- Configure LVM on Linux Mint – Linux Hint
- What is LVM?
- LVM vocabulary
- Configure LVM on Linux Mint
- Create the Physical Volume (PV)
- Create the Volume Group (VG)
- Create the logical volumes (LV)
- Increase or decrease the size of the logical volume
- Final thoughts
- Configure LVM on Linux Mint
- What is LVM in Linux Mint install?
- How do I activate LVM?
- How do I use LVM in Linux?
- Should I encrypt Linux Mint installation?
- Should I encrypt my home folder Linux?
- What is use LVM with the new Ubuntu installation?
- What is LVM and its use?
- How do I know if my LVM is active?
- How do you check if VG is active or not?
- How enable and disable LVM in Linux?
- What is the advantage of LVM in Linux?
- What is LVM in Linux with example?
- How extend LVM size in Linux?
Configure LVM on Linux Mint – Linux Hint
Imagine that you have a Hard Disk that requires you to resize a chosen partition. This is possible on Linux thanks to LVM. With this in mind, this article will teach you how to Configure LVM on Linux Mint. However, you can apply this tutorial to any Linux distribution.
What is LVM?
LVM is a logical volume manager developed for the Linux Kernel. Currently, there are 2 versions of LVM. LVM1 is practically out of support while LVM version 2 commonly called LVM2 is used.
LVM includes many of the features that are expected of a volume manager, including:
- Resizing logical groups.
- Resizing logical volumes.
- Read-only snapshots (LVM2 offers read and write).
To give you an idea of the power and usefulness of LVM, I will give you the following example: Suppose we have a small hard drive, for example, 80Gb. The way the disk is distributed would be something like that:
- The 400Mb /boot partition
- For root partition / 6Gb
- In the case of the home partition /home 32Gb
- And the swap partition is 1Gb.
This distribution could be correct and useful but imagine that we install many programs and the root partition fills up, but in personal files, there is practically no data and the /home partition has 20 Gb available. This is a bad use of the hard disk. With LVM, the solution to this problem is simple, since you could simply reduce the partition containing /home and then increase the space allocated to the root directory.
LVM vocabulary
In order to make this post as simple as possible for the reader, it is necessary to take into account some concepts intimately related to LVM. Knowing these concepts effectively will make better understand the full potential of this tool:
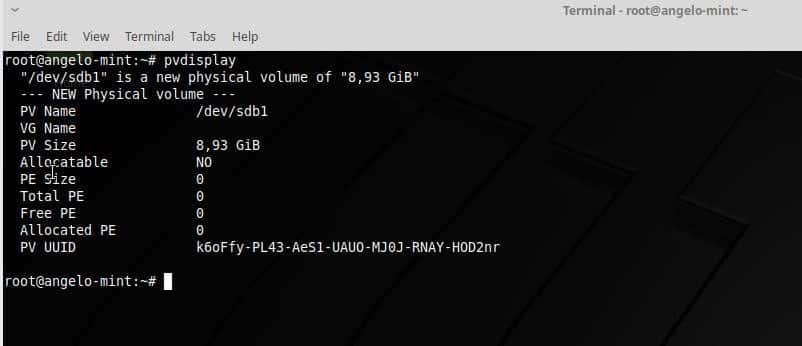
- Physical Volume (PV): A PV is a physical volume, a hard drive, or a particular partition.
- Logical Volume (LV): an LV is a logical volume, it is the equivalent of a traditional partition in a system other than LVM.
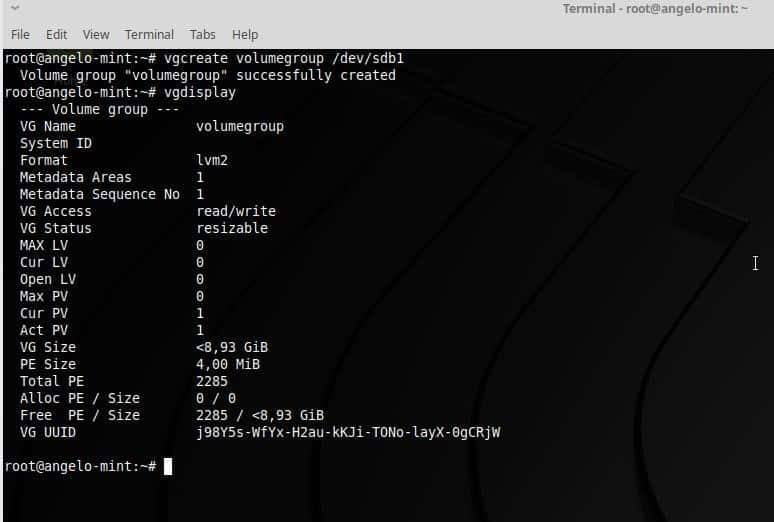
- Volume Group (VG): a VG is a group of volumes, it can gather one or more PV.
