- Understanding Disk Partition in Linux – MBR vs GPT
- Understanding MBR Partition table
- Understanding GPT Partition table
- Difference between MBR and GPT
- How to choose between GPT and MBR?
- Check disk partition table in Linux command line
- The Linux Booting Process — 6 Steps Described in Detail
- 1. BIOS
- 2. MBR
- 3. GRUB
- 4. Kernel
- 5. Init
- 6. Runlevel programs
- What is the purpose of MBR partition in Linux?
- What is MBR partition in Linux?
- What is MBR format?
- Can I install logical partition Linux?
- How is GPT better than MBR partition system?
- Which is best MBR or GPT?
Understanding Disk Partition in Linux – MBR vs GPT
A disk partition is a contiguous space of storage on a physical or logical disk that functions as if it were a physically separate disk.
Partitions are visible to the system firmware and the installed operating systems. Access to a partition is controlled by the system firmware before the system boots the operating system, and then by the operating system after it is started.
A partition table tells the operating system how the partitions and data on the drive are organized.
There are two main types of partition tables: MBR and GPT.
Understanding MBR Partition table
- MBR stands for Master Boot Record and is a bit of reserved space at the beginning of the drive that contains information about how the partitions are organized.
- The MBR also contains code to launch the operating system, and it’s sometimes called the Boot Loader. MBR also known as MS-DOS, is what we might call the original standard.
MBR is still the most widely used partition table, it comes with two major limitations.
- It does not allow us to create more than four main partitions. Those partitions are called primary partitions.
- Disk partitions may not exceed 2 TB.
Understanding GPT Partition table
- GPT is an abbreviation of GUID Partition Table, and is a newer standard that’s slowly replacing MBR.
- The GUID Partition Table (GPT) was introduced as part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) initiative. GPT provides a more flexible mechanism for partitioning disks than the older Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme that was common to PCs.
- Unlike an MBR partition table, GPT stores the data about how all the partitions are organized and how to boot the OS throughout the drive. That way if one partition is erased or corrupted, it’s still possible to boot and recover some of the data. We can have multiple primary partitions, and the drive sizes can exceed 2 TB.
Difference between MBR and GPT
Compare with the MBR partitioning style, the GPT disk has more advantages. It allows each disk to have up to 128 primary partitions, and the maximum volume size can grow up to 18 petabytes, allowing using primary and backup partition tables for redundancy.
Also, it supports each GPT partition to have a unique identification ID (GUID). However, the maximum volume size supported by MBR disk is only 2 TB (terabytes) and each disk can only have at most 4 primary partitions (or 3 primary partitions + 1 extended partition, in this way unlimited logical partitions can be created on the extended partition).
How to choose between GPT and MBR?
- If we are installing on older hardware, especially on old laptops, consider choosing MBR because its BIOS might not support GPT
- If we are partitioning a disk that is larger than 2 TiB, we need to use GPT.
- It is recommended to always use GPT for UEFI boot, as some UEFI implementations do not support booting to the MBR while in UEFI mode.
- If none of the above apply, choose freely between GPT and MBR. Since GPT is more modern, it is recommended in this case.
Check disk partition table in Linux command line
Parted command should work on all Linux distributions. Open a terminal and use the following command with sudo:
The above command is actually a CLI-based partitioning manager in Linux. With the option -l, it lists the disks on our system along with the details about those disks. It includes partitioning scheme information.
- parted /dev/sdc print
- Model: ORICO H/ W RAID0 (scsi)
- Disk /dev/sdc: 6001GB
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/4096B
- Partition Table: gpt
In the above output, look for the line starting with Partition Table: the disk has GPT partitioning scheme.
For MBR, it would show msdos like below.
- Model: ATA TOSHIBA MQ01ACF0 (scsi)
- Disk /dev/sda: 320GB
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/4096B
- Partition Table: msdos
David is a Cloud & DevOps Enthusiast. He has years of experience as a Linux engineer. He had working experience in AMD, EMC. He likes Linux, Python, bash, and more. He is a technical blogger and a Software Engineer. He enjoys sharing his learning and contributing to open-source.
howtouselinux.com is dedicated to providing comprehensive information on using Linux.
We hope you find our site helpful and informative.
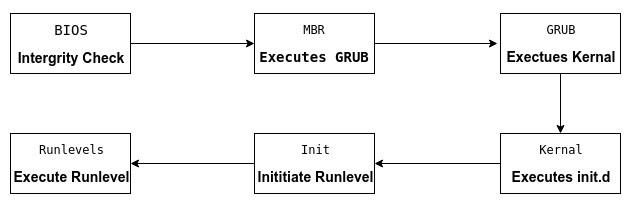
The Linux Booting Process — 6 Steps Described in Detail
An operating system (OS) is the low-level software that manages resources, controls peripherals, and provides basic services to other software. In Linux, there are 6 distinct stages in the typical booting process.
1. BIOS
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. In simple terms, the BIOS loads and executes the Master Boot Record (MBR) boot loader.
When you first turn on your computer, the BIOS first performs some integrity checks of the HDD or SSD.
Then, the BIOS searches for, loads, and executes the boot loader program, which can be found in the Master Boot Record (MBR). The MBR is sometimes on a USB stick or CD-ROM such as with a live installation of Linux.
Once the boot loader program is detected, it’s then loaded into memory and the BIOS gives control of the system to it.
