- Linux DevOps Tutorial для новичков
- Дистрибутивы и Linux Shell
- Дистрибутивы
- Что такое Linux Shell?
- Linux Best Practices
- Rethinking DevOps: What is it all About?
- What is DevOps?
- Application Development Life Cycle (ADLC)
- System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Presenting the new DevOps Triangle
- Humility in the Workplace: Ultimate Precision in Pivoting
Linux DevOps Tutorial для новичков
В IT-направлении навыки работы с консолью Linux ー базовое требование для работы с большинством технологий. Чтобы начать развиваться в DevOps, новичку обязательно уметь работать на Unix-ядре ー скорее всего, большинство рабочих задач вы будете выполнять на этом сервере.
В свою очередь, Linux для DevOps ー абсолютный мастхэв. И Junior System Administrator, и Junior Software Developer (равно как и специалисты Middle и Senior), которые приходят в девопс, работают на этой ОС. К примеру, установка и настройка сервера входит в функциональные обязанности Junior System Administrator, который легко может вырасти до девопса. Связь между DevOps и Linux довольно тесная, поэтому мы подготовили краткий Linux DevOps Tutorial для начинающих специалистов Linux и DevOps engineer.
Дистрибутивы и Linux Shell
Linux превалирует на большинстве встроенных систем, серверов и облаков, кроме десктопов и мейнфреймов. Экосистема продолжает расти благодаря свободным лицензиям, а также высокому уровню защиты локальных систем. А DevOps с хорошими навыками программирования может даже пофиксить код программы.
Дистрибутивы
Дистрибутив ー своеобразный установочный пакет для развертывания ОС Линукс на пользовательском оборудовании. Включает в себя ядро, утилиты GNU, специально настроенные программы, диспетчер пакетов.
У Линукс есть более шестисот разных дистрибутивов. Наиболее популярные ー Debian, openSUSE, Arch, RHEL, SLED, Fedora, Ubuntu, Calculate, NixOS, Gentoo. Или, к примеру, дистрибутив от компании Red Hat Red.
В некоторых идет упор на корпоративную инфраструктуру, другие берут универсальностью или, наоборот, узкой специализацией для рабочих станций, роботов, медиацентров. И сетевой администратор, и SRE, и DevOps Engineer выбирают подходящий дистрибутив для своих рабочих задач.
Что такое Linux Shell?
Для связи user и системы нужен программный интерфейс, уровень, обеспечивающий ввод команд и parameters ー shell (или оболочка). Самые популярные оболочки: sh (Bourne shell), bash (Bourne Again), ksh ー Korn shell, csh (синтаксис C programming language), tcsh (версия C shell). Можно использовать несколько shell для отдельных пользователей. Чтобы проверить оболочку, выполняем одну из команд:
echo $SHELL echo $0 ps -ef | grep $ | grep -v grep
Легче запомнить, что Shell ー та же CLI, командная строка, консоль или терминал. Это более привычные термины, которые можно услышать от коллег.
Linux Best Practices
Линукс ー мощная, гибкая и максимально функциональная ОС, которую можно адаптировать для множества задач в разработке. Работа на Unix-ядре и применение Linux Best Practices будут вашей основой для развития в DevOps или другом IT-направлении. Делимся некоторыми Linux Best Practices, которые пригодятся начинающему специалисту.
Backups. В вашей зоне ответственности определить, как часто вы будете делать бэкап и каким способом. Можно бэкапить важные файлы на файловом сервере или локальных дисках. Храните энергонезависимые файлы не на машине, а на любом цифровом носителе с копией на диске компьютера.
Security. Если нет необходимости в использовании SSH-соединения, отключайте его. Рекомендуем отключить SSH для входа через root. Эта учетка самая уязвимая, поэтому обезопасьте ее от внешнего доступа.
Firewall. Убедитесь, что в системе есть Firewall. Для большинства дистрибутивов Линукс используют iptables. Не разрешайте соединение с неизвестными источниками.
Учетные записи. Для учетной записи root установите сложный пароль, не менее 10 символов. Для администрирования используйте только root user через команду su к root. Минимум раз в год удаляйте или закрывайте неиспользуемые учетные записи и меняйте пароли для активных пользователей.
Следите за обновлениями. Подпишитесь на рассылки поставщиков ПО, которое используете. Следите за изменениями в правилах безопасности, версионности и рекомендациями по усилению секьюрности.
Rethinking DevOps: What is it all About?
A new model you can adopt that simplifies how those DevOps tools we talk about can be made and managed by the DevOps community.
Ever since I started working with diverse web-apps at Linux Handbook and High On Cloud, the DevOps term has grabbed my attention many a time since that is something we specifically cover at Linux Handbook.
