- Wifi Monitoring Mode – Ultimate Guide
- Establishing a Wi-fi Connection for Monitor Mode
- The Basics of Monitor Mode
- Use Airmon-ng
- Use Iw Configuration Tool
- Check Interface Information
- Accessing Other Users’ Traffic
- Returning to Managed Mode using the sudo ip link set
- Does My Wi-fi Support Monitor Mode?
- Checking Wi-fi Support in Ubuntu Linux
- Find the Network Interface Name
- Disable Wifi
- Switch to Monitor Mode
- Alternative Managed Mode
- No Internet During Monitor Mode
- The Use of Monitor Mode
- Conclusion
- What is monitor mode in wifi?
Wifi Monitoring Mode – Ultimate Guide
It’s the era of network engineers, so if you’re a starter in the field of networking, gear up to enhance your skill set by learning about the monitor mode. When you analyze packets and do your penetration testing, it is essential to understand how the Wi-fi monitor mode works.
Establishing a Wi-fi Connection for Monitor Mode
When you connect to a wireless network or Wi-fi, your system sends a packet to the Wi-fi device. Once the device receives the packet, it sends back an acknowledgment that confirms the establishment of the connection.
Likewise, if you want to connect to another device on the same network, the Wi-fi will send the same packet to that device.
The Basics of Monitor Mode
In Linux operating systems understanding the monitor, the mode is quite simple. You need to run a few commands that we will discuss further. But what exactly is a Wi-fi monitor mode?
There is a central device or system in the monitor mode that monitors all the packets sent to the Wi-fi over that specific network. In this mode, the Wi-fi itself doesn’t have the monitoring capability.
Effectively, the system in monitor mode receives all the packets that circulate over that network. To set your system to the monitor mode, there are three simple ways to configure it in Linux operating systems. Let’s explore these methods:
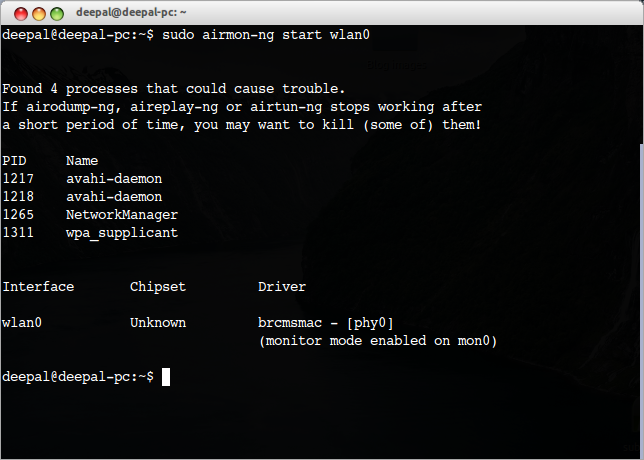
Use Airmon-ng
To use the Airmon-ng method, you will first need the aircrack-ng. Here is a quick guide:
sudo apt-get install aircrack-ng
- Once you enter the command, it will output the successful installation of the packages. Next, you need to check the Wi-fi interface. To do that, type the following command:
- It will display the drivers, chipset and the Wi-fi interface on the system. After checking the wi-fi interface, it’s time to check for any interfering processes. Use this command:
- It will display the number of processes that might potentially cause trouble in the monitor mode. So, it would help if you killed these processes by using the kill command. Type in the following:
- The system will summarize all the processes that it has killed. It’s time for the interface to enable monitor mode. Type the following command:
sudo airmon-ng start wlp1s0
- In Kali Linux, you can enter the monitor mode on a wireless network through the ‘airmon-ng start wlan0’ command.
- As it creates a new interface, you can proceed to check it through the iwconfig command. Type the following:
sudo airmon-ng stop wlp1s0mon
Use Iw Configuration Tool
Using the iw wifi configuration tool is a simple option to manage wireless network settings. It’s mainly more potent than some of the other tools. For example, you can use the same tool to obtain wifi network info, different wifi commands, wireless wlan0, bit rates, scanning, interface modes, HT, etc.
Check Interface Information
First, you must check the information of the interface. Use the following instruction:
Accessing Other Users’ Traffic
Next, you may need to access other users’ traffic, so you must switch to the Monitor mode. Use the following set of commands to switch to monitor mode. We will assume the interface name as wlp1s0.
$ sudo ip link set wlp1s0 down
$ sudo iw wlp1s0 set monitor control
$ sudo ip link set wlp1s0 up
You may recheck the interface by typing the following:
Returning to Managed Mode using the sudo ip link set
To return the mode to manage, use the following set of commands.
