- Introduction to Linux Operating System
- Linux Distribution
- Architecture of Linux
- Advantages of Linux
- Disadvantages of Linux
- What Is Linux? and How Does Linux Work?
- What Is Linux?
- What is a Linux Command Line?
- How Does Linux Work?
- What is a Linux Desktop Environment
- Linux and Open Source
- What is a “Distribution?” and List of Linux Distros
- Which Linux Distribution is Right for You?
- Beginner-Friendly Linux Distributions
- Intermediate to Advanced Linux Distributions
- Linux distributions for Servers
- Linux Distributions for Multimedia Purposes
- Security-Centric Linux Distributions
Introduction to Linux Operating System
Linux is a community of open-source Unix like operating systems that are based on the Linux Kernel. It was initially released by Linus Torvalds on September 17, 1991. It is a free and open-source operating system and the source code can be modified and distributed to anyone commercially or noncommercially under the GNU General Public License.
Initially, Linux was created for personal computers and gradually it was used in other machines like servers, mainframe computers, supercomputers, etc. Nowadays, Linux is also used in embedded systems like routers, automation controls, televisions, digital video recorders, video game consoles, smartwatches, etc. The biggest success of Linux is Android(operating system) it is based on the Linux kernel that is running on smartphones and tablets. Due to android Linux has the largest installed base of all general-purpose operating systems. Linux is generally packaged in a Linux distribution.
Linux Distribution
Linux distribution is an operating system that is made up of a collection of software based on Linux kernel or you can say distribution contains the Linux kernel and supporting libraries and software. And you can get Linux based operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions and these distributions are available for different types of devices like embedded devices, personal computers, etc. Around 600 + Linux Distributions are available and some of the popular Linux distributions are:
- MX Linux
- Manjaro
- Linux Mint
- elementary
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Solus
- Fedora
- openSUSE
- Deepin
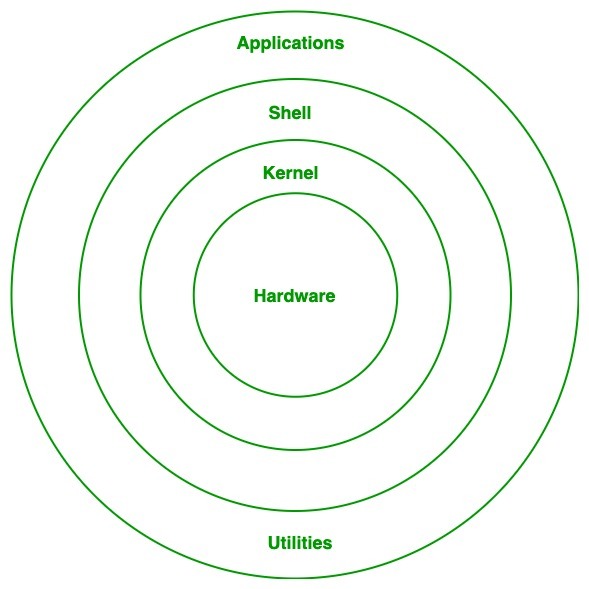
Architecture of Linux
Linux architecture has the following components:
- Kernel: Kernel is the core of the Linux based operating system. It virtualizes the common hardware resources of the computer to provide each process with its virtual resources. This makes the process seem as if it is the sole process running on the machine. The kernel is also responsible for preventing and mitigating conflicts between different processes. Different types of the kernel are:
- Monolithic Kernel
- Hybrid kernels
- Exo kernels
- Micro kernels
- System Library: Isthe special types of functions that are used to implement the functionality of the operating system.
- Shell: It is an interface to the kernel which hides the complexity of the kernel’s functions from the users. It takes commands from the user and executes the kernel’s functions.
- Hardware Layer: This layer consists all peripheral devices like RAM/ HDD/ CPU etc.
- System Utility: It provides the functionalities of an operating system to the user.

Advantages of Linux
- The main advantage of Linux, is it is an open-source operating system. This means the source code is easily available for everyone and you are allowed to contribute, modify and distribute the code to anyone without any permissions.
