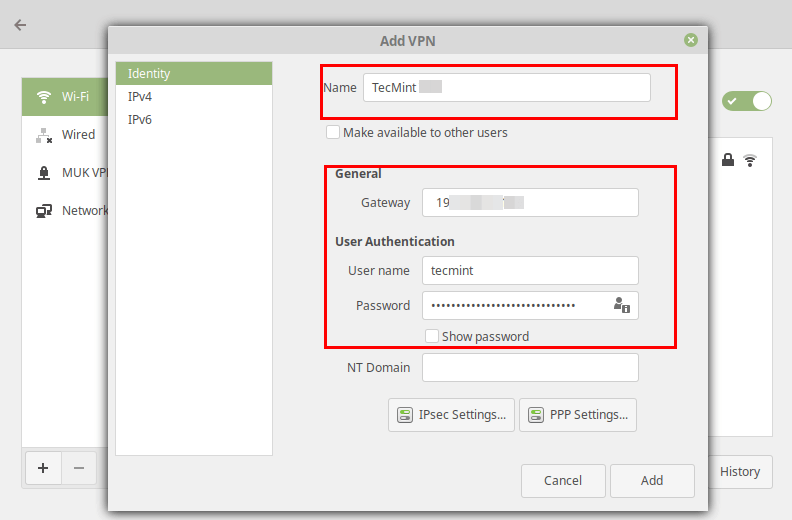
Next, enter the VPN connection details (gateway IP address or hostname, username and password) you received from the system administrator, in the following window.
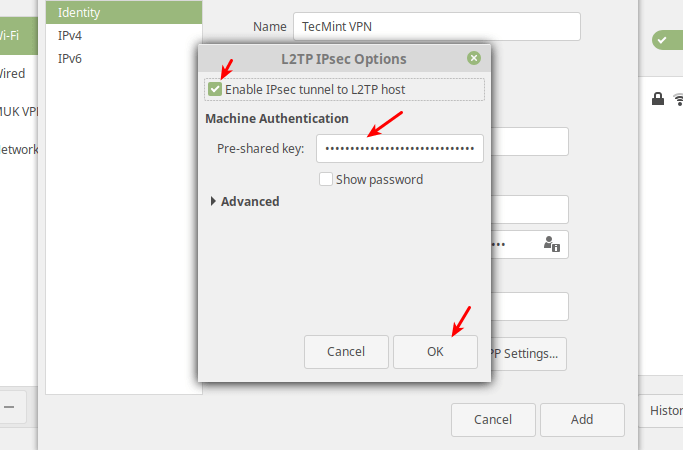
Next, click IPsec Settings to enter the pre-shared key for the connection. Then enable IPsec tunnel to L2TP host, enter (or copy and paste the) the Pre-shared key and click Ok.
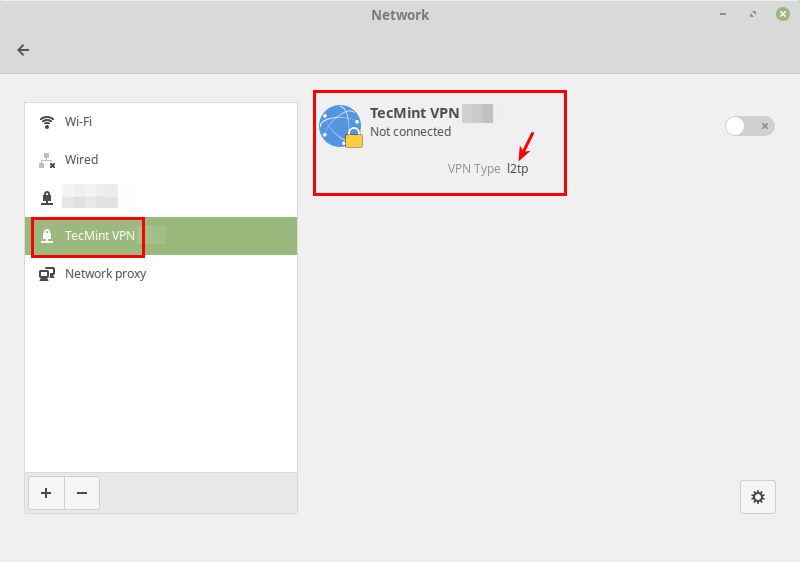
After that, click Add. Now your new VPN connection should be added.
