- How To Find Absolute Full Path Of Command On Linux / Unix : which command
- Table of Contents
- Print multiple command’s absolute path
- print all matching pathnames of each argument
- Which command terminal linux
- Learn Latest Tutorials
- Preparation
- Trending Technologies
- B.Tech / MCA
- Javatpoint Services
- Training For College Campus
- How to Use the which Command in Linux
- Linux which Command Syntax and Options
- Linux which Command Examples
- 1. Display the Path of Any Executable File
- 2. Display Multiple Paths of Executable Files
- 3. List All Instances
- 4. Find Symbolic Links
- 5. Exclude Shell Built-ins
- Команда which в Linux [с примерами]
- Linux, Примеры команды which
- Использование команды which с несколькими исполняемыми файлами
- Показать все пути с командой which
- Статус вывода команды which
How To Find Absolute Full Path Of Command On Linux / Unix : which command
In Linux and Unix systems, commands are executable files. The commands may be specific with user environment. We can set the absolute path of specific command as per user in environment. If we require the information, to get the absolute path of command. In that case we will use which command.
Table of Contents
To find the absolute path of command in Linux/Unix system, we use which command. Given below is the Syntax.
which command-name # OR which executable-file-name
Note: The echo $PATH command will show the directory path. The which command, locate the command from these directories.
root@tuxworld:/# echo $PATH /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-2.1.0/bin:/usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-2.1.0@global/bin:/usr/local/rvm/rubies/ruby-2.1.0/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/local/rvm/bin root@tuxworld:/#
Example : In this example,we will find the absolute path of useradd command.
The output from which command is showing the absolute path.
root@tuxworld:/# which useradd /usr/sbin/useradd root@tuxworld:/#
Print multiple command’s absolute path
We can use multiple arguments in which command. Hence,we can show two or more executable files absolute path on terminal.
which command-1 command-2 command-N
Example: In this example,we are finding the absolute path of ls,chown,chgrp and usermod command.
root@tuxworld:/# which ls chown chgrp usermod /bin/ls /bin/chown /bin/chgrp /usr/sbin/usermod root@tuxworld:/#
print all matching pathnames of each argument
To print all matching pathnames of each argument,we use -a option with arguments i.e command name.
Example: In this example, we are searching absolute path of echo command
root@tuxworld:/# which -a echo /usr/sbin/echo /bin/echo root@tuxworld:/#
Which command terminal linux
Learn Latest Tutorials
Preparation
Trending Technologies
B.Tech / MCA
Javatpoint Services
JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services. Mail us on h[email protected], to get more information about given services.
- Website Designing
- Website Development
- Java Development
- PHP Development
- WordPress
- Graphic Designing
- Logo
- Digital Marketing
- On Page and Off Page SEO
- PPC
- Content Development
- Corporate Training
- Classroom and Online Training
- Data Entry
Training For College Campus
JavaTpoint offers college campus training on Core Java, Advance Java, .Net, Android, Hadoop, PHP, Web Technology and Python. Please mail your requirement at [email protected].
Duration: 1 week to 2 week
Like/Subscribe us for latest updates or newsletter 




How to Use the which Command in Linux
The which command allows users to search the list of paths in the $PATH environment variable and outputs the full path of the command specified as an argument. The command works by locating the executable file matching the given command.
In this tutorial, you will learn to use the which command.
Linux which Command Syntax and Options
The syntax for the which command is:
The [argument] variable specifies the command or commands you want to find.
For example, the following command outputs the location of the cat command:
The which command has only one option, -a . It is optional and used to print all the matches it finds.
The command searches for matches from left to right. If there are multiple matches found in the directories listed in $PATH , which prints only the first one. The -a option instructs which to print all the matches.
Important: On many Linux distributions, which excludes the shell built-in commands and does not output their location.
Having multiple matches sometimes means one match is a symlink to the other. However, it is possible to have two versions of the same command in different locations or two different commands using the same name.
Note: Unlike many other commands, which has no —help option. To see the command description and help, run man which .
Exit Status
The which command returns one of the following values that indicate its exit status:
- 0 . All arguments were found and executable.
- 1 . One or more arguments don’t exist or aren’t executable.
- 2 . An invalid option has been specified.
Linux which Command Examples
The following examples showcase how the which command works and how to use the available option.