$ sudo ip link set wlp1so down
$ sudo iw wlp1so set type managed
$ sudo ip link set wlp1so up
Does My Wi-fi Support Monitor Mode?
One of the critical aspects of using the monitor mode is Wi-fi support. So, you must first ensure that your Wi-fi card support monitor mode. The checking method varies according to the operating system, so we will see how it works for Ubuntu Linux.
So, before you buy a new wifi adapter, let’s see if you can work with the current model.
Checking Wi-fi Support in Ubuntu Linux
Ubuntu Linux has a relatively simple way to check the mode monitor. You don’t need any additional tools. Here is how to do it:
Find the Network Interface Name
First, you must find out the wifi interface name. Go to your Linux command line and type the following command:
This command outputs all wireless and wired connections. The display will show the IP address and state of your connection. In this example, let’s assume your wifi interface name is ‘wlp1s0’.
Disable Wifi
Next, you must turn down the Wi fi network. You don’t need to switch off the wireless adapter. Instead, write this command:
sudo ip link set dev wlp1s0 down
Switch to Monitor Mode
Once you’ve set down the interface, it’s time to switch your Wi-fi card to monitor mode. Type this command.
sudo iwconfig wlp1s0 mode monitor
This command does two things. Firstly, it will verify if your wifi card supports monitor mode. Secondly, it will successfully switch your wifi to monitor mode. In case there is monitor mode support, it will give an error.
You can also double check by:
Alternative Managed Mode
If the previous command doesn’t run successfully, your wi-fi will switch to managed mode. Unfortunately, it also means that the monitor mode isn’t supported.
No Internet During Monitor Mode
Remember that the Wi-fi monitor mode disables the internet. So, you need to turn the way back to manage if you want to turn on the internet. Here is how to do it:
sudo iwconfig wlp1s0 mode managed
sudo ip link set dev wlp1s0 up
The Use of Monitor Mode
If you’re an ethical hacker, you need to learn how to use and enable monitor mode. It helps capture data packets to check if any wi-fi adapter or access point is left vulnerable on the line. In addition, you can access critical information about the network to enhance security and traffic using the monitor mode.
Conclusion
It doesn’t matter if you’re using mac or windows or any other operating system. Whether it’s Ethernet or wi-fi connection, monitor mode gives you a lot of power as an analyst and network manager. For example, you can configure different networks.
Now that you know how to configure your way to the monitor mode, you can efficiently analyze packet capture, configure channel settings, monitor data reception, and view all devices available on the networks.
Also, we saw how to check if your adapter supports monitor mode. So, if you find that your internet hardware peripherals support monitor mode, it will be easier for you to practice ethical hacking on your device.
Hedayat S
Hedayat is the new Editor-in-Chief of Rottenwifi and has been writing about computer networking since 2012. Hedayat’s strong background in computer science helped him cement his position in the ever-expanding tech blogging world. As a network engineer, systems administrator, and systems analyst during his decade-long career in Information Technology, he has a passion for the internet & technology in his DNA.
Blog.rottenwifi.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program which means we may get paid commissions on editorially chosen products purchased through our links to retailer sites. All names, logos, brands, and images are trademarks or copyrighted materials of their respective owners. Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc., or its affiliates.
What is monitor mode in wifi?
Monitor mode or RFMON (Radio Frequency Monitor) mode, enables a device with a wireless network interface controller to monitor all traffic received from the wireless network. Unlike promiscuous mode, which is also used for packet sniffing, RFMON mode enables packets to be captured without having to connect or link with an access point. RFMON mode only works with wireless networks, while promiscuous mode can be applied to both wired and wireless networks.
RFMON mode is not really a wireless mode but it is especially important in attacking wireless networks. In a nutshell, it allows a wireless card to “monitor” the packets that are received without any filtering. Monitor mode is essentially the “promiscuous mode” equivalent for wireless. When using some wireless drivers, this mode allows for the sending of raw 802.11 frames. Airodump-ng, Aireplay-ng, and many other wireless tools require that the adapter be placed in monitor mode in order to operate.
The difference between promiscuous mode and Monitor mode:
The promiscuous mode works by sniffing the packets after associating with the access point. This is likely because the wireless devices send the packets in the air but only “mark” them to be processed by the proposed receiver.
The monitor mode works by sniffing the packets in the air without associating or linking with any access point.
Unallocated Author
Please note that the article you are reading has an unallocated author as the original author is no longer employed at latesthackingnews.com, this has been put in place to adhere with general data protection regulations (GDPR). If you have any further queries, please contact: [email protected]