- The Basics of RPM — Red Hat Package Management [Linux 101]
- What are the basic components of RPM?
- What package manager does Red Hat use?
- How do I run an RPM on Redhat Linux?
- How do I know if RPM is installed on Linux?
- How do I calculate RPM?
- What are the two parts of an RPM package in Linux?
- What is RPM also explain the benefits of RPM?
- Why do we need rpm?
- What is difference between RPM and Yum in Linux?
- What is sudo yum?
- What does yum stand for?
- Linux package management with YUM and RPM
The Basics of RPM — Red Hat Package Management [Linux 101]
RPM Package Manager (RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager, now a recursive acronym) is a free and open-source package management system. . RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base.
What are the basic components of RPM?
A set of components packed with the RPM engine is also called an RPM and is also packed with the following data: Date, time, version, release, and environment (such as Intel or zSeries)
What package manager does Red Hat use?
YUM is the primary package management tool for installing, updating, removing, and managing software packages in Red Hat Enterprise Linux. YUM performs dependency resolution when installing, updating, and removing software packages. YUM can manage packages from installed repositories in the system or from .
How do I run an RPM on Redhat Linux?
- How to Install . rpm File. Use rpm command to install any packages on Redhat based systems. .
- Upgrade . rpm Package. Use “-U” command line switch to upgrade the current packages installed on your system. .
- Remove . rpm Package.
How do I know if RPM is installed on Linux?
- If you are on a RPM-based Linux platform (such as Redhat, CentOS, Fedora, ArchLinux, Scientific Linux, etc.), here are two ways to determine the list of packages installed. Using yum:
- yum list installed. Using rpm:
- rpm -qa. .
- yum list installed | wc -l.
- rpm -qa | wc -l.
How do I calculate RPM?
How to Calculate Motor RPM. To calculate RPM for an AC induction motor, you multiply the frequency in Hertz (Hz) by 60 — for the number of seconds in a minute — by two for the negative and positive pulses in a cycle. You then divide by the number of poles the motor has: (Hz x 60 x 2) / number of poles = no-load RPM.
What are the two parts of an RPM package in Linux?
- The package file used to install the packaged software. This is sometimes called the binary package.
- The package file containing the source code and other files used to create the binary package file. This is known as the source RPM package file.
What is RPM also explain the benefits of RPM?
RPM is a package management system that bundles software source code or binaries together for easy installation on a computer. These files are tracked and allow for easy installation, upgrading, and removal.
Why do we need rpm?
RPM is a powerful software manager which can be used to build, install, query, verify, update, and uninstall individual software packages. An RPM package consists of an archive of files, and package information such as name, version, a description and information about dependencies on other RPM packages.
What is difference between RPM and Yum in Linux?
The major differences between YUM and RPM are that yum knows how to resolve dependencies and can source these additional packages when doing its work. Though rpm can alert you to these dependencies, it is unable to source additional packages. As to installing vs. upgrading.
What is sudo yum?
Yum is an automatic updater and package installer/remover for rpm systems. It automatically computes dependencies and figures out what things should occur to install packages. It makes it easier to maintain groups of machines without having to manually update each one using rpm.
What does yum stand for?
The Yellowdog Updater, Modified (YUM) is a free and open-source command-line package-management utility for computers running the Linux operating system using the RPM Package Manager. Though YUM has a command-line interface, several other tools provide graphical user interfaces to YUM functionality.
Disable Save to Pocket for FirefoxType about:config in the address bar and press Enter. A warning page may appear. Click. I accept the risk! . Type .
Theme
How to Make Your Own Windows 10 ThemeOpen the Start menu and select Settings.Choose Personalization from the settings screen.Change one or more of the.
Notifications
Make your favorite app’s notifications top priority, and you’ll always see its new notifications at the top of action center. Go to Settings > Syst.
Fresh articles, interesting news and useful guides from the world of modern technologies. We know everything about computers and gadgets that you encounter every day
Linux package management with YUM and RPM
Installing, patching, and removing software packages on Linux machines is one of the common tasks every sysadmin has to do. Here is how to get started with Linux package management in Linux Red Hat-based distributions (distros).
Package management is a method of installing, updating, removing, and keeping track of software updates from specific repositories (repos) in the Linux system. Linux distros often use different package management tools. Red Hat-based distros use RPM (RPM Package Manager) and YUM/DNF (Yellow Dog Updater, Modified/Dandified YUM).
Yellow Dog Updater, Modified (YUM)
[ Editor’s Note: DNF or Dandified YUM is the updated default since Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, CentOS 8, Fedora 22, and any distros based on these. Generally, the options are the same. Read more about DNF here. ]
YUM is the primary package management tool for installing, updating, removing, and managing software packages in Red Hat Enterprise Linux. YUM performs dependency resolution when installing, updating, and removing software packages. YUM can manage packages from installed repositories in the system or from .rpm packages. The main configuration file for YUM is at /etc/yum.conf , and all the repos are at /etc/yum.repos.d .
You can learn more about adding repositories to your system from this article on how to add a YUM repo from Amy Marrich.
It’s easy to manage packages in Linux with YUM . At the command line, enter:
There are many options and commands available to use with YUM . I’ve listed some commonly-used commands for YUM below:
| Command | Purpose |
| yum install | Installs the specified packages |
| remove | Removes the specified packages |
| search | Searches package metadata for keywords |
| info | Lists description |
| update | Updates each package to the latest version |
| repolist | Lists repositories |
| history | Displays what has happened in past transactions |
The following are commonly-used options with YUM :
| Options | Purpose |
| -C | Runs from system cache |
| —security | Includes packages that provide a fix for a security issue |
| -y | Answers yes to all questions |
| —skip-broken | Skips packages causing problems |
| -v | Verbose |
The history option gives you an overview of what happened in past transactions. This provides some useful information, like the date when the transaction happened and what command was run.
