- Управление дисками
- KDE Partition Manager
- Duc
- Gnome Disk Utility
- GdMap
- Disk Usage Analyzer (Baobab)
- GParted
- Top 6 Partition Managers (CLI + GUI) for Linux
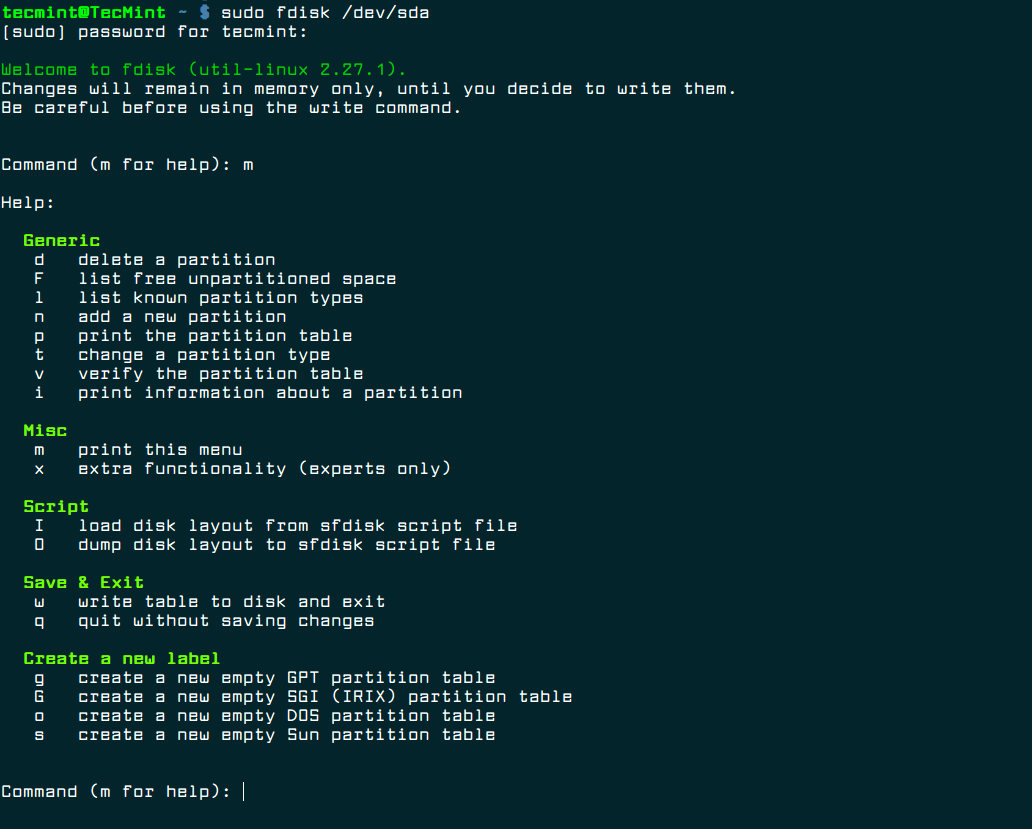
- 1. Fdisk
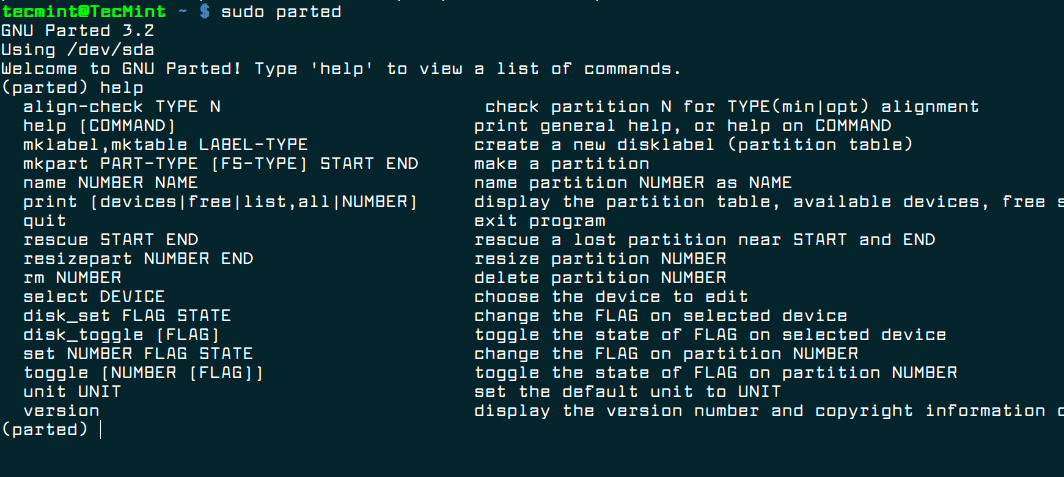
- 2. GNU Parted
- 3. Gparted
- 4. GNOME Disks a.k.a ( GNOME Disks Utility)
- 5. KDE Partition Manager
- 6. Qtparted
- 6 приложений для анализа жесткого диска в Linux
- Командная строка
- Baobab
- KDirStat и GdMap
- Filelight
- Philesight
- xdiskusage
