What is Linux Virtual Server Project (LVS)?
The Linux Virtual Server Venture (LVS) permits load adjusting of organized administrations, for example, web and mail servers utilizing Layer 4 Exchanging. It is to a great degree quick and permits such administrations to be scaled to administration 10s or 100s of a large number of concurrent associations. The motivation behind this instructional exercise is to exhibit how to utilize different components of LVS to load parity Web administrations, and how this can be made exceptionally accessible utilizing apparatuses, for example, pulse and keepalived. It will cover more propelled points which have been the subject of late improvement incorporating keeping up dynamic associations in a very accessible environment and utilizing dynamic criticism to better convey load.
Presentation
The Linux Virtual Server Venture (LVS) actualizes layer 4 exchanging in the Linux Portion. This permits TCP and UDP sessions to be burden adjusted between different genuine servers. Along these lines it gives an approach to scale Web administrations past a solitary host. HTTP and HTTPS activity for the Internet is presumably the most widely recognized use. Despite the fact that it can likewise be utilized for pretty much any administration, from email to the X Windows Framework.
LVS itself keeps running on Linux and it can stack parity associations from end clients running any working framework to genuine servers running any working framework. For whatever length of time that the associations use TCP or UDP, LVS can be utilized.
LVS is superior. It can deal with upwards of 100,000 synchronous associations. It is effectively ready to load an adjusted soaked 100Mbit ethernet, utilizing economical item equipment. It is additionally ready to load equalization immersed 1Gbit connection and past utilizing higher-end item equipment.
Linux Director: Host with Linux and LVS introduced which gets bundles from end clients and advances them to genuine servers.
End Client: Have that begins an association.
Genuine Server: This will run some kind of daemon, for example, Apache. A solitary host might be act in more than one of the above parts in the meantime.
Virtual IP Address (VIP): The IP address doled out to an administration that a Linux Chief will handle.
Genuine IP Address (Tear): The IP location of a Genuine Server.
Layer 4 Switching
Layer 4 Exchanging works by multiplexing approaching TCP/IP associations and UDP/IP datagrams to genuine servers. Parcels are recieved by a Linux Executive and a choice is made as to which genuine server to forward the bundle to. When this choice is made parcels for the same association will be sent to the same genuine server. Essentially, the trustworthiness of the association is upheld.
Packets Forwarding
The Linux Virtual Server has three diverse methods for sending parcels; system address interpretation (NAT), IP-IP encapsulation (tunneling) and direct routing.
Network Address Translation (NAT): A technique for controlling the source and/or destination port and/or location of a parcel. The most widely recognized utilization of this is IP disguising which is regularly used to empower RFC 1918 private systems to get to the Web. With regards to layer 4 exchanging, parcels are gotten from end clients and the destination port and IP location are changed to that of the picked genuine server. Return parcels go through the Linux executive at which time the mapping is fixed so the end client sees answers from the normal source.
Direct Routing: Bundles from end clients are sent specifically to the genuine server. The IP bundle is not adjusted, so the genuine servers must be designed to acknowledge movement for the virtual server’s IP address. This should be possible utilizing a fake interface or bundle separating to divert movement tended to the virtual server’s IP location to a neighborhood port. The genuine server may send answers specifically back to the end client. Along these lines, the Linux executive should not be in the way of arrival.
IP-IP encapsulation (tunneling): This permits parcels tended to an IP location which are diverted to another location, potentially on an alternate system. With regards to layer 4, exchanging the conduct is fundamentally the same as direct steering, aside from when parcels are sent they are exemplified in an IP bundle, instead of simply controlling the Ethernet outline. The fundamental preferred standpoint of utilizing burrowing is that genuine servers can be on an alternate system.
Virtual Administrations
On the Linux Executive a virtual administration is characterized by either an IP location, port, and convention, or a firewall-mark. A virtual administration may alternatively have a persistence timeout connected with it. In the event that this is set and an association is gotten from the same IP address before the timeout has terminated, then the association will be sent to the same genuine server as the first association.
