- What is an ramdisk and How ramdisks can be created. (Doc ID 2349947.1)
- Solution
- To view full details, sign in with your My Oracle Support account.
- Don’t have a My Oracle Support account? Click to get started!
- How to Create a Ramdisk in Linux
- Tmpfs and Ramfs:
- How to Create a Ramdisk in Linux Using Tmpfs:
- SSD vs. Tmpfs:
- Creating a Ramdisk in Linux Using Ramfs:
- Tmpfs vs. Ramfs:
- Conclusion
- About the author
- David Adams
- How to Create and Use a Ramdisk on Ubuntu 18.04
- How do I use ramdisk?
- How do you mount a ramdisk?
- How do I mount a ramdisk image in Linux?
- What is a RamDisk in Linux?
- What is Ramfs in Linux?
- Is ramdisk faster than SSD?
- Is RAM faster than NVMe?
- Can you convert memory to RAM?
- How do I mount a tmp?
- How do I mount Tmpfs fstab?
- When should I use ramdisk?
What is an ramdisk and How ramdisks can be created. (Doc ID 2349947.1)
The RAM disk drive is a way to use main system memory as a block device ( Memory used as Disk partition to store data ). It is required for initrd, an initial filesystem used if you need to load modules in order to access the root filesystem. This can be the RAM disk device itself, or an unused disk partition (such as an unmounted swap partition).
*) What are some of the other uses of the RAM disk.
It may have other uses. It can also be used for a temporary filesystem for crypto work, since the contents are erased on reboot. One of the adventages to use this as data store is that the files stored inside ramdisk partition will have the faster access as compared to hard drive as memory is faster than disk. It will help to increase the performance if some data is accessed constantly.
*) What is tmpfs.
Just to other options; Tmpfs is an alternative of Ramdisk as it’s a file system which keeps all files in virtual memory. Everything in tmpfs is temporary in the sense that no files will be created on your hard drive. If you unmount a tmpfs instance, everything stored therein is lost. If you compare it to ramfs (which was the template to create tmpfs) you gain swapping and limit checking. Another similar thing is the RAM disk (/dev/ram*), which simulates a fixed size hard disk in physical RAM, where you have to create an ordinary filesystem on top. Ramdisks cannot swap and you do not have the possibility to resize them.
*) How to create a ram disks
In order to create a Ramdisk some values need to be added in the grub.conf of the Server.
*) One example to use :
The application requirements needed one 16GB ramdisk but the kernel is defaulting to sixteen 16MB ramdisk.
Solution
To view full details, sign in with your My Oracle Support account.
Don’t have a My Oracle Support account? Click to get started!
My Oracle Support provides customers with access to over a million knowledge articles and a vibrant support community of peers and Oracle experts.
Oracle offers a comprehensive and fully integrated stack of cloud applications and platform services. For more information about Oracle (NYSE:ORCL), visit oracle.com. � Oracle | Contact and Chat | Support | Communities | Connect with us | | | | Legal Notices | Terms of Use
How to Create a Ramdisk in Linux
A ramdisk is a volatile storage space defined in the RAM memory. Using this feature increases file processing performance ten times over the best SSD hard disks. Implementing a ramdisk is very advantageous for users whose tasks require significant amounts of hardware resources. In addition, media editors and gamers can enjoy this implementation.
A ramdisk is a volatile space, all information stored in it will be lost if the device is turned off or reboots.
In Linux, ramdisks can be created using the command mount and the filesystems tmpfs and ramfs. This tutorial shows how to create a ramdisk in Linux using both of them.
Tmpfs and Ramfs:
Tmpfs: Tmpfs is a temporary file system stored in the RAM memory (and/or swap memory). By specifying this file system with the argument -t of the command mount, you can assign limited memory resources to a temporary file system. As a result, applications stored in this filesystem will perform several times faster than they would on conventional storage devices, including cssd devices.
Ramfs: Ramfs is similar to Tmpfs, but the user can’t ensure a limit, and the allocated resource grows dynamically. If the user doesn’t control the ramfs consumption, ramfs will keep using all the memory until hanging or crashing the system.
Tmpfs vs. Ramfs: There is no notable difference between the performance of tmpfs and its predecessor ramfs. The reason behind ramfs being replaced by tmpfs is the unlimited RAM consumption risk by ramfs which may lead to a system crash.
Another advantage of tmpfs over ramfs is the ability to use the swap space while ramfs are limited to hardware memory.
How to Create a Ramdisk in Linux Using Tmpfs:
First, let’s see the free memory we can use before creating a tmpfs mount point. To check the available ram and swap, you can use the command free. To print the results in gigabytes, you can add the argument –giga, as shown in the example below:
As you can see in the output above, I have two physical GB and two on the swap space.
Now, create a mount point under the directory /mnt using the command mkdir as shown in the example below. The mount point name choice is arbitrary. If you are going to use the ramdisk for a specific application, you can name the mount point after it. In the example below I call it /mnt/tmp:
Now you can create the ramdisk using the mount command. The following example shows how to create a ramdisk using tmpfs on 2GB Ram/Swap, on the mount point /mnt/tmp.
