- Best Task Managers for Linux
- Does Todoist work on Linux?
- What is the standard console Task Manager in Linux?
- What Linux command is similar to Windows Task Manager?
- Does Ubuntu have a task manager?
- How do I show Task Manager in Linux?
- How do I install Todoist on Ubuntu?
- How do I see CPU usage on Linux?
- How do you kill a process in Linux?
- How do I open Task Manager?
- What is the Ctrl Alt Del for Ubuntu?
- How do I open Task Manager in elementary OS?
- How do I open Task Manager in lubuntu?
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor the system
- How to install a task manager on Ubuntu to monitor the system
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor system processes
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor system resources
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor file systems
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor all system process
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor sorted processes
- How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to kill a process
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sharqa Hameed
- linux gui task manager
- Where is Task Manager in Linux?
- How do I get to the Task Manager in Ubuntu?
- How do I open Task Manager in terminal?
- How do you kill a process?
- What does Ctrl Alt Del do in Linux?
- What is the equivalent of Ctrl Alt Delete on Linux?
- How do I see CPU usage on Linux?
- How do I see running processes in Linux?
- How do I kill a process in Ubuntu?
- Is there a Ctrl Alt Delete for Ubuntu?
- How do I install a Linux monitor?
Best Task Managers for Linux
In Windows you can easily kill any task by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del and bringing up the task manager. Linux running the GNOME desktop environment (i.e. Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc.) has a similar tool that can be enabled to run exactly the same way.
Does Todoist work on Linux?
Prepare for a productivity boost because an official Todoist app for Linux desktops has been released.
What is the standard console Task Manager in Linux?
1. Top. “top” is one of the most common task managers used by Linux users. Unlike other tools, the top task-manager comes preinstalled on all Linux distributions.
What Linux command is similar to Windows Task Manager?
On every Linux-based system, we have a task manager equivalent named “System Monitor”. The “System Monitor” application shows all the running processes, their CPU consumption, memory information, and many more. However, we can also use the top command on terminal to get the processes’s information.
Does Ubuntu have a task manager?
You may want an Ubuntu equivalent of the Windows Task Manager and open it via Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination. Ubuntu has the built-in utility to monitor or kill system running processes which acts like the “Task Manager”, it’s called System Monitor.
How do I show Task Manager in Linux?
How to open Task Manager in Ubuntu Linux Terminal. Use Ctrl+Alt+Del for Task Manager in Ubuntu Linux to kill unwanted tasks and programs. Just like Windows have Task Manager, Ubuntu has a built-in utility called System Monitor which can be used to monitor or kill unwanted system programs or running processes.
How do I install Todoist on Ubuntu?
Installing Todoist on Linux
You can easily install it using the snap package manager. Make sure you have snapd support in your Linux distribution. Some distros like Ubuntu, KDE Neon, Manjaro, and Zorin has snapd pre-installed. However, many distributions do not have snap support by default so you have to set it up.
How do I see CPU usage on Linux?
- 1) Top. The top command displays real-time view of performance-related data of all running processes in a system. .
- 2) Iostat. .
- 3) Vmstat. .
- 4) Mpstat. .
- 5) Sar. .
- 6) CoreFreq. .
- 7) Htop. .
- 8) Nmon.
How do you kill a process in Linux?
- What Processes Can You Kill in Linux?
- Step 1: View Running Linux Processes.
- Step 2: Locate the Process to Kill. Locate a Process with ps Command. Finding the PID with pgrep or pidof.
- Step 3: Use Kill Command Options to Terminate a Process. killall Command. pkill Command. .
- Key Takeaways on Terminating a Linux Process.
How do I open Task Manager?
Hit Ctrl + Alt + Del and say that you want to run Task Manager. Task Manager will run, but it’s covered by the always-on-top fullscreen window. Whenever you need to see Task Manager, use Alt + Tab to select Task Manager and hold the Alt for a few seconds.
What is the Ctrl Alt Del for Ubuntu?
CTRL + ALT + DEL will bring you back to the default screen after 60 s, at least if the system hasn’t hung, and will pop up a window prompting to cancel or confirm log out. CTRL + ALT + ESC does nothing by default.
How do I open Task Manager in elementary OS?
To start htop you have to run htop in terminal. It can list all the processes with CPU/RAM usage, Overall CPU/RAM usage and more. It can also kill a process. You have to use up and down arrow keys to navigate.
How do I open Task Manager in lubuntu?
