- Команда echo в Linux
- Команда echo linux
- Примеры работы echo
- Выводы
- 15 Practical Examples of ‘echo’ command in Linux
- Echo Command in Linux (With Examples)
- Echo Command Syntax
- Echo Command Options
- Examples of Echo Command
- Changing the Output Format
- Writing to a File
- Displaying Variable Values
- Displaying Command Outputs
Команда echo в Linux
Команда echo — это очень простая и в то же время часто используемая встроенная команда оболочки Bash. Она имеет только одно назначение — выводить строку текста в терминал, но применяется очень часто в различных скриптах, программах, и даже для редактирования конфигурационных файлов.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим что представляет из себя команда echo linux, как ее можно использовать и в каких ситуациях. Но сначала рассмотрим синтаксис самой команды.
Команда echo linux
Команда echo — это не системная утилита, у нее нет исполняемого файла. Она существует только внутри интерпретатора Bash. Синтаксис команды echo linux очень прост:
$ echo опции строка
Опций всего несколько, давайте рассмотрим их, чтобы вы могли лучше ориентироваться в работе утилиты:
- -n — не выводить перевод строки;
- -e — включить поддержку вывода Escape последовательностей;
- -E — отключить интерпретацию Escape последовательностей.
Это все опции, если включена опция -e, то вы можете использовать такие Escape последовательности для вставки специальных символов:
- /c — удалить перевод строки;
- /t — горизонтальная табуляция;
- /v — вертикальная табуляция;