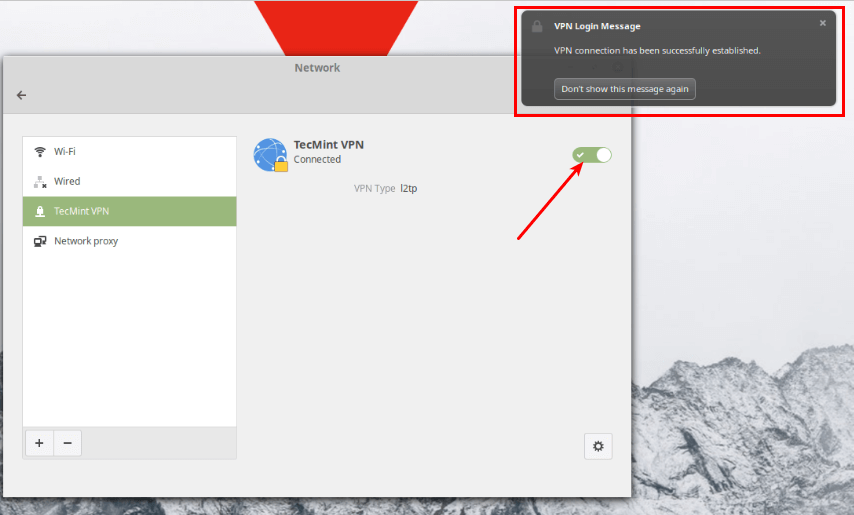
Next, turn on the VPN connection to start using it. If the connection details are correct, the connection should be established successfully.
Last but not least, test if the VPN is working fine. You can check your computer’s public IP address to confirm this from a web browser: it should now point to the IP of the gateway.
That’s the end of this article. If you have any queries or thoughts to share, reach us via the feedback form below.
How to Create Your Own IPsec VPN Server in Linux
There are so many benefits of using a VPN (Virtual Private Network), some of which include keeping you safe on the internet by encrypting your traffic and helping you to access blocked content/sites/web applications from anywhere. Not to mention, VPN also helps you to browse the internet anonymously.
In this article, you will learn how to quickly and automatically set up your own IPsec/L2TP VPN server in CentOS/RHEL, Ubuntu, and Debian Linux distributions.
Prerequisites:
- A fresh CentOS/RHEL or Ubuntu/DebianVPS (Virtual Private Server) from any provider such as Linode.
Setting Up IPsec/L2TP VPN Server in Linux
To set up the VPN server, we will use a wonderful collection of shell scripts created by Lin Song, that installs Libreswan as the IPsec server, and xl2tpd as the L2TP provider. The offering also includes scripts to add or delete VPN users, upgrade the VPN installation and much more.
First, log into your VPS via SSH, then run the appropriate commands for your distribution to set up the VPN server. By default, the script will generate random VPN credentials (pre-shared key, VPN username, and password) for you and display them at the end of the installation.
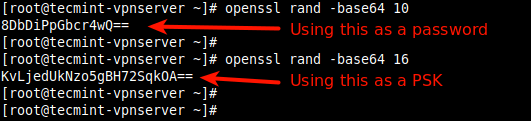
However, if you want to use your own credentials, first you need to generate a strong password and PSK as shown.
# openssl rand -base64 10 # openssl rand -base64 16
Next, set these generated values as described in the following command all values MUST be placed inside ‘single quotes‘ as shown.
- VPN_IPSEC_PSK – Your IPsec pre-shared key.
- VPN_USER – Your VPN username.
- VPN_PASSWORD – Your VPN password.