- Disk Utilities in Linux
- Disk Utilities in Linux
- 1. fdisk
- 2. sfdisk
- 3. cfdisk
- 4. parted
- 5. lsblk
- 6. blkid
- 7. hwinfo
- 8. df command
- 9. pydf
Управление дисками
Программы для управления дисками в Linux. Создание, изменение разделов дисков в Linux. Программы для форматирования, разметки дисков.
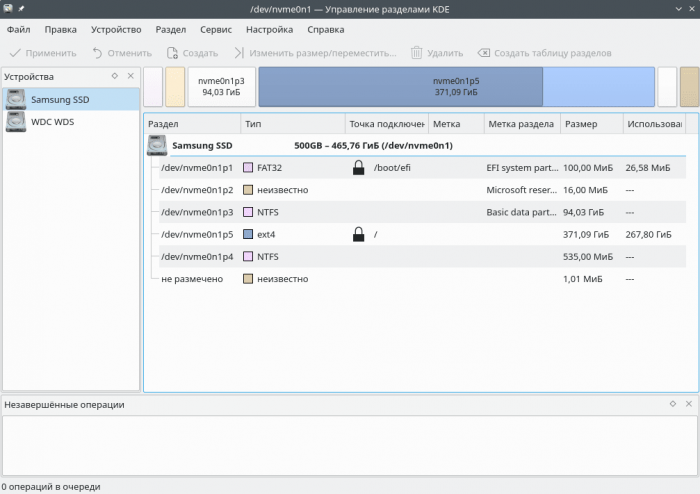
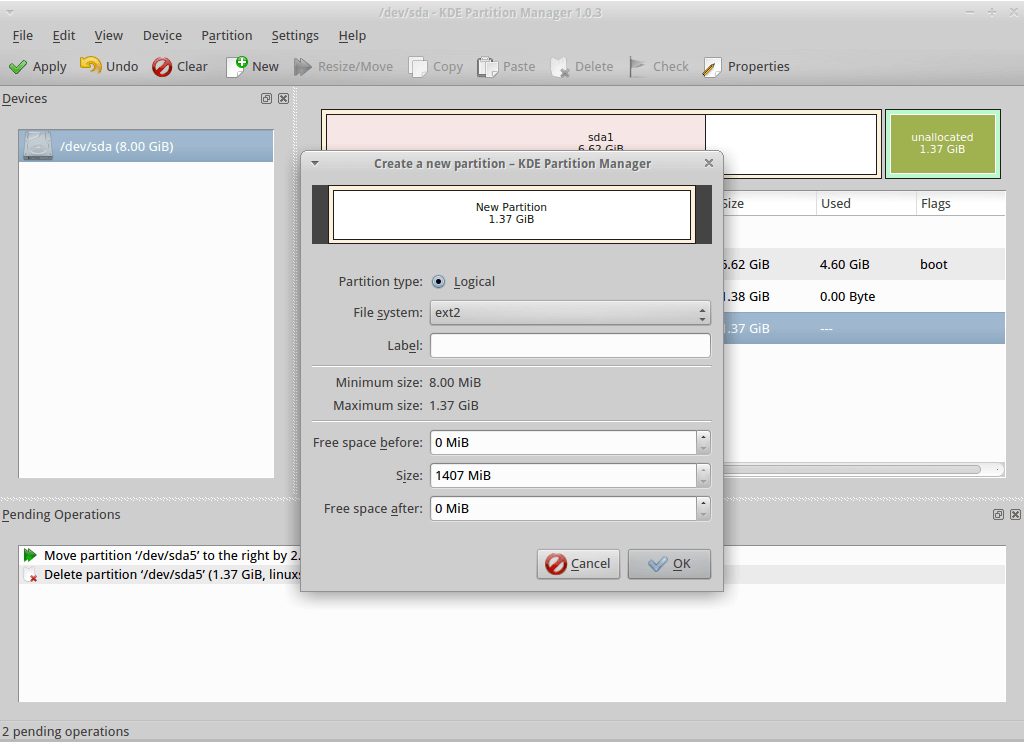
KDE Partition Manager
KDE Partition Manager — программа для работы с дисковыми разделами (создание, форматирование разделов и так далее).