1. Display the Path of Any Executable File
To display the path of any command, pass the command name as an argument after which .
The output shows the path to the tr command executable file, located in /usr/bin/tr.
2. Display Multiple Paths of Executable Files
which accepts multiple arguments and outputs the path to each one in the specified order.
The command works through the supplied list and outputs the results for the nc command, mount command, and sort command, separating each result with a newline character.
3. List All Instances
which only shows the first match it finds in the $PATH variable directory list. Use the -a option to show every match for the specified command.
For example, searching for instances of the less command outputs two results when using the -a option:
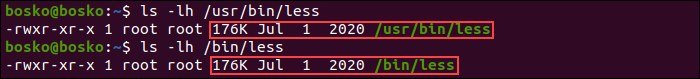
Use the ls command to check file details and determine if both versions are executable files. Run:
ls -lh /usr/bin/less ls -lh /bin/lessThe output shows two identical versions of the same command in two locations, both 176 KB large, and both executable.
Note: The /bin directory contains executables that can be used by the system administrator and any other user, and which are required for emergency system repairs. The /usr/bin directory is the primary directory for executable commands on the system.
4. Find Symbolic Links
Using the -a option lists all the paths containing an instance of the specified program. While multiple versions of the same program can exist on a system, sometimes one of the instances is only a symbolic link and not a binary file.
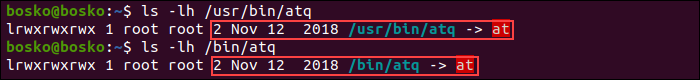
For example, running the following command outputs two instances of the atq command:
Again, use the ls command to check the details for both files. Run:
ls -lh /usr/bin/atq ls -lh /bin/atqThe output shows that both files are symbolic links ( -> ) only 2 bytes large and pointing to the at command.
5. Exclude Shell Built-ins
As previously mentioned, the which command excludes shell built-ins from its output.
For example, asking for the location of the read and man commands only outputs the location for the man command executable file, as read is a bash shell command.
This tutorial showed how to use the which command in Linux to find the path to a command’s executable binary. See and download our Linux commands cheat sheet for other essential Linux commands and examples of using them.
Команда which в Linux [с примерами]
Добавить в избранное
К оманда which в Linux используется для поиска любой команды в Linux. Команда — это исполняемый файл, который вы можете запустить. Команда which находит исполняемый файл в пути поиска вашей оболочки.
Другими словами, если вам интересно, где именно находится определенная программа, просто используйте which. Команда Linux имеет простой синтаксис:
Давайте посмотрим, как использовать эту простую, но полезную команду.
Linux, Примеры команды which
Допустим, вы хотите знать, где находится исполняемый файл Java, используйте команду:
destroyer@andreyex:~$ which java
/usr/bin/java
Обратите внимание, что работает только с исполняемыми файлами. Таким образом, вы должны использовать which только с аргументом. Например, вы устанавливаете Java с помощью пакета JDK, но не запускаете команду с именем «jdk», вы запускаете «java». Таким образом, вы используете команду which на Java, а не JDK.
Если команда which не находит исполняемый файл в текущем пути, она ничего не возвращает.
Использование команды which с несколькими исполняемыми файлами
Вы можете предоставить более одного аргумента для команды which:
which man java python nada
destroyer@andreyex:~$ which man java python nada
/usr/bin/man
/usr/bin/java
/usr/bin/python
Вы заметили что-то здесь? Мы дали ему четыре аргумента, но результат отображается только для трех из них. Это потому, что «nada» не исполняемый файл. Там нет вывода для which.
Показать все пути с командой which
Команда which в Linux имеет только одну опцию -a. По умолчанию эта команда печатает только один путь для своих аргументов.
Если программа имеет исполняемый файл в двух местах, например, в /usr/bin/program и в /usr/local/bin/program, вы можете отобразить оба пути с помощью опции -a.
Статус вывода команды which
Если вы используете команду which в скрипте bash, вам может потребоваться узнать ее состояние завершения.
Команда which имеет следующий статус выхода:
- 0 — все аргументы найдены и выполняются
- 1 — один или несколько аргументов не существуют или не выполняются
- 2 — если указан неверный параметр
Это все, что вам нужно знать о команде which в Linux. Если у вас есть вопросы или предложения, дайте нам знать в комментариях ниже.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.