Open a terminal and run openbox —reconfigure . If you’ve done everything correctly (and if you haven’t already messed up the file), you should just get back the terminal prompt. Now, when you press Ctrl Alt Del , the task manager should open.
Code
How do I download Vscode Debian?How do I install Visual Studio code in terminal?How do I install Visual Studio on Linux?How do I run a Visual Studio c.
Mongodb
How do I download MongoDB for Mac?How do I start MongoDB on Mac?Where is MongoDB installed on Mac?How do I know if MongoDB is installed on Mac?How do .
Command
The following commands will get you the private IP address of your interfaces:ifconfig -a.ip addr (ip a)hostname -I | awk ‘print $1’ip route get 1.2. .
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor the system
Ubuntu beginners frequently ask: Is there any task manager in Ubuntu? If yes, then how we can use the task manager for monitoring the system.
Firstly, you should know what a task manager does. The task manager displays all currently active processes and their memory usage. It also manages processes and provides you the option of terminating or killing a process. Although an experienced Ubuntu user prefers the command-line method of locating processes and memory use, you do not have to use it when you are just getting started with Ubuntu. Instead, you can utilize the “System Monitor” that serves as a task manager in your Ubuntu system.
In this article, we will talk about how to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor the system. So let’s start!
How to install a task manager on Ubuntu to monitor the system
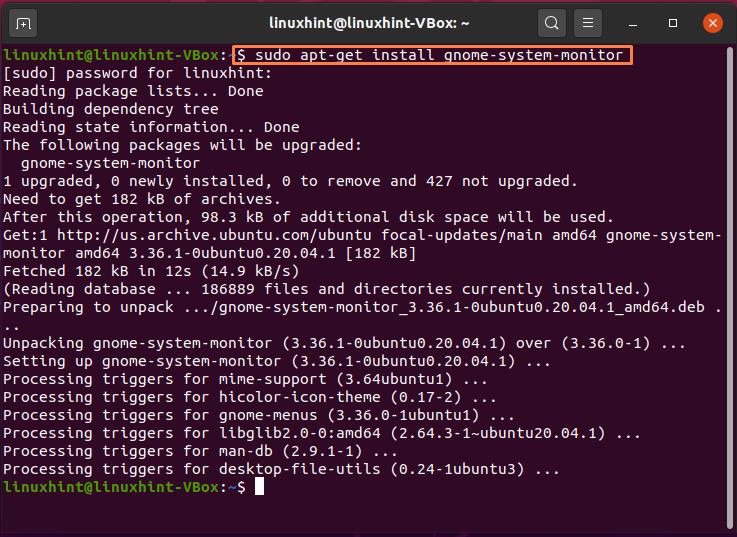