The -t (type) argument allows to specify the file system (in this case, tmpfs). The -o (options) argument is used to define the space for the ramdisk.
The ramdisk was created under /mnt/tmp.
SSD vs. Tmpfs:
I copied an Ubuntu image from a user’s home directory to the root directory in the following screenshot.
Using the command time to display timing, you can see the copying process took 0:55.290s
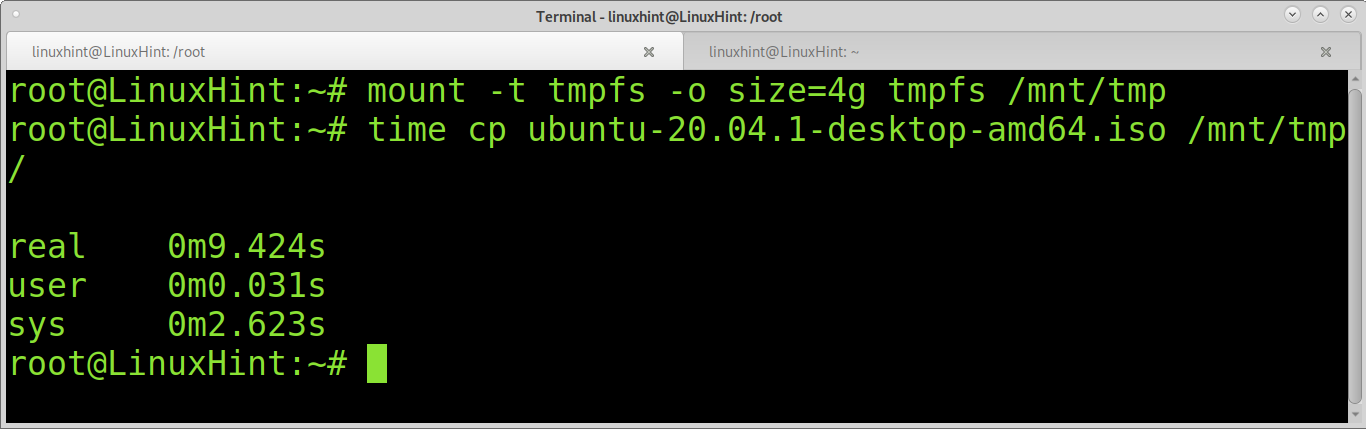
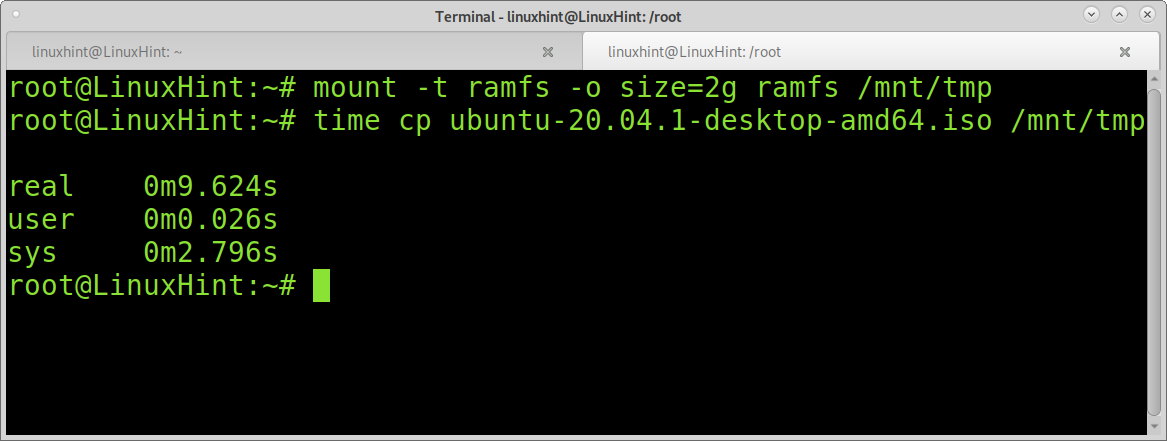
In the following screenshot, you can see how copying the same Ubuntu iso image to the ramdisk takes 0:9.424s:
As you can see, the difference is titanic, and the ramdisk is very advantageous for tasks with large amounts of file writing.
To remove the ramdisk, just unmount it by running the following command and replacing tmp with your mount point:
Creating a Ramdisk in Linux Using Ramfs:
The procedure to create a ramdisk using ramfs is the same as with tmpfs. The following command will create a dynamic ramdisk on the mount point /mnt/tmp.
Tmpfs vs. Ramfs:
Now let’s test the ramfs performance against tmpfs, and let’s see what happens when each ramdisk type reaches the defined limit.
In the first example, I will create a 2GB ramdisk using tmpfs, and I will try to copy a bigger iso inside:
As you can see, the cp returned an error because the ramdisk space isn’t enough for the iso image. I only assigned 2GB for the ramdisk.