- /b — удалить предыдущий символ;
- /n — перевод строки;
- /r — символ возврата каретки в начало строки.
Пожалуй, это все, что нужно знать о команде echo, а теперь давайте рассмотрим как с ней работать.
Примеры работы echo
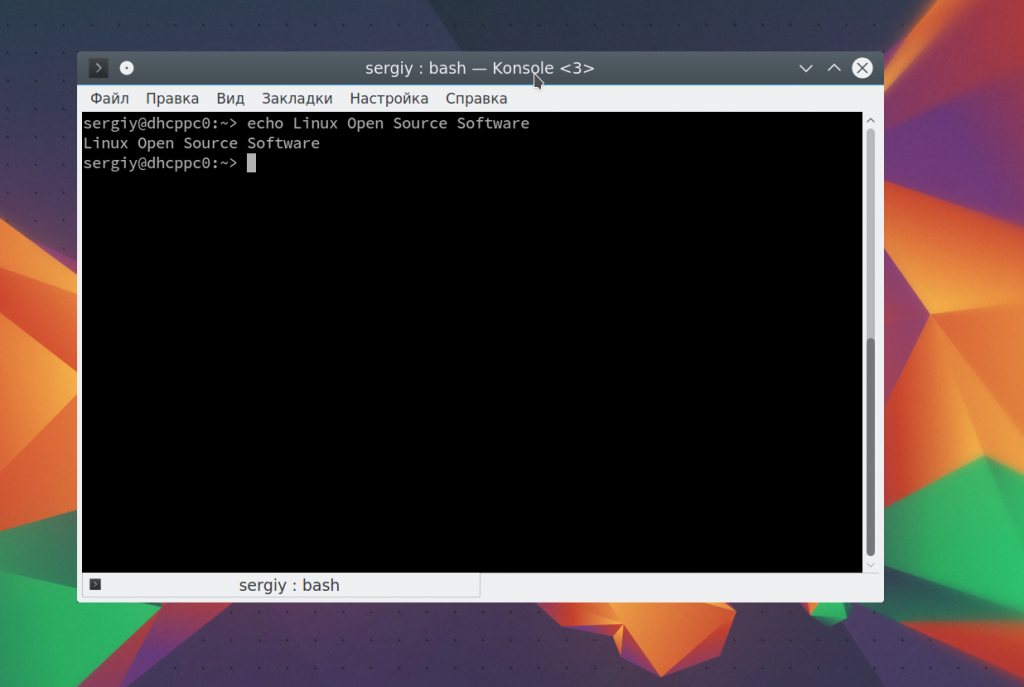
Давайте рассмотрим как пользоваться echo. Сначала просто выведем строку на экран:
echo Linux Open Source Software Technologies
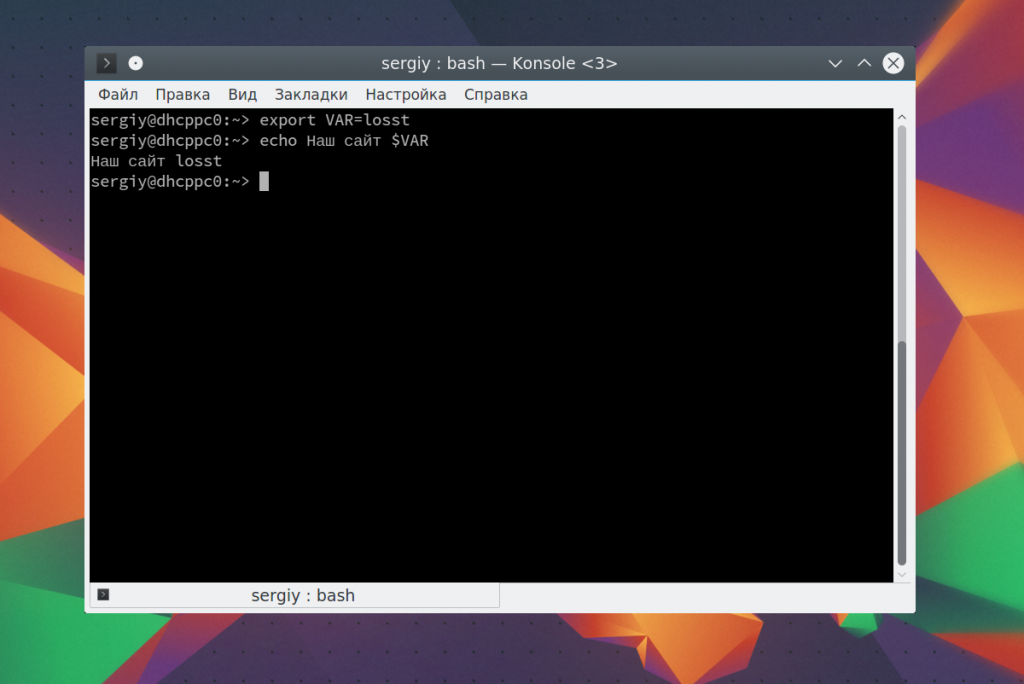
Также можно вывести значение переменной. Сначала объявим переменную:
Затем выведем ее значение:
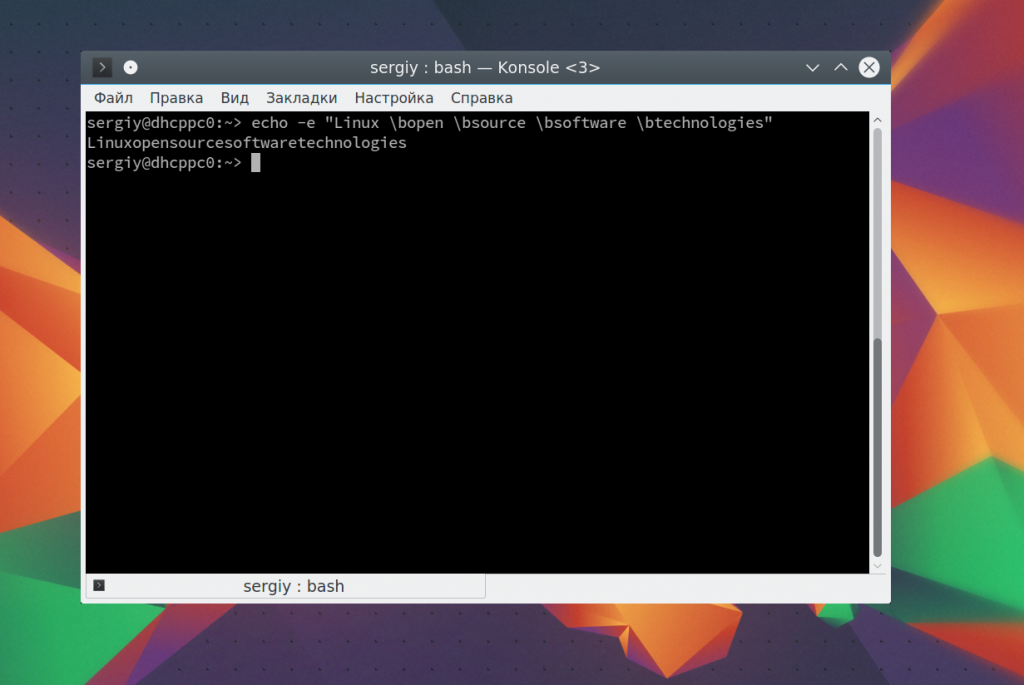
Как уже говорилось, с помощью опции -e можно включить интерпретацию специальных последовательностей. Последовательность \b позволяет удалить предыдущий символ. Например, удалим все пробелы из строки:
echo -e «Linux \bopen \bsource \bsoftware \btechnologies»
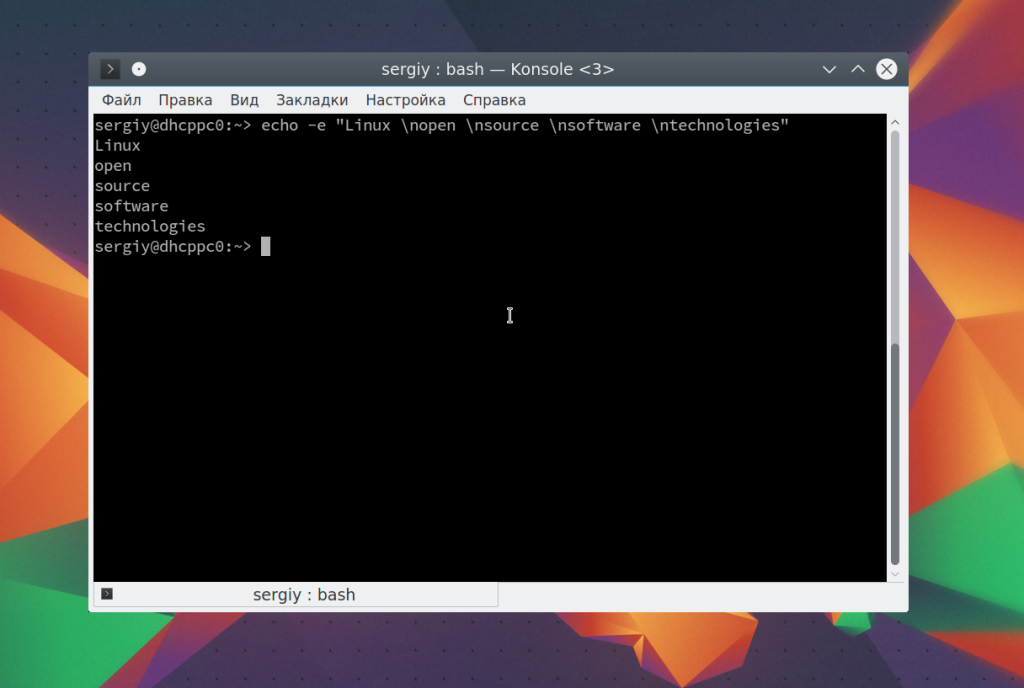
Последовательность \n переводит курсор на новую строку:
echo -e «Linux \nopen \nsource \nsoftware \ntechnologies»
С помощью \t вы можете добавить горизонтальные табуляции:
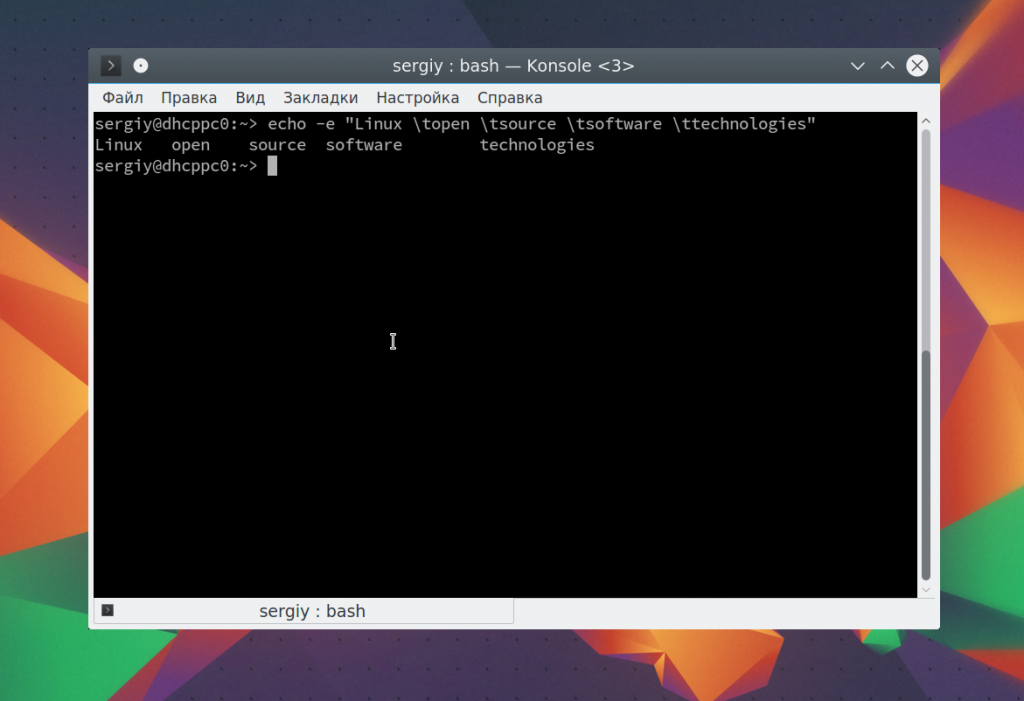
echo -e «Linux \topen \tsource \tsoftware \ttechnologies»
Можно совместить переводы строки и табуляции:
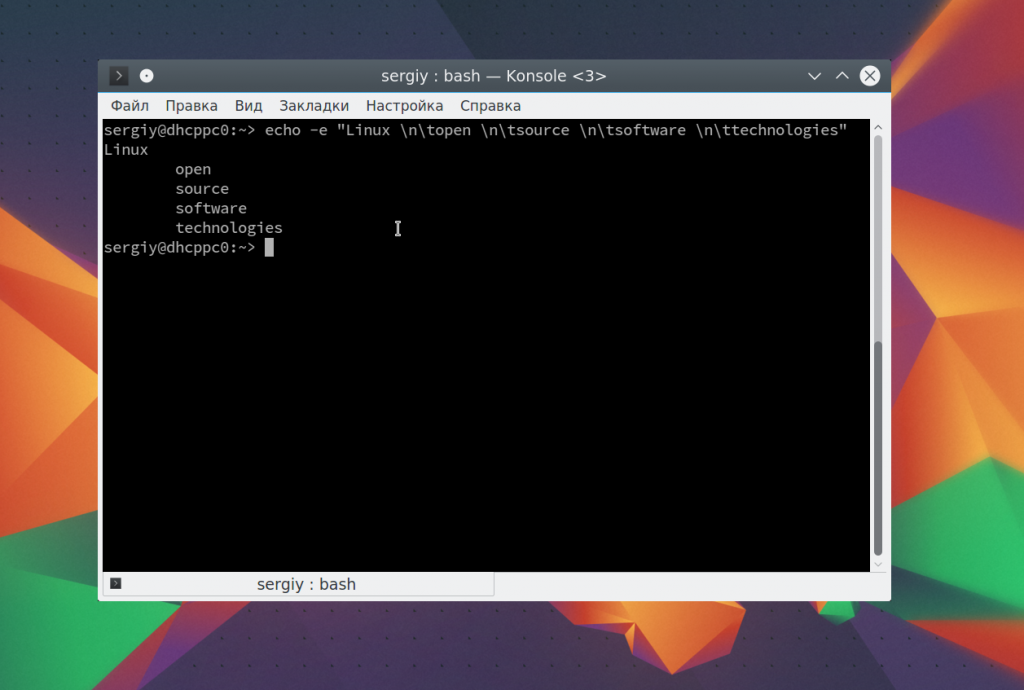
echo -e «Linux \tnopen \tnsource \tnsoftware \tntechnologies»
Точно так же можно применить вертикальную табуляцию:
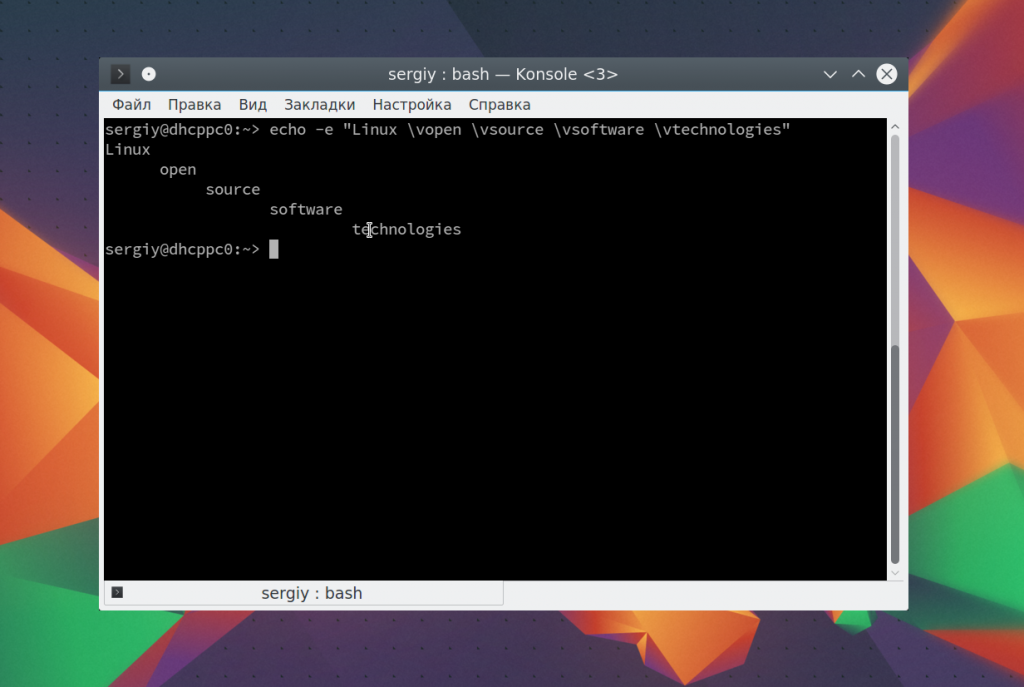
echo -e «Linux \vopen \vsource \vsoftware \vtechnologies»
С помощью последовательности \r можно удалить все символы до начала строки:
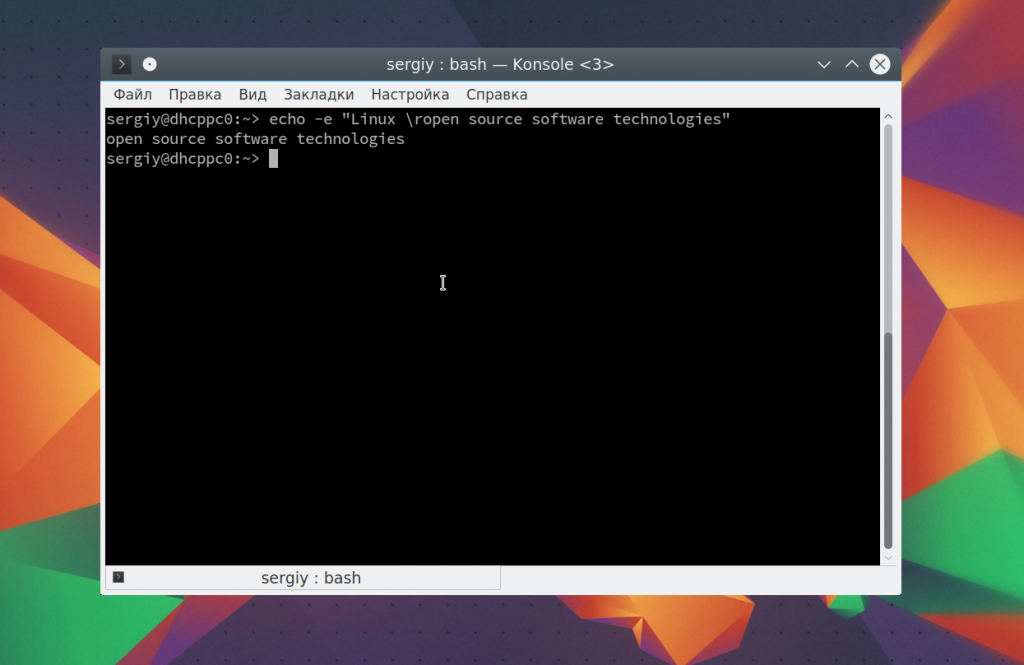
echo -e «Linux \ropen source software technologies»
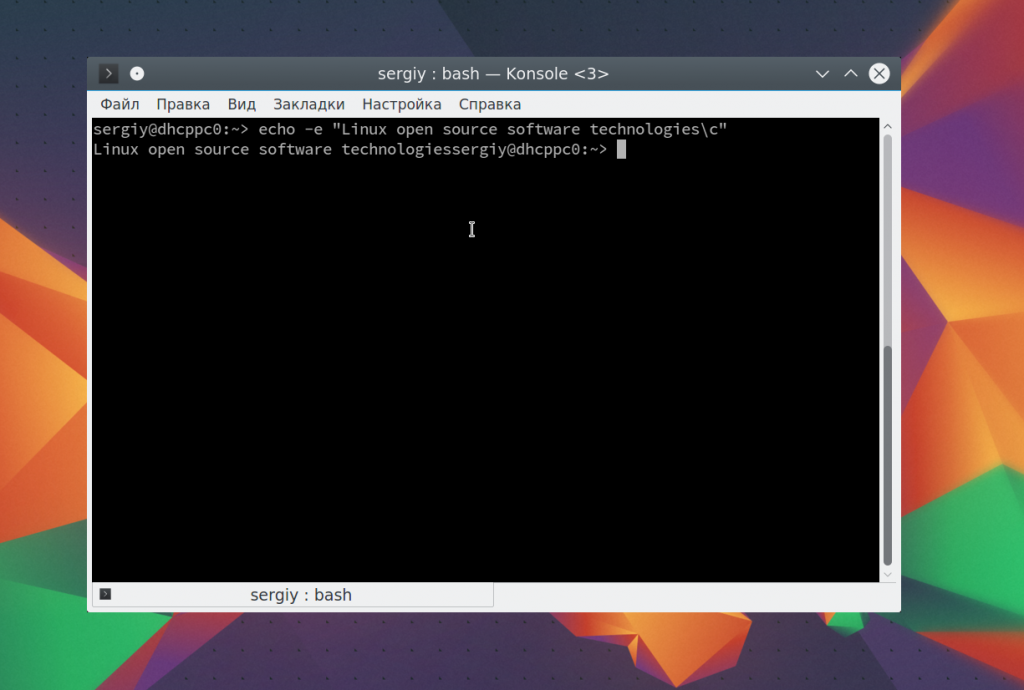
Последовательность -c позволяет убрать перевод на новую строку в конце сообщения:
echo -e «Linux open source software technologies\c»
Дальше — больше. Вы можете разукрасить вывод echo с помощью последовательностей управления цветом Bash. Для доступны такие цвета текста:
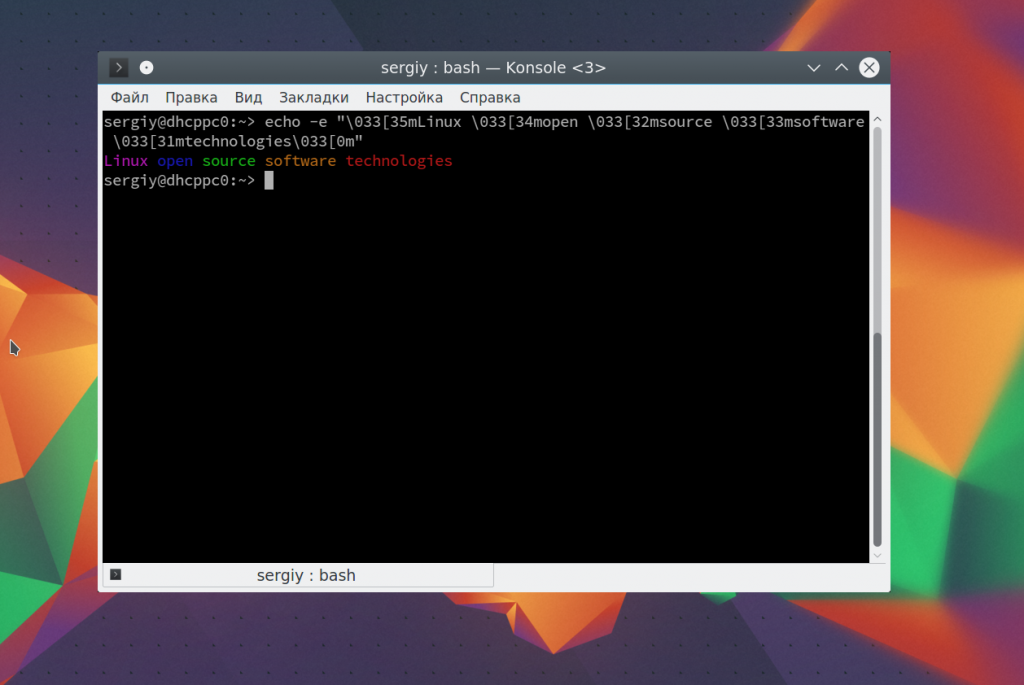
Например. раскрасим нашу надпись в разные цвета:
echo -e «\033[35mLinux \033[34mopen \033[32msource \033[33msoftware \033[31mtechnologies\033[0m»
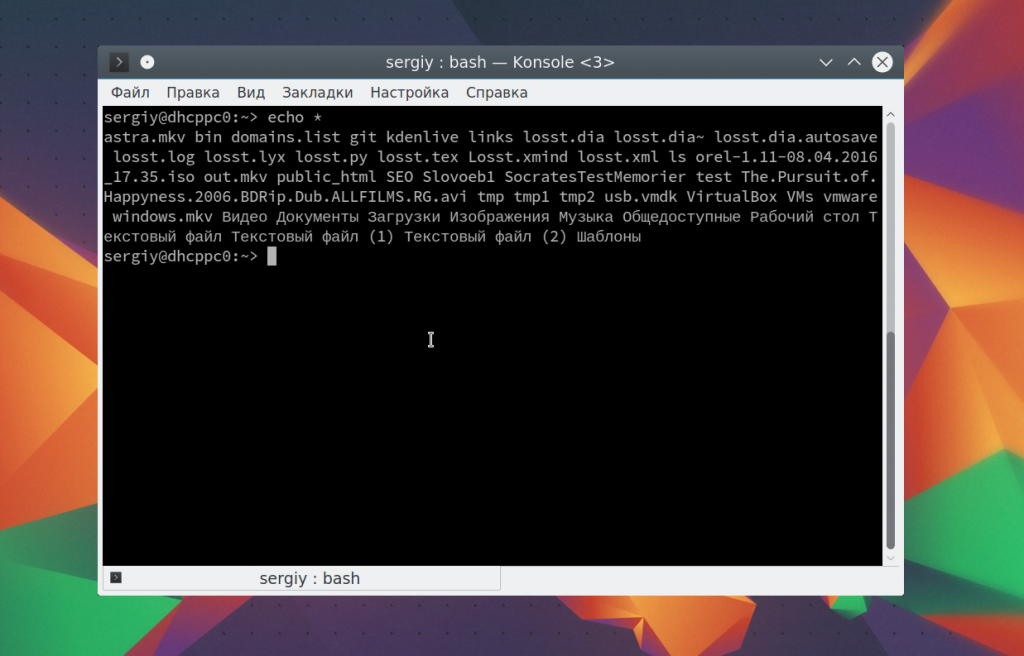
С основными параметрами команды echo разобрались, теперь рассмотрим еще некоторые специальные символы bash. Вы можете вывести содержимое текущей папки просто подставив символ *:
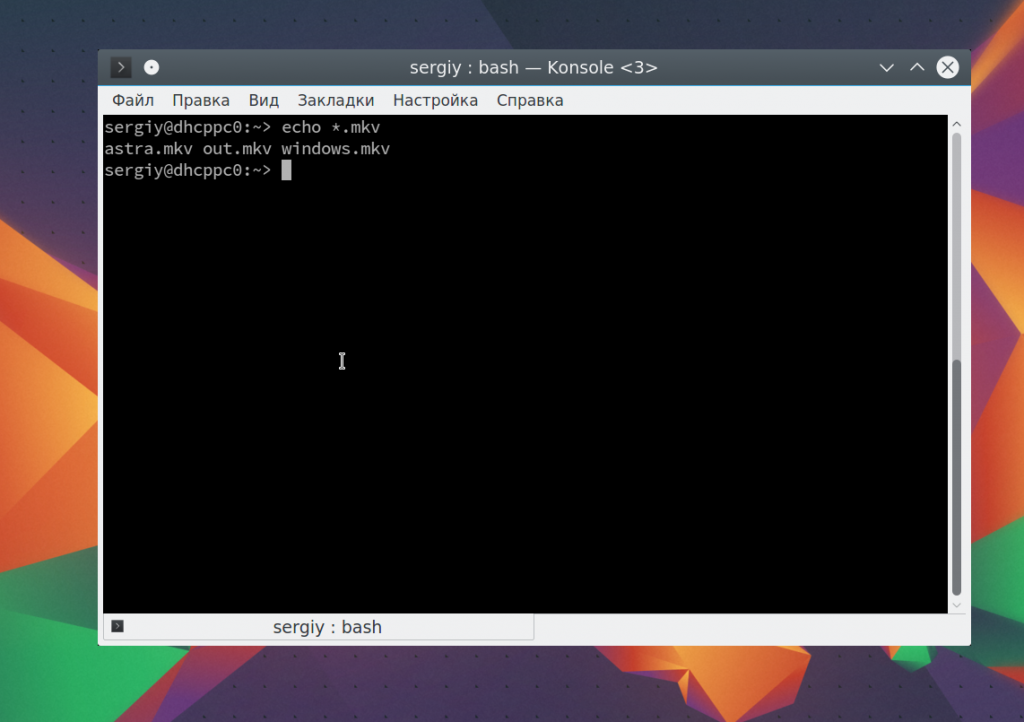
Также можно вывести файлы определенного расширения:
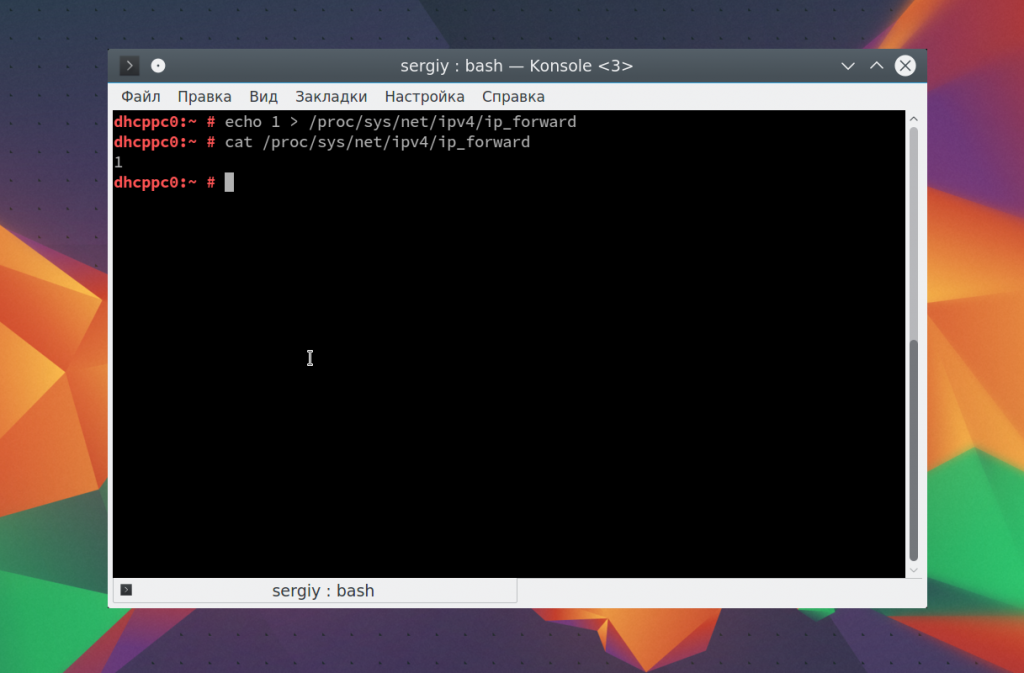
Я уже говорил, что echo можно использовать для редактирования конфигурационных файлов. Вы можете использовать запись echo в файл linux, если он пуст:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Если файл не пуст, и вам необходимо добавить свою строчку в конец файла используйте символ перенаправления вывода >>:
echo «UUID=09ec0871-2f55-4dd5-aeb2-cacc4a67907c /var/tmp btrfs subvol=@/var/tmp 0 0» >> /etc/fstab
Если строка содержит какие-либо специальные символы или может быть понята интерпретатором неоднозначно, следует заключить ее в кавычки.