Duc
Duc — утилита для вывода информации об использовании дисков в Linux. Выводит информацию о размерах директорий и файлов.
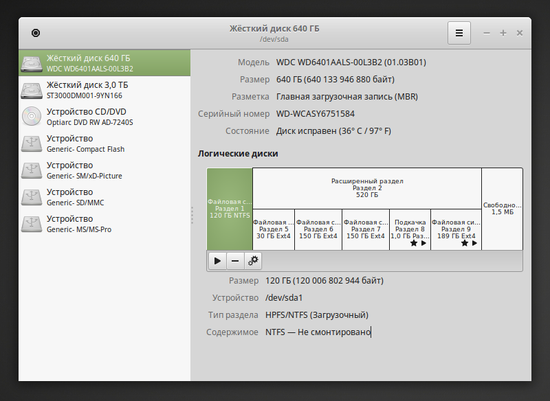
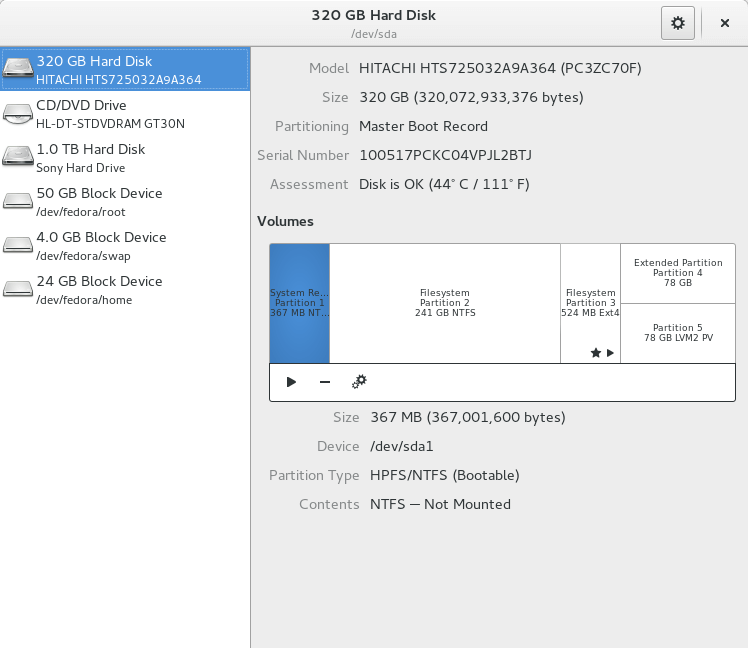
Gnome Disk Utility
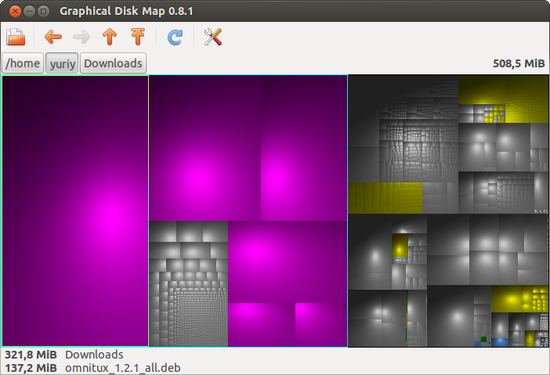
GdMap
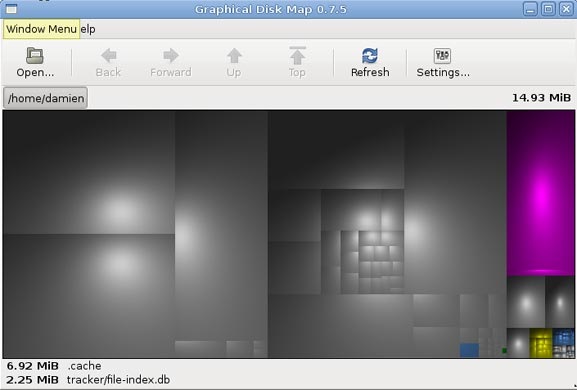
GdMap — Graphical Disk Map (Графическая карта диска) — программа для наглядного отображения занятого на диске пространства. Позволяет быстро определить директории и файлы, которые занимают больше всего места.
