- What is tty within Linux? [duplicate]
- What is TTY in Linux?
- History Behind the Term ‘TTY’
- The (relatively) Modern Concept
- So, What is TTY in Linux?
- How to Access TTY in Linux?
- When Would You Use TTY in Linux?
- TTY as a Command in Linux
- What Is TTY and How To Use It In Linux?
- TTY History
- TTY Types
- Hardware TTY
- Software TTY
- Linux TTY
- Open TTY In Silent Mode
- Navigate between TTYs In Linux Console
What is tty within Linux? [duplicate]
In the old days Teletypewriters were typewriters that translated what was typed locally on a mechanical typewriter into EBCDIC or ASCII codes and then transmitted over a cable to a remote computer. Hence the prefix «tele», which means «at a distance». The word «terminal» was sometimes used, because the teletype was the terminal end of the wire where data was entered and transmitted to the computer or receiving station. Each «tty» device was connected via a serial port, because copper wire was expensive and so «parallel» port devices were mainly used for short-distance interfaces like to a local printer. This is before wireless networks were widely used. In the old days of multi-user computer environments you could have multiple «terminal devices», i.e., ‘tty’ devices connected to the same central computer. This is the original hardware environment in which Unix was developed. That hardware legacy is still with us in the naming of the software components in the Linux operating system.
Today in Linux, the tty is a legacy name used to refer to the user interface for text-based input and output, otherwise known as a «terminal». In Linux systems, there can be multiple tty device «consoles», to support potentially dozens of serial ports or more. tty0 is the current one in use, but Linux allows you to switch to another session by changing to a different tty, e.g., tty1. Linux (e.g., Ubuntu) supports up to 6 ttys by default, but this number is configurable.
In practical terms, think of a tty as a serial communication channel that a Linux session uses to communicate with a user.
How it works is that there is a parsing process bound to the tty session that parses the user’s input and passes valid commands to the computer to execute.
What is TTY in Linux?
Sooner or later, you’ll come across the term tty while using Linux. Learn what it is and what is its significance.
You must have heard about the term “TTY” when it comes to Linux and UNIX. But, what is it? Is it useful to you as a desktop user? Do you need it? And, what can you do with it? In this article, let me mention everything essential to get you familiar with the term TTY in Linux. Do note that there’s no definitive answer to this, but it relates to how input/output devices interacted in the past. So, you will have to know a bit of history to get a clear picture.
History Behind the Term ‘TTY’
It all starts with a Teleprinter in the 1830s. Teleprinters let you send/receive text messages over the wire. It was a replacement to Morse code communication, where two operators were needed to effectively communicate with one another. And, a Teleprinter just needed a single operator to easily convey a message. While it did not have a modern-layout keyboard, its system was later evolved by Donald Murray in 1901 to include a typewriter-like keyboard. The Murray code reduced the effort for operators to send a message. And, this made it possible for a Teleprinter to evolve as a commercial Teletypewriter in 1908. TTY is shorthand for Teletypewriter. The difference between the Teletypewriter and a regular typewriter was that a Teletypewriter was attached to a communication device to send the typed message. Teletypewriter made it possible for humans to communicate faster over a wire without any computers until now. And, this is where “TTY” came into existence.
The (relatively) Modern Concept
Now, you must be wondering, how did it land into modern computing and in Linux? Well, for starters, when Teletypewriter hit the market, some years later semiconductor transistors were developed which then evolved into microprocessors making a computer possible. Initial computers didn’t have the concept of a keyboard. Punch cards were the input method. 

So, What is TTY in Linux?
When it comes to Linux, TTY is an abstract device in UNIX and Linux. Sometimes it refers to a physical input device such as a serial port, and sometimes it refers to a virtual TTY where it allows users to interact with the system (reference). TTY is a subsystem in Linux and Unix that makes process management, line editing, and session management possible at the kernel level through TTY drivers. In terms of programming, you need to dive in deep. But, considering the scope of this article, this could be an easy definition to digest. If you are curious, you can explore an old resource (TTY Demystified) that tries to clear up TTY in Linux and Unix systems with all the technical details you need. In fact, whenever you launch a terminal emulator or use any kind of shell in your system, it interacts with virtual TTYs that are known as pseudo-TTYs or PTY. You can just type in TTY in your terminal emulator to find the associated PTY.
How to Access TTY in Linux?
CTRL + ALT + F2 – Desktop Environment
CTRL + ALT + F3 – TTY3
CTRL + ALT + F4 – TTY4
CTRL + ALT + F5 – TT5
CTRL + ALT + F6 – TTY6 You can access up to six TTYs in total. However, the first two shortcuts point to the distribution’s lock screen and the desktop environment. 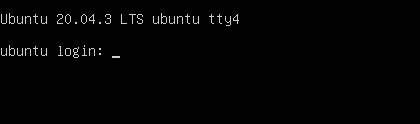
When Would You Use TTY in Linux?
