What is wifi direct share
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Modern smartphones are loaded to the hilt with features and can literally do anything under the sun. An unintended outcome of this, however, is that many of these features remain hidden under sub-menus and are never really used to their full potential. Wi-Fi Direct is a prime example of this. In this article, we explain what Wi-Fi Direct really is and tell you how you may have used the feature even without realizing it.
nextpit TV
What is Wi-Fi Direct?
The simplest way to explain what Wi-Fi Direct is to tell you that it is a form of direct, device-to-device communication. Unlike ‘normal’ Wi-Fi, which requires several devices to connect to a centralized device (like a router), Wi-Fi Direct lets users directly connect one device to another (hence the term Direct). The reason for it being termed as Wi-Fi Direct is because it uses the same security protocols as our normal Wi-Fi connections do (WPS and WPA/WPA2).
Wi-Fi Direct can be seen as a sort of second-generation Wi-Fi, as it allows compatible devices which do not have their own internet connection, to establish a mutual connection with ones that do (Hotspots, modems, or routers). Thanks to Wi-Fi Direct, you can build up a wireless network between multiple devices. In addition, you can use Wi-Fi Direct in combination with Miracast to screencast onto another device with a display. The newest generation of Wi-Fi Direct is also NFC compatible.
Wi-Fi Direct is widely supported by a large pool of devices – most notably smartphones, tablets, laptops, digital cameras, and TVs. The Samsung Galaxy S (launched in 2010) was one of the first smartphones to include this feature, and starting Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich, all Android smartphones have this feature included natively. In case you were wondering, Apple products also support the Wi-Fi Direct feature — except — they have chosen to rebrand it to AirDrop and AirPlay.
In simpler terms, Wi-Fi direct allows devices without their own internet connection to connect to one which does. In the case of Android smartphones and devices, you can connect them and quickly transfer files without the hassle of cables. So, is Wi-Fi Direct just a glorified version of Bluetooth? Well, yes and no. The advantage of using Wi-Fi Direct over Bluetooth is that the Wi-Fi range and transfer speeds are significantly higher than those of Bluetooth. So, in short — use Wi-Fi Direct if you want a better way to send files from one device to another.
What is Wi-Fi Direct used for?
As of 2021, the feature is used for a range of applications that range from file sharing and data transfer to screen sharing and even playing games together. Let us take a look at some use cases with examples.
1. File sharing between phones
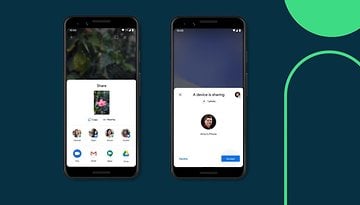
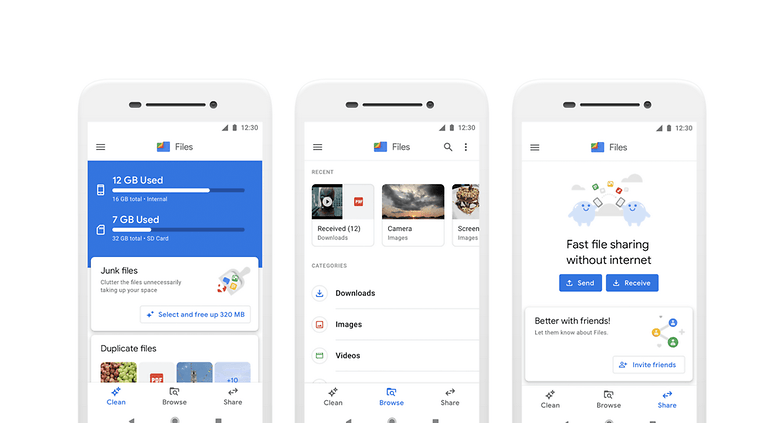
Sharing large files between smartphones wasn’t very straightforward a few years ago. The only options you had were Bluetooth and cable. While using Bluetooth was OK when it came to small files, using it to share larger files meant waiting for several minutes (or hours) for the transfer to complete. Data transfers using cables were faster — but then it was cumbersome. With the advent of Wi-Fi Direct, however, large file transfers between smartphones (and even laptops/ computers) have become much easier. To learn how to transfer files using Wi-Fi Direct, please check our next section.
Wi-Fi sharing is also used to quickly move data from an old phone to a new phone while setting it up for the first time.
2. Wireless Printing
Most modern printers support Wi-Fi Direct — thereby enabling them to communicate wirelessly with computers and smartphones and easily handle wireless printing jobs.
3. Playing games and screen-sharing
Other areas where we have seen Wi-Fi Direct being used extensively include offline, close-range smartphone gaming, and screen-sharing. You heard that right. The wireless screen sharing feature supported by your phone comes courtesy of Wi-Fi Direct. There are some games that use the same feature and let users play multiplayer games without the need for an internet connection.
How to set up Wi-Fi Direct
Every Android smartphone that uses Android 4.0 and above has Wi-Fi Direct functionality (bar some very rare exceptions). While the systems’ user interfaces might vary, setting this functionality up is relatively simple and unified across all devices. Wi-Fi Direct, until recently, did not offer native support for file transfers. That no longer is the case, thanks to a newly introduced feature called Nearby Share. Google also has its own app called ‘Files’ that includes a File transfer functionality (which uses Wi-Fi Direct).
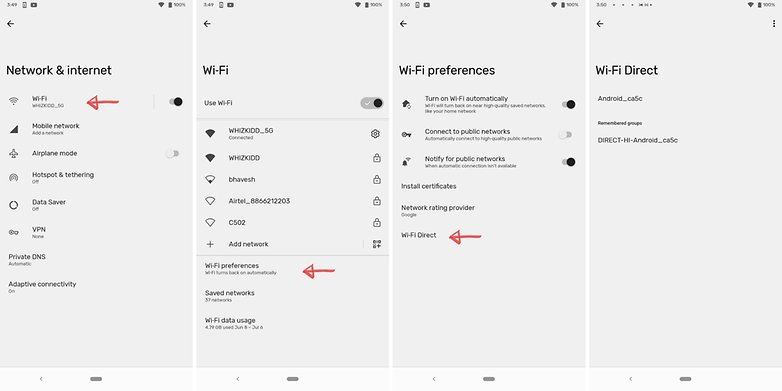
Most modern smartphones do not require you to manually ‘turn on’ Wi-Fi Direct. The feature is automatically turned on when you turn the Wi-Fi on. To check the status of Wi-Fi Direct on your device, go into Settings -> Network & internet -> Wi-Fi -> Wi-Fi preferences and then tap Wi-Fi Direct. Your smartphone will start scanning for devices that you can connect to.
Unlike with Bluetooth, there is no button or anything that you need to tap to turn Wi-Fi Direct on. Wi-Fi Direct is enabled the moment you have a stable internet connection. This doesn’t mean that Wi-Fi Direct is on all the time. Your smartphone only starts scanning for nearby devices to connect to when you tap on the Wi-Fi Direct tab.
Important: You also need to turn on Wi-Fi direct on your laptop, television, printer, or whichever device you are connecting to, as well as having activated it on your smartphone using the steps above.
Have you used the Wi-Fi direct feature on your smartphone before reading this article? Of course, if you have any questions about this topic, do leave them below in the comments!
This article was last updated in July 2021. Older comments have been retained.