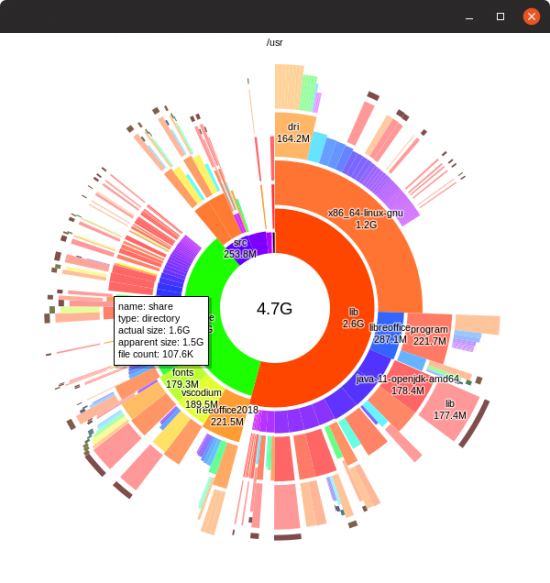
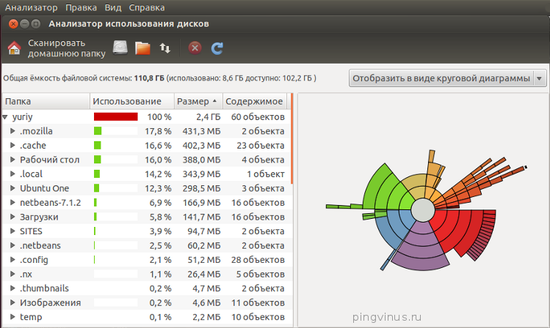
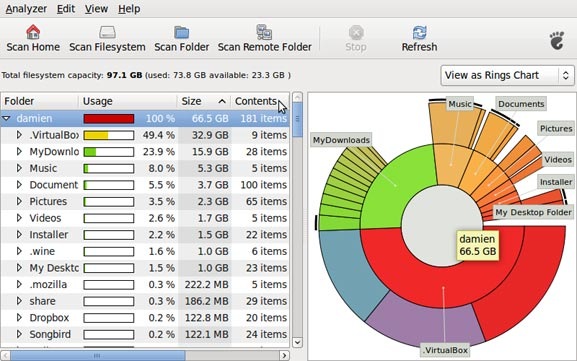
Disk Usage Analyzer (Baobab)
Disk Usage Analyzer (Baobab) — программа под Linux для анализа использования дисков. Выводит наглядную графическую диаграмму использования диска (директории), отображает объем директорий и количество файлов в них.
