- What is repository server?
- What does a repository do?
- What is repository server in Linux?
- What is repository example?
- What is a repository on the Internet?
- What is a Repository
- What is called repository?
- What is a common repository?
- Is SQL a repository?
- How do I use crud repository?
- What is a repository drug?
- How do I setup a server for repository?
- What are the three kinds of repositories in Linux?
- How do I find my yum repository?
- What is a repository system?
- How do repositories work?
- Why is repository important?
- What is the use of crud repository?
- What is a crud repository?
- What is the use of JPA repository?
- What are different types of repositories?
- Creating a Yum Repository Server for Red Hat and CentOS
- Install Createrepo
- Create the Repository
- Prepare Repository Directory
- Initialize The Repository
- Updating a Repository
- Mirror a Base Repository
- Using the ISO or Installation Disc
- Mirroring an Online Base Repository
- Publish Your Local Repository
- Over HTTP using Apache
- Over FTP using VSFTPD
- Configure Repository on Client
- Related Posts:
- Republish This Article
- RECOMMENDED BOOKS
- Recent Posts
- Tags
- Recent Comments
What is repository server?
The Repository Server is the place for coursework and projects that use databases or Java Server Pages (JSP) and last one quarter. That means that during the quarter, you may use this server for your coursework, but after the quarter ends, any information stored on this server will be deleted.
What does a repository do?
Repositories are classes or components that encapsulate the logic required to access data sources. They centralize common data access functionality, providing better maintainability and decoupling the infrastructure or technology used to access databases from the domain model layer.
What is repository server in Linux?
A Linux repository is a storage location from which your system retrieves and installs OS updates and applications. Each repository is a collection of software hosted on a remote server and intended to be used for installing and updating software packages on Linux systems. . Repositories contain thousands of programs.
What is repository example?
The definition of a repository is a place where things are stored for safe keeping, or where there is an ample supply of something, or a person or thing with a lot of information about something. A building where weapons are stored is an example of a repository for weapons.
What is a repository on the Internet?
In information technology, a repository is «a central place in which an aggregation of data is kept and maintained in an organized way, usually in computer storage.» It «may be just the aggregation of data itself into some accessible place of storage or it may also imply some ability to selectively extract data.»
What is a Repository
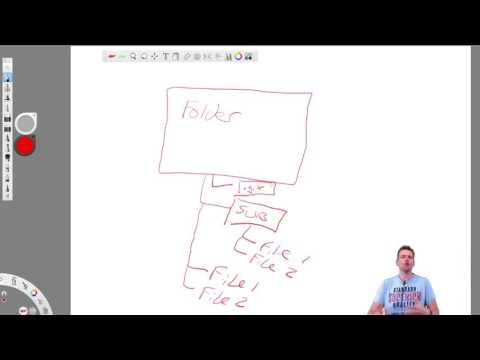
44 related questions found
What is called repository?
a receptacle or place where things are deposited, stored, or offered for sale: a repository for discarded clothing. an abundant source or supply; storehouse: a repository of information. a burial place; sepulcher. a person to whom something is entrusted or confided.
What is a common repository?
The Common Repository is a solution that is hosted at the data centre of the EMA. It is implemented within the context of the introduction of electronic submissions, as part of the human centralised procedure for the marketing authorisation of medicinal products in the European market.
Is SQL a repository?
An SQL database provides fast, scalable storage and retrieval of persistent information. The SQL repository works with an SQL database to store objects and make those objects visible inside an ATG application as Dynamic Beans. The uses of an SQL repository can be as varied as the uses of a relational database.
How do I use crud repository?
It provides generic Crud operation on a repository. If we want to use CrudRepository in an application, we have to create an interface and extend the CrudRepository. where, T is the domain type that repository manages.
.
For example:
What is a repository drug?
A drug repository program is a program that receives eligible donated drugs to provide to patients who have no reasonable financial means to pay for the drug or who are patients of a nonprofit clinic.
How do I setup a server for repository?
- Log onto the client computer.
- Navigate to the directory hosting the Yum repository configuration files. cd /etc/yum.repos.d.
- Create a configuration file for your local repository. nano local.repo.
- Save your changes and exit the text editor.
What are the three kinds of repositories in Linux?
- Main — Canonical-supported free and open-source software.
- Universe — Community-maintained free and open-source software.
- Restricted — Proprietary drivers for devices.
- Multiverse — Software restricted by copyright or legal issues.
How do I find my yum repository?
Run command yum repolist and it will show you all repositories configured under YUM and enabled for use on that server. To view, disabled repositories or all repositories refer below section in this article. In the above output, you can see the repo list with repo id, repo name, and status.
What is a repository system?
In software development, a repository is a central file storage location. It is used by version control systems to store multiple versions of files. While a repository can be configured on a local machine for a single user, it is often stored on a server, which can be accessed by multiple users.
How do repositories work?
A repository is usually used to organize a single project. Repositories can contain folders and files, images, videos, spreadsheets, and data sets – anything your project needs. We recommend including a README, or a file with information about your project.
Why is repository important?
Repositories provide a method of sharing content for different audiences. For example research outputs such as publications and data are not only used by other researchers but are also important resources for students. Research outputs as well as learning objects are important parts of the learning lifecycle.
