- What is Bluetooth 4.0?
- Stay in the know with Laptop Mag
- What are Classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy or Bluetooth Smart
- Bluetooth – from beginning
- ‘Old’ Classic Bluetooth (versions from 1.0 to 3.0)
- Bluetooth Smart (versions from 4.0 to 5)
- Bluetooth Low Energy summary
- 4 Key Differences : Bluetooth Classic Vs Bluetooth Smart Vs Bluetooth Smart Ready
- 4 key differences between Classic Bluetooth, Bluetooth Smart and Bluetooth Smart Energy devices
- 1 Bluetooth 4.0 vs Classic Bluetooth : Lets start at the very beginning
- 2 What’s different between Bluetooth Smart and Bluetooth Smart Ready Devices
- 3 Bluetooth Smart Vs Bluetooth Smart Ready : Communication with Bluetooth Classic devices
- 4 Bluetooth Smart devices can operate in a master-slave relationship as well
- 5 Related posts:
What is Bluetooth 4.0?
Bluetooth is a technology people know but don’t necessarily love. That’s because Bluetooth gadgets can be tough to pair, and they tend to run out of juice too quickly. Bluetooth 4.0—or Bluetooth Smart—gives the standard a brain transplant. The new specification uses improved technology that helps everyday gadgets stay paired longer while using less power. Plus, Bluetooth 4.0 enables a new class of gadgets such as fitness trackers, medical devices, key fobs for your car, and even home lighting controls.
Want to get up to speed? Our guide to Bluetooth 4.0 explains all.
How is Bluetooth 4.0 Different?
This generation of Bluetooth is split into two groups: Bluetooth Smart Ready and Bluetooth Smart. To understand why the tech has been split, you first have to look at the challenges facing Bluetooth as we know it. Those challenges are battery drain and the constant pairing and re-pairing of connected gadgets.
Bluetooth 4.0 is designed to be more intelligent (hence: Bluetooth Smart) about managing those connections, especially when it comes to conserving energy. The new generation of Bluetooth tech places less emphasis on maintaining a constant stream of information. Instead, it focuses on sending smaller bits of data when needed and then puts the connection to sleep during periods of non-use.
When two 4.0 devices are paired, they waste less battery power because the connection is dormant unless critical data is being shared. With the previous generation of Bluetooth, it was best to shut down your hardware when it was not in use. Now the Bluetooth Special Interest Group estimates between 1 and 2 years of battery power in some devices with Bluetooth 4.0.
What is Bluetooth Smart Ready?
Bluetooth Smart Ready gadgets are primary devices—think smartphones, notebooks, and tablets—that can receive and share Bluetooth signals from such accessories as speakers, headphones, fitness accessories, and even medical tools such as heart-rate monitors and electronic thermometers. Think of Bluetooth Smart Ready devices as a mothership, waiting to send and receive data from smaller drone ships around it.
What is Bluetooth Smart?
Using that analogy, the drone ships are Bluetooth Smart devices. These peripherals connect to Bluetooth Smart Ready smartphones, tablets, and notebooks. Bluetooth Smart gadgets can also remain paired with Smart Ready devices even when they’re not used for hours or days at a time. Thanks to Bluetooth 4.0’s emphasis on wake and sleep modes, Smart peripherals that aren’t in use can remain in sleep mode indefinitely; they can also wake from that sleep mode in an instant, paired and ready to share data with a Smart Ready tablet, notebook, or smartphone.
For instance, a heart monitor can be worn for hours yet only send data to a Smart Ready smartphone when a heart rate reaches a certain number of beats per minute during exercise. Likewise, a wireless thermometer can remain paired for days, but it will send temperature readings to a notebook only when that device is used to take a child’s temperature.
Does Bluetooth 4.0 Make Existing Bluetooth Products Obsolete?
Newer laptops, phones, and slates with Bluetooth Smart Ready radios built in will work with previous-generation Bluetooth peripherals. Essentially, if you have a Bluetooth Smart Ready smartphone or notebook, you can still use it to stream podcasts to your Bluetooth 3.0 wireless speaker system or headphones. So no need to throw out those headsets or portable speakers.
On the other hand, Bluetooth Smart peripherals only work with a Smart Ready counterpart. So if you want to take advantage of Bluetooth 4.0’s new low-power capabilities, get ready to go shopping—you’ll need a new Bluetooth Smart Ready phone, computer, or tablet in addition to a Bluetooth Smart accessory or peripheral.
What Products are Available with Bluetooth 4.0?