If you do not have a System Monitor in your Ubuntu system, then write out the below-given command for its installation:
After completing the installation, search “System Monitor” in the application’s search bar:
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor system processes
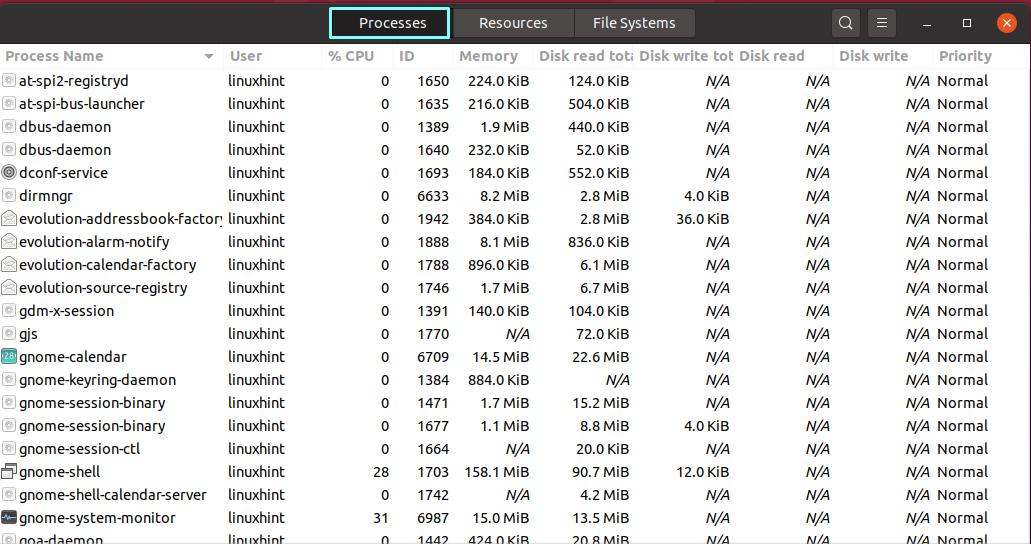
A process is a program that operates and runs in memory. It utilizes computer resources such as memory and CPU load. The “Processes” Tab is the first view you will see after opening the System Monitor in your Ubuntu. This view comprises a table with rows and columns of your active processes running on the system. It shows process information, including the CPU, memory usage, IDs, etc:
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor system resources
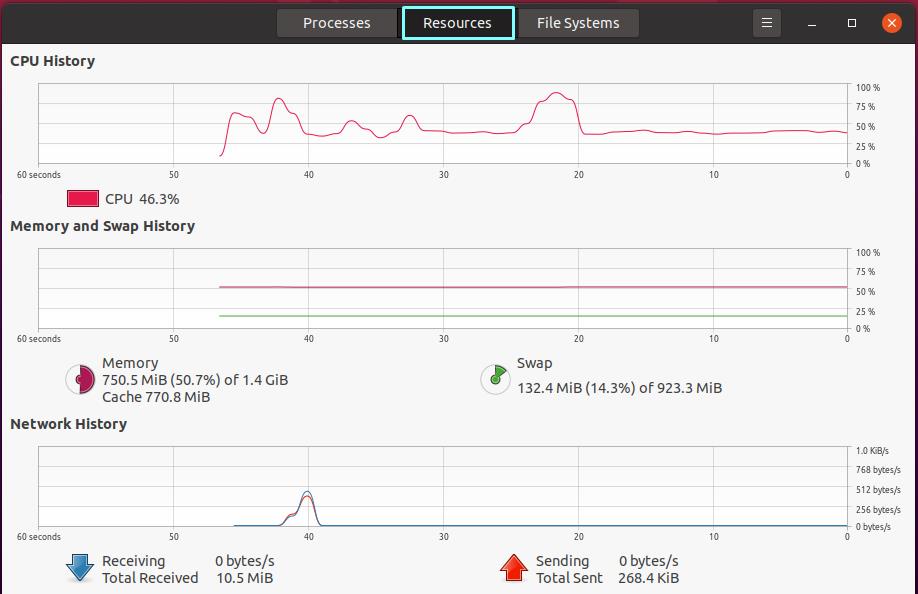
To monitor the system resources, click on the “Resources” tab in the middle of the three buttons at the top bar. There are three plots in this view: Network history, Memory and Swap history, and CPU history. The CPU history section shows a moving graph of processor loads over time and the percentages. Individual CPU cores will be displayed in various colors. Moving graphs and numbers in MB shows memory consumption as well as swap utilization. Network history shows the network consumption by the system resources:
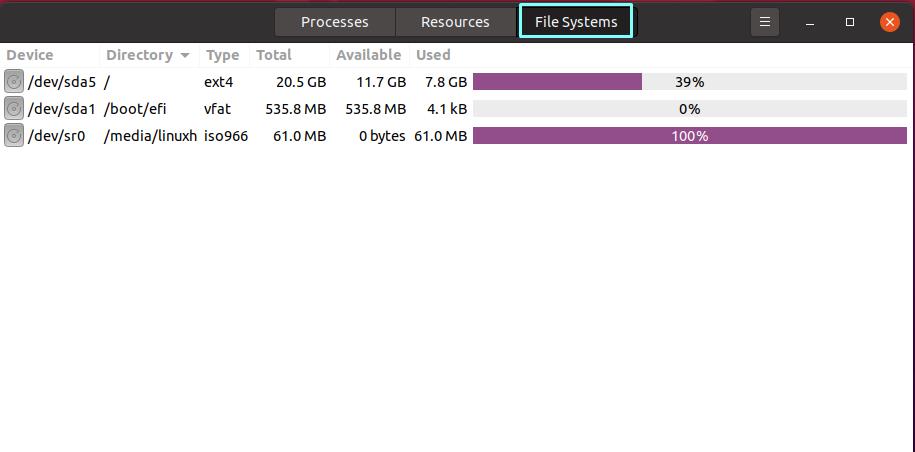
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor file systems
Click the File Systems tab next to Resources to monitor the files. File system view displays the hard disk drive that is currently installed in your system, as well as its partitions, total capacity, file system types, usage in MB or GB, as well as a percentage bar for each one. For example, the image below depicts a machine with one hard disk “sda” and two partitions, “sda5” and “sda1” formatted in EXT4 and VFAT file systems, with 20.5 GB and 535.8 MB respective size:
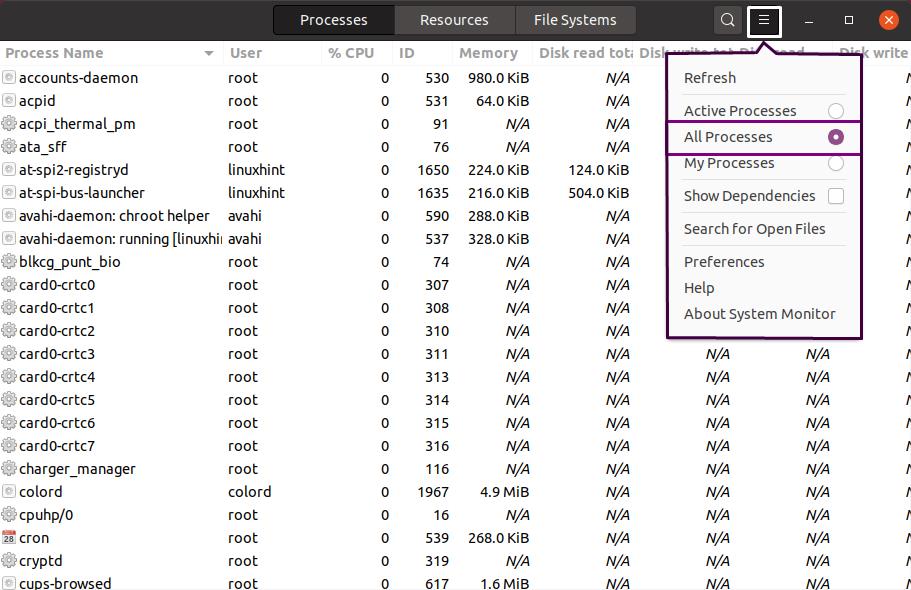
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor all system process
Typically, the Process tab displays the list of active processes on your system. If you want to explore all of the processes, then click on the Hamburger icon ≡, which is present next to the search button, and then select “All processes” from its context menu:
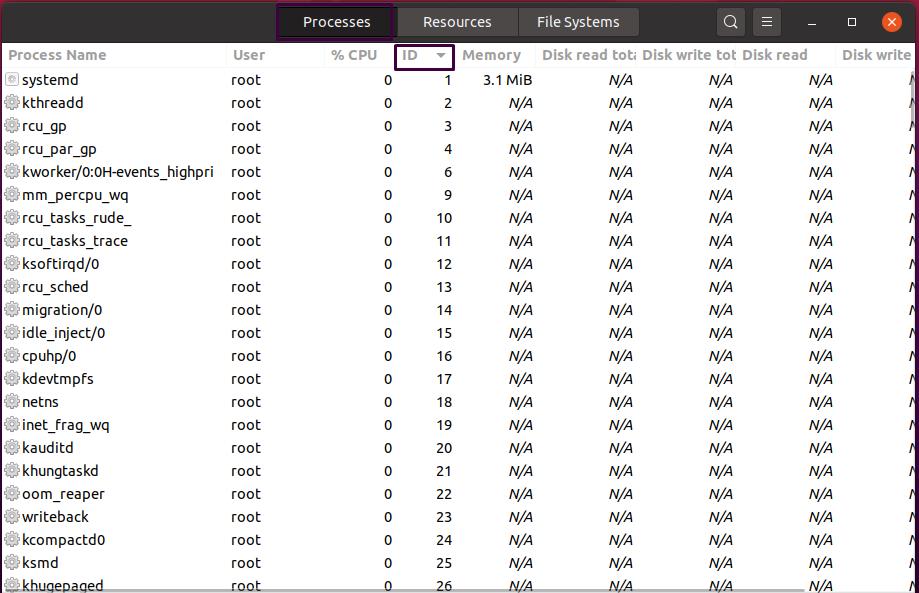
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor sorted processes
To sort out the processes based on their IDs, click on the ID column present at the top of this view. From the below-given example, you can see that we have sorted our system process in the way that the process with PID “1” is now on the top of the list:
How to use a task manager in Ubuntu to kill a process
If you want to kill an unresponsive process, you can easily do this operation with the help of a system monitor. To do so, select the required process and from the right-click context menu, click on the “Kill” option. You can also press “CTRL+K” to perform the same operation:
Conclusion
Ubuntu users can use System monitor, which serves as a task manager in their systems. System monitor has all the functionalities that a task Manager has in Windows. It can be used to view system processes, file systems, and resources. In Ubuntu, you can also utilize a System Monitor for killing an unresponsive process. I hope this post explaining how to use a task manager in Ubuntu to monitor the system was helpful.
