- Can A Microwave Oven Interfere With Wireless Devices?
- Question: Can A Microwave Oven Interfere With Wireless Devices?
- Why could a microwave interfere with your Wi-fi?
- What can I do to solve this issue?
- Can this interference damage the devices that are affected?
- Does this mean that my microwave is letting out dangerous radiation?
- Do Microwaves Interfere With WiFi Signals?
- What Is Electromagnetic Radiation?
- Microwave Ovens And WiFi Routers
- A Clash Of Frequencies
- Is This Interference Dangerous?
- How To Eliminate The Interference Between Microwave And WiFi Signals?
Can A Microwave Oven Interfere With Wireless Devices?
We can all agree that wireless devices and microwaves are in the top 10 creations, one heat up our food and one gives us comfort.
However, while they might work great by themselves, they might cause problems for each other when used at the same time.
Related Product: Want a microwave that works with Alexa? Check out the Toshiba EM34P (click to view on Amazon)
I love wireless products and use wireless mouses, headphones, earbuds, chargers, you name it.
One thing that I have noticed when using my wireless headphones is that sometimes when turning on my microwave, I hear this static sound in my headphones if I’m nearby.
This static sound confused me for a long time and I decided that I had to figure out what was causing the problem.
Question: Can A Microwave Oven Interfere With Wireless Devices?
Yes. Both your microwave and Wi-fi generally operate on the same 2.4GHz frequency.
While your microwave is shielded from leaking radiation, some small amounts may pass through. This could cause problems in the connection between your devices and it’s operating station.
Let’s look into why this happens and what you can do to prevent it.
How does a microwave oven work?
Microwave ovens work by converting the electricity into radio waves.
That will send radio waves into the sealed metal box which will bounce off its wall. If there is an object like food or liquid inside, the radio waves will hit the object and vibrate through them on a level not able to be seen by our eyes.
This will, in turn, make the molecules inside the food or liquid move much faster which in turns heat up the object. Liquid molecules will generally heat up faster.
You may have noticed this at some point if the outside of a microwaved chocolate chip muffin seems cool while the inside is steaming hot. This could be because the inside is denser in liquid and the outside is drier.
Some mention microwave ovens as heating up objects from the inside out, rather than outside in an electrically heated oven. It sounds like a fair statement but it’s technically not the truth.
A microwave oven will basically just heat up food faster and more evenly since the radio waves are going straight through the object, rather than just exposing heat on the outside of the object.
Microwaves are made to contain all radiation within and not let any out, however, there could potentially be small amounts leaking out anyways.
Why could a microwave interfere with your Wi-fi?
Generally, our microwaves and Wi-fi operate on the same frequency at 2.4GHz.
This means that if a microwave is somehow leaking radiation into our home at a level close to 2.4Ghz, that could potentially cause a problem in the connection for your Wi-fi.
You may not notice it until you use other devices, like in my case, my wireless headphones.
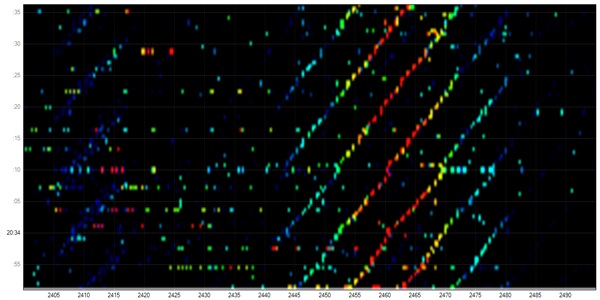
Here you can see the radio signal spectrum for a Wi-fi. For an untrained eye, this is a quite clean spectrum in general with little interference.