You can undo or redo certain transactions using the history command. Here is an example of undoing a transaction:
YUM provides many options for package management. For detailed option information, look at man yum and yum –help . Also, here is a link to YUM documentation.
RPM is a popular package management tool in Red Hat Enterprise Linux-based distros. Using RPM , you can install, uninstall, and query individual software packages. Still, it cannot manage dependency resolution like YUM . RPM does provide you useful output, including a list of required packages. An RPM package consists of an archive of files and metadata. Metadata includes helper scripts, file attributes, and information about packages.
RPM maintains a database of installed packages, which enables powerful and fast queries. The RPM database is inside /var/lib , and the file is named __db* .
RPM has some basic modes: query, verify, install, upgrade, erase, show querytags, show configuration. At least one of these modes needs to be selected to perform package management tasks. Every mode has its own set of options. For example, install mode i has its own set of installation options. Options for the modes are found on the RPM man pages at man rpm .
Some commonly-used modes are listed below:
| Mode | Description |
| -i | Installs a package |
| -U | Upgrades a package |
| -e | Erases a package |
| -V | Verifies a package |
| -q | Queries a package |
Here are some commonly-used general options:
| General options | Purpose |
| -? | —help | Prints help |
| —version | Prints version number |
| -v | Prints verbose output |
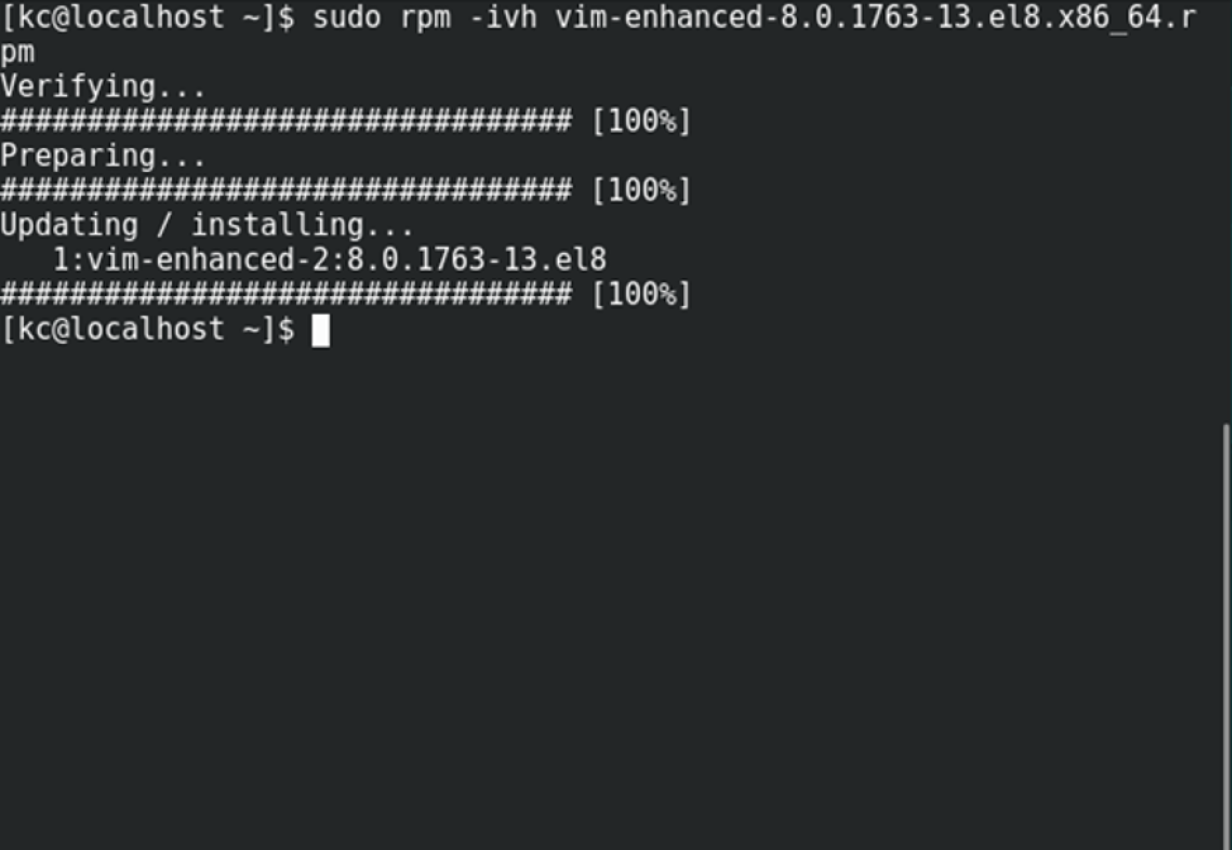
To install or upgrade an .rpm package using RPM, issue this command:
The flag -i is for install, U is for upgrade, v for verbose, h for hash (this option displays the # as a progress bar for the operation). In this example, v and h are optional flags.
To query for a package using RPM issue following command:
rpm -q query-options package
Option a queries all installed packages on the system.
To erase a package, use the following command:
rpm -e erase-options package-name
Package management is a common task for every system. YUM and RPM provide efficient ways to install, upgrade, remove, and track software packages on Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems.
[ Want to try out Red Hat Enterprise Linux? Download it now for free. ]