- Date Command in Linux
- Using the Linux date Command #
- Date Formatting Options #
- Date String #
- Override the Timezone #
- Epoch Converter #
- Using date with Other Commands #
- Display the Last Modification Time of a File #
- Set the System Time and Date #
- Conclusion #
- Команда date в Linux
- Синтаксис команды date
- Примеры использования date
- Выводы
- How to Use the Date Command in Linux
- Use the Linux date Command
- Formatting Options
- Override the Timezone
- Examples
- Seconds from epoch
- Seconds from epoch to the provided date/time
- Convert epoch to a date
- Determine which day of the week a given date was
- Use date in Scripts and Commands
- Set the Date Manually from the Linux Terminal
Date Command in Linux
In this tutorial, we’ll cover the basics of the date command.
The date command displays or sets the system date. It is most commonly used to print the date and time in different formats and calculate future and past dates.
Using the Linux date Command #
The syntax for the date command is as follows:
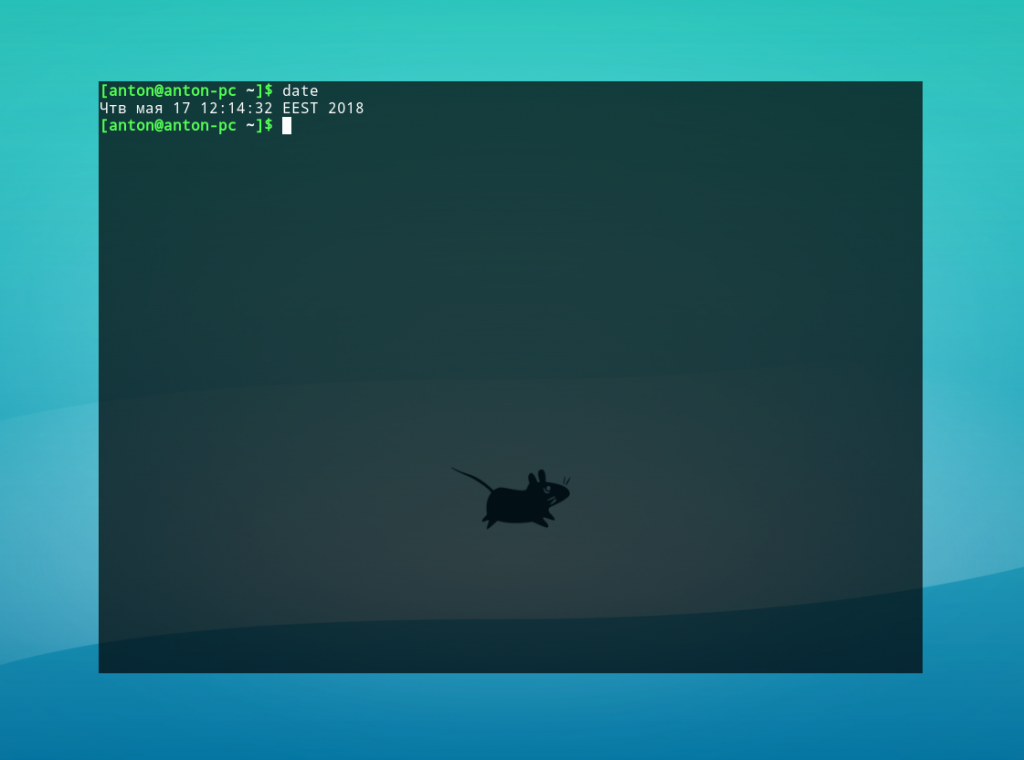
To display the current system time and date using the default formatting, invoke the command without any options and arguments:
The output includes the day of the week, month, day of the month, time, timezone, and year:
Sat Jun 1 14:31:01 CEST 2019 Date Formatting Options #
The output of the date command can be formatted with a sequence of format control characters preceded by a + sign. The format controls start with the % symbol and are substituted by their values.