2. MBR
MBR stands for Master Boot Record, and is responsible for loading and executing the GRUB boot loader.
The MBR is located in the 1st sector of the bootable disk, which is typically /dev/hda , or /dev/sda , depending on your hardware. The MBR also contains information about GRUB, or LILO in very old systems.
3. GRUB
Sometimes called GNU GRUB, which is short for GNU GRand Unified Bootloader, is the typical boot loader for most modern Linux systems.
The GRUB splash screen is often the first thing you see when you boot your computer. It has a simple menu where you can select some options. If you have multiple kernel images installed, you can use your keyboard to select the one you want your system to boot with. By default, the latest kernel image is selected.
The splash screen will wait a few seconds for you to select and option. If you don’t, it will load the default kernel image.
In many systems you can find the GRUB configuration file at /boot/grub/grub.conf or /etc/grub.conf . Here’s an example of a simple grub.conf file:
#boot=/dev/sda default=0 timeout=5 splashimage=(hd0,0)/boot/grub/splash.xpm.gz hiddenmenu title CentOS (2.6.18-194.el5PAE) root (hd0,0) kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.18-194.el5PAE ro root=LABEL=/ initrd /boot/initrd-2.6.18-194.el5PAE.img4. Kernel
The kernel is often referred to as the core of any operating system, Linux included. It has complete control over everything in your system.
In this stage of the boot process, the kernel that was selected by GRUB first mounts the root file system that’s specified in the grub.conf file. Then it executes the /sbin/init program, which is always the first program to be executed. You can confirm this with its process id (PID), which should always be 1.
The kernel then establishes a temporary root file system using Initial RAM Disk (initrd) until the real file system is mounted.
5. Init
At this point, your system executes runlevel programs. At one point it would look for an init file, usually found at /etc/inittab to decide the Linux run level.
Modern Linux systems use systemd to choose a run level instead. According to TecMint, these are the available run levels:
Run level 0 is matched by poweroff.target (and runlevel0.target is a symbolic link to poweroff.target).
Run level 1 is matched by rescue.target (and runlevel1.target is a symbolic link to rescue.target).
Run level 3 is emulated by multi-user.target (and runlevel3.target is a symbolic link to multi-user.target).
Run level 5 is emulated by graphical.target (and runlevel5.target is a symbolic link to graphical.target).
Run level 6 is emulated by reboot.target (and runlevel6.target is a symbolic link to reboot.target).
Emergency is matched by emergency.target.
systemd will then begin executing runlevel programs.
6. Runlevel programs
Depending on which Linux distribution you have installed, you may be able to see different services getting started. For example, you might catch starting sendmail …. OK .
These are known as runlevel programs, and are executed from different directories depending on your run level. Each of the 6 runlevels described above has its own directory:
- Run level 0 – /etc/rc0.d/
- Run level 1 – /etc/rc1.d/
- Run level 2 – /etc/rc2.d/
- Run level 3 – /etc/rc3.d/
- Run level 4 – /etc/rc4.d/
- Run level 5 – /etc/rc5.d/
- Run level 6 – /etc/rc6.d/
Note that the exact location of these directories varies from distribution to distribution.
If you look in the different run level directories, you’ll find programs that start with either an «S» or «K» for startup and kill, respectively. Startup programs are executed during system startup, and kill programs during shutdown.
That’s everything you need to know about the Linux booting process. Now go out there and make Tux proud.
What is the purpose of MBR partition in Linux?
The most common partitioning scheme for x86 and x86-64 computers is MBR (Master Boot Record). This method stores its data in the first sector of the disk, called the Master Boot Record. Assuming 512-byte sectors, MBR partitions can’t support disks larger than 2 TB.
What is MBR partition in Linux?
The master boot record (MBR) is a small program that is executed when a computer is booting (i.e., starting up) in order to find the operating system and load it into memory. This is commonly referred to as the boot sector. …
Can Linux be install on MBR partition?
Linux supports BIOS+MBR, BIOS+GPT, UEFI+MBR and UEFI+GPT.
Does Linux use MBR?
If you have Linux installed, the GRUB boot loader will typically be located in the MBR. MBR works with disks up to 2 TB in size, but it can’t handle disks with more than 2 TB of space.
What is MBR format?
MBR stands for Master Boot Record and was the default partition table format before hard drives were larger than 2 TB. The maximum hard drive size of MBR is 2 TB. As such, if you have a 3 TB hard drive and you use MBR, only 2 TB of your 3 TB hard drive will be accessible.
Can I install logical partition Linux?
Personally, I would recommend that any Linux installation be done on a Logical partition. Linux will boot from either, and it will save you problems later down the road should you need or want to create additional partitions beyond the four Primary partitions allowed.
Is Ubuntu MBR or GPT?
If you boot (or dual-boot) Windows in EFI mode, using GPT is required (it’s a Windows limitation). IIRC, Ubuntu won’t install to an MBR disk in EFI mode, either, but you could probably convert partition table type and get it to boot after installing it.
Does Linux need MBR or GPT?
It is common for Linux servers to have several hard disks so it’s important to understand that large hard disks with more than 2TB and many newer hard disks use GPT in place of MBR to allow for the additional addressing of sectors.
How is GPT better than MBR partition system?
Which is best MBR or GPT?
What is GPT and MBR when partitioning a drive?
What is full form of MBR?