---------------- On CentOS/RHEL ---------------- # wget https://git.io/vpnsetup-centos -O vpnsetup.sh && VPN_IPSEC_PSK='KvLjedUkNzo5gBH72SqkOA==' VPN_USER='tecmint' VPN_PASSWORD='8DbDiPpGbcr4wQ==' sh vpnsetup.sh ---------------- On Debian and Ubuntu ---------------- # wget https://git.io/vpnsetup -O vpnsetup.sh && VPN_IPSEC_PSK='KvLjedUkNzo5gBH72SqkOA==' VPN_USER='tecmint' VPN_PASSWORD='8DbDiPpGbcr4wQ==' sudo sh vpnsetup.sh
The main packages that will be installed are bind-utils, net-tools, bison, flex, gcc, libcap-ng-devel, libcurl-devel, libselinux-devel, nspr-devel, nss-devel, pam-devel, xl2tpd, iptables-services, systemd-devel, fipscheck-devel, libevent-devel, and fail2ban(to protect SSH), and their respective dependencies. Then it downloads, compiles and installs Libreswan from source, enables and starts the necessary services.
Once the installation is complete, the VPN details will be displayed as shown in the following screenshot.
Next, you need to set up a VPN client, for desktops or laptops with a graphical user interface, refer to this guide: How To Setup an L2TP/Ipsec VPN Client on Linux.
To add the VPN connection in a mobile device such as an Android phone, go to Settings –> Network & Internet (or Wireless & Networks –> More) –> Advanced –> VPN. Select the option to add a new VPN. The VPN type should be set to IPSec Xauth PSK, then use the VPN gateway and credentials above.
How to Add or Remove a VPN User in Linux
To create a new VPN user or update an existing VPN user with a new password, download and use the add_vpn_user.sh script using the following wget command.
$ wget -O add_vpn_user.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hwdsl2/setup-ipsec-vpn/master/extras/add_vpn_user.sh $ sudo sh add_vpn_user.sh 'username_to_add' 'user_password'
To delete a VPN user, download and use the del_vpn_user.sh script.
$ wget -O del_vpn_user.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hwdsl2/setup-ipsec-vpn/master/extras/del_vpn_user.sh $ sudo sh del_vpn_user.sh 'username_to_delete'
How to Upgrade Libreswan Installation in Linux
You can upgrade the Libreswan installation using the vpnupgrade.sh or vpnupgrade_centos.sh script. Make sure to edit the SWAN_VER variable to the version you want to install, within the script.
---------------- On CentOS/RHEL ---------------- # wget https://git.io/vpnupgrade-centos -O vpnupgrade.sh && sh vpnupgrade.sh ---------------- On Debian and Ubuntu ---------------- # wget https://git.io/vpnupgrade -O vpnupgrade.sh && sudo sh vpnupgrade.sh
How to Uninstall the VPN Server in Linux
To uninstall the VPN installation, do the following.
On RHEL/CentOS
Then open /etc/sysconfig/iptables configuration file and remove the unneeded rules and edit /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/rc.local file, and remove the lines after the comment # Added by hwdsl2 VPN script, in both files.
On Debian/Ubuntu
Next, edit /etc/iptables.rules configuration file and remove any unneeded rules. Additionally, edit /etc/iptables/rules.v4 if it exists.
Then edit /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/rc.local files, remove the lines after the comment # Added by hwdsl2 VPN script, in both files. Do not remove exit 0 if it exists.
Optionally, you can remove certain files and directories that were created during the VPN set up.
# rm -f /etc/ipsec.conf* /etc/ipsec.secrets* /etc/ppp/chap-secrets* /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd* /etc/pam.d/pluto /etc/sysconfig/pluto /etc/default/pluto # rm -rf /etc/ipsec.d /etc/xl2tpd
To set up a site-to-site IPSec-based VPN with Strongswan, check out our guides:
At this point, your own VPN server is up and running. You can share any queries or give us feedback using the comment form below.