- How to enable monitor mode on your wireless interface
- inkyvoxel
- Quick guide
- Three ways to set wireless interface to Monitor mode and Managed mode
- 1. How to enable monitor mode using iw
- 2. How to enable monitor mode using Airmon-ng
- 3. How to enable monitor mode using iwconfig
- NetworkManager prevents monitor mode
- Related articles:
How to enable monitor mode on your wireless interface
If you want to be able to capture all packets within the range of your wireless device, you need to enable «Monitor» mode. Here’s a quick guide on how to do that.
inkyvoxel
By default, your wireless interfaces are set to «Managed» mode. A wireless interface set to «Managed» mode can only capture packets with a «Destination MAC» set to its own MAC address.
If you want to be able to capture all packets within the range of your wireless device, you need to set the mode of your wireless interface to «Monitor».
However, not all wireless devices support monitor mode, so you will need to check that your device is compatible.
Quick guide
If you have Aircrack-ng installed, you can run the following commands in your terminal:
- Run airmon-ng to list all your network interfaces.
- Run arimon-ng check kill to stop interfering network processes.
- Run airmon-ng start wlan0 to start your network interface in monitor mode, in this case we are using wlan0 .
If you are not using Aircrack-ng, you can run the following commands in your terminal:
- Run iwconfig to view your wireless interfaces and check their current mode.
- Run ifconfig wlan0 down to disable the network interface you wish to change, in this case it is wlan0 .
- Run iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor to change the mode of wlan0 to «monitor».
- Run ifconfig wlan0 up to re-enable your network interface.
You may need to run these commands as root or a user with privileges.
Once you have re-enabled your network interface, you can run iwconfig to confirm your wireless interface is running with «Monitor» mode:
wlan0 IEEE 802.11b ESSID:"" Nickname:"" Mode:Monitor Frequency:2.412 GHz Access Point: Not-Associated Three ways to set wireless interface to Monitor mode and Managed mode
You can use the following command to set wireless interface to Monitor mode and Managed mode on any Linux distro. The only requirement is availability wireless adapter that supports monitor mode. This one is recommended.
1. How to enable monitor mode using iw
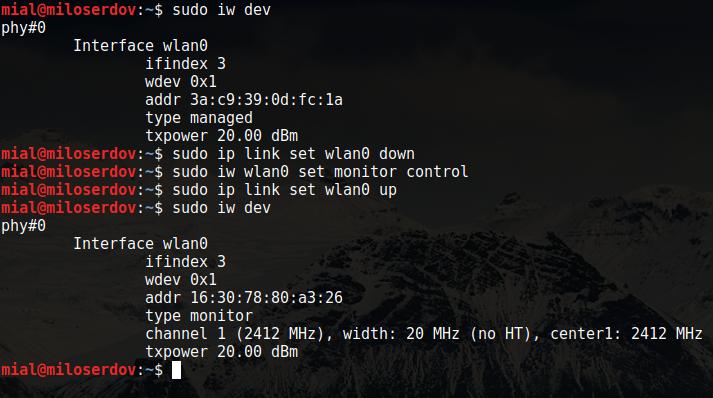
You should check whether the operating system is able to recognize your Wi-Fi card. In addition, you need to know the name of the wireless interface.
Get to know the wireless interface name:
phy#0 Interface wlan0 ifindex 3 wdev 0x1 addr 3a:c9:39:0d:fc:1a type managed txpower 20.00 dBm

As you can see, the name of my wireless interface is wlan0. In addition, you can see that it is in managed mode.
To set wireless interface to Monitor mode with iw you can use the following command sequence:
sudo ip link set IFACE down sudo iw IFACE set monitor control sudo ip link set IFACE up
Where IFACE replace with actual name of your wireless interface. In may example:
sudo ip link set wlan0 down sudo iw wlan0 set monitor control sudo ip link set wlan0 up
Then check the status of you wireless interface one more time:
sudo iw dev phy#0 Interface wlan0 ifindex 3 wdev 0x1 addr 16:30:78:80:a3:26 type monitor channel 1 (2412 MHz), width: 20 MHz (no HT), center1: 2412 MHz txpower 20.00 dBm
As you can see, now type monitor. Note: the name of interface is not changed by this method.