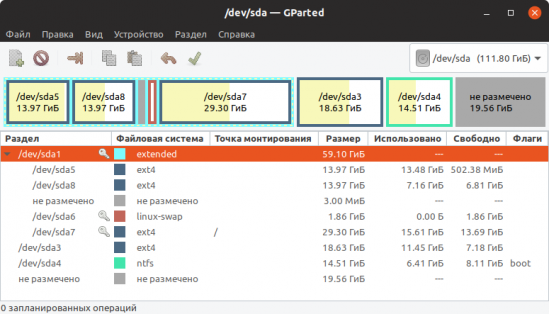
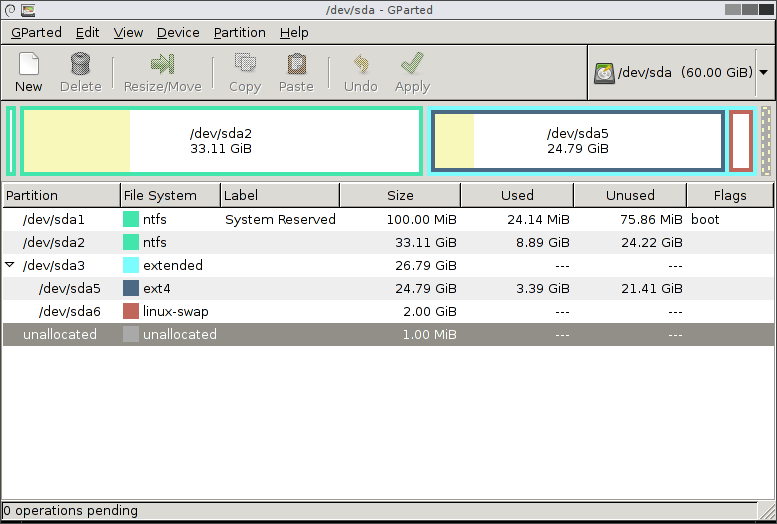
GParted
GParted — программа для управления дисками в Linux. Позволяет выполнять все необходимые операции над разделами дисков.
Top 6 Partition Managers (CLI + GUI) for Linux
Are you looking to tweak or manage your disks partitions in Linux? In this article, we will review some of the best tools that help Linux users partition and manage their disks. We will see both command line utilities as well as GUI applications for managing disk partitions in Linux.
I favor the command line over GUI (graphical user interface), I will start by describing the text based utilities and then GUI applications as follows.
1. Fdisk
fdisk is a powerful and popular command line tool used for creating and manipulating disk partition tables. It supports multiple partition tables formats, including MS-DOS and GPT. It provides a user-friendly, text based and menu driven interface to display, create, resize, delete, modify, copy and move partitions on disks.
2. GNU Parted
Parted is a popular command line tool for managing hard disk partitions. It supports multiple partition table formats, including MS-DOS, GPT, BSD and many more. With it, you can add, delete, shrink and extend disk partitions along with the file systems located on them.
It can help you create space for installing new operating systems, reorganizing disk usage, and move data to new hard disks.
3. Gparted
GParted is a free, cross platform and advanced graphical disk partition manager that works on Linux operating systems, Mac OS X and Windows.
It is used to resize, copy, move, label, check or delete partitions without data loss, enabling you to grow or shrink root partition, create space for new operating systems and attempt data rescue from lost partitions. It can be used to manipulate file systems including EXT2/3/4.
4. GNOME Disks a.k.a ( GNOME Disks Utility)
GNOME Disks is a core system utility used for disk partition management and S.M.A.R.T monitoring. It is used to format and create partition on drives, mount and unmount partitions. It ships in with the well known GNOME desktop environment.
Lately, it’s been gaining features for advanced usage. The latest version (at the time of this writing) has a new feature for adding, resizing partitions, checking filesystems for any damages and repairing them.
5. KDE Partition Manager
KDE partition manager is a useful graphical utility for managing disk devices, partitions and file systems on your computer. It comes with the KDE desktop environment.
Most of its underlying work is performed by programs. It can be used to easily create, copy, move, delete, resize without losing data, backup and restore partitions. It supports various including EXT2/3/4, BTRFS NTFS, FAT16/32, XFS, and more.