Выводы
В этой статье была рассмотрена команда echo linux. Несмотря на свою простоту, она может применяться для решения различных задач и незаменима при написании простых скриптов. Надеюсь, эта информация была вам полезной.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
15 Practical Examples of ‘echo’ command in Linux
The echo command is one of the most commonly and widely used built-in commands for Linux bash and C shells, that typically used in a scripting language and batch files to display a line of text/string on standard output or a file.
The syntax for the echo command is:
1. Input a line of text and display it on standard output
$ echo Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
Outputs the following text:
Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
2. Declare a variable and echo its value. For example, Declare a variable of x and assign its value=10.
$ echo The value of variable x = $x The value of variable x = 10
Note: The ‘-e‘ option in Linux acts as an interpretation of escaped characters that are backslashed.
3. Using option ‘\b‘ – backspace with backslash interpretor ‘-e‘ which removes all the spaces in between.
$ echo -e "Tecmint \bis \ba \bcommunity \bof \bLinux \bNerds" TecmintisacommunityofLinuxNerds
4. Using option ‘\n‘ – New line with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ treats new line from where it is used.
$ echo -e "Tecmint \nis \na \ncommunity \nof \nLinux \nNerds" Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
5. Using option ‘\t‘ – horizontal tab with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have horizontal tab spaces.
$ echo -e "Tecmint \tis \ta \tcommunity \tof \tLinux \tNerds" Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
6. How about using option new Line ‘\n‘ and horizontal tab ‘\t‘ simultaneously.
$ echo -e "\n\tTecmint \n\tis \n\ta \n\tcommunity \n\tof \n\tLinux \n\tNerds" Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
7. Using option ‘\v‘ – vertical tab with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have vertical tab spaces.
$ echo -e "\vTecmint \vis \va \vcommunity \vof \vLinux \vNerds" Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
8. How about using option new Line ‘\n‘ and vertical tab ‘\v‘ simultaneously.
$ echo -e "\n\vTecmint \n\vis \n\va \n\vcommunity \n\vof \n\vLinux \n\vNerds" Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
Note: We can double the vertical tab, horizontal tab, and new line spacing using the option two times or as many times as required.
9. Using option ‘\r‘ – carriage return with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have specified carriage return in output.
$ echo -e "Tecmint \ris a community of Linux Nerds" is a community of Linux Nerds
10. Using option ‘\c‘ – suppress trailing new line with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to continue without emitting new line.
11. Omit echoing trailing new line using the option ‘-n‘.
12. Using option ‘\a‘ – alert return with backspace interpretor ‘-e‘ to have the sound alert.
$ echo -e "Tecmint is a community of \aLinux Nerds" Tecmint is a community of Linux Nerds
Note: Make sure to check the Volume key, before firing.
13. Print all the files/folders using echo command (ls command alternative).
$ echo * 103.odt 103.pdf 104.odt 104.pdf 105.odt 105.pdf 106.odt 106.pdf 107.odt 107.pdf 108a.odt 108.odt 108.pdf 109.odt 109.pdf 110b.odt 110.odt 110.pdf 111.odt 111.pdf 112.odt 112.pdf 113.odt linux-headers-3.16.0-customkernel_1_amd64.deb linux-image-3.16.0-customkernel_1_amd64.deb network.jpeg
14. Print files of a specific kind. For example, let’s assume you want to print all ‘.jpeg‘ files, use the following command.
15. The echo can be used with a redirect operator to output to a file and not standard output.
echo Options
| Options | Description |
| -n | do not print the trailing newline. |
| -e | enable interpretation of backslash escapes. |
| \b | backspace |
| \\ | backslash |
| \n | new line |
| \r | carriage return |
| \t | horizontal tab |
| \v | vertical tab |
That’s all for now and don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below.
Echo Command in Linux (With Examples)
The echo command is a built-in Linux feature that prints out arguments as the standard output. echo is commonly used to display text strings or command results as messages.
In this tutorial, you will learn about all the different ways you can use the echo command in Linux.
Echo Command Syntax
The echo command in Linux is used to display a string provided by the user.
For example, use the following command to print Hello, World! as the output:
Note: Using the echo command without any option returns the provided string as the output, with no changes.
Echo Command Options
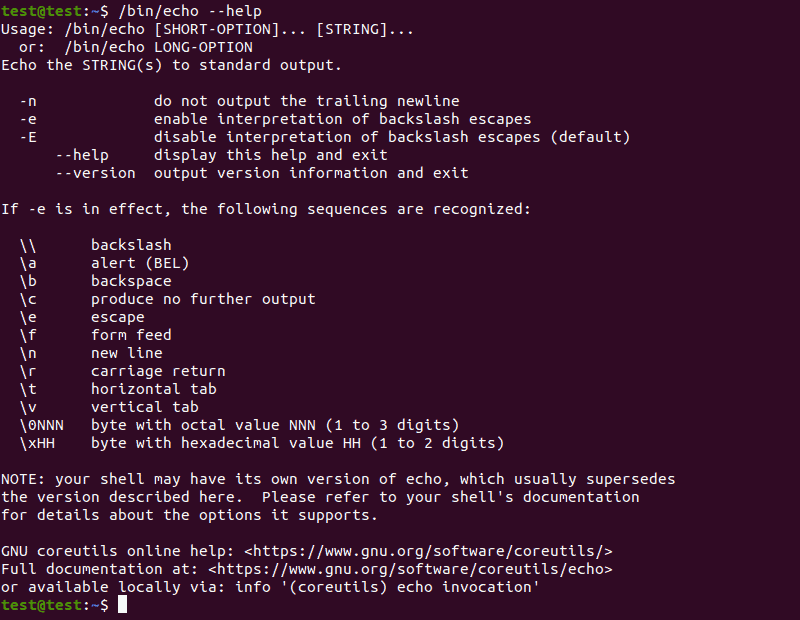
Use the —help argument to list all available echo command options:
Note: Using the echo —help command returns —help as the output.