- Physical Extent (PE): a PE is a part of each physical volume, of a fixed size. A physical volume is divided into multiple PEs of the same size.
- Logical extent (LE): an LE is a part of each fixed-size logical volume. A logical volume is divided into multiple LEs of the same size.
- Device mapper: is a generic Linux kernel framework that allows mapping one device from blocks to another.
Configure LVM on Linux Mint
First of all, you must install the lvm2 package in your system. To do this, open a terminal emulator and write. Note that to execute this command you need super user privileges.
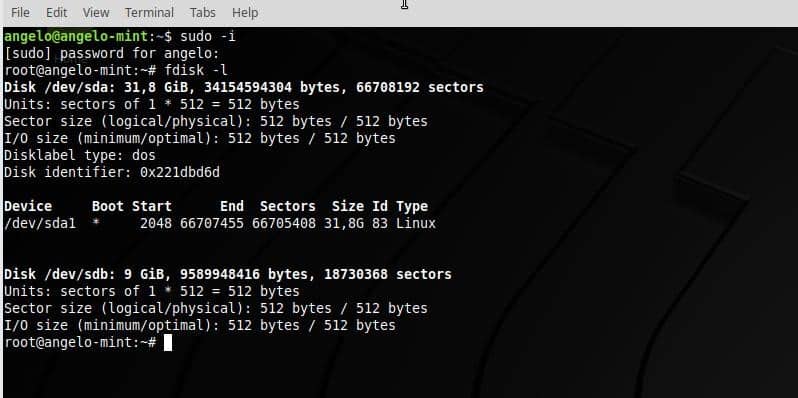
Next, I am going to use fdisk to verify which partitions I have. Of course, you must also do this to ensure which are your partitions as well.
As you can see, I have a second hard drive. In order for LVM to do its job, it is necessary to prepare the disk or partitions to be of the LVM type. Therefore, I have to do some work on the second hard disk called sdb.
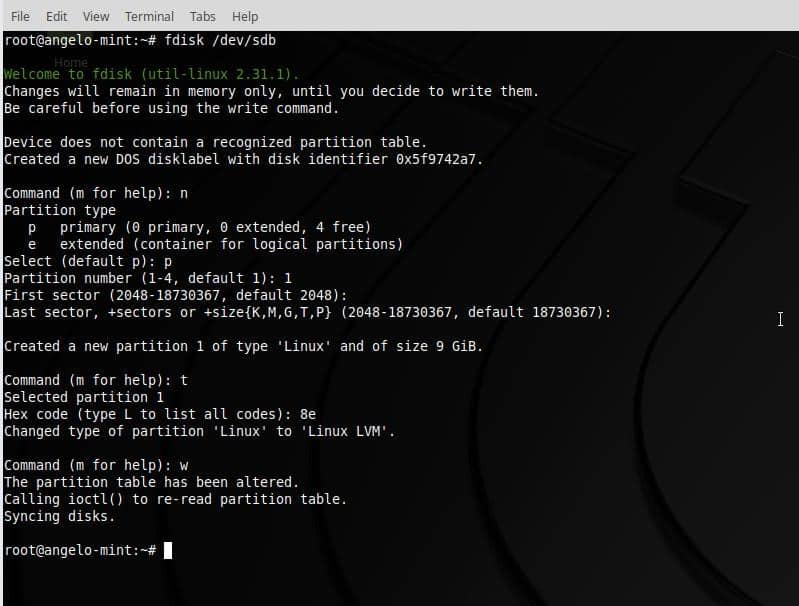
Next, press “n” key to create a new partition. Then, Press enter. Next, press “p” key to set the partition as a primary. Then, Press enter. Now, you have to press 1 to create it as the first partition of the disk. Then, Press enter.