date +"Year: %Y, Month: %m, Day: %d"The %Y character will be replaced with the year, %m with month and %d with the day of the month:
Year: 2019, Month: 06, Day: 02 Below is a small list of the some of the most common formatting characters:
- %a — Locale’s abbreviated short weekday name (e.g., Mon)
- %A — Locale’s abbreviated full weekday name (e.g., Monday)
- %b — Locale’s abbreviated short month name (e.g., Jan)
- %B — Locale’s abbreviated long month name (e.g., January)
- %d — Day of month (e.g., 01)
- %H — Hour (00..23)
- %I — Hour (01..12)
- %j — Day of year (001..366)
- %m — Month (01..12)
- %M — Minute (00..59)
- %S — Second (00..60)
- %u — Day of week (1..7)
- %Y — Full year (e.g., 2019)
To get a full list of all formatting options run date —help or man date in your terminal.
Date String #
The -d option allows you to operate on a specific date. You can specify the date as a human-readable date string like below:
Sun Feb 7 12:10:53 CET 2010 Using the custom formatting:
date -d '16 Dec 1974' +'%A, %d %B %Y'The date string accepts values such as “tomorrow”, “friday”, “last friday” “next friday”, “next month”, “next week” ..etc.
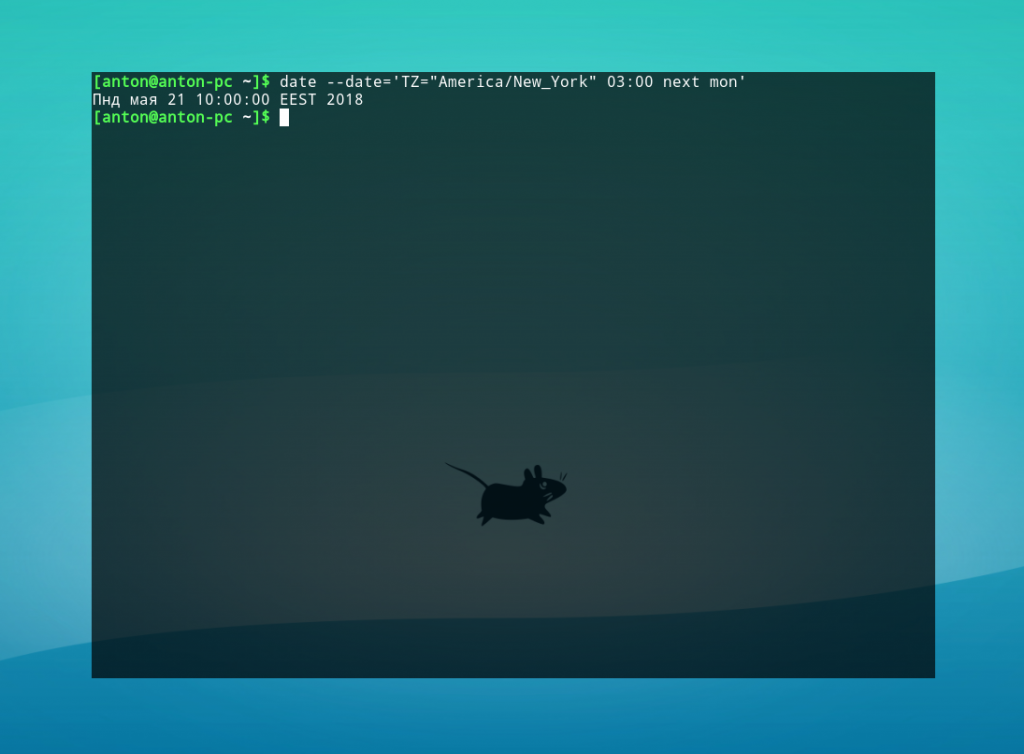
Sat May 25 14:31:42 CEST 2019 You can also use the date string option to show the local time for different timezones. For example, to show the local time for 6:30AM next Monday on the Australian east coast, you would type:
date -d 'TZ="Australia/Sydney" 06:30 next Monday'Sun Jun 2 22:30:00 CEST 2019Override the Timezone #
The date command returns the date in the default system timezone . To use a different timezone set the environment variable TZ to the desired timezone.
