- Linux Wireless
- Out of the tree drivers(Unsupported)
- Abandoned/Deprecated Drivers(Unsupported)
- Page Tools
- How to Install Realtek Wifi Drivers in Ubuntu 22.04 | Linux Mint 21/20
- How to Tell Which Wi-Fi Chipset you have?
- Install Realtek Wi-Fi Driver from PPA:
- Step 1: Disable Secure Boot
- Step 2: Add the Ubuntu PPA
- Step 3: Update the cache
- Step 4: Select install driver package for your chipset
- Step 5: Load the driver (Kernel Module)
- How to Uninstall:
- How to install “Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200 driver”
- Method for the Installation of Intel Wi-Fi-6 AX200
- Conclusion
Linux Wireless
We currently have a fair amount of working drivers that cover most of the available wireless networking cards. However, they don’t implement all features and may have some issues, due to various reasons like companies not providing specs. Below is an alphabetically sorted list of drivers and what they currently can and can’t do.
NOTE: All drivers can of course run in station mode, but only a few drivers support the other available wireless modes! Support of cfg80211 also offers benefits.
| Driver | Manufacturer | cfg80211 | AP | IBSS | mesh | monitor | PHY modes | Buses |
| adm8211 | ADMtek/Infineon | yes | no | no | no | ? | B | PCI |
| airo | Aironet/Cisco | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | PCI / PCMCIA |
| ar5523 | Atheros | yes | no | no | no | yes | A(2)/B/G | USB |
| at76c50x-usb | Atmel | yes | no | no | no | no | B | USB |
| ath5k | Atheros | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A/B/G | PCI / PCI-E / PCMCIA |
| ath6kl | Atheros | yes | no | yes | no | no | A/B/G/N | SDIO / USB |
| ath9k | Atheros | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A/B/G/N | PCI / PCI-E / AHB / PCMCIA |
| ath9k_htc | Atheros | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | B/G/N | USB |
| ath10k | Atheros | yes | yes | yes (6) | yes (6) | yes (6) | A/B/G/N/AC | PCI-E / AHB / SDIO |
| ath11k | Atheros | yes | yes | no | yes (6) | yes (6) | A/B/G/N/AC/AX | PCI-E / AHB |
| atmel | Atmel | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | PCI / PCMCIA |
| b43 | Broadcom | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(2)/B/G | SSB / PCI / PCI-E / PCMCIA |
| b43legacy | Broadcom | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(2)/B/G | PCI / SSB |
| brcmfmac | Broadcom | yes | yes | yes | no | no | A(1)/B/G/N/AC | USB / SDIO / PCI-E |
| brcmsmac | Broadcom | yes | yes | no | no | yes | A(1)/B/G/N | PCI-E / AXI |
| carl9170 | ZyDAS/Atheros | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(1)/B/G/N | USB |
| cw1200 | ST-Ericsson | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | A/B/G/N | SPI / SDIO |
| hostap | Intersil/Conexant | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | PCI / PCMCIA |
| ipw2100 | Intel | no | no | yes | no | no | B | PCI |
| ipw2200 | Intel | no | no (3) | yes | no | no | A/B/G | PCI |
| iwlegacy | Intel | yes | no | yes | no | no | A/B/G | PCI-E |
| iwlwifi | Intel | yes | yes (6) | yes | no | yes | A/B/G/N/AC | PCI-E |
| libertas | Marvell | no | no | yes | yes (4) | no | B/G | USB / PCMCIA / SDIO / GSPI |
| libertas_tf | Marvell | yes | yes | no | yes | ? | B/G | USB |
| mac80211_hwsim | Jouni | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | A/B/G/N | NONE! |
| mt76 | Mediatek | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A/B/G/N/AC/AX | PCIe / SoC / USB / SDIO |
| mt7601u | Mediatek | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N/ | USB |
| mwifiex | Marvell | yes | yes | yes | ? | ? | A/B/G/N | SDIO / PCI-E / USB |
| mwl8k | Marvell | yes | yes | ? | ? | yes | A/B/G/N | PCI |
| orinoco | Agere/Intersil/Symbol | yes | no | yes | no | yes | B | PCI / PCMCIA / USB |
| p54pci | Intersil/Conexant | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(1)/B/G | PCI / PCMCIA |
| p54spi | Conexant/ST-NXP | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(1)/B/G | SPI |
| p54usb | Intersil/Conexant | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(1)/B/G | USB |
| ** prism2_usb | Intersil/Conexant | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | USB |
| qtnfmac | Quantenna | yes | yes | no | no | no | A/B/G/N/AC | PCI-E |
| ** r8192e_pci | Realtek | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | PCI-E |
| ** r8192u_usb | Realtek | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | USB |
| ** r8712u | Realtek | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | USB |
| ray_cs | Raytheon | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | pre802.11 | PCMCIA |
