- Wi-Fi
- How does Wi-Fi work?
- Wi-Fi vs. Internet
- Wi-Fi enabled devices
- Top 5 Wi-Fi Related Questions
- How to enable and disable Wi-Fi
- How to enable Wi-Fi on a laptop
- Enable with laptop Wi-Fi button
- Enable with laptop Fn and function key
- Enable Wi-Fi in Windows
- Enable Wi-Fi in Windows Device Manager
- Enable Wi-Fi in BIOS setup
- How to disable Wi-Fi on a laptop
- Disable with laptop Wi-Fi button
- Disable with laptop Fn and function key
- Disable in Windows
- Disable in Windows Device Manager
- Disable in BIOS setup
- Wi-Fi on desktop computers
- Wi-Fi on Android smartphones and tablets
- Wi-Fi on Apple iPhone and iPad
- Related information
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide wireless high-speed Internet access. A common misconception is that the term Wi-Fi is short for “wireless fidelity,” however Wi-Fi is a trademarked phrase that refers to IEEE 802.11x standards.
Wi-Fi originated in Hawaii in 1971, where a wireless UHF packet network called ALOHAnet was used to connect the islands. Later protocols developed in 1991 by NCR and AT&T called WaveLAN became the precursor to the IEEE 802.11 standards.
The Wi-Fi Alliance was formed in 1999 and currently owns the Wi-Fi registered trademark. It specifically defines Wi-Fi as any “ wireless local area network (WLAN) products that are based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers’ (IEEE) 802.11 standards.”
Initially, Wi-Fi was used in place of only the 2.4GHz 802.11b standard, however the Wi-Fi Alliance has expanded the generic use of the Wi-Fi term to include any type of network or WLAN product based on any of the 802.11 standards, including 802.11b, 802.11a, etc. in an attempt to stop confusion about wireless LAN interoperability .
How does Wi-Fi work?
Wi-Fi networks have no physical wired connection between sender and receiver. Instead, they function by using radio frequency (RF) technology a frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum associated with radio wave propagation. When an RF current is supplied to an antenna, an electromagnetic field is created that then is able to propagate through space.
The cornerstone of any wireless network is an access point (AP) . The primary job of an access point is to broadcast a wireless signal that computers can detect and use to establish a connection to the network. In order to connect to an access point and join a wireless network, computers and devices must be equipped with wireless network adapters.
Wi-Fi vs. Internet
Wi-Fi and Internet are closely related and often used interchangeably, but there are important distinctions between the two. First and foremost, the Internet is a wide area network (WAN) that uses a series of protocols to transmit information between networks and devices around the world. Wi-Fi, on the other hand, is simply a means for connecting devices without cables.
It’s entirely possible to have a Wi-Fi connection with no Internet access if there is no modem or Internet service from an ISP. For this reason, the signal strength of a Wi-Fi network is not directly correlated to the Internet speed a user might experience when connected. It is also why isolated Internet connectivity issues are usually attributed to the user’s device or Wi-Fi network router as opposed to the ISP’s service.
Wi-Fi enabled devices
Wi-Fi is supported by many applications and devices including video game consoles , smart home devices, tablets , mobile phones , and other types of consumer electronics. This level of support sometimes requires a differentiation between Wi-Fi and Internet of Things (IoT). Whereas Wi-Fi is often used as a component of IoT, a complete IoT ecosystem is much more complex and enables multiple devices to communicate with one another simultaneously. With Wi-Fi, communication is usually restricted to one channel between the user and a device at a time.
Any products that are tested and approved as “Wi-Fi Certified” (a registered trademark) by the Wi-Fi Alliance are guaranteed to be interoperable with each other, even if they are from different manufacturers. This means a user with a Wi-Fi Certified product can use any brand of router or modem with any other brand of client hardware that is also deemed Wi-Fi Certified.