TTY is not just a technical treasure. It is useful even for users like me who aren’t developers. It should come in handy in case the graphical desktop environment freezes. In some cases, reinstalling the desktop environment from the TTY helps resolve the program. Or, you can also choose to carry out tasks in TTY like updating the Linux system and similar, where you do not want visual issues to interrupt your process. Worst-case scenario, you can go to the TTY and reboot the computer if your graphical user interface is unresponsive. Some users also prefer to perform large file transfers with the help of TTY (I am not one of them).
TTY as a Command in Linux
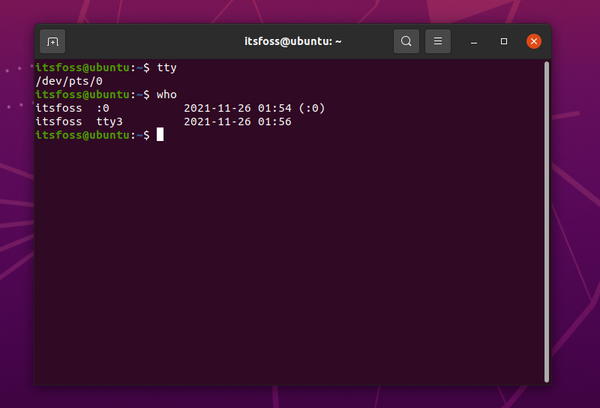
When you type in TTY in your terminal emulator, it will print the file name of the terminal connected to the standard input, as described by the man page. In other words, to know the TTY number you are connected to, just type in TTY. And, if there are multiple users connected to the Linux machine remotely, you can use the who command to check what other users are connected to.
What Is TTY and How To Use It In Linux?
TTY or Tele Type Writer is a device that is used to provide input into the destination system. TTY is a generic term that is used for different hardware and software for different systems.
TTY History
First TTYs are created in the 1830s with the name of teleprinters. Teleprinters were hardware devices that are used to get input from the user and send this input into remote locations. Over years different types of TTY are created for different use methods and cases. Modern TTY’s are used with computers in order to input and output them.
TTY Types
TTY devices are used to input and output in a simple matter into a system or computer. While input/output process the data is typed -> encoded -> sent -> received by the destination system -> decoded and printed. There are two types of TTY devices called “Hardware TTY” and “Software TTY“.
Hardware TTY
Hardware TTY is a hardware device that contains keys and a monitor in order to send input into the remote system and print returned data in the monitor. Between the 1960s and 1990s mainframes are used the hardware TTYs. There are protocols used to transmit data which is input and output between hardware TTY and the remote system. These protocols are DEC VT05, DECVT100, etc.
Software TTY
Software TTY is a software which provides the function of the TTY. Software TTY is a emulator which is used in Linux, Unix and BSD systems to use them like a main frame. Linux provides the tty command.
Linux TTY
Linux is the derivative of the Unix operating system. Terminals and hardware TTY was very popular with the Unix operating system. Linux provides the same even more advenced experience with the TTY where it provides the tty tool and console access. Linux tty is a pseudo-teletype which is also called as PTS. The PTS is a device and located under the “/dev/pts”. For example the first TTY is named as “/dev/pts/0“.
We can get the current TTY number and device with the tty command like below.
Open TTY In Silent Mode
The tty provides the silent mode where no output is generated. The -s option is provided for the silent console.
Navigate between TTYs In Linux Console
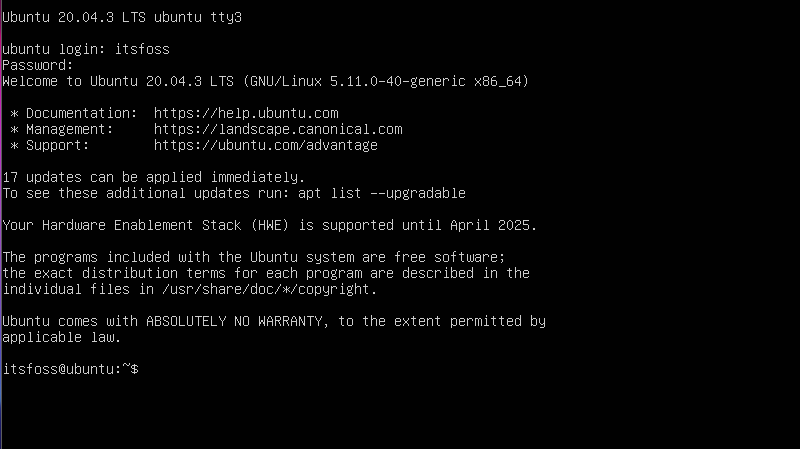
Linux provides multiple consoles where one or two consoles are GUI simply a desktop environment. Other consoles are TTY consoles which are command-line consoles like below. For example, when we press CTRL+ALT+F3 keys at the same time we will see the following tty console which is named tty3.
Also, numbers from F1 to F7 can be used to get different Linux console. Generally, F1 and F2 provide the desktop environment and other consoles are text-based consoles simply command-line interfaces.
- CTRL+ALT+F1 opens a desktop environment with the login screen.
- CTRL+ALT+F2 open desktop environment with the current desktop.
- CTRL+ALT+F3 open TTY3
- CTRL+ALT+F4 open TTY4
- CTRL+ALT+F5 open TTY5
- CTRL+ALT+F6 open TTY6