| rndis_wlan | Broadcom | yes | no | yes | no | no | B/G | USB |
| rt61pci | Ralink | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | A(1)/B/G | PCI |
| rt73usb | Ralink | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | A(1)/B/G | USB |
| rt2400pci | Ralink | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | B | PCI |
| rt2500pci | Ralink | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | A(1)/B/G | PCI |
| rt2500usb | Ralink | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | A(1)/B/G | USB |
| rt2800pci | Ralink | yes | yes | ? | ? | yes | A(1)/B/G/N | PCI |
| rt2800usb | Ralink | yes | yes | yes | yes(5) | yes | A(1)/B/G/N | USB |
| rtl8xxxu | Realtek | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | A(1)/B/G/N | USB |
| rtl8180 | Realtek | yes | no | no | no | ? | B/G | PCI |
| rtl8187 | Realtek | yes | no | yes | no | yes | B/G | USB |
| rtl8188ee | Realtek | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | PCI-E |
| rtl8192ce | Realtek | yes | ? | ? | ? | yes | B/G/N | PCI-E |
| rtl8192cu | Realtek | yes | yes | ? | ? | yes | B/G/N | USB |
| rtl8192de | Realtek | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | PCI-E |
| rtl8192se | Realtek | yes | yes | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | PCI-E |
| rtl8723ae | Realtek | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | PCI-E |
| rtl8723bs | Realtek | ? | ? | ? | no | no | B/G/N | SDIO |
| ** r8723au | Realtek | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G/N | USB |
| ** vt6655 | VIA | yes | yes | yes | no | no | A/B/G | PCI |
| ** vt6656 | VIA | yes | yes | yes | no | no | A/B/G | USB |
| wcn36xx | Qualcomm Atheros | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A/B/G/N | |
| wfx | Silicon Laboratories | yes | yes | no | no | no | A/B/G/N | SPI / SDIO |
| wil6210 | Atheros | yes | yes | no | no | yes | AD | PCI-E |
| ** winbond | Winbond | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | USB |
| ** wilc | Microchip | yes | yes | no | no | no | A/B/G/N | SPI / SDIO |
| wl1251 | Texas Instruments | yes | no | yes | ? | yes | B/G | SPI / SDIO |
| wl12xx | Texas Instruments | yes | yes | yes | no | no | A(1)/B/G/N | SPI / SDIO |
| wl18xx | Texas Instruments | yes | yes | yes | ? | ? | A/B/G/N | SDIO |
| wl3501_cs | Z-Com | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | pre802.11 | PCMCIA |
| ** wlags49_h2 | Lucent/Agere | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G | PCI / PCMCIA |
| zd1201 | ZyDAS/Atheros | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | USB |
| zd1211rw | ZyDAS/Atheros | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | A(2)/B/G | USB |
Note: ** staging drivers
Out of the tree drivers(Unsupported)
| Driver | Manufacturer | cfg80211 | AP | IBSS | mesh | monitor | PHY modes | Buses |
| acx1xx | Texas Instruments | yes | ? | ? | no | ? | B | PCI / PCMCIA / USB |
| agnx | Airgo/Qualcom | yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | A/B/G | PCI |
| ar6k | Atheros | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | B/G | ? |
| poldhu | NWN | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | B | PCMCIA |
| RT2880 iNIC | Ralink | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | PCI |
802.11a devices exist, but currently can’t be used with this driver, A/B/G devices will work in B/G mode only.
There is support with a special, out-of-tree driver and special firmware, see http://sf.net/projects/ipw2200-ap.
Abandoned/Deprecated Drivers(Unsupported)
| Driver | Manufacturer | cfg80211 | AP | ad-hoc | mesh | monitor | PHY modes | BUS | Replaced by |
| ar9170usb | ZyDAS/Atheros | yes | no | yes | no | yes | A(1)/B/G/N | USB | carl9170 |
| arlan | Aironet/Cisco | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | pre802.11 | ISA | — |
| at76_usb | Atmel | no | no | no | no | no | B | USB | at76c50x-usb |
| netwave_cs | Netwave/Xircom | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | pre802.11 | PCMCIA | — |
| otus | ZyDAS/Atheros | no | ? | no | no | no | A/B/G/N | USB | carl9170 |
| prism54 | Intersil/Conexant | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | A/B/G | PCI / PCMCIA | p54pci |
| stlc45xx | ST/Nokia | yes | no | no | no | no | B/G | SPI | p54spi |
| wavelan | Lucent | no | ? | ? | ? | ? | pre802.11 | ISA / PCMCIA | — |
Page Tools
How to Install Realtek Wifi Drivers in Ubuntu 22.04 | Linux Mint 21/20
Linux Kernel keeps updating with new device drivers. But, there are still some devices lack out-of-box support. Thanks to the open-source community, there are always a group of people maintaining missing drivers.