For example, to show the Melbourne, Aus time, you would type:
TZ='Australia/Melbourne' dateSat Jun 1 22:35:10 AEST 2019 To list all available time zones , you can either list the files in the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory or use the timedatectl list-timezones command.
Epoch Converter #
The date command can be used as an Epoch converter. Epoch, or Unix timestamps, is the number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970 at 00:00:00 UTC.
To print the number of the seconds from the epoch to the current day, invoke date with the %s format control:
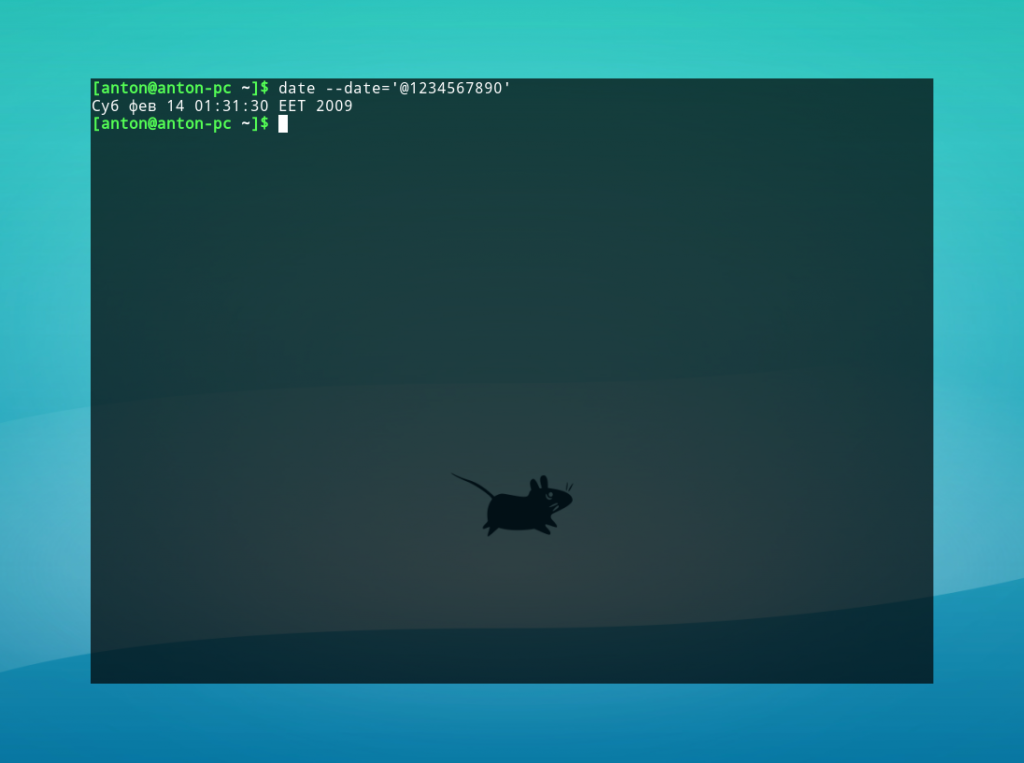
To convert seconds since the epoch to date, set the seconds as a date string prefixed with @ :
Sat Feb 14 00:31:30 CET 2009 Using date with Other Commands #
The date command is most frequently used to create filenames that contain the current time and date.
The command below will create a Mysql backup file in the following format database_name-20190601.sql
mysqldump database_name > database_name-$(date +%Y%m%d).sqlYou can also use the date command in your shell scripts. In the example below we are assigning the output of date to the date_now variable:
date_now=$(date "+%F-%H-%M-%S") echo $date_now Display the Last Modification Time of a File #
The date command with the -r option shows the last modification time of a file. For example:
Tue Jul 24 11:11:48 CEST 2018 If you want to modify the file timestamp, use the touch command .
Set the System Time and Date #
Setting the system time and date manually with the date command is not recommended because on most Linux distributions, the system clock is synchronized using the ntp or the systemd-timesyncd services.