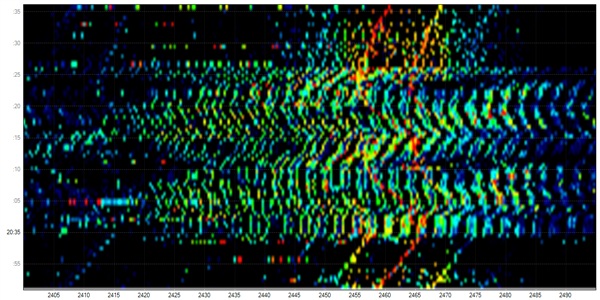
This picture shows what the radio signal spectrum looks like after running a cup of water in the microwave for 30 seconds. As you can see, there is much more interference in terms of radio signals in that spectrum. If your microwave is leaking radio signals or some of your other devices are interfering, this is what is happening in what we can’t see.
For more pictures and more tech-detailed discussions, you can find more information in Peter Grace’s article about Wi-fi interference.
These pictures were made by using a frequency analyzer that can view radio signals that obviously aren’t visible to our eyes.
Other than microwave ovens, there are many other household electronics that could cause problems because they operate on the same frequency. Such as baby monitors, cordless telephones as well as other Bluetooth devices.
What can I do to solve this issue?
Before you throw out our microwave, make sure to try de-activate the other devices in your home that could cause the problem in case it’s not the microwave.
Also, If you are currently operating Wi-fi at 2.4GHz, upgrading to 5GHz could solve the issue as the interference frequencies shouldn’t affect the Wi-fi at that level. One downside with 5GHz technology is that it has less range than 2.4Ghz, while still being stronger.
If you are still experiencing problems after that, you might want to consider returning your microwave to the manufacturer as it shouldn’t be leaking that much radio signals.
As for audio devices, like my wireless headphones, I have yet to find a solution to this. However, the inconvenience is rather small and it doesn’t bug me enough to deal with getting a new microwave at this moment.
Can this interference damage the devices that are affected?
There should not be any damage to any of your devices regardless if there is an interference.
It’s not the actual device that is being damaged but rather just the radio signal spectrum being too crowded in a certain area. In my case, that is in my kitchen.
Does this mean that my microwave is letting out dangerous radiation?
You shouldn’t be too concerned with this issue in terms of safety unless the microwave seems to be underperforming all of a sudden while also causing a Wi-fi interference.
As for any product, if it seems to be malfunctioning, you could and should contact the manufacturer or seller and try to solve the issue.
Technically, any GHz for a long period of time could potentially be harmful, but as for with Wi-fi signals, you shouldn’t worry about it too much.
If you are concerned, there are some radiation protection guards out there that can act as protecting agent for your router without interfering too many signals.
But based on the guess that you don’t sit next to your microwave or router 24/7, there is not enough danger to panic.
In order for a radio frequency to be harmful or carcinogenic (meaning it could cause cancer), you would have to exposed to a higher GHz than 2.4 or even 5.
Do Microwaves Interfere With WiFi Signals?
Yes. Microwaves and radio waves are physically the same, i.e. both are forms of electromagnetic radiation. Some microwave rays can leak out and interfere with WiFi signals.
If you have a microwave, you may have noticed that when it is in use, you may also have problems loading web pages on your smartphone, laptop, or other Internet-enabled device, especially if your router and microwave are in close proximity.
Why does this happen? Why does turning on the microwave hinder your WiFi connectivity?
Like most things that have to do with “electrical signals,” the answer begins with the following term: electromagnetic radiation.
Recommended Video for you:
What Is Electromagnetic Radiation?
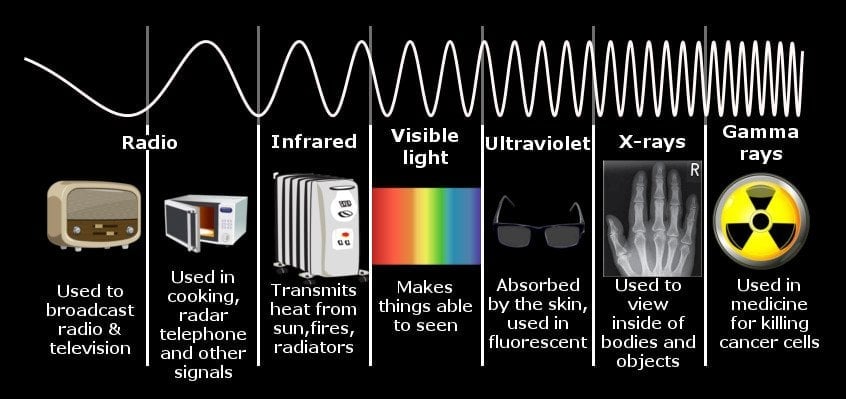
We are basically constantly surrounded by electromagnetic radiation. Visible light, something that permeates everything around us, is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Likewise, many other things, including mobile phones, television remote controls, microwave ovens, WiFi, work via electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation comes in different forms depending on the frequency. Gamma rays and X-rays have high frequencies and therefore high energies, while radio waves and microwaves are on the other side of the band as they have lower frequencies. You may remember the following chart of the electromagnetic spectrum from your high school science class.