To return wireless interface in Managed mode with iw you can use the following command sequence:
sudo ip link set IFACE down sudo iw IFACE set type managed sudo ip link set IFACE up
Where IFACE replace with actual name of your wireless interface. In may example:
sudo ip link set wlan0 down sudo iw wlan0 set type managed sudo ip link set wlan0 up
2. How to enable monitor mode using Airmon-ng
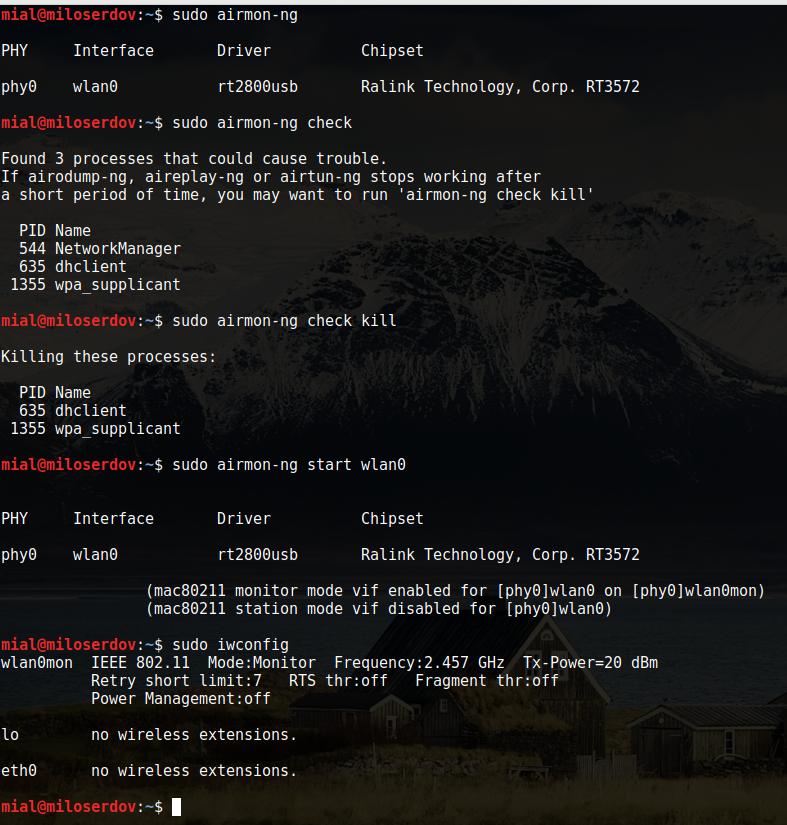
Again, we should get information about our wireless interface:
PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0 rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT3572
The name of interface is wlan0.
Checking for interfering processes
Before putting a card into monitor mode, it will automatically check for interfering processes. It can also be done manually by running the following command:
This command stops network managers then kill interfering processes left:
At last, we start monitor mode:
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0 PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0 rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT3572 (mac80211 monitor mode vif enabled for [phy0]wlan0 on [phy0]wlan0mon) (mac80211 station mode vif disabled for [phy0]wlan0)
As you can see, it created a monitor mode interface called wlan0mon.
sudo iwconfig wlan0mon IEEE 802.11 Mode:Monitor Frequency:2.457 GHz Tx-Power=20 dBm Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Power Management:off lo no wireless extensions. eth0 no wireless extensions.
Disable monitor mode
sudo airmon-ng stop wlan0mon PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0mon rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT3572 (mac80211 station mode vif enabled on [phy0]wlan0) (mac80211 monitor mode vif disabled for [phy0]wlan0mon)
Don’t forget to restart the Network Manager. It is usually done with the following command:
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager
3. How to enable monitor mode using iwconfig
As usual, start from checking interface name:
sudo iwconfig lo no wireless extensions. eth0 no wireless extensions. wlan0 IEEE 802.11 ESSID:off/any Mode:Managed Access Point: Not-Associated Tx-Power=20 dBm Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Encryption key:off Power Management:off
The network interface with wireless extension is called wlan0.
sudo ifconfig IFACE down sudo iwconfig IFACE mode monitor sudo ifconfig IFACE up
sudo ifconfig wlan0 down sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor sudo ifconfig wlan0 up
Disable monitor mode:
sudo ifconfig wlan0 down sudo iwconfig wlan0 mode managed sudo ifconfig wlan0 up
NetworkManager prevents monitor mode
If NetworkManager restarts automatically after each kill, and it pretends monitor mode, you can stop it manually:
In Kali Linux, BlackArch, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager
Note: when you stop NetworkManager, your Internet access disappears!