Now, see what happens when I do the same procedure using ramdisk:
As you can see, the ramfs kept writing into /mnt/tmp even though I have defined a 2GB limit. This is ramfs disadvantage because it may hang a system by consuming all its RAM memory. On the contrary, tmpfs is limited to the memory amount we define.
You can also see in the output that the copying task was done within 0:9.624s, almost the same performance shown by tmpfs in the test against SSD.
Note: The same iso image was used.
Conclusion
Creating a ramdisk is a one-minute process with significant benefits for any user who needs to process big files. The reading and writing speed increase exponentially over the best hard disks in the market. Portable software can be executed from a ramdisk, though changes won’t be persistent. This implementation is being highly appreciated by media editors whose tasks require long periods of media conversion.
Using ramfs may be risky if the system runs out of resources. That’s why tmpfs became the first method.
I hope this tutorial to create a ramdisk in Linux was useful. Keep following Linux Hint for more Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.
How to Create and Use a Ramdisk on Ubuntu 18.04
Create a folder to use as a mount point for your RAM disk. Then use the mount command to create a RAM disk. Substitute the following attirbutes for your own values: [TYPE] is the type of RAM disk to use; either tmpfs or ramfs.
How do I use ramdisk?
- Install DataRAM RAMDisk. Just click next and «I agree» at the various prompts. .
- Launch RamDisk Configuration Utility from the Start Menu.
- Set the RAMDisk Size and Type under the settings tab. .
- Enable Load Disk Image at Startup under the Load and Save tab. .
- Configure the Save Image Settings. .
- Click Start RAMDisk.
How do you mount a ramdisk?
Edit /etc/fstab file. x-gvfs-show will let you see your RAM disk in file manager. Save and close the file. Your Linux system will automatically mount the RAM disk when your computer boots up.
How do I mount a ramdisk image in Linux?
- Extract the initrd image from the gzip archive. ? gunzip ramdisk.image.gz.
- Mount the initrd image. ? chmod u+rwx ramdisk.image. mkdir tmp_mnt/ sudo mount -o loop ramdisk.image tmp_mnt/ cd tmp_mnt/
- Make changes in the mounted filesystem.
- Unmount the initrd image and compress the image.
What is a RamDisk in Linux?
In computing (specifically as regards Linux computing), initrd (initial ramdisk) is a scheme for loading a temporary root file system into memory, which may be used as part of the Linux startup process. . Both are commonly used to make preparations before the real root file system can be mounted.
What is Ramfs in Linux?
Ramfs is a very simple FileSystem that exports Linux’s disk cacheing mechanisms (the page cache and dentry cache) as a dynamically resizable ram-based filesystem. Normally all files are cached in memory by Linux. . Basically, you’re mounting the disk cache as a filesystem.
Is ramdisk faster than SSD?
Even if you’re already rocking a fast SSD (one of the best upgrades you can make), you can still improve your computer’s performance by adding more memory and turning it into a RAM disk, which can be as much as 70 times faster than a regular hard drive or 20 times faster than an SSD.
Is RAM faster than NVMe?
Since most data is not bulk but bits, it is more important how fast the data is accessed than it is how much it can carry in one trip. . This means that RAM can serve up data in memory 1000 times faster than a NVMe drive even though the file size they can carry is about the same.
Can you convert memory to RAM?
CONVERT MEMORY TO RAM :- Allow you to convert yout internal memory to Ram, which will Allow you to fast your device and play some extra games in your android device. In this Application you can make your android Device fast . you can Increase Your RAM upto 2 Gb , for Optimal Performance.
How do I mount a tmp?
- Prepare new disk for /tmp. Create LV on new disk (pvcreate, lvcreate) .
- Copy data from /tmp directory to the new disk. .
- Reboot server into single-user mode.
- Prepare new /tmp mount point. .
- Reboot server normally.
- Log in and check /tmp is mounted as the sperate mount point.
How do I mount Tmpfs fstab?
Under systemd, /tmp is automatically mounted as a tmpfs, if it is not already a dedicated mountpoint (either tmpfs or on-disk) in /etc/fstab . To disable the automatic mount, mask the tmp. mount systemd unit.
When should I use ramdisk?
Whether you have a hard drive or an SSD, your computer’s RAM is it’s fastest storage medium by a wide margin. If you have at least 4GB of memory, you can use this speed to your advantage, turning some of it into a small RAMDisk.
Module
OS Module Common Functionschdir()getcwd()listdir()mkdir()makedirs()rmdir()removedirs()Which module of Python gives methods related to operating system.
Linux
MX Linux. MX Linux tops the list thanks to its high stability, elegant and efficient desktop, and also an easy learning curve.Manjaro. . Linux Mint.
Prometheus
Install and Configure Prometheus on CentOS 7Step 1 – Update System. yum update -y.Step 2 – Disable SELinux. . Step 3 – Download Prometheus package. .
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system