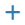Setting up wifi as WAN interface
Only install packages for your version, or risk breaking it. If yours is older, select it in System/Update/Update Settings.
When upgrading, let it finish. Allow 10-15 minutes, or more depending on packages and device speed.
Upvote 👍 helpful posts!
I see that pfSense has added a iwn0_wlan0 interface but I don’t know how to configure it. There is no /etc/rc.conf in pfSense. I have added a /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf, but I don’t know how to enable DHCP since the interface does not show up I try assign interfaces or IP addresses from the main menu.
@balanga You can do it in the GUI, Interfaces/Assignments.
https://docs.netgate.com/pfsense/en/latest/interfaces/configure.html
Once assigned as WAN then (re)configure the WAN interface as desired. Normally DHCP would be enabled on an internal interface not WAN. But that would be on the Services menu.
Only install packages for your version, or risk breaking it. If yours is older, select it in System/Update/Update Settings.
When upgrading, let it finish. Allow 10-15 minutes, or more depending on packages and device speed.
Upvote 👍 helpful posts!
You have to add it as a wireless interface in Interface > Wireless first. It should be added in Infrastructure mode to be a client.
Then it will show as available to assign as WAN. Nothing at the CLI should be required. Anything you have added there is more likely to break stuff! Steve
No. Why can’t you access the gui from the LAN? (or another internal interface). What do you see in Interfaces > Wireless when you try to add it?
No. Why can’t you access the gui from the LAN? (or another internal interface). What do you see in Interfaces > Wireless when you try to add it?
The other system with a LAN connection is running FreeBSD without Xorg and it doesn’t have Internet access. I was hoping to install pfSense to enable that system to access the Internet. Maybe I can somehow incorporate pfSense routing functionality into an existing FreeBSD installation.
Hmm, well FreeBSD already has all of that built in if, you just need to configure it. Technically you could probably configure enough in pfSense by just editing the config by hand and loading it. But the chances of getting that right first time are pretty low! Can you not just connect a laptop there to configure it?
Technically you could probably configure enough in pfSense by just editing the config by hand and loading it. But the chances of getting that right first time are pretty low!
Eventually I managed to get a broken laptop to work and have got as far as Interfaces -> Wireless -> Edit My Intel Wireless NIC is identified, but I’m not sure about what mode to use or where to provide wpa_supplicant.conf data.
The wpa data is added via the interface config page once it’s assigned in pfSense. But you could just use the FreeBSD box directly if you want:
https://docs.freebsd.org/en/books/handbook/advanced-networking/#network-wireless-quick-start
The wpa data is added via the interface config page once it’s assigned in pfSense. But you could just use the FreeBSD box directly if you want:
https://docs.freebsd.org/en/books/handbook/advanced-networking/#network-wireless-quick-start I do know how to get wifi working on FreeBSD, what I was unclear about was how to set up FreeBSD as a basic router, ie configure basic pfSense routing capabilities. Anyhow, I finally got my WAN interface set up to use wifi, but I am unable to access the Internet from my LAN, and I’m not sure that this is possible. My Internet access is via a wifi broadband router (192.168.1.1) which assigns 192.168.1.15 to the WAN of my pfSense box and I can ping the outside world from there, but my internal network (192.168.2.0) cannot. I seem to be missing something.
I’ve been happily using pfSense for over six years on my home lan and have been blissfully unaware of such things. everything just worked. In this particular case pfSense I have setup pfSense as an intermeiary router hoping I could set up a route between one system and the internet. The pfSense system uses wifi to access the Internet via a broadband router which acts as a DHCP server for the WAN port. The Gateway is 192.168.1.1 — the broadband router. There are no firewall rules.
I’m looking for advice on setting up the parameters you mention.
It should work given what you’ve said here. So something must be missing. Try to ping out from pfSense itself but set the source as the LAN address. If that fails then you have a NAT problem. Usually that’s because the gateway is not applied on the interface but that cannot happen with a DHCP interface.
Wifi as wan pfsense
Welcome to your friendly /r/homelab, where techies and sysadmin from everywhere are welcome to share their labs, projects, builds, etc.
EDIT: This is for using the pfSense box as a CLIENT to an AP, not as a bridge or repeater.
First off, I thought it was simple, I was wrong. If anyone ever needs this odd scenario, here’s how to do it.
- Install a fresh pfSense OS as normal and accept an Ethernet port (lan0, alc0, or eth0) as a WAN port initially to let it stop complaining. I did this without an actual internet connection, it still complained. I left the LAN blank.
- Log into pfSense web interface. I had to use the magic of auto-DHCP from a different source (Windows shared connection for instance). Having an intelligent Ethernet switch works wonders too.
- Navigate to Interfaces -> Assignments -> Wireless; make sure your Wireless adapter or embedded WiFi is recognize and set it up as «Infrastructure (BSS)»
4a) Navigate to Interfaces -> Assignments; add your WiFi as LAN, initially. save. then flip them: xxx_wlan0 as WAN and alc0/eth0 as LAN
4b) Make sure your private subnet, mask, and DHCP server is setup on LAN before or during these sequence of events, I forgot to document when I actually did this, it could have been before I flipped the WAN and LAN assignments.
5) Navigate to Interfaces -> WAN; Configure your Wireless settings and enter all information to CONNECT to the wireless Access Point. It may seem it is being setup as an Access Point, don’t worry, it’s not.