We’ve covered tutorials on many tools related to DevOps but we’ve never really tried to explore the actual concept in depth. Since Linux Handbook is dedicated to Linux Servers, we also need to explore their important role in the DevOps field.
But before we do so, it is essential to understand what DevOps really is. DevOps is an extremely popular buzzword and you will find multiple definitions of it across the web. But based on my own experiences, I have arrived at the following conclusive definition and thoughts henceforth. This is an attempt to revisit existing DevOps norms and rethink them in the form of a new model that I propose here.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a continuous simplification process of maintaining a delicate balance among functionality, usability and security of an application both in terms of its Development and Operations.
How to ensure that?
Ensuring that an application evolves efficiently while also being operational is a continuous challenge for DevOps Engineers. To do that, the most fundamental components of DevOps need to be continuously monitored.
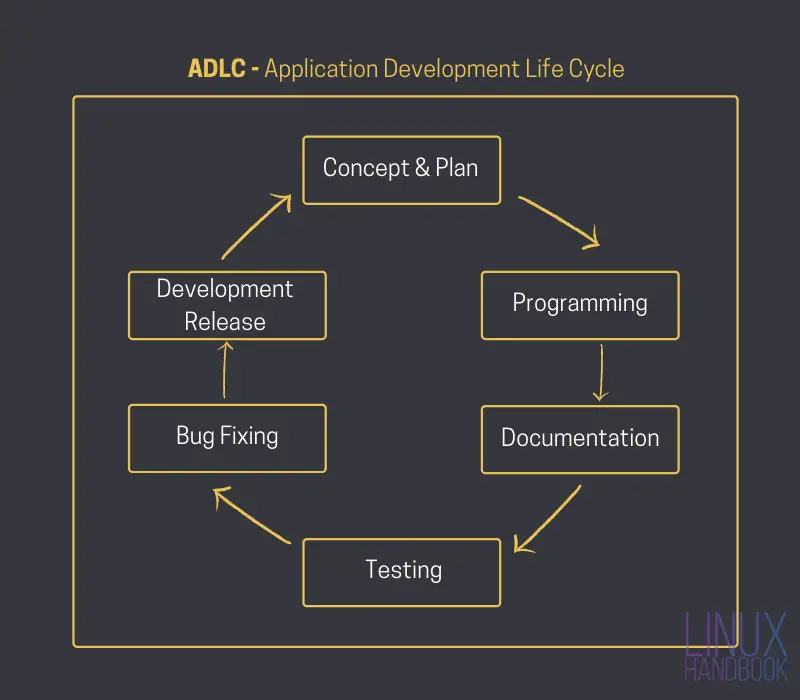
Application Development Life Cycle (ADLC)
Creating a new application? You start right here!
Application Development Life Cycle is the fundamental motivation behind the development of any application. Unless the development process is not carefully and consistently monitored, you cannot be absolutely sure of its flawless development. An application will always be under ADLC until it is production ready.
ADLC is an essential software engineering principle which consists of six essential stages. The development of an application involves the following steps:
- Concept Plan: Shaping the core idea behind the application.
- Programming: This is when the application is created and developed.
- Documentation: An excellent application is useless without careful (human readable) documentation.
- Testing for Quality Assurance: Making sure the end product is functional, usable and secure.
- Debugging: Bugs reported during testing are fixed.
- Development Release: The first version of the application is released.
Until and unless a stable release is available, this cycle will continue to exist. Once a software is released as a production-ready stable version, it no longer falls under ADLC. It eventually falls under System Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
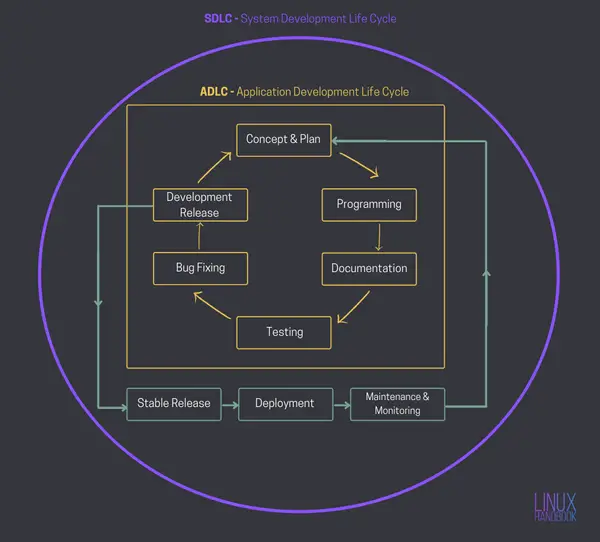
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
A part of our DevOps community might say that both ADLC and SDLC are one and the same. But in the real-world scenario, what I see is ADLC and SDLC are quite different.