However, if you want to set the system clock manually, you can use the —set= option. For example, if you want to set the date and time to 5:30pm, June 01, 2019, you would type:
Conclusion #
The Linux date command displays or set the system date and time.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Команда date в Linux
Главное свойство утилит GNU/Linux — делать что-то одно, но эффективно. Яркий пример — команда date Linux, работающая с датой и временем. С её помощью можно извлекать любую дату в разнообразном формате, в том числе и рассчитывать прошлое и будущее время. Привилегированные пользователи могут перезаписывать системное время, используя её.
Утилита предустановлена во всех дистрибутивах GNU/Linux. В этой статье будут рассмотрены возможности date и способы применения этой команды.
Синтаксис команды date
Программа может выполнятся от имени обычного пользователя. Стандартный синтаксис команды (квадратные скобки обозначают необязательное наличие):
date [ ОПЦИИ ] . [ +ФОРМАТ ]
Ниже представлена таблица с часто применяемыми опциями для date.
| Опция | Длинный вариант | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| -d STRING | —date=STRING | Вывод даты по указанной строке (например ‘yesterday’, ‘tomorrow’, ‘last monday’). |
| -I | —iso-8601[=FMT] | Вывод даты в формате ISO 8601. FMT по умолчанию содержит ‘date’. Также может содержать ‘hourse’, ‘minutes’, ‘seconds’, ‘ns’ для отображения соответствующих значений и часовой пояс относительно UTC рядом с датой. |
| —rfc-3339=FMT | Вывод даты в формате RFC 3339. FMT по умолчанию содержит ‘date’. Также может содержать ‘seconds’ и ‘ns’ для отображения секунд или наносекунд. | |
| -r FILE | —reference=FILE | Вывод даты последней модификации указанного файла в формате по умолчанию. |
| -u | —utc | Вывод UTC-даты |
Аргумент ФОРМАТ отвечает за форматирование вывода даты. Для его указания необходимо поставить знак «+» и написать нужную маску. Наиболее популярные форматы:
| Формат | Значение |
|---|---|
| %% | Знак процента |
| %a | День недели текущей локали в короткой форме («Чтв») |
| %A | День недели текущей локали в длинной форме («Четверг») |
| %b | Месяц года текущей локали в короткой форме в родительном падеже («янв») |
| %B | Месяц года текущей локали в длинной форме в родительном падеже («января») |
| %c | Дата и время текущей локали без указания часового пояса |
| %С | Первые две цифры текущего года |
| %d | Числовой день месяца с ведущим нулём |
| %D | Дата в формате %m/%d/%y |
| %e | День месяца; аналог %_d |
| %F | Дата в формате %Y-%m-%d |
| %h | Аналог %b |
| %H | Часы (00..23) |
| %I | Часы (01..12) |
| %j | День года (001..366) |
| %m | Месяц (01..12) |
| %M | Минуты (00..59) |
| %n | Новая строка |
| %q | Квартал года |
| %S | Секунды (00..59) |
| %t | Знак табуляции |
| %T | Время в формате %H:%M:%S |
| %u | Числовой день недели; 1 — понедельник |
| %x | Дата в локальном формате |
| %X | Время в локальном формате |
| %Z | Аббревиатура временной зоны |
Примеры использования date
Введем команду без параметров.
Будет отображена текущая дата и время в соответствии с настройками локали системы.
Команда date без параметров по умолчанию применяет маску %a %b %d %X %Z. Поскольку все форматы должны быть переданы как один параметр (из-за принципа обработки данных командным интерпретатором Bash), пробелы между ними необходимо экранировать обратным слэшем (\) или взять в кавычки.
Особое внимание следует уделить параметру -d (—date). Его функциональность не слишком очевидна, но при этом наиболее обширна.
Пример 1. Вычисление даты по числу секунд, прошедших с 1 января 1970 года.
Пример 2. Вычисление даты и времени следующего понедельника при указании часового пояса Нью-Йорка в 03:00.
date —date=’TZ=»America/New_York» 03:00 next mon’
Обратите внимание: указывать название дня недели или месяца можно в любом регистре, в короткой или длинной форме. Параметры next и last обозначают следующий и прошедший, соответственно, ближайшие дни недели.
Пример 3. Если текущий день месяца — последний, сформировать отчет о занятости дискового пространства корневого и домашнего каталога в файл report.