What is the use of crud repository?
CrudRepository is a Spring Data interface for generic CRUD operations on a repository of a specific type. It provides several methods out of the box for interacting with a database. In this tutorial, we’ll explain how and when to use the CrudRepository save() method.
What is a crud repository?
CrudRepository is a Spring data interface and to use it we need to create our interface by extending CrudRepository for a specific type. Spring provides CrudRepository implementation class automatically at runtime. It contains methods such as save , findById , delete , count etc.
What is the use of JPA repository?
The Java Persistence API (JPA) is the standard way of persisting Java objects into relational databases. The JPA consists of two parts: a mapping subsystem to map classes onto relational tables as well as an EntityManager API to access the objects, define and execute queries, and more.
What are different types of repositories?
- Flat directory repository.
- Maven Central repository.
- JCenter Maven repository.
- Google Maven repository.
- Local Maven repository.
- Custom Maven repositories.
- Custom Ivy repositories.
- Supported metadata sources.
Creating a Yum Repository Server for Red Hat and CentOS
There are many reasons why you may want to have a local repository for your Red Hat or CentOS servers. You may be in an isolated network that has no connection to the outside world, yet you still want to keep your servers up-to-date or have all of the default packages available. Another may be that you develop and maintain your own software and need a central location to store it, where other servers can easily access it.
This tutorial will show you how to configure a Yum repository server. And I promise, it is actually really simple. There are a few ways to give your other servers access to it, including HTTP, FTP, and NFS.
Install Createrepo
To create and intialize your Yum repository, you must first download and install the createrepo package – available from the default CentOS repos. If you do not have access to the Internet, you can install by using the Red Hat or CentOS installation disc as a repository.
Create the Repository
Prepare Repository Directory
Your repository needs a directory where the package are stored. Ideally, you will want the repository to be in its own volume, and preferably on its own disk. For the purpose of showing how to create a repo, I’ll just be adding it to the root volume. My repository will created in /repos/CentOS/6/5/. When dealing with multiple Red Hat based distributions and versions, it’s best to create a directory structure that’s easy to understand and manage.
- Create a new directory for the repository.
mkdir -p /repos/CentOS/6/5/Packages
Initialize The Repository
Repositories use a simple database to keep track of all the packages and their dependancies. This is how it can provide you with all the packages required to be installed so quickly. The initialization step creates the database and prepares the directory to host the repository, allowing clients to connect to it.
- Initialize the repository.
Updating a Repository
Not all repositories are stagnant. Usually you will want to add new packages or package updates. Adding them to your Packages directory isn’t enough to make it available to clients. You also need to update the repositorie’s package database.
- Add new packages to the repositories Package directory.
- Update the repository’s database.
createrepo --update /repos/CentOS/6/5
Mirror a Base Repository
Using the ISO or Installation Disc
The installation disc for Red Hat and CentOS comes with an entire library of the base packages, which mirrors the online repository. The packages will be out of date, but you can update them later on yourself. Seeding your repository using the installation disc is the easist way to create a base repository.
- Mount the installation disc or ISO.
- Copy the packages on the disc to your repository. As an example, I’ve mounted my disc to /media/CentOS.
cp -arv /media/CentOS/Packages/* /repos/CentOS/6/5/
Mirroring an Online Base Repository
Another approach is to download the packages from the online repository. This will ensure you have the most up-to-date versions of the packages for your repository.
- Find the an existing mirror by going to http://centos.org/download/mirrors/. Look for a site near you and grab the address under the Rysnc Location column. As an example, I’ll be using a Univerity near my location.
- Use Rsync to download the entire repository. I am only interested in CentOS 6.5, so I’m targeting the directory for it at the local university.
rsync -rz --progress rsync://mirror.csclub.uwaterloo.ca/centos/os/x86_64/ /repos/CentOS/6/5/
Publish Your Local Repository
The repository is ready, but unless you publish the repository using HTTP or FTP you’re clients won’t be able to use it.
Over HTTP using Apache
ln -s /var/www/html/CentOS /repos/CentOS
Over FTP using VSFTPD
ln -s /var/ftp/public/CentOS /repos/CentOS
Configure Repository on Client
Our repository is now ready for your clients. Before they can access it, we need to create a Yum repository configuration file.
- Log onto the client computer.
- Navigate to the directory hosting the Yum repository configuration files.
[mylocalrepo] name=Local CentOS Repo baseurl=http://my-repo-server/CentOS/6/5 gpgcheck=0
Related Posts:
Republish This Article
We believe in the free flow of information. We use a Creative Commons license, so you can republish our articles for free, online or in print.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS
Continuous Delivery should be considered the bible for anyone in Ops, Dev, or DevOps. The book provides key strategies for improving system reliability, configuration management, and ensuring web applications can be delivered to production frequently, and easily. A recommended buy for anyone in IT.
Recent Posts
Tags
Recent Comments
- Manoel Campos da Silva Filho on How to Set Default Maven and Java settings per Project
- Fauzi Hassan on How to set the Proxy for Docker on Ubuntu
- Yassine Akermi on How to Reset Jenkins Admin users Password
- István Siroki on How to Configure Networking in Ubuntu 20.04 with NetPlan
- Mihamina Rakotomandimby on How to Reset Jenkins Admin users Password