As of press time, the Apple MacBook Air and the Mac Mini desktop were the only Bluetooth Smart Ready computers. Compatible smartphones include the Motorola Droid RAZR and the Apple iPhone 4S.
Some Bluetooth Smart peripherals include the MotoACTV fitness tracker and music player, as well as an exercise heart-rate monitor from fitness gadget manufacturer Dayton Industrial. The Bluetooth SIG expects nearly every new smartphone and notebook shipping this year to include a Smart Ready radio.
The Bluetooth SIG told us that many Bluetooth Smart peripherals will be released in 2012, including wireless 3D glasses, home entertainment remote controls, and medical devices. The Bluetooth SIG also hopes to see Bluetooth expand into ovens, refrigerators, thermostats, and lighting systems. If that happens, dimming the lights or checking on the turkey could be a simple matter of using an app on your phone.
Stay in the know with Laptop Mag
Get our in-depth reviews, helpful tips, great deals, and the biggest news stories delivered to your inbox.
By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.
What are Classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy or Bluetooth Smart
This article is only a small picture of Bluetooth technology knowledge. It contains information from (alphabetical order): Bluetooth SIG, Cambridge Silicon Radio, Cypress Semiconductor, Nordic Semiconductor, Texas Instruments and Wikipedia.
If you are inspired please learn more from those sources.
Bluetooth – from beginning
… there was a king Harald Bluetooth…
…but has been forgotten until now XXI century…
Development of the short radio link technology, later named Bluetooth, was initiated in 1989 by Nils Rydbeck, CTO at Ericsson Mobile in Lund, Sweden, and by Johan Ullman.
The name “Bluetooth” is an Anglicised version of the Scandinavian Blatand/Blatann (Old Norse blátonn), the epithet of the king Harald Bluetooth who united dissonant Danish tribes into a single kingdom.
The Bluetooth logo refers to the Harald’s initials. It is a bind rune merging the Younger Futhark runes Runic letter H (Hagall) and Runic letter B (Bjarkan).
And now bluetooth is managed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), which has more than 30,000 member companies.
‘Old’ Classic Bluetooth (versions from 1.0 to 3.0)
Bluetooth operates in the globally unlicensed (but not unregulated) industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) 2.4 GHz short-range radio frequency band between 2400 and 2485 MHz. The band is divided into 80 channels (numbered from 0 to 79) each 1 MHz wide. There are two additional guard bands 2 MHz wide at the bottom end and 3.5 MHz wide at the top.
Range of Classic Bluetooth Devices depends from output power:
| Bluetooth Class | Max. permitted power [mW/dBm] | Typ. range [m] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 / 20 | ca. 100 |
| 2 | 2,5 / 4 | ca. 10 |
| 3 | 1 / 0 | ca. 1 |
| 4 | 0,5 / -3 | ca. 0,5 |
Bluetooth 1.0 and 1.0B
First versions with many problems. Bitrate: 21 kb/s
Bluetooth 1.1
Many errors found in Bluetooth 1.0 were fixed. Added possibility of non-encrypted channels and Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). Ratified as IEEE Standard 802.15.1–2002. Bitrate: 124 kb/s
Bluetooth 1.2
Main improvements:
- Faster Connection and Discovery. Introduced Flow Control and Retransmission Modes for L2CAP.
- Adaptive frequency-hopping spread spectrum (AFH), which improves resistance to radio frequency interference by avoiding the use of crowded frequencies in the hopping sequence. Host Controller Interface (HCI) operation with three-wire UART.
Ratified as IEEE Standard 802.15.1–2005. Bitrate: 328 kb/s.
Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR
Released in 2004. EDR (Enhanced Data Rate) can provide a lower power consumption through a reduced duty cycle. Bitrate: up to 2,1 Mb/s
Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR
Released on 26 July 2007. Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) feature improves the pairing experience and strength of security.
Extended Inquiry Response” (EIR) provides more information during the inquiry procedure to allow better filtering of devices before connection.
Bluetooth 3.0 + HS
Released on 21 April 2009. Bluetooth v3.0 + HS (High Speed) provides theoretical data transfer speeds of up to 24 Mbit/s.
The Bluetooth link is used for negotiation and setting up. The high data rate traffic is carried over a 802.11 wireless link (WLAN).
Bluetooth 3.1 + HS
Bluetooth 3.1 is a small variation of the core 3.0 standard with data rate up to 40 Mb/s.
Bluetooth Smart (versions from 4.0 to 5)
Bluetooth 4.0 + LE
Bluetooth Smart Specification (Bluetooth Core Specification version 4.0) was released in June 2010 including Bluetooth Low Energy, Bluetooth High Speed and Bluetooth Classic protocols.
