- jcberthon / networkmanager-wifi-powersave.md
- Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode [Explained]
- What Is Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode?
- Why Use Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode?
- Does Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode Affect Wi-Fi?
- How to Toggle Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode?
- Windows Wi-Fi Power-Saving Mode
- Android Wi-Fi Power-Saving Mode
- iOS Wi-Fi Power-Saving Mode
- Conclusion
- Turn off WiFi adapter power saving mode
- Comments
jcberthon / networkmanager-wifi-powersave.md
NetworkManager supports WiFi powersaving but the function is rather undocumented.
From the source code: wifi.powersave can have the following value:
- NM_SETTING_WIRELESS_POWERSAVE_DEFAULT (0): use the default value
- NM_SETTING_WIRELESS_POWERSAVE_IGNORE (1): don’t touch existing setting
- NM_SETTING_WIRELESS_POWERSAVE_DISABLE (2): disable powersave
- NM_SETTING_WIRELESS_POWERSAVE_ENABLE (3): enable powersave
Then I propose 2 files, only one of them needs to be put under /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ .
One is forcing to disable powersaving, while the other one enable it.
Once you have put the file in the right folder, simply restart NetworkManager:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters. Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| # File to be place under /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d |
| [connection] |
| # Values are 0 (use default), 1 (ignore/don’t touch), 2 (disable) or 3 (enable). |
| wifi.powersave = 2 |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters. Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| # File to be place under /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d |
| [connection] |
| # Values are 0 (use default), 1 (ignore/don’t touch), 2 (disable) or 3 (enable). |
| wifi.powersave = 3 |
Thnaks for this, used for my connection and latency in ssh sessions seems to be imroved:
CONN=»my wifi conn»; nmcli con mod «$CONN» 802-11-wireless.powersave 2
Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode [Explained]
The technology is advancing and looking for more permanent solutions to power usage. Also, most of us use multiple devices daily, and these devices run on batteries . However, the batteries they run on are not that permanent.
So, we come up with different ways to save battery life and improve the performance of our devices. One of those ways is the Wi-Fi power-saving mode. So, we’ll discuss what Wi-Fi power-saving mode is, its benefits, how it can affect Wi-Fi, and how to toggle it on different devices.
What Is Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode?
The Wi-Fi power saving mode is a neat feature you may have on your device that comes with two significant benefits. The first one is, as it’s called, battery saving. It’s because as long as we’re connected to Wi-Fi, our device is using up battery power.
The second benefit is related to data usage. It’s quite common to disregard data usage when you’re connected to an unlimited plan. However, if you have a limited plan with your ISP (Internet Service Provider), you should mind the data usage, and this is where Wi-Fi power saving mode comes in handy.
Usually, what the Wi-Fi power saving mode feature does is analyze the way you use your device in terms of wireless connection and change the time Wi-Fi is on. Luckily, we can turn the feature off if we don’t want to use it.
Recommended reading:
There’s actually only one good reason you might not want to turn off Wi-Fi power-saving mode, and that’s being disconnected. Being disconnected can mean that you don’t get notifications about your emails, messages, etc. Especially if you’re using apps to communicate instead of regular messaging.
Why Use Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode?
The reason you should use Wi-Fi power-saving mode is the longer battery life for your battery-powered devices. This is a major benefit, and it’s provided by different power-saving features. These power-saving features are:
- DMS : The Directed Multicast Service means that broadcast and multicast transmission rates are much faster because they are directed at the device. Also, it reduces the traffic on different channels.
- Proxy ARP : This is the Proxy Address Resolution Protocol, and to put it simply, the main router within a network answers requests that are meant for other devices. Thus, it lessens the load on those devices and saves power.
- Idle period : Instead of devices constantly communicating with internet access points, they are simply associated with them, and they can conserve battery life.
- Neighbor discovery : It’s quite similar to the Proxy Address Resolution Protocol, and it preserves power by responding instead of the client. So, these are four features that are meant to preserve battery power.
Does Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode Affect Wi-Fi?
The obvious answer is yes, in terms of when the device connects to the wireless network. But, it doesn’t affect the data in any way. As mentioned, it can be annoying if you’re expecting an email or a message on social media because you might not get the notification.
If you disable Wi-Fi power saving mode , it can considerably increase the power consumption on your device. Having the adapter working when there’s no wireless hotspot available also drains power.
Most devices have it enabled by default, so the fundamental question we get from our readers is how to turn it off. Luckily, there are different procedures for different devices and we’re going to discuss where this setting is located.
How to Toggle Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode?
The most common devices people use to browse the internet and do other things while maintaining a wireless internet connection usually run on Windows 10, Android, or iOS. So, we will not discuss how to do it on Linux-based systems, even if there is such an option.
Windows Wi-Fi Power-Saving Mode
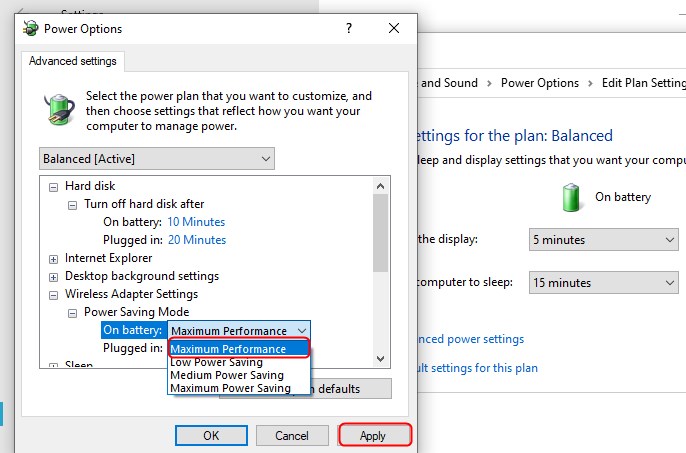
For Windows 10 devices, you need to go to Settings > System . Once you’re there, click on Power & Sleep on the left pane. Locate the Additional power settings button under Related settings .
Click on it, and click Change plan settings next to your current plan. After that, you need to click on Change advanced power settings . A window will pop up, and you need to locate Wireless Adapter Settings .
Expand the section and expand the Power Saving Mode section. There, you’ll see two options, On battery and Plugged in . You need to select Maximum Performance for both to disable Wi-Fi power saving. Click Apply , and that’s it. If you prefer to leave it on, just change the settings.
Android Wi-Fi Power-Saving Mode
To disable the Wi-Fi power saving mode on any Android device, the procedure goes like this. Go to your device’s Settings . Tap on Wireless and network . Once you’re there, go to Wi-Fi settings . Then, tap on Advanced .
You’ll need to locate the Wi-Fi sleep policy . It should say Never . Once you’re finished with this, the Wi-Fi power-saving mode will be disabled. The steps may vary between system versions, but they’re all more or less the same.
iOS Wi-Fi Power-Saving Mode