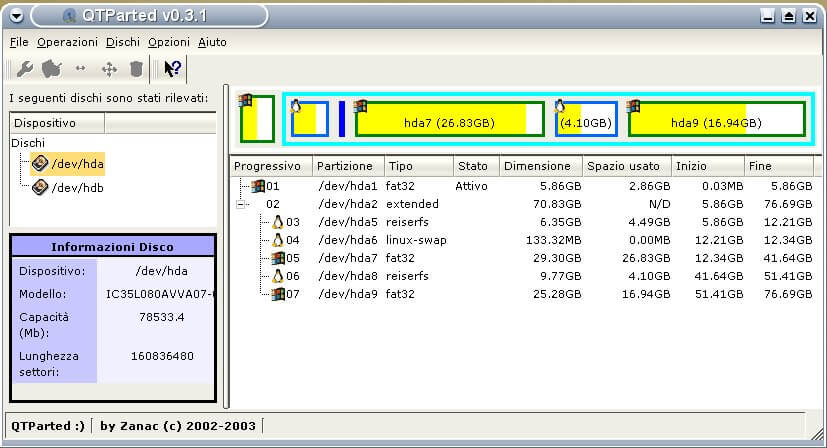
6. Qtparted
In addition, you can also use Qtparted, is a Partition Magic (proprietary software for Windows) clone and Qt front-end to GNU Parted. Note that it still in development and you may likely experience any kind of problem with latest release. In that case try to use the CVS version or a previous stable version.
It may not be one of the best options now but you can give it a try. More features are yet being added to it.
You might also like to read these following related articles.
These are the best partition managers and editors available for Linux operating systems. Which tool do you use? Let us know via the comment section below. Also let us know of any other partition managers for Linux, missing in the list above.
6 приложений для анализа жесткого диска в Linux
Вы недавно купили винт на терабайт, но при попытке установить новую программу появляется сообщение «Your disk is full». Знакомая ситуация?
При покупке жесткого диска, я обычно стараюсь взять самый большой, чтобы было где разместить всю коллекцию видео и музыки, а также была возможность устанавливать и тестировать любое ПО. Однако, я заметил, что независимо от того, насколько велик жесткий диск, свободное место на нем быстро заканчивается.Если у вас та же проблема, значит пришло время проанализировать загрузку жесткого диска, и удалить все лишнее.
Далее по тексту, несколько способов сделать это в Linux.
Командная строка
Если вы истинный линуксоид, самый легкий и быстрый способ – использовать команду «df» в командной строке. Просто напечатать:
в терминале, и он покажет вам загрузку жесткого диска в процентах
Как видно из представленного выше скриншота, способ может служить лишь в качестве быстрого просмотра доступного места на диске и определенно не является самым удобным для проведения анализа жесткого диска.
Baobab
Большинство линукс-дистрибутивов с Gnome(в частности Убунту), используют Baobab в качестве дефолтного приложения для просмотра диска.Это замечательное приложение, способное до последней папки разделить и проанализировать структуру хранения данных на жестком диске. Просто укажите папки необходимые для сканирования, и в результате получите круговую диаграмму, отражающую количество занимаемого места каждым файлом.
KDirStat и GdMap
Если вы использовали WinDirStat в Windows, то согласитесь, что это очень удобное приложение, позволяющее анализировать и оптимизировать ваше дисковое пространство. Однако мало людей знают, что WinDirStat это на самом деле клон KDirStat. KDirStat обладает той же функциональностью что и WinDirStat (или может быть наоборот), за исключением того, что он предназначен для использования в Linux. Несмотря на то, что KDirStat разрабатывался для KDE, он также совместим с любым оконным менеджером X11.
KDirStat отображает ваши папки/файлы в виде прямоугольников. Чем больше размер файла, тем больше прямоугольник. Это позволяет вам быстро просмотреть файловую систему, и легко определить какая папка/файл занимают много места на жестком диске.
Gd Map это эквивалент KDirStat для Gnome, кроме того что он не отображает древовидную структуру папок, и не позволяет очищать жесткий диск.
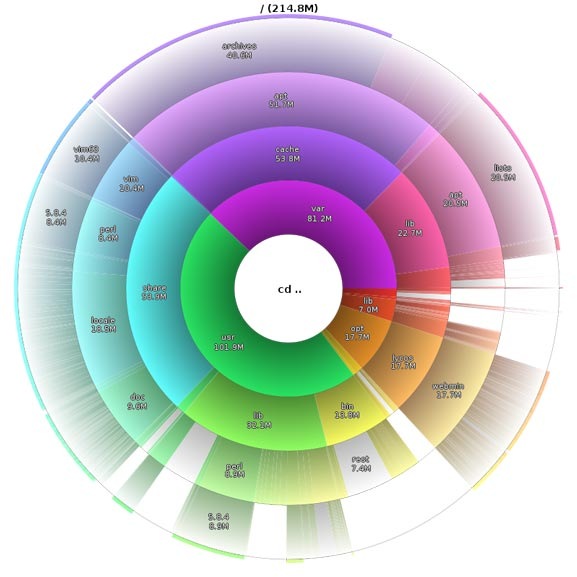
Filelight
Подобно Baobab, Filelight, создает интерактивную карту концентрических, сегментированных колец, помогающих визуализировать использование диска на вашем компьютере.Вы легко можете приблизить нужные папки, путем клика на соответствующем сегменте колец.
