- Чем Wi-Fi отличается от Bluetooth: главные отличия и какая технология лучше
- Сходства
- Различия
- Вывод
- Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi
- Comparison chart
- Video Explaining the Differences
- References
- Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi: What’s the Difference?
- In This Article
- Overall Findings
- Speed: Higher Power Delivers Higher Speeds
- Use Cases: Peripherals vs. Whole Home Internet Access
- Networking: All Route to the Modem
- Final Verdict
Чем Wi-Fi отличается от Bluetooth: главные отличия и какая технология лучше
Всем привет! В статье сегодня мы разберем вопрос – чем отличается Блютуз от Вай Фай. Как не странно, но эти технологии частенько путают между собой. И это понятно, так как Wi-Fi и Bluetooth используют в своем вооружении передачу данных по воздуху беспроводным путем с помощью банальных радиоволн.
Есть правда очень много общего у двух этих технологий, но обо все по порядку. В статье я постараюсь рассказать и раскрыть этот вопрос как можно проще и понятнее, но если у вас возникнут вопросы – то смело пишите о них в комментариях.
Сходства
Как я уже упомянул, главным сходством является передача информации с помощью радиоволн. При этом, как и в Wi-Fi, так и в Bluetooth используется диапазон частот 2,402 ГГц — 2,48 ГГц. В обоих случаях с помощью радиоволн передается информация от одного устройства к другому и обратно. На этом, наверное, самое главное сходство заканчивается.
Различия
А вот теперь мы рассмотрим главное различие. В первую очередь давайте посмотрим на само слово Wi-Fi, или развёрнуто «Wireless Fidelity» – что в переводе обозначает «Беспроводная сеть». Про беспроводную, мы уже поняли, но вот что именно обозначает слово сеть.
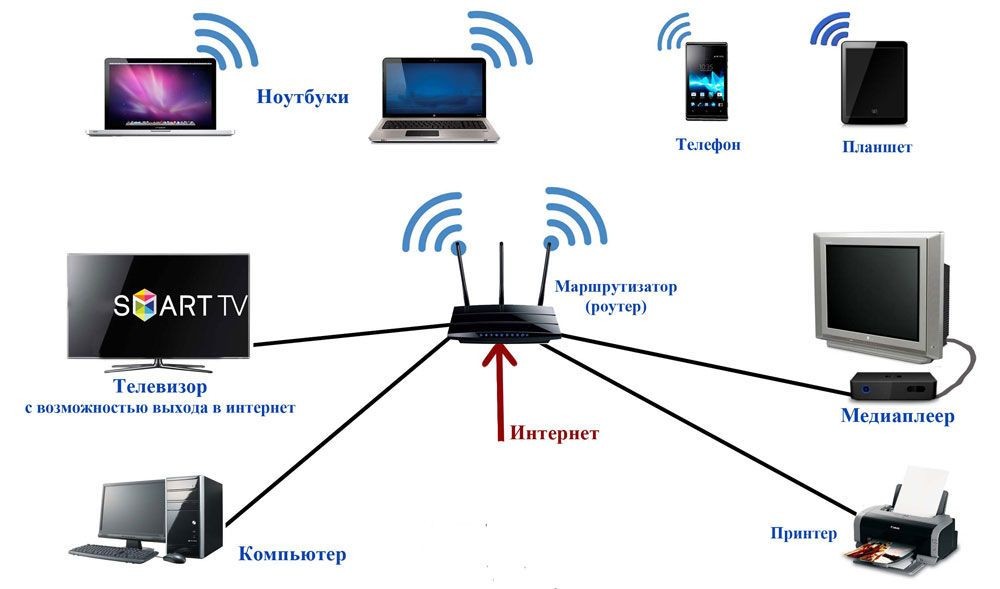
Многие люди путают слово «Wi-Fi» и «Интернет», но на самом деле это разные вещи, хоть они и могут быть связаны друг с другом. Для того чтобы работала беспроводная сеть или WiFi – нужно специальное устройство: маршрутизатор или роутер. Роутер – начинает строить вокруг себя беспроводную сеть, к которой могут подключиться другие аппараты: телефон, планшет, ноутбук, телевизор и т.д.