Bluetooth Low Energy is a subset of Bluetooth v4.0 with an entirely new protocol stack. The main advantage is ability to dramatically reducing devices power consumption.
As a result, battery powered devices with Bluetooth Low Energy chips can work even for years. For example average current consumes by BBMagic sensors is about microamps. So one 220mAh CR2032 coin battery can provide power to the sensor for hundreds thousands hours.
Bluetooth 4.1
This specification is not a hardware update but only an incremental software update to Bluetooth 4.0.
Bluetooth 4.2
It was released in 2014. Contains further software updates and introduces features for the Internet of Things.
Bluetooth 5
To keep it simple: It provides options that can up the speed to 2 Mbit/s burst at the expense of range.
Bluetooth Low Energy summary
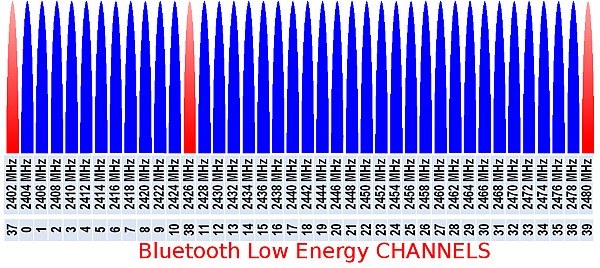
Bluetooth Low Energy uses the same 2.4 GHz radio frequencies as ‘Old’ Classic Bluetooth. The whole band is divided into 40 channels. Three of them (marked red below) are using for advertising.
Unfortunately it is not backward-compatible with ‘Old’ Bluetooth protocol. The Bluetooth 4.0 specification permits devices to implement either or both of the LE and ‘Old’ Classic systems.
- Dual-mode devices are compatible with both Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy – called ‘Bluetooth Smart Ready’
- ‘Bluetooth Smart’ or ‘Bluetooth LE’ indicates that it is Bluetooth Low Energy device which can play with either a Smart Ready or another Bluetooth Smart device.
Bluetooth Low Energy is natively supported by (alphabetical order):
- Android 4.3 and later
- BlackBerry 10
- iOS 5 and later
- Linux 3.4 and later through BlueZ 5.0
- Windows 8 and later
- Windows Phone 8.1
4 Key Differences : Bluetooth Classic Vs Bluetooth Smart Vs Bluetooth Smart Ready
4 key differences between Classic Bluetooth, Bluetooth Smart and Bluetooth Smart Energy devices
You have hearing these buzzwords “Bluetooth Classic”, “Bluetooth Smart”, “Bluetooth Smart Energy”, “Bluetooth LE”, “Bluetooth 4.0” & “Bluetooth Low Energy” for a long time.After understanding the
1 Bluetooth 4.0 vs Classic Bluetooth : Lets start at the very beginning
At first, there was just Classic Bluetooth. Then, the Bluetooth 4.0 specification came along, heralding the world of BLE aka Bluetooth LE aka Bluetooth Low Energy. Bluetooth Smart Ready and Bluetooth Smart devices correspond to devices built around the Bluetooth 4.0 specification.
2 What’s different between Bluetooth Smart and Bluetooth Smart Ready Devices
In a classic master-slave analogy, Bluetooth Smart Ready devices act as the “master” device that typically receives and adds meaning to the data it receives. Bluetooth Smart devices are typically devices that collect some useful sensor data (in a IOT scenario) and transmit it back to the “master” Bluetooth Smart Ready Device
For example, if you have a smart watch, it is likely to be a Bluetooth Smart Ready device that acts as the master device. The fitness band is likely to be one of the Bluetooth Smart devices that transmit important sensor data to the Bluetooth Smart ready smartwatch
3 Bluetooth Smart Vs Bluetooth Smart Ready : Communication with Bluetooth Classic devices
Apart from being the “master” in the relationship, Bluetooth Smart Ready devices also have the ability to communicate with “Classic” Bluetooth devices, unlike Bluetooth Smart devices. Classic Bluetooth still have their advantages in headphones and other continuously streaming products. By communicating with both “newer” Bluetooth Smart devices and “Classic” Bluetooth devices, Bluetooth Smart Ready act as the ultimate master!
4 Bluetooth Smart devices can operate in a master-slave relationship as well
Just to confuse you further (or clarify things further), Bluetooth Smart devices can themselves operate in a master-slave mode. But there is only one master to rule them all, and that’s the Bluetooth Smart Ready device. In today’s world, the Bluetooth Smart Ready device is like to be a smartphone, a laptop computer or perhaps in a complicated industrial IOT scenario, even a server.