IP Location, Port and Convention: A virtual server might be determined by:
An IP Address: The IP address that end clients will use to get to the administration.
A port: The port that end clients will associate with.
A convention. Either UDP or TCP.
Firewall-Mark: Parcels might be set apart with a 32-bit unsigned worth utilizing ipchains or iptables. The Linux Virtual Server can utilize this imprint to assign parcels bound for a virtual administration and control them as necessary. This is especially helpful if countless IP based virtual administrations are required with the same genuine servers. On the other hand, it requires gathering diligence between various ports. A given end client is guaranteed that it will be sent to the same genuine server for both HTTP and HTTPS.
The virtual administration is relegated to do booking calculation. This is utilized to apportion approaching associations with the genuine servers. In LVS, the schedulers are actualized as partitioned piece modules. Consequently, new schedulers can be actualized without adjusting the center LVS code.
There are a wide range of planning calculations accessible to suit an assortment of necessities. The easiest are round-robin and slightest associated. This work utilizes a basic system of distributing associations with every genuine server. Thus assigning associations with the genuine server with minimal number of associations individually. Weighted variations of these schedulers permit associations with the assigned relative to the weighting of the genuine server. All the more intense genuine servers can be set with a higher weight and in this manner, will be apportioned more associations.
More intricate booking calculations have been intended for particular purposes. For example, to guarantee that solicitations for the same IP location are sent to the same genuine server. This is helpful when utilizing LVS to load parity straightforward intermediaries.
If you need any further assistance please contact our support department.
What is linux virtual server
Linux Virtual Server (LVS) — это набор интегрированных программных компонентов для распределения нагрузки между несколькими реальными серверами. LVS работает на двух одинаково настроенных компьютерах: один из них явлается активным LVS-маршрутизатором, а второй- резервным LVS-маршрутизатором. Активный LVS-маршрутизатор выполняет две задачи:
Резервный LVS-маршрутизатор отслеживает состояние активного LVS-маршрутизатора и берет на себя функции последнего в случае выхода его из строя.
1.1. Простая конфигурация Linux Virtual Server
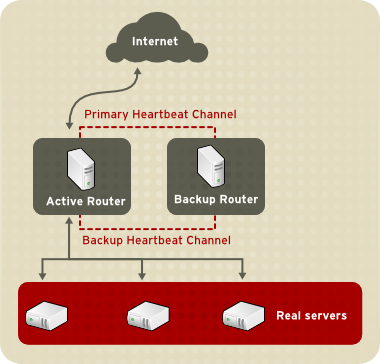
На рисунке Рисунок 1.1. Простая конфигурация Linux Virtual Server” показана простая конфигурация LVS, состоящая из двух уровней. На первом уровне расположены два LVS-маршрутизатора — активный и резервный. Каждый LVS-маршрутизатор имеет два сетевых интерфейса, один для внешней сети (Интернет) и один для внутренней сети, что позволяет контролировать трафик между двумя сетями. В этом примере активный LVS-маршрутизатор использует Network Address Translation или NAT для распределения трафика из внешней сети между произвольным количеством реальных серверов, расположенных на втором уровне и, в свою очередь, предоставляющих доступ к необходимым сервисам. Реальные серверы в этом примере подключены к выделенному сегменту внутренней сети и направляют весь внешний трафик обратно через активный LVS-маршрутизатор. Для пользователей внешней сети все серверы выглядят как единое целое.