Вот именно маршрутизатор грамотно связывает все эти устройства. Если к роутеру подключить кабель от провайдера и настроить, то на всех устройствах, подключенных к маршрутизатору, будет интернет. Но как я и говорил, интернета может и не быть, но вот WiFi спокойно может существовать. Например, если вас отключат от интернета за не уплату, то подключиться к беспроводной сети вы всё равно сможете, но вот интернета там конечно же не будет. Теперь надеюсь вы понимаете, что вай-фай и интернет – имеют только косвенную связь.
Bluetooth же использует для прямого подключения. Например, при подключении Блютус наушников к телефону, информация идет на прямую от смартфона на второе устройства – без участия роутера.

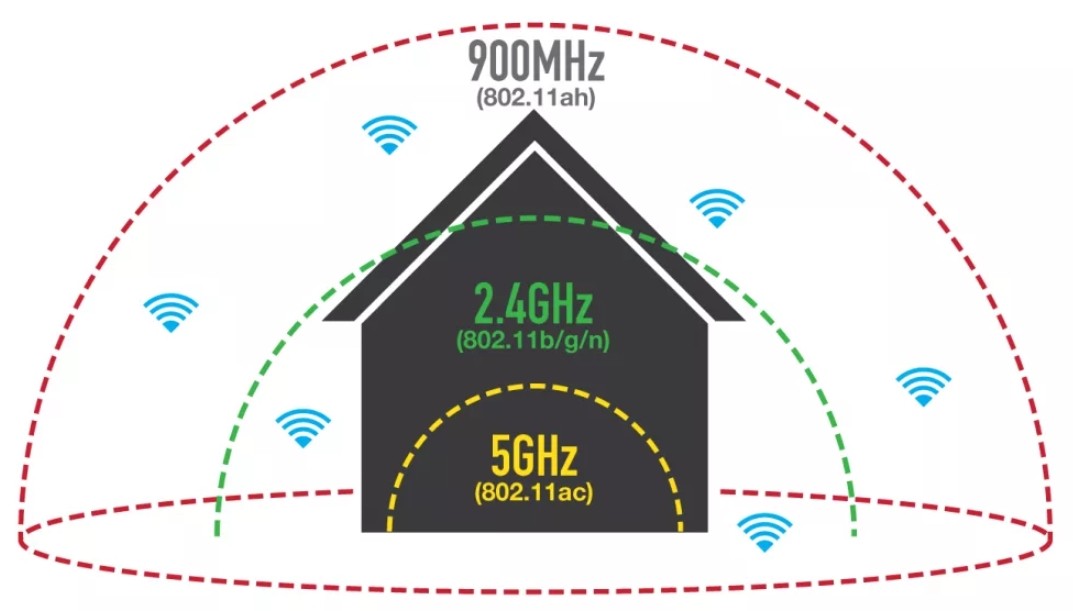
Ещё одним главным отличием является диапазон действия радиоволны. Bluetooth бьет максимально на метров 10-20. Wi-Fi сеть может бить на сотни метров, а при использовании узконаправленных вай-фай пушек и на несколько километров.
При передаче данных в Bluetooth используются совершенно разные стандарты и протоколы. Например, в нем же используется отдельный профиль, который позволяет управлять внешним устройством. У меня дома стоит телевизор, а пульт ДУ от него работает как раз на данном протоколе Bluetooth.
В Wi-Fi есть так называемые стандарты, от которых зависит скорость передачи данных:
- IEEE 802.11b – 11 Мбит в секунду
- IEEE 802.11g – 54 Мбит в секунду
- IEEE 802.11n – 150 Мбит в секунду при использовании одного канал и ширины в 20 Мгц. В перспективе можно увеличить скорость до 600 Мбит в секунду.
Хочется отдельно рассказать про частоту 5 ГГц, которую также в последнее время стали использовать в беспроводных сетях. При этом появился новый стандарт IEEE 802.11ac, который при желании можно разогнать до скорости 6.77 Гбит в секунду. У Bluetooth скорость передачи данных в разы меньше, а также используется другой стандарт передачи информации – IEEE 802.15.4.
Если говорить проще, то в первую очередь разница именно в способе применения. Если Wi-Fi используется именно для подключения большого количества устройств в одну локальную сеть для дальнейшего доступа к интернету. То у Блютус задача связи между двумя устройствами на прямую как в беспроводных: наушниках, мышках, клавиатурах, пультах дистанционного управления и т.д.