- In terms of security, Linux is more secure than any other operating system. It does not mean that Linux is 100 percent secure it has some malware for it but is less vulnerable than any other operating system. So, it does not require any anti-virus software.
- The software updates in Linux are easy and frequent.
- Various Linux distributions are available so that you can use them according to your requirements or according to your taste.
- Linux is freely available to use on the internet.
- It has large community support.
- It provides high stability. It rarely slows down or freezes and there is no need to reboot it after a short time.
- It maintain the privacy of the user.
- The performance of the Linux system is much higher than other operating systems. It allows a large number of people to work at the same time and it handles them efficiently.
- It is network friendly.
- The flexibility of Linux is high. There is no need to install a complete Linux suit; you are allowed to install only required components.
- Linux is compatible with a large number of file formats.
- It is fast and easy to install from the web. It can also install on any hardware even on your old computer system.
- It performs all tasks properly even if it has limited space on the hard disk.
Disadvantages of Linux
- It is not very user-friendly. So, it may be confusing for beginners.
- It has small peripheral hardware drivers as compared to windows.
Is There Any Difference between Linux and Ubuntu?
The answer is YES. The main difference between Linux and Ubuntu is Linux is the family of open-source operating systems which is based on Linux kernel, whereas Ubuntu is a free open-source operating system and the Linux distribution which is based on Debian. Or in other words, Linux is the core system and Ubuntu is the distribution of Linux. Linux is developed by Linus Torvalds and released in 1991 and Ubuntu is developed by Canonical Ltd. and released in 2004.

What Is Linux? and How Does Linux Work?
In this article, we explore what Linux is and some of the attributes and components associated with the Linux operating system.
What Is Linux?
Linux is an open-source, community-developed operating system with the kernel at its core, alongside other tools, applications, and services.
Like any other operating system like Windows or MAC, it manages the hardware resources of a system such as CPU, RAM, and storage. The kernel interfaces the operating system and the underlying hardware and facilitates communication between the two.
What is a Linux Command Line?
A command line is an interface that allows you to type and run Linux commands which instruct the operating system on what actions to carry out. A command-line interface is provided by a terminal or terminal emulator such as GNOME Terminal, Konsole, and XTERM.
Working on the command line is the ideal way of administering a Linux system, especially when working with a headless server or a minimal system (A Linux system that does not provide a GUI).
How Does Linux Work?
At the core of every Linux system is the kernel. The kernel is what sets apart Linux from other operating systems. It is the central component of the operating system and acts as a bridge between the user-level applications and the underlying hardware components.
It enables the communication between the software and the underlying physical hardware. The kernel manages all the running processes, memory, files, and so on. In a nutshell, the kernel takes care of the following:
- Memory Management – The kernel keeps track of memory usage by various applications on the system.
- Device Management – It also manages various devices that are connected to the system, such as input and output devices.
- Process Management – The kernel manages running processes in order to avoid conflicts and deadlocks and also for the optimal functioning of the system.
- System Calls and Security – The kernel receives and handles requests for service from the processes.
As mentioned before, the kernel sits right in the middle of User processes and the underlying hardware which comprises RAM, CPU, I/O devices, storage, graphics, and networking.
Apart from the kernel, the Linux Operating system includes other essential components such as GNU tools, system utilities, installed applications, and many others. All of these bundled together constitute a functional operating system.
What is a Linux Desktop Environment
A desktop environment is a collection of components that provide a Graphical User Interface (GUI) that allows users to seamlessly interact with the operating system. It comprises graphical elements such as icons, menus, windows, taskbars, wallpapers, widgets, and panels to mention a few.
A desktop environment is provided, by default, in modern graphical Linux distributions such as Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, Rocky, and AlmaLinux. It enhanced user interaction and enables users to easily manage the system as opposed to the command line interface which requires a high skill set to use.
Examples of popular desktop environments include GNOME, Cinnamon, KDE Plasma, MATE, Deepin, XFCE, LXDE, and LXQt.