Рисунок 1.1. Простая конфигурация Linux Virtual Server
Запросы к сервисам, приходящие на LVS-маршрутизаторы, отправлены на виртуальные IP-адреса, или VIP (Virtual IP). Это публично маршрутизируемые адреса, ассоциированные администратором сайта с определенным доменным именем, например, www.example.com, и выделенные под один или несколько виртуальных серверов. Виртуальный сервер — это сервис, настроенный на прослушивание выделенного виртуального IP. Для получения подробной информации о настройке виртуальных серверов при помощи Piranha Configuration Tool обратитесь к странице 4.6. Раздел “ VIRTUAL SERVERS ”. VIP-адреса мигрируют с одного LVS-маршрутизатора на другой в случае возникновения сбоев, обеспечивая таким образом доступность IP-адресов (известных также как плавающие IP-адреса ).
VIP-адреса могут быть псевдонимами того же устройства, с помощью которого LVS-маршрутизатор подключен к Интернет. Например, если интерфейс eth0 подключен к Интернет, то несколько виртуальных серверов может быть ассоциировано с eth0:1 . В качестве альтернативы, каждый виртуальный сервер может быть ассоциирован с отдельным устройством. Например, HTTP-трафик может обрабатываться на интерфейсе eth0:1 , а FTP-трафик — на eth0:2 .
В любой отдельно взятый момент времени активен только один LVS-маршрутизатор. Одной из основных задач активного LVS-маршрутизатора является перенаправление запросов, поступающих на виртуальные IP-адреса, к реальным серверам. Перенаправление основывается на одном из восьми поддерживаемых алгоритов балансировки нагрузки. Эти алгоритмы описаны в разделе 1.3, “Обзор планировщика LVS”.
Активный маршрутизатор также динамически отслеживает текущее состояние сервисов на реальных серверах при помощи простых send/expect-скриптов. Для определения состояния таких сервисов, как HTTPS или SSL, администратор имеет возможность вызывать внешние исполняемые файлы. Если сервис на реальном сервере отказывает, активный маршрутизатор перестает перенаправлять запросы на этот сервер до тех пор, пока сервис не начнет функционировать нормально..
Периодически активный и резервный LVS-маршрутизаторы обмениваются heartbeat-сообщениями через основной внешний интерфейс, а в случае сбоя — через внутренний интерфейс. Если резервный узел не может получить heartbeat-сообщение в течение заданного интервала времени, он инициирует процедуру восстановления после отказа и берет на себя роль активного маршрутизатора. Во время процедуры восстановления после отказа резервный маршрутизаторе активизирует VIP-адреса, облуживавшиеся ранее отказавшим маршрутизатором, используя метод, известный как ARP spoofing. В ходе этой процедуры резервный LVS-маршрутизатор объявляет себя получателем всех IP-пакетов, адресованных сбойному узлу. После того, как отказавший узел вновь начинает нормально функционировать, резервный узел возвращается в свое исходное состояние.
Поскольку отдельные виртуальные серверы в двухуровневой конфигурации, показанной на Рисунке 1.1., не осуществляют автоматическую синхронизацию данных между собой, это решение является оптимальным для случаев, когда данные на реальных серверах изменяются не очеь часто, например, это могут быть статичные web-страницы.
1.1.1. Репликация между реальными серверами и общий доступ к данным
Поскольку в LVS нет компонента, предоставляющего общий доступ к данным для реальных серверов, у администратора имеется два способа решить эту проблему:
Первый способ является предпочтительным для случаев, когда не требуется изменение или загрузка данных на серверы большим количеством пользователей. В противном случае предпочтительным способом является добавление третьего уровня в инфраструктуру LVS.
1.1.1.1. Настройка синхронизации данных на реальных серверах.
Существует множество способов синхронизировать данные в пуле реальных серверов. Например, можно написать shell-скрипт, который в случае изменения данных растиражирует изменения на все серверы в пуле. Также, возможно использование программ типа rsync для периодической репликации данных между реальными серверами.
Тем не менее, такой подход к синхронизации данных оказывается неэффективным в тех случаях, когда большое количество пользователей загружают на сервер файлы или проводят большое количество транзакций. В таких случаях трехуровневая топология является идеальным решением.