System Development Life Cycle is the fundamental motivation behind both the development and operation of an application. It involves the continuous development of the application after its first stable release and ensures its continuous operability.
- Concept Plan: Revisiting the core idea behind the application.
- Programming: This is when the application is further developed.
- Documentation: Continuous update of human readable documentation.
- Testing new releases for quality: Making sure the new end product is functional, usable and secure.
- Debugging: Bugs reported during testing are fixed.
- Development Release: For a new application(version-wise or as the app itself), a development release evolves into its first stable release in this stage.
- Stable Release: The latest stable version is released as a product with fixes related to bugs/security along-with new features.
- Deployment: The stable product is deployed on server(s).
- Maintenance & Monitoring: Consistent and periodic monitoring of servers and the applications that run on them.
A community powered open model will always have smoothest maintenance. The last step in the cycle is truly achievable only with an Open Source model. It is the greatest deciding factor in terms of the evolution of any application.
An application that does not yet have a stable release cannot be regarded as completed. As soon as an application is completely built, ADLC evolves into SDLC. Why?
Do you get my point now? Under ADLC, an application is not production ready, which is why it would still be under barebone development. Therefore, we cannot call it DevOps. Only when the first stable release is out, it evolves into SDLC which is DevOps because a production-ready application will then onwards become continuously operational.
As it is evident from the two abbreviations and the diagram above, an application is very different from an entire system. An application is but a part of a complete systemic process. This is what differentiates SDLC from ADLC. So, ADLC is actually a subset of SDLC.
SDLC needs to be continuously pivoted by us as a community, keeping in mind the delicate balance among functionality, usability and security.
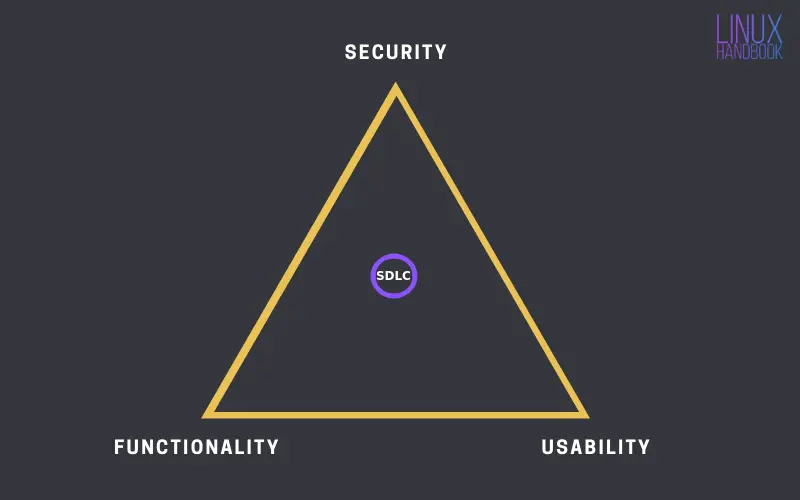
Presenting the new DevOps Triangle
This diagram is never the same because SDLC is never stationary. It is SDLC that is being continuously pivoted within the triangle by the community based on the continuous feedback of developers, testers and users.
Such a pivoting process is ever-changing according to the requirements of the application under deployment. This ever-changing model in the real world is the process of DevOps.
Where SDLC lies within the triangle will always vary from application to application. The pivoted location is actually dependent on the nature of the application under deployment while being developed with a close eye on:
Functionality: The primary function of the application. For example, the ability to send messages via Rocket.Chat.
Usability: The ease of use of the application. For example, how conveniently you can send messages via Rocket.Chat.
Security: Degree of security of the application. For example, a bug fix that addresses a Rocket.Chat vulnerability such as this one.
A diverse community that backs an Open Source application need to always maintain a delicate balance among functionality, usability and security.
Humility in the Workplace: Ultimate Precision in Pivoting
At the end of the day, developers, users and testers are all human. Be it local or virtual, DevOps cultures and workplaces need to adopt the simple idea of compassion. A workplace that practices kindness among co-workers is bound to enhance both ADLC and SDLC productivity!
It’s not just about web-apps, it’s about people as well. They are the ones who are continuously creating, deploying and maintaining them. That is what community is all about and this is why DevOps is also a culture. The DevOps culture spans around managing not only a web app but also the people who make it a reality.
An Open Source approach makes this entire process far more achievable than a proprietary one. This is what I have felt while working with this collective system of people, practices and technology.
I look forward to continue sharing my thoughts in this genre through a series of articles to follow. What I feel is, be it a small, medium or large-scale enterprise, DevOps is applicable everywhere but in the form of personified models.
This is just a small part of what I’m eager to explore through this series. Please share your thoughts in the comments section below. Thanks for visiting Linux Handbook!