How to Tell Which Wi-Fi Chipset you have?
Firstly, you may want to find out the device name of your wireless network card. In Ubuntu or Linux Mint, you may just search for and open “hardinfo” (aka, System Profiler and Benchmark) either from start menu or ‘Activities’ overview.
Install "hardinfo" via Ubuntu Software or Synaptic Package Manager if you don't have it.
When it opens, navigate to “Devices -> PCI Devices“. Then, find out the network controller information in the right. For USB Wi-Fi adapter, go find it under “Devices -> USB Devices“.
For those familiar Linux command, use lspci command to find integrated network card or lsusb for USB adapter:
Install Realtek Wi-Fi Driver from PPA:
There’s a github repository that maintains RTL8822BE, RTL8822CE, RTL8821CE, RTL8723DE, RTL8723AU, RTL8723BU, RTL8188EU driver source codes. Advanced users may go to that page, grab the source and build by yourself.
To make life easier, the kablosuz-wireless PPA maintains the driver packages for:
- rtl8723bu, rtl8822bu, rtl8188eu, rtl8188eus, rtl8188fu, rtl8188gu, rtl8192cu, rtl8192du, rtl8192ee, rtl8192eu, rtl8192fu, rtl8723au, rtl8723bu, rtl8723de, rtl8723ds, rtl8723du, rtl8812au, rtl88XXau, rtl8814au, rtl8821ce, rtl8821cu, rtl8822bu, rtl8822ce, rtl8852au, rtw88, and rtw89.
The guy also maintains another PPA with packages for:
- r8101, r8125, RTL8152/RTL8153/RTL8156, r8168, rts5139, and rts5229 network drivers.
Step 1: Disable Secure Boot
The drivers are built in DKMS mode that will work (rebuild automatically) even after update to new Kernel series. If you have your system installed in UEFI mode, you have to disable secure boot first.
1. To verify if your system is installed in UEFI mode, open terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and run command:
[ -d /sys/firmware/efi ] && echo "EFI" || echo "BIOS"
2. To check the status of secure boot:
If secure boot is enabled, reboot into BIOS/UEFI settings and disable it!
Step 2: Add the Ubuntu PPA
First, open terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T key combination on keyboard. When it opens, run the command below to add the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kelebek333/kablosuz
For r8101, r8125, RTL8152/RTL8153/RTL8156, r8168, rts5139, and rts5229 network drivers, add another PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kelebek333/drivers
Step 3: Update the cache
Ubuntu 22.04 now automatically updates the cache while adding PPA. But, Linux Mint does not. So you have to manually run the command below to refresh cache:
Step 4: Select install driver package for your chipset
Open “Synaptic Package Manager“, navigate to “Origin” tab in the left. Finally click on “LP-PPA-kelebek333-drivers” or “LP-PPA-kelebek333-kablosuz” to list all the packages from that repository. Finally, right-click on desired driver package, mark for installation, and click Apply.
Install Synaptic Package Manager from Ubuntu Software if you don't have it.
Or, you can install the package via apt command (for example, install r8822bu driver):
sudo apt install r8822bu-dkms
Keep an eye on output info while installing the package. It tells where to install the Kernel modules.
Step 5: Load the driver (Kernel Module)
After installing the driver package, restart your computer. Then, you may find out the modules via:
ls /usr/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/updates/dkms
The command should outputs the previously installed Kernel modules in .ko files. You can finally, load the driver ( 8723ds for example) via command:
And, verify via lsmod command with ‘grep’ filter:
If you have loaded the correct network driver, Wi-Fi should work now!
How to Uninstall:
To unload the driver module, use modprobe command with -r flag. For example, unload ‘8723ds’ via command:
And, to remove the driver package, either use “Synaptic Package Manager” or run apt remove command:
sudo apt remove package_name
To remove the Ubuntu PPAs, use command:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:kelebek333/kablosuz
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:kelebek333/drivers
How to install “Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200 driver”
Intel AX200 is one of the latest adapters that is used to access Wi-Fi on your system. It can access networks such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth at high speeds. It also supports Wi-Fi 6 (and lower versions) and Bluetooth 5.0 (and its lower releases). Through this article, you will learn how you can download and install the driver for the Intel wifi 6 AX200 on your Ubuntu system.