Products that pass this certification are required to carry an identifying seal on their packaging that states “Wi-Fi Certified” and indicates the radio frequency band used (2.5GHz for 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n, and 5GHz for 802.11a). New generations of the 802.11x standard are released every few years to offer improved performance and security.
Top 5 Wi-Fi Related Questions
UPDATED: This definition was updated on April 5, 2021 by Web Webster.
How to enable and disable Wi-Fi
Laptops today all have Wi-Fi (wireless Internet) built-in, allowing people to connect to the Internet from almost anywhere. For security, compatibility, or other reasons, you may want to enable and disable the Wi-Fi on your laptop. To do so, make a selection from the list below and follow the steps.
After enabling Wi-Fi on your computer, you need to connect to a Wi-Fi network to access the Internet. See: How to connect to a Wi-Fi network.
If your Wi-Fi is not working or the suggested buttons do not work, for troubleshooting steps, see: Why is my Wi-Fi not working?
How to enable Wi-Fi on a laptop
Wi-Fi can be enabled by performing any of the steps below.
Enable with laptop Wi-Fi button
Some laptops have an On/Off button or switch for the Wi-Fi connection, as shown in the picture. It is usually found on the laptop’s front edge or above the keyboard. Find the button or switch, and make sure it’s enabled. When enabled, the button should be illuminated as blue, or the switch should be in the On position.
Enable with laptop Fn and function key
Some laptops enable and disable Wi-Fi using the Fn key and one of the function keys (F1-F12). As seen in the picture, some laptops use the Fn and F12 keys to enable and disable Wi-Fi. The F12 key also has an orange LED when disabled and blue when enabled, shown in the picture.
Enable Wi-Fi in Windows
Look in the Windows notification area to find the Wi-Fi or wireless Internet icon. Right-click with your mouse on the icon and select the option for enabling (or turning off) the Wi-Fi device in the pop-up menu. If no Enable option is available in the pop-up menu, there may be an option called Open Network and Sharing Center. If so, select this option and then select Change adapter settings. Once the wireless network card icon is seen, right-click it and select Enable.
In Windows 8, when you right-click the Wi-Fi icon, check if Airplane Mode is turned on. Turn it off to enable the wireless network card if it’s turned on.
The Wi-Fi adapter can also be enabled in the Control Panel. Click the Network and Sharing Center option, then click the Change adapter settings link in the left navigation pane. Right-click the Wi-Fi adapter and select Enable.
Enable Wi-Fi in Windows Device Manager
Access the Device Manager by right-clicking with your mouse on the My Computer icon on your desktop or in the Windows Start menu. Select Properties from the pop-up menu, click the Hardware tab in the window that opens up and click the Device Manager button.
In Windows Vista, and later, there is no Hardware tab. Click the Device Manager link in the System window.
Find the Wi-Fi adapter in the list of hardware devices. Right-click the adapter name and select Enable from the pop-up menu. If no Wi-Fi adapter is found in Device Manager, the Wi-Fi adapter drivers are not installed.
Enable Wi-Fi in BIOS setup
Finally, there is also the option of enabling the Wi-Fi device in the computer’s BIOS setup. However, it is very unlikely the Wi-Fi device would be disabled in BIOS.
How to disable Wi-Fi on a laptop
Wi-Fi can be disabled by performing any of the steps below.
Disable with laptop Wi-Fi button
Some laptops have an On/Off button or switch for the Wi-Fi device, like the button shown in the picture. It is usually found on the front of the laptop or above the keyboard. Find the button or switch and make sure it is disabled. When disabled, the button should not be illuminated or illuminated as orange or red, or the switch should be in the Off position.
Disable with laptop Fn and function key
Some laptops enable and disable Wi-Fi using the Fn key and one of the function keys (F1-F12). Some laptops use Fn and F12 keys to enable and disable Wi-Fi and show an orange LED when disabled and blue when enabled.