The echo command uses the following options:
- -n : Displays the output while omitting the newline after it.
- -E : The default option, disables the interpretation of escape characters.
- -e : Enables the interpretation of the following escape characters:
- \\: Displays a backslash character (\).
- \a : Plays a sound alert when displaying the output.
- \b : Creates a backspace character, equivalent to pressing Backspace.
- \c : Omits any output following the escape character.
- \e : The escape character, equivalent to pressing Esc.
- \f : The form feed character, causes the printer to automatically advance to the start of the next page.
- \n : Adds a new line to the output.
- \r : Performs a carriage return.
- \t : Creates horizontal tab spaces.
- \v : Creates vertical tab spaces.
- \NNN : Byte with the octal value of NNN .
- \xHH : Byte with the hexadecimal value of HH .
Examples of Echo Command
Here are some ways you can use the echo command in Linux:
Changing the Output Format
Using the -e option allows you to use escape characters. These special characters make it easy to customize the output of the echo command.
For instance, using \c let you shorten the output by omitting the part of the string that follows the escape character:
echo -e 'Hello, World! \c This is PNAP!'Note: If you are using the -e option, enter your string enclosed in single quotation marks. This ensures that any escape characters are interpreted correctly.
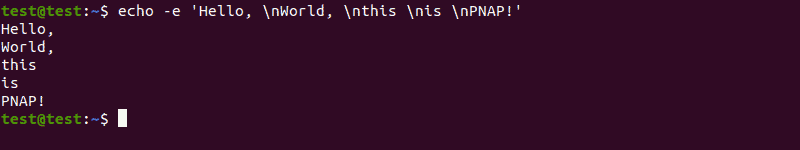
Use \n any time you want to move the output to a new line:
echo -e 'Hello, \nWorld, \nthis \nis \nPNAP!'Add horizontal tab spaces by using \t :
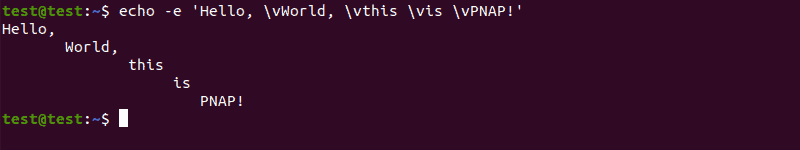
Use \v to create vertical tab spaces:
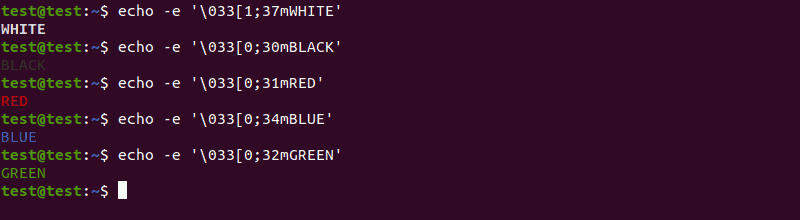
echo -e 'Hello, \vWorld, \vthis \vis \vPNAP!'Using ANSI escape sequences lets you change the color of the output text:
echo -e '\033[1;37mWHITE' echo -e '\033[0;30mBLACK' echo -e '\033[0;31mRED' echo -e '\033[0;34mBLUE' echo -e '\033[0;32mGREEN'Writing to a File
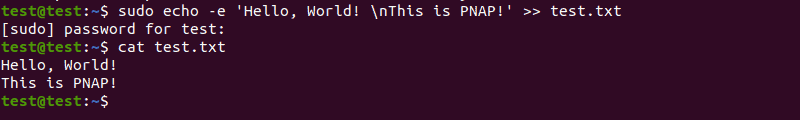
Use > or >> to include the string in an echo command in a file, instead of displaying it as output:
sudo echo -e 'Hello, World! \nThis is PNAP!' >> test.txtIf the specified text file doesn’t already exist, this command will create it. Use the cat command to display the content of the file:
Note: Using > overwrites the content of the text file with the new string, while >> adds the new string to the existing content.
Displaying Variable Values
The echo command is also used to display variable values as output. For instance, to display the name of the current user, use:
Displaying Command Outputs
The echo command allows you to include the result of other commands in the output:
- [string] : The string you want to include with echo
- [command] : The command you want to combine with the echo command to display the result.
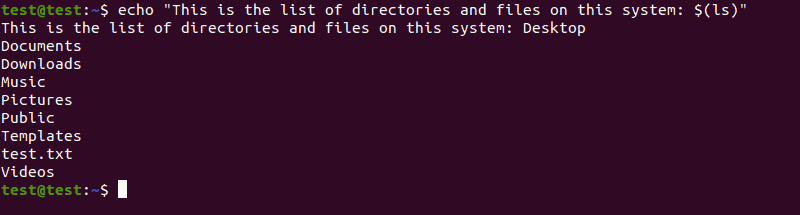
For instance, list all the files and directories in the Home directory by using:
echo "This is the list of directories and files on this system: $(ls)"After reading this tutorial, you should know how to use the echo command in Linux.
For more Linux commands, check out our Linux Command Cheat Sheet