Linux and Open Source
Linux is a free and open-source operating system that was initially released to the general public in 1991. It is currently under the GNU General Public License (GPL). Opensource implies that anyone can study, modify and redistribute the source code, provided they do so under the GNU GPL license terms.
Over time, Linux has grown in leaps and bounds to become one of the biggest open-source projects in the world. It has won the hearts of IT professionals, desktop lovers, and hobbyists from all over the globe.
It enjoys a wide community of vibrant and indefatigable developers who contribute to the kernel, search and fix bugs, add new features and brainstorm new ideas while sharing their views and opinions with the community.
What is a “Distribution?” and List of Linux Distros
Often abbreviated as ‘distro’ a Linux distribution is a version of the Linux operating system that is based on the Linux kernel. It ships with other components such as system tools and services, applications, and additional programs such as LibreOffice, GIMP, and Firefox web browser.
Popular free Linux distributions include Ubuntu from Canonical, Debian from the Debian Project, Fedora from the Fedora Project, OpenSUSE from SUSE, and Rocky and AlmaLinux both of which are 100% binary compatible with Red Hat.
Commercial distributions include Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), and SUSE Enterprise Server (SLES).
Which Linux Distribution is Right for You?
There are tons of Linux distributions and choosing the right one usually boils down to what you want to accomplish with it. Before opting for your distribution of choice, it’s worth taking time to familiarize yourself with the differences and nuances that exist between various Linux distributions.
At a glance, Linux distributions differ in the following ways.
- Package Management – This is how packages are installed and managed. Debian distributions use APT, Red Hat variants use DNF, SUSE distributions use zypper and Arch distributions use Pacman to mention a few examples. )
- Cost – Where it’s completely free, subscription-based (in the case of RHEL and SUSE), or partly paid in the case of subscription-based customer support.
- Documentation – Extensive documentation and manuals or lack thereof.
- Quality of Software – Some distributions provide the latest versions of software, while others don’t.
- Customer Support – Whether the vendor offers exemplary support to users or not.
- Ease of Use – Most of the distros are user-friendly and easy to use.
With that in mind, choosing the right distribution is mostly a personal thing and depends on what your goal is. So here is a breakdown of Linux distributions suited for particular use cases:
Beginner-Friendly Linux Distributions
When it comes to choosing a beginner-friendly Linux distro for learners or beginners in Linux, Ubuntu leads the pack. It’s a completely free and open-source distribution that provides an intuitive and user-friendly user interface that offers a seamless user experience.
Out of the box, you also get essential applications needed to get off the ground such as LibreOffice suite, Firefox browser, audio & video player, photo viewer, screenshot tool, thunderbird email client, calendar, and many more. It’s highly customizable and versatile.
Other beginner-friendly distributions include Linux Mint, Zorin, Elementary OS, MX Linux, and Linux Lite. It’s worth noting that most of these are based either on Debian or Ubuntu.
Intermediate to Advanced Linux Distributions
For intermediate to advanced users such as developers and system engineers and administrators, Debian, SUSE Linux, RHEL, Rocky, AlmaLinux, and Fedora are recommended.
These are excellent all-rounders that can serve both as desktop distributions and also in enterprise setups handling production workloads.
Linux distributions for Servers
Linux distributions optimized for server environments, including bare-metal and cloud deployments include RHEL, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES), Debian stable, Ubuntu Server, and Fedora (Fedora Server and Fedora CoreOS for containerized workloads.
They are considered ideal due to their high performance, impressive stability, and security.
Linux Distributions for Multimedia Purposes
For artists, content creators, and producers of multimedia content, Ubuntu Studio and Fedora Design Suite come in handy.
Security-Centric Linux Distributions
Kali Linux, Black Arch, and Parrot OS are Linux distributions considered ideal for security-related tasks such as penetration testing, and digital forensics.
Conclusion
This was a brief introduction to Linux. We have covered essential sub-topics such as various desktop environments, desktop environments, and tips on how you can go about choosing the right Linux distribution for your day-to-day tasks.
Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned system administrator or engineer, there’s a Linux distribution for everyone.