Disable in Windows
Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the Windows notification area and select Disable (or Turn off) from the pop-up menu. If no Disable option is available in the pop-up menu, there may be an option called Open Network and Sharing Center. If so, select this option and then select Change adapter settings. Once the wireless network card icon is seen, right-click it and select Disable.
In Windows 8, when you right-click the Wi-Fi icon, you can turn off Wi-Fi by turning on Airplane Mode.
The Wi-Fi adapter may also be disabled from the Control Panel. Click the Network and Sharing Center option, then click Change adapter settings in the left navigation pane. Right-click the Wi-Fi adapter and select Disable.
Disable in Windows Device Manager
Access the Device Manager by right-clicking with your mouse on the My Computer icon on your desktop or in the Windows Start menu. Select Properties from the pop-up menu, click the Hardware tab in the window that opens up and click the Device Manager button.
In Windows Vista, and later, there is no Hardware tab. Click the Device Manager link in the System window.
Find the Wi-Fi adapter in the list of hardware devices. Right-click the adapter name and select Disable from the pop-up menu. If no Wi-Fi adapter is found in Device Manager, the Wi-Fi adapter drivers are not installed.
Disable in BIOS setup
As is the case with enabling the Wi-Fi device, it can also be disabled in the computer’s BIOS setup.
Wi-Fi on desktop computers
Wi-Fi adapters are also available for desktop computers. The Wi-Fi button mentioned above is not available with most desktop computers. However, there is the possibility that the Wi-Fi adapter itself (e.g., an external version, like a USB Wi-Fi adapter) has an On/Off button or switch. If there is no button or switch, disconnecting the adapter from the computer disables the device.
If the Wi-Fi adapter is not an external device, it is either an internal PCI expansion card or built onto the motherboard. When you install the software for the Wi-Fi adapter, an icon shows in the Windows notification area, giving you access to enable and disable the device. Alternatively, you can enable and disable the Wi-Fi adapter through the Device Manager or the BIOS.
Wi-Fi on Android smartphones and tablets
There are many variants of Android-based smartphones and tablets. These steps are for a device with the stock Android operating system. You may have to adjust the instructions based on the brand of phone or tablet you have.
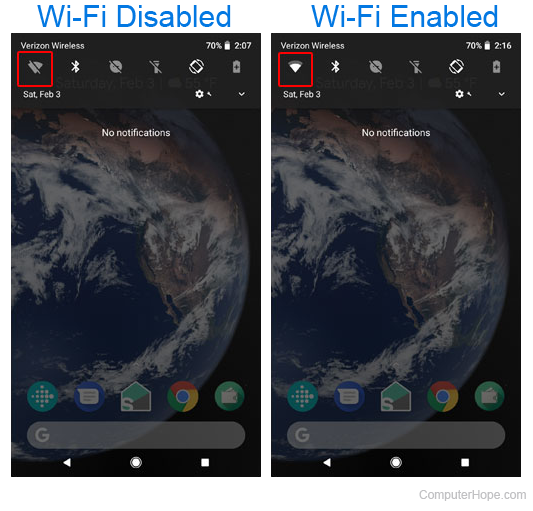
- On the home screen, place your finger near the top of the screen and swipe downward.
- Once a menu similar to the one below is seen, look for the Wi-Fi symbol.
Wi-Fi on Apple iPhone and iPad
Follow the steps below to enable or disable Wi-Fi on an iPhone or iPad.
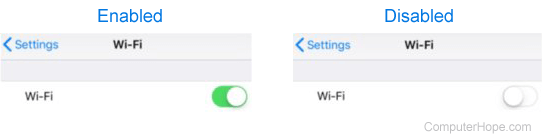
- Open the Settings utility on the iPhone or iPad.
- On the Settings screen, tap the Wi-Fi option.
- On the Wi-Fi screen, for the Wi-Fi entry, tap the toggle switch. Wi-Fi is enabled when the toggle switch is green and disabled when the toggle switch is white, as shown below.