About the author
Sharqa Hameed
I am a Linux enthusiast, I love to read Every Linux blog on the internet. I hold masters degree in computer science and am passionate about learning and teaching.
linux gui task manager
How to open Task Manager in Ubuntu Linux Terminal. Use Ctrl+Alt+Del for Task Manager in Ubuntu Linux to kill unwanted tasks and programs. Just like Windows have Task Manager, Ubuntu has a built-in utility called System Monitor which can be used to monitor or kill unwanted system programs or running processes.
Where is Task Manager in Linux?
You press Ctrl+Alt+Del to get to the task manager in Windows. This task manager shows you all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can choose to end a process from this task manager application. When you’re just starting out with Linux, you may look for a task manager equivalent on Linux as well.
How do I get to the Task Manager in Ubuntu?
You may want an Ubuntu equivalent of the Windows Task Manager and open it via Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination. Ubuntu has the built-in utility to monitor or kill system running processes which acts like the “Task Manager”, it’s called System Monitor.
How do I open Task Manager in terminal?
An easier way to open Task Manager is to press Ctrl + ⇧ Shift + Esc simultaneously. Once you open Command Prompt, you can run this command on any Windows computer to open Task Manager, though you may need to type taskmgr.exe instead on Windows XP.
How do you kill a process?
- What Processes Can You Kill in Linux?
- Step 1: View Running Linux Processes.
- Step 2: Locate the Process to Kill. Locate a Process with ps Command. Finding the PID with pgrep or pidof.
- Step 3: Use Kill Command Options to Terminate a Process. killall Command. pkill Command. .
- Key Takeaways on Terminating a Linux Process.
What does Ctrl Alt Del do in Linux?
On some Linux-based operating systems including Ubuntu and Debian, Control + Alt + Delete is a shortcut for logging out. On Ubuntu Server, it is used to reboot a computer without logging in.
What is the equivalent of Ctrl Alt Delete on Linux?
In the Linux console, by default in most distributions, Ctrl + Alt + Del behaves as in the MS-DOS — it restarts the system. In the GUI, Ctrl + Alt + Backspace will kill the current X server and start a new one, thus behaving like the SAK sequence in Windows ( Ctrl + Alt + Del ). REISUB would be the closest equivalent.
How do I see CPU usage on Linux?
- 1) Top. The top command displays real-time view of performance-related data of all running processes in a system. .
- 2) Iostat. .
- 3) Vmstat. .
- 4) Mpstat. .
- 5) Sar. .
- 6) CoreFreq. .
- 7) Htop. .
- 8) Nmon.
How do I see running processes in Linux?
- Open the terminal window on Linux.
- For remote Linux server use the ssh command for log in purpose.
- Type the ps aux command to see all running process in Linux.
- Alternatively, you can issue the top command or htop command to view running process in Linux.
How do I kill a process in Ubuntu?
- First select the process that you want to end.
- Click on the End Process button. You will get a confirmation alert. Click on “End Process” button to confirm that you want to kill the process.
- This is the simplest way way to stop (end) a process.
Is there a Ctrl Alt Delete for Ubuntu?
You can now use Ctrl + Alt + Del to launch the task manager on your Ubuntu system. That can be very useful in situations where your system has frozen, and you need to kill some applications forcefully.
How do I install a Linux monitor?
Install System Monitor through the UI
For a person who does not want to open the Command Line much, installing a software present in the Ubuntu repository through the UI is very simple. On your Ubuntu desktop Activities toolbar, click the Ubuntu Software icon. Click the Install button to begin the installation process.
Node
How To Install Node. js on Fedora 33/32/31Install Node. js from Default Package Repository. The Fedora default package repositories contains a stable .
Data
Convert XML to PHP Associative ArrayStep1: Create XML Data File. First we will create XML data file using following XML. . Step2: Read XML Data File.
Server
How to Install and Configure an NFS Server on Ubuntu 20.04Prerequisites.Set Up the NFS Server. Installing the NFS server. Creating the file systems. E.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system