Philesight
Philesight это реализация Filelight в качестве веб-приложения, может быть запущена на удаленном сервере, не имеющим графического интерфейса. Philesight использует командную строку для генерации PNG-файлов в браузере и включает CGI-скрипты для навигации по файловой системе. Одна из ее особенностей, красочная радуга концентрических колец, что делает ее весьма приятной на вид.
xdiskusage
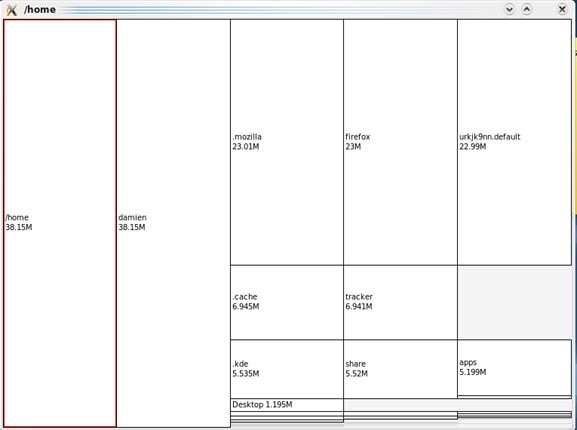
xdiskusage маленькая программка, отображающая файловую систему иерархически, слева направо, прямоугольными фигурами, с размерами, соответствующими размеру файлов. Если вы сканируете домашнюю папку, слева будет находится прямоугольник, отображающий полностью папку home, а справа все файлы, находящиеся внутри нее.
Вы легко можете приближать/удалять, нужные папки, по двойному щелчку на соответствующем прямоугольнике.
Disk Utilities in Linux
Disk Utilities make it easy for system administrators to easily monitor and manage disk partitions in Linux. In this article, we will look at the most popular disk utilities in Linux. Most of them are available in almost every Linux distribution, by default.
Disk Utilities in Linux
Here are the top disk utilities in Linux.
1. fdisk
fdisk (for fixed disk) is a popular disk utility to create and manage disk partitions in Linux. It supports GPT, MBR, Sun, SGI, and BSD partition tables. You can use it to create, resize, modify, delete and move disk partitions. The following command will display all partition tables on your disk.
2. sfdisk
sfdisk (for scriptable fdisk) is another disk utility that is similar to fdisk but offers more features. It also supports GPT, MBR, Sun, SGI, BSD partition tables. Here is the command to display all partition tables on your system.
3. cfdisk
cfdisk (curses fdisk) is a simple disk partitioning utility that allows you to manage disk partitions on your system. Like fdisk and sfdisk, it allows you to create, modify, resize and delete disk partitions. You can navigate through its output using right & left arrow keys.
4. parted
parted is another popular command for managing disk partitions. It is used to create new partitions and re-organize existing partitions. You can also use it to copy data across disk partitions as well as hard disks. Like other tools mentioned above, it also supports GPT and MBR partition table formats.
5. lsblk
lsblk command (list block) displays all available information about available and mounted block devices, such as name, type, mountpoint.
6. blkid
blkid (block id) is a utility that displays block device attributes such as deice or partition name, label, and filesystem.
7. hwinfo
If you need to get hardware info about your system, you can use hwinfo command. You can also use — option to list all hardware of specified type. You can also use –short option to get summarized information.
8. df command
If you want to monitor the disk usage, then df is the most popular command for this purpose. Here is a command to display total disk size, used space, available space and usage percent in human readable formats.
9. pydf
pydf is an alternative to df command to monitor disk usage. It is a python script that displays disk usage and free disk using system colors. It is a great alternative to df command.
In this article, we have learnt about the different disk utilities that system administrators can use to monitor and manage their disk partitions.