В качестве дополнения хочу порекомендовать несколько более подробных статей:
Вывод
Как видите разница между вай-фай и Bluetooth не очевидна, но она все же есть. Также помимо отличий есть и сходства, о которых можно было заметить по прочтению данной статьи. Также пока невозможно сказать, что лучше: вайфай или Блютуз, так как обе эти технологии используются в разных местах и имеют разное назначение. Если у вас ещё остались вопросы или быть может есть дополнение, то смело пишем в комментарии.
Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi
Bluetooth and WiFi are different standards for wireless communication.
Bluetooth technology is useful when transferring information between two or more devices that are near each other when speed is not an issue, such as telephones, printers, modems and headsets. It is best suited to low-bandwidth applications like transferring sound data with telephones (i.e. with a Bluetooth headset) or byte data with hand-held computers (transferring files) or keyboard and mice.
Wi-Fi is better suited for operating full-scale networks because it enables a faster connection, better range from the base station, and better wireless security (if configured properly) than Bluetooth.
Comparison chart
Bluetooth versus Wi-Fi comparison chart| Bluetooth | Wi-Fi | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz | 2.4, 3.6, 5 GHz |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Bandwidth | Low ( 800 Kbps ) | High (11 Mbps ) |
| Specifications authority | Bluetooth SIG | IEEE, WECA |
| Security | It is less secure | Security issues are already being debated. |
| Year of development | 1994 | 1991 |
| Primary Devices | Mobile phones, mouse, keyboards, office and industrial automation devices. Activity trackers, such as Fitbit and Jawbone. | Notebook computers, desktop computers, servers, TV, Latest mobiles. |
| Hardware requirement | Bluetooth adaptor on all the devices connecting with each other | Wireless adaptors on all the devices of the network, a wireless router and/or wireless access points |
| Range | 5-30 meters | With 802.11b/g the typical range is 32 meters indoors and 95 meters (300 ft) outdoors. 802.11n has greater range. 2.5GHz Wi-Fi communication has greater range than 5GHz. Antennas can also increase range. |
| Power Consumption | Low | High |
| Ease of Use | Fairly simple to use. Can be used to connect upto seven devices at a time. It is easy to switch between devices or find and connect to any device. | It is more complex and requires configuration of hardware and software. |
| Latency | 200ms | 150ms — Average Latency. (It depends on the speed of connection) |
| Bit-rate | 2.1Mbps | 600 Mbps |
Video Explaining the Differences

References
Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi: What’s the Difference?
Jeremy Laukkonen is automotive and tech writer for numerous major trade publications. When not researching and testing computers, game consoles or smartphones, he stays up-to-date on the myriad complex systems that power battery electric vehicles .
In This Article
Bluetooth is a standard that connects computer peripherals wirelessly to a host device. The most common uses connect speakers, head units, keyboards, printers, and headsets to a phone, tablet, or computer. Wi-Fi is a standard that enables wireless internet access for devices on a local area network (LAN). While dependent on modems, Wi-Fi networks use wireless routers instead of Ethernet cables to connect devices to the internet. We take a deep dive into the similarities and differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
Overall Findings
- Mostly for connecting devices to each other.
- Lower power, shorter range, and slower data speeds.
- Operates on the RF (radio frequency) spectrum.
- Mostly for connecting devices to the internet.
- Higher power, wider range, and faster data speeds.
- Operates on the RF (radio frequency) spectrum.
Bluetooth is a wireless networking protocol that allows two devices to communicate with each other through a radio frequency (RF). With Bluetooth, you can wirelessly control a speaker through an app on your phone or to print documents on a printer that isn’t physically connected to your computer. Bluetooth is also used with hands-free headsets, wireless navigation systems, and remote mouse and keyboards.
A Wi-Fi network is the wireless extension of a wired modem connection. Wi-Fi is the wireless connectivity protocol used instead of a wired connection such as Ethernet. It requires a wireless router, through which all Wi-Fi devices on the network are channeled.
The term Wi-Fi is sometimes used interchangeably with the internet. Wi-Fi is not the same as the internet. The modem connects to the internet.
