- The Linux / run directory
- What is run folder in Linux?
- What is in the run directory?
- What is run used for in Linux?
- What is the SRV folder in Linux?
- What is run user?
- How do I run a directory in Linux?
- How do you open a file in Linux?
- How do I run a Linux file?
- Where is sbin in Linux?
- What is MNT in Linux?
- What is TMP in Linux?
- What is bin sh Linux?
- What is enable linger?
- How do I see users in Linux?
- What is run user in Linux?
- What are .run files?
- 2 Answers 2
The Linux / run directory
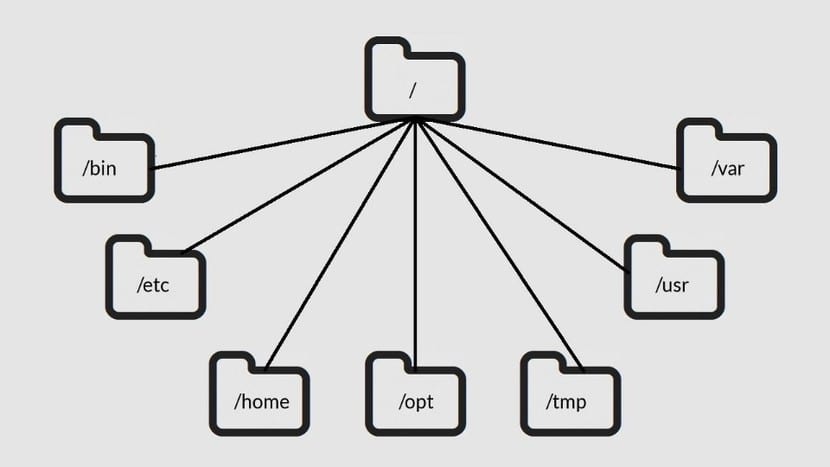
On other occasions I have already written about other interesting directories in LxA, even about the directory tree of GNU / Linux distributions. But this time, we are going to focus on a specific one. Its about / run directory, of which we are going to reveal all the details so that it does not have secrets for you. It may not be one of the most visited or popular directories, but it is quite important for the system .
The new / run directory represents a small change in how Linux works with respect to temporary data at runtime. The new directory replaces / var / run in current distros. Now, / var / lock will also be found in / run / lock and / dev / shm in / run / shm, among other changes. To keep everything working properly, symbolic links are used for these directories. That way, there are no apparent changes for the old programs that depend on them.
You can use the following command to get information about the occupied space:
This lets us see that it is about a directory marked as tmpfs, that is, temporary. It is not actually stored on the hard drive, but rather in main memory or RAM. If you go to the directory, you will see some subdirectories and files inside:
It is home to lots of data used at runtime. For example, you can see that inside / run / user there is a directory with a number for each user on the system:
If you access the directory corresponding to your user, you will see that it contains data that the current running processes. Some have a * .pid extension with the name of the process to which they correspond. Like gdm3.pid, sshd.pid, etc. I invite you to use the concatenator to see the content of one of them. For example:
And it will show the PID corresponding to said process. You can keep exploring other interesting ones like / run / sudo, / run / sshd, etc. As you can see, everything that is currently running has some residual or temporary data there .
The content of the article adheres to our principles of editorial ethics. To report an error click here.
Full path to article: Linux Addicts » GNU / Linux » The Linux / run directory
What is run folder in Linux?
The /run directory is the companion directory to /var/run . Like for example /bin is the companion of /usr/bin .
What is in the run directory?
This directory contains system information data describing the system since it was booted. Files under this directory must be cleared (removed or truncated as appropriate) at the beginning of the boot process. The purposes of this directory were once served by /var/run .
What is run used for in Linux?
/run is the “early bird” equivalent to /var/run , in that it’s meant for system daemons that start very early on (e.g. systemd and udev ) to store temporary runtime files like PID files and communication socket endpoints, while /var/run would be used by late-starting daemons (e.g. sshd and Apache).
What is the SRV folder in Linux?