#!/bin/bash
if [[ $(date —date=’next day’ +%d) = ’01’ ]]; then
df -h / /home > report
Такой скрипт можно использовать для автоматизации работы с помощью демона crontab или anacron.
Выводы
Команда date Linux является эффективным инструментом работы с датой и временем, с широкой возможностью их расчёта для прошедших или будущих показателей. Также она применяется в написании сценариев в командном интерпретаторе Bash.

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Use the Date Command in Linux
Estamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
The date command displays the current date and time. It can also be used to display or calculate a date in a format you specify. The super-user (root) can use it to set the system clock.
Use the Linux date Command
When used without options, the date command displays the current system date and time, including the day of the week, month, time, timezone, and year:
date Thu Apr 13 10:04:04 EDT 2017 To operate on a specific date, you can provide one with the -d flag:
date -d "1974-01-04" Fri Jan 4 00:00:00 EST 1974 date has many display formatting options. Provide date with the formatting string by prefixing it with a plus sign:
date +"Week number: %V Year: %y" Week number: 33 Year: 10 The format string is then output with each formatting token substituted by its value. %V is the formatting option to display the current week number, and %y represents the last two digits of the year.
Formatting Options
Run date —help to display a list of formatting options.
Here’s a small sample of the formatting tokens date supports:
| Token | Output |
|---|---|
| %a | locale’s abbreviated weekday name (e.g., Sun) |
| %A | locale’s full weekday name (e.g., Sunday) |
| %b | locale’s abbreviated month name (e.g., Jan) |
| %B | locale’s full month name (e.g., January) |
| %c | locale’s date and time (e.g., Thu Mar 3 23:05:25 2005) |
| %F | full date; same as %Y-%m-%d |
| %s | seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC |
For more details, run man date to view the entire man page.
Override the Timezone
By default, date uses the timezone defined in /etc/localtime . The environment variable TZ can be used to override this behavior. For example:
$ TZ=GMT date Fri Aug 20 15:15:36 GMT 2010 Valid timezones are defined in /usr/share/zoneinfo/ .
Examples
The following examples illustrate how you can use the date command to find the date and time at various points in time.
$ date -d now Wed Aug 18 16:47:31 EDT 2010 $ date -d today Wed Aug 18 16:47:32 EDT 2010 $ date -d yesterday Tue Aug 17 16:47:33 EDT 2010 $ date -d tomorrow Thu Aug 19 16:46:34 EDT 2010 $ date -d sunday Sun Aug 22 00:00:00 EDT 2010 $ date -d last-sunday Sun Aug 15 00:00:00 EDT 2010 Other valid date time strings include: last-week , next-week , last-month , next-month , last-year , and next-year .
Seconds from epoch
date has other surprising uses. For example, it can be used to convert a given date/time to Unix epoch time (seconds since 00:00:00, Jan 1, 1970) and back. The following example will show you the seconds from epoch to the current time:
Seconds from epoch to the provided date/time
$ date -d "1974-01-04" +"%s" 126507600 Convert epoch to a date
$ date -d "UTC 1970-01-01 126507600 secs" Fri Jan 4 00:00:00 EST 1974 $ date -d @126507600 Fri Jan 4 00:00:00 EST 1974 Determine which day of the week a given date was
Use date in Scripts and Commands
You can assign the output of date to a shell variable and then use it later in your scripts. For instance:
$ STARTTIME=`date` $ echo $STARTTIME Fri Aug 20 11:46:48 EDT 2010 $ sleep 5 $ echo $STARTTIME Fri Aug 20 11:46:48 EDT 2010 You can also use date to create filenames that contain the current day:
tar cfz /backup-`date +%F`.tar.gz /home/caker/ This would tar and gzip the files in /home/caker/ into a filename called backup-2010-08-20.tar.gz .
Set the Date Manually from the Linux Terminal
If your system is running ntpd , and you’ve set your timezone correctly, you shouldn’t have to change this setting. However, if you find you need to set the system clock manually, use the —set option. In this example, we’re setting the date and time to 9:14pm on Thursday, April 13, 2017:
This page was originally published on Monday, August 23, 2010.