Also Read: Why Are Infrared Waves Associated With Heat?
Microwave Ovens And WiFi Routers
As mentioned earlier, many everyday appliances rely on electromagnetic waves to function. Two of the most common household appliances are microwave ovens and WiFi routers, both of which emit electromagnetic radiation to function; microwave ovens emit microwaves to heat food, while WiFi routers emit radio waves. Microwave ovens convert electricity into longer-wavelength electromagnetic waves, called microwaves, which are emitted inside a tightly sealed metal box. Theoretically, these waves bounce back from the wall and should not bypass the wall. Although it is still not quite clear how the heat is distributed throughout the food being subjected to the waves, microwaves are known to be extremely adept at exciting and vibrating water molecules, and most natural food has some water constituent in it. These microwaves lead to vigorous motion of the water molecules, creating intermolecular friction, which generates the heat to cook the food. Also Read: How Does A Microwave Oven Work?
A Clash Of Frequencies
If you are a science freak like us, constantly looking for causality and correlation between almost everything that exists, you may have noticed that the moment you stuff your food into the microwave and turn it on, your WiFi connection becomes unpredictable. In some cases, your device may not connect at all, but after you turn off the microwave, the Internet connection is back to normal. If you haven’t observed this, try it for yourself. Put your WiFi modem and microwave in the immediate vicinity and turn on the microwave. Install some Internet speed tests, such as Speedtest of Ookla. Try to heat water in the microwave and check your Internet connection while the microwave is running. You will likely experience connection problems or speed degradation… but why does that happen? 

Is This Interference Dangerous?
Of course, mixing and mashing electromagnetic waves emanating from the WiFi device and emerging from the microwave could make us nervous if it could damage the device. Fortunately, this is not the case, and you should not worry that your device or gizmo will be damaged by this interference from electromagnetic waves. Remember that it is not the actual devices that mix, but only the waves emanating from them. Nor should you worry about radiation, as we are all surrounded by giants and devices that constantly emit these high-frequency electromagnetic waves, including our smartphones, computers, appliances, power lines, baby monitors, etc. Only if your microwave completely strangles the Internet, even though the WiFi router is several meters away, should you give enough thought to asking the manufacturer for replacement / repair. Also Read: What Is Electromagnetic Pollution?
How To Eliminate The Interference Between Microwave And WiFi Signals?
The best solution to this problem would be to upgrade your WiFi equipment to a system that operates in the 5 GHz band. Modern 802.11n routers operate in this band, not in the 2.4 GHz band. As you can see, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz are two bands that your router can use for its signals. The advantage of using 5 GHz is that it not only prevents interference from the above mentioned devices that operate in the 2.4 GHz band, but also supports better connectivity (to the order of more than 1,000 Mbps). However, the operating range of a 5 GHz router is smaller than one operating at 2.4 GHz. Another way to minimize interference is to keep the microwave a few meters away from the router. Since water is also a good absorber of electromagnetic waves, if you have a fish tank, it should also be kept a few meters away from the router. Finally, a cheap way to improve this situation is to interrupt the “Internet work” while the microwave is still on. Or you can just get used to the fact that the Internet behaves badly when surfing next to the microwave. Best of all, the interruption of the Internet connection should rarely last more than two minutes! Also Read: Does Distance From The Wi-Fi Router Impact Download Speeds?