The /srv/ Directory. The /srv/ directory contains site-specific data served by your system running Red Hat Enterprise Linux. This directory gives users the location of data files for a particular service, such as FTP, WWW, or CVS. Data that only pertains to a specific user should go in the /home/ directory.

What is run user?
/run/user/$uid is created by pam_systemd and used for storing files used by running processes for that user. These might be things such as your keyring daemon, pulseaudio, etc. Prior to systemd, these applications typically stored their files in /tmp .
How do I run a directory in Linux?
To navigate to your home directory, use “cd” or “cd ~” To navigate up one directory level, use “cd ..” To navigate to the previous directory (or back), use “cd -” To navigate through multiple levels of directory at once, specify the full directory path that you want to go to.
How do you open a file in Linux?
Following are some useful ways to open a file from the terminal:
- Open the file using cat command.
- Open the file using less command.
- Open the file using more command.
- Open the file using nl command.
- Open the file using gnome-open command.
- Open the file using head command.
- Open the file using tail command.
How do I run a Linux file?
To execute a RUN file on Linux:
- Open the Ubuntu terminal and move to the folder in which you’ve saved your RUN file.
- Use the command chmod +x yourfilename. run to make your RUN file executable.
- Use the command ./yourfilename. run to execute your RUN file.

Where is sbin in Linux?
/sbin is a standard subdirectory of the root directory in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that contains executable (i.e., ready to run) programs. They are mostly administrative tools, that should be made available only to the root (i.e., administrative) user.
What is MNT in Linux?
This is a generic mount point under which you mount your filesystems or devices. Mounting is the process by which you make a filesystem available to the system. After mounting your files will be accessible under the mount-point. Standard mount points would include /mnt/cdrom and /mnt/floppy. …
What is TMP in Linux?
In Unix and Linux, the global temporary directories are /tmp and /var/tmp. Web browsers periodically write data to the tmp directory during page views and downloads. Typically, /var/tmp is for persistent files (as it may be preserved over reboots), and /tmp is for more temporary files.
What is bin sh Linux?
/bin/sh is an executable representing the system shell and usually implemented as a symbolic link pointing to the executable for whichever shell is the system shell. The system shell is basically the default shell that the script should use.
What is enable linger?
Enable/disable user lingering for one or more users. If enabled for a specific user, a user manager is spawned for the user at boot and kept around after logouts. This allows users who are not logged in to run long-running services. Takes one or more user names or numeric UIDs as argument.
How do I see users in Linux?
How to List Users in Linux
- Get a List of All Users using the /etc/passwd File.
- Get a List of all Users using the getent Command.
- Check whether a user exists in the Linux system.
- System and Normal Users.
What is run user in Linux?
runuser can be used to run commands with a substitute user and group ID. If the option -u is not given, runuser falls back to su-compatible semantics and a shell is executed.
What are .run files?
What exactly are .run files and what are they used for? I’ve seen a couple of those lately and I’m simply wondering what file format it is used for.
2 Answers 2
A .run file is normally a custom made program which needs to be executed in order to install a program. These are not supported generally as they don’t track where files go and don’t normally provide an uninstall method. there is no way to be sure what the script will do to your system so they’re considered unsafe.
They are close to the windows exe file and as such come with the same issues. If you know what you’re doing and are happy about taking the risks, you can execute them with these commands:
chmod 755 programinstall.run sudo ./programinstall.run They are usually executables of some form. They’re not neccessarily installers although most of the ones you’ll see are.
As Martin says, and assuming we’re talking about an installer, they’re usually not as good as packages for when you want to remove them however there are some installers (I’m thinking mainly of the Loki and LGP game installers) do track where they install to and provide a pretty robust uninstall binary.
And what Martin says will work for most binaries, most .run files I’ve seen are hybrid shell script and compressed binary elements. This means you can just run them through sh . An example with the NVIDIA driver installer:
sudo sh NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-260.19.06.run You can check to see what a file really is (well it works most of the time) with file :
file NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-260.19.06.run NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-260.19.06.run: POSIX shell script text executable