So, the next step is press “t” key to change the system identifier of a partition. Then, Press enter. And select LVM partition. To do it, type “8e”. Then, Press enter. So, type “w” key to write all the changes.
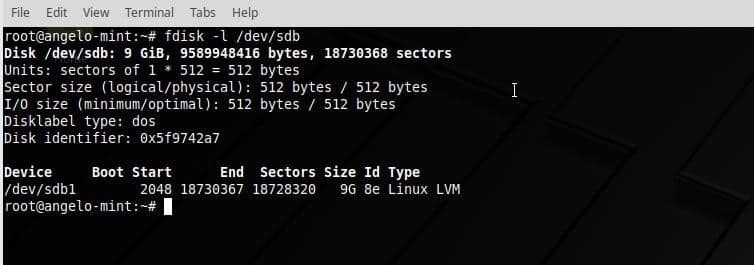
Finally, check the partition.
NOTE: If you are going to work with several partitions, you must repeat this process with each of them.
Now, we are ready to continue.
Create the Physical Volume (PV)
To work with LVM we must first define the Physical Volumes (PV), for this we will use the pvcreate command. So, let us go.
NOTE: If we had more than one partition, we would have to add them all to the PV.
Create the Volume Group (VG)
Once you have the partitions ready, you have to add them to a volume group. So, type this command:
Replace “volumegroup” by the name you want. If you had more partitions you would only have to add them to the command. For example:
You can write the name what you want for the VG. So, check the volume group with this command:
Create the logical volumes (LV)
This is the central moment of the post because in this part we will create the logical volumes that will be like a normal partition.
This command creates a logical volume of 4G of space over the previously created group.
With lvdisplay you can check the LV.
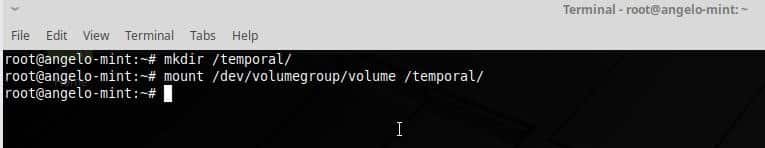
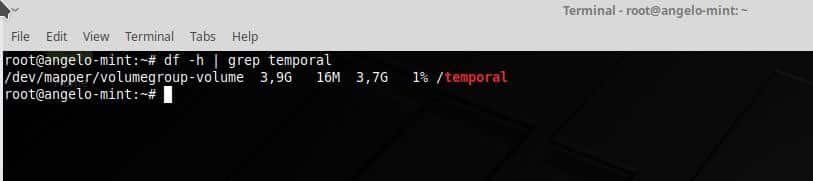
The next step is to format and mount the VL.
Now, create a temporal folder and mount the VL on it.
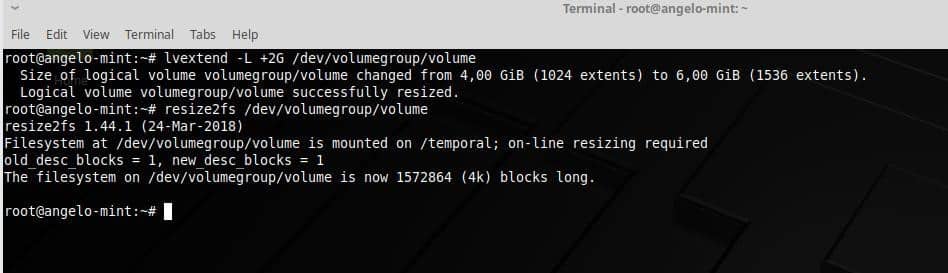
Increase or decrease the size of the logical volume
One of the most phenomenal possibilities of LVM is the possibility to increase the size of a logical volume in a very simple way. To do this, type the following command.
Finally, it is necessary to reflect the same change in the file system, for this, run this command.