Both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth operate via radio frequency, though the range of a Wi-Fi network is typically larger than a Bluetooth connection. Although many Wi-Fi networks use the same 2.4 GHz band as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi uses more power.
| Wi-Fi | Bluetooth | |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Since 1994 | Since 1991 |
| Frequency | 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 11 Mbps | 800 Kbps |
| Range | Up to 92 meters | 1 to 100 meters depending on class |
| Latency | 150 ms | 200 ms |
| Bit-rate | 2.1 Mbps | 600 Mbps |
| Typical devices | Computers, game consoles, phones, smart TVs, and internet of things (IoT) devices. | Computers, phones, input devices like mice and keyboards, fitness trackers, headsets, and smart speakers. |
| Required hardware | Wi-Fi adapter connected to each device, and a wireless router or wireless access points. | Built-in bluetooth radio or a Bluetooth adapter connected to each device. |
| Typical use | Networking | Connecting devices |
Speed: Higher Power Delivers Higher Speeds
Bluetooth is typically slower and offers less bandwidth than Wi-Fi. This is one of the reasons why Bluetooth audio quality is considered inferior. Wi-Fi can be used to stream high-quality music, video content, and other large data streams.
Bluetooth 4.0 offers greater speeds than previous versions of the technology. However, it is capped at 25 Mbps, and the effective rate is lower than that. Wi-Fi network speeds vary depending on the protocol, but the slowest tolerable connections are faster than the theoretical limit of Bluetooth 4.0.
Use Cases: Peripherals vs. Whole Home Internet Access
- Mostly for connecting peripheral devices like speakers, printers, keyboards, and headphones.
- Shorter operational range than Wi-Fi.
- Mostly for connecting to the internet.
- Establishes a wireless LAN (local area network) accessible by any device with login credentials.
Bluetooth is primarily used to connect two devices over a short range using low energy. This makes it ideal for transmitting audio from a phone or tablet to a speaker system, or for enabling hands-free calls in a car. Bluetooth also provides an easy way to listen to music while driving, functioning as a wireless auxiliary cable.
Wi-Fi isn’t used in these situations, as the main purpose is to create a network for other devices to access the internet. Accordingly, it’s more useful in home and office settings than in cars.
Networking: All Route to the Modem
- Wirelessly connects speakers, head units, keyboards, printers, and headsets to control devices—usually a phone, tablet, or computer.
- Wirelessly connects a device to a modem, which connects to the internet. Can also connect to other devices in a LAN.
Both wired and wireless devices need to be routed through a modem, which is the actual portal to the internet. As long as the modem is connected to the internet, any device connected to the modem is (or has the capacity to be) connected to the internet.
Bluetooth connections can stem from either an Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection. A successful Bluetooth pairing will range up to about 30 feet. However, in most situations, the effective range is shorter. Bluetooth uses comparatively little energy and is fit for a personal area network, or PAN. PANs are used for communication among personal devices and contrast with a LAN.
A Wi-Fi network is the LAN through which devices can connect to a modem and, in turn, the internet. For that reason, it’s possible to use a wireless router to establish a Wi-Fi network without any internet connection involved. This allows devices on the network to share data with each other, though these devices won’t be able to connect to the internet without a modem.
Final Verdict
Comparing Wi-Fi and Bluetooth is like comparing apples and oranges. Wi-Fi is superior to Bluetooth in terms of range and speed. Bluetooth is favored for its low energy and narrow RF range, which Wi-Fi lacks.
Wi-Fi is the favored standard for establishing wireless home networks. Bluetooth is the favored standard for wirelessly connecting computer peripherals. Bluetooth is also increasingly found in head units, speakers, and home theater receivers. It’s hard to conceive of much competition for either, but the closest would be Wi-Fi Direct.
Wi-Fi Direct is a newer take on the device-to-device standard that Bluetooth has dominated for the last couple of decades. Like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct is designed to allow devices to find each other without setting up an ad hoc network. The biggest difference between traditional ad hoc Wi-Fi connections and Wi-Fi Direct is that the latter includes a discovery tool. The other issue with Wi-Fi and Wi-Fi Direct is power consumption, which is heavy and always an issue with mobile devices.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Bluetooth-vs-Wifi-9056516fca7541d2b34da5ecff3dd200.jpg)