Method for the Installation of Intel Wi-Fi-6 AX200
Modern computing devices tend to use Wi-Fi rather than ethernet. To properly utilize it, the appropriate drivers must be installed on the system. This section will show you how you can find and install the Intel Wi-Fi AX200 driver on your system successfully.
Step 1: Check system adapter
Firstly, it is important to ensure that AX200 is correctly implemented into your system. To check which wireless device your system has, open the terminal and enter this statement:
If you have AX200 in your system, you should find a message like this in the outcome:
05:00.0 Network controller: Intel Corporation WiFi 6 AX200 (rev 1a)Step 2: Find and download your driver
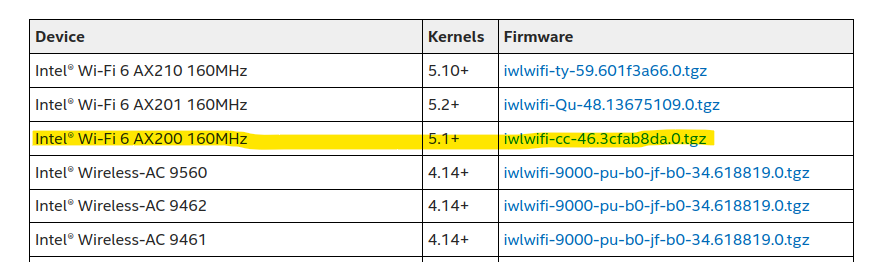
Open this link and find the corresponding driver that you need and download it:
In this case, we need the following driver as highlighted down below:
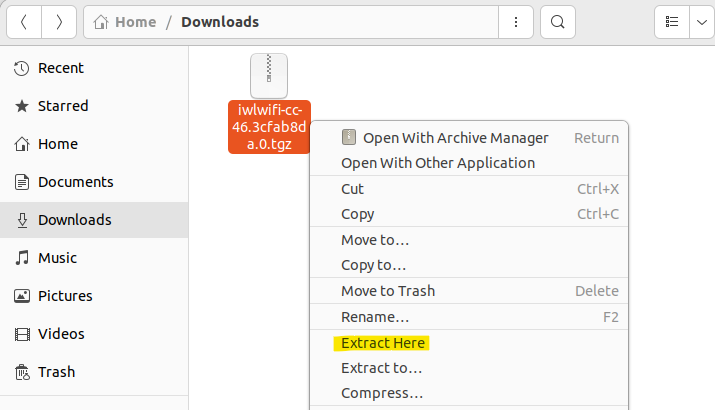
Step 3: Extract the downloaded file
After downloading the driver. Open your “Downloads” folder and extract the file as shown:
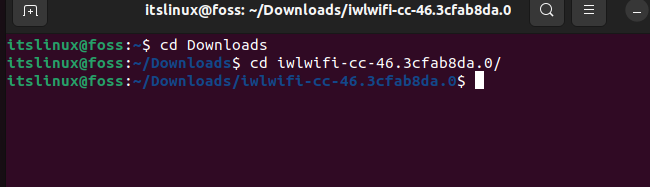
Step 4: Change the present directory
Once extracted, you can open the terminal and go into the directory where your extracted files are present. In our case, the files are in the “Downloads/iwlwifi-cc-46.3cfab8da.0” directory. The following commands lead us to that directory:
$ cd Downloads $ cd iwlwifi-cc-46.3cfab8da.0Step 5: Install the driver
Once you are inside the directory (where the files are extracted), you can install the wifi 6 ax200 driver via the following command. The command copies the “iwlwifi-cc-a0-46.uncode” file to “/lib/firmware” which ultimately installs the intel wifi 6 ax200 driver on Linux:
$ sudo cp iwlwifi-cc-a0-46.ucode /lib/firmwareThe file is copied to this directory since it is linked directory to the hardware of the system. The driver will be read by the system hardware once it is transferred to this directory.
This should install the driver onto your system. Reboot your system, and it will start working
Conclusion
The “Intel wifi 6 ax200 driver” can be installed by downloading the “tar” file from the website and extract/copy the installation files into “/lib/firmware”. Once this driver is successfully installed on your system, the wifi card that is installed on your system will be able to perform its function to its maximum potential. This post has demonstrated the method to install “Intel wifi 6 ax200 driver” in Linux.
TUTORIALS ON LINUX, PROGRAMMING & TECHNOLOGY