Final thoughts
Learning to configure LVM in Linux Mint is a simple process that can save many problems when working with partitions. To do this, I invite you to read more about the subject since here I have shown you practical and simple examples on how to configure it.
Configure LVM on Linux Mint
LVM is a fine idea for multiple small drives or larger servers but with the lower cost of multi-terabyte drives it’s not a lot of use for home users. There is, however, one thing that I found it good for. LVM works great for striping multiple drives together for raid 0 type configurations.
What is LVM in Linux Mint install?
LVM is a logical volume manager developed for the Linux Kernel. Currently, there are 2 versions of LVM. LVM1 is practically out of support while LVM version 2 commonly called LVM2 is used. LVM includes many of the features that are expected of a volume manager, including: Resizing logical groups.
How do I activate LVM?
- Run vgscan command scans all supported LVM block devices in the system for VGs.
- Execute vgchange command to activate volume.
- Type lvs command to get information about logical volumes.
- Create a mount point using the mkdir command.
How do I use LVM in Linux?
- Install LVM on major Linux distros. .
- Create partitions. .
- Create physical volumes. .
- Create a virtual group. .
- Create logical volumes. .
- Create a filesystem on logical volumes. .
- Edit fstab to automatically mount partitions. .
- Mount logical volumes.
Should I encrypt Linux Mint installation?
If Linux Mint is the only operating system you want to run on this computer and all data can be lost on the hard drive, choose Erase disk and install Linux Mint. Encrypt the new Linux Mint installation for security refers to full disk encryption.
Should I encrypt my home folder Linux?
Encrypting your home folder keeps your data and documents safe. Even though you must log into the system to access your files, a person accessing your computer through a USB-based live operating system could still mount your home folder and access your files.
What is use LVM with the new Ubuntu installation?
Ubuntu’s installer offers an easy “Use LVM” checkbox. The description says it enables Logical Volume Management so you can take snapshots and more easily resize your hard disk partitions — here’s how to do that. LVM is a technology that’s similar to RAID arrays or Storage Spaces on Windows in some ways.
What is LVM and its use?
LVM stands for Logical Volume Management. It is a system of managing logical volumes, or filesystems, that is much more advanced and flexible than the traditional method of partitioning a disk into one or more segments and formatting that partition with a filesystem.
How do I know if my LVM is active?
Try running lvdisplay on command line and is should display any LVM volumes if they exist. Run df on the MySQL data directory; this will return the device where the directory resides. Then run lvs or lvdisplay to check if the device is an LVM one.
How do you check if VG is active or not?
You may check the status of the volume group by issuing the lsvg command. Depending on your configuration, the lsvg command returns the following settings: VG STATE will be active if it is varied on either actively or passively.
How enable and disable LVM in Linux?
You may need to make a LVM volume group inactive and thus unknown to the kernel. To deactivate a volume group, use the -a ( —activate ) argument of the vgchange command.
What is the advantage of LVM in Linux?
The main advantages of LVM are increased abstraction, flexibility, and control. Logical volumes can have meaningful names like “databases” or “root-backup”. Volumes can be resized dynamically as space requirements change and migrated between physical devices within the pool on a running system or exported easily.
What is LVM in Linux with example?
Logical Volume Management (LVM) creates a layer of abstraction over physical storage, allowing you to create logical storage volumes. . You can think of LVM as dynamic partitions. For example, if you are running out of disk space on your server, you can just add another disk and extend the logical volume on the fly.
How extend LVM size in Linux?
- To Create new partition Press n.
- Choose primary partition use p.
- Choose which number of partition to be selected to create the primary partition.
- Press 1 if any other disk available.
- Change the type using t.
- Type 8e to change the partition type to Linux LVM.
Centos
When was RHEL 8.1 release?What is the latest kernel version for CentOS 8?Is CentOS based on Redhat?Is CentOS same as RHEL?Why Red Hat Linux is not fre.
Ovirt
Network Interface: 1 Network Interface Card (NIC) with bandwidth of at least 1 Gbps.Step 1: Enable oVirt 4.4 and PostgreSQL Repositories. Update your .
Shutdown
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del and you will see the Power Off dialog box. Click on the Power Off button to power off your system. In case, you want to cancel the .
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system