6) We’re not even close to being done. Mine might be buggy, so I needed a way to auto-connect on boot because it derps. So I created a file called «wifi.sh» in the folder «/usr/local/etc/rc.d» and had just two lines:
ifconfig _wlan0 down ifconfig _wlan0 up
Replace with the actual interface prefix.
Notes: I did try the way with «wpa_supplicant» and configuring, but it either worked half the time, or just threw continuous errors on the prompt.
7) Make some adjustments to the WAN wireless settings for quicker connection on boot (like setting the channel number to a fixed value if your wifi router will never change its channel).
What I have right now works 100% and I’m enjoying my firewall that is connected to a wireless access point and using that adapter as a WAN port while the Ethernet port goes directly to my switch and serving+protecting the internet to all my racks and devices connected via Ethernet.
If you’re too lazy like I was for over three years, you can always use Windows internet connection sharing (easy in 7/8.1/10/2008). :p I finally got the chance to re-purpose gear into a 1U just to pull this off. It would have been overkill before as pfSense on a 2U hosting a mid-high range CPU with a compliment of hard drives is kinda silly. It was easier just to enable ICS and have Wifi be the shared adapter at the time.
Wireless¶
pfSense® software includes built in wireless capabilities that allow a firewall running pfSense software to be turned into a wireless access point, to use a wireless 802.11 connection as a WAN connection, or both. This chapter covers how to configure pfSense software for these roles as well as suggested means of securely accommodating external wireless access points and how to securely deploy a wireless hotspot. In-depth coverage of 802.11 in general is outside the scope of this documentation. For those seeking such information, see other works such as 802.11 Wireless Networks: The Definitive Guide.
Hangouts Archive to view the May 2015 Hangout on Wireless Access Points.
For assistance in solving software problems, please post your question on the Netgate Forum. If you see anything that’s wrong or missing with the documentation, please suggest an edit by using the feedback button in the upper right corner so it can be improved.
© 2023 Electric Sheep Fencing LLC and Rubicon Communications LLC. All Rights Reserved. | Privacy Policy | Legal
This page was last updated on Jul 06 2022.
Other Resources
Our Mission
We provide leading-edge network security at a fair price — regardless of organizational size or network sophistication. We believe that an open-source security model offers disruptive pricing along with the agility required to quickly address emerging threats.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Product information, software announcements, and special offers. See our newsletter archive for past announcements.
Wireless WAN¶
A wireless card in a firewall running pfSense® software can be used as the primary WAN interface or an additional WAN in a multi-WAN deployment.
Interface assignment¶
If the wireless interface has not yet been assigned, there are two possible choices: Add it as an additional OPT interface or reassign it as WAN.
Before starting, create the wireless instance as described in Creating and Managing Wireless Instances if it does not already exist. When working as a WAN, it must use Infrastructure mode (BSS).
To add the interface as a new OPT interface:
- Browse to Interfaces > Assignments
- Select the wireless interface from the Available network ports drop-down below the other interfaces
- Click Add to add the interface as an OPT interface
To reassign the wireless interface as WAN:
- Browse to Interfaces > Assignments
- Select the wireless interface as WAN
- Click Save
Figure Wireless WAN Interface Assignment shows an Atheros card assigned as WAN.
Wireless WAN Interface Assignment ¶
Configuring the wireless network¶
Most wireless WANs need only a handful of options set, but specifics vary depending on the Access Point (AP) to which this client interface will connect.
- Browse to the Interfaces menu for the wireless WAN interface, for example Interfaces > WAN
- Select the type of configuration (DHCP, Static IP, etc.)
- Scroll down to Common Wireless Configuration
- Set the Standard to match the AP, for example 802.11g
- Select the appropriate Channel to match the AP
- Scroll down to Network-specific Wireless Configuration
- Set the Mode to Infrastructure (BSS) mode
- Enter the SSID for the AP
- Configure encryption such as WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) if in use by the AP
- Review the remaining settings if necessary and select any other appropriate options to match the AP
- Click Save
- Click Apply Changes
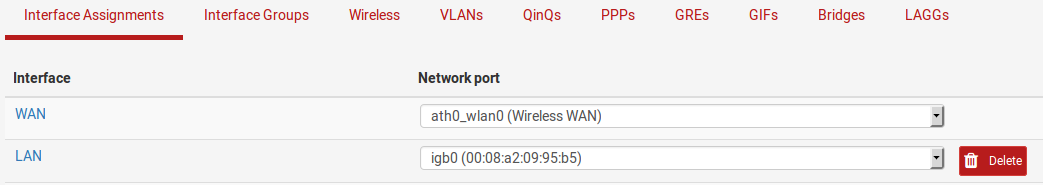
Checking wireless status¶
Browse to Status > Interfaces to see the status of the wireless interface. If the interface has successfully associated with the AP it will be indicated on the status page. A status of associated means the interface has connected to the AP successfully, as shown in Figure Associated Wireless WAN Interface
Associated Wireless WAN Interface ¶
If the interface status shows No carrier, it was unable to associate. Figure No carrier on wireless WAN shows an example of this, where the antenna was disconnected so it could not connect to a wireless network that was some distance away.
No carrier on wireless WAN ¶
Showing available wireless networks and signal strength¶
The wireless access points visible by the firewall may be viewed by navigating to Status > Wireless as shown in Figure Wireless Status .
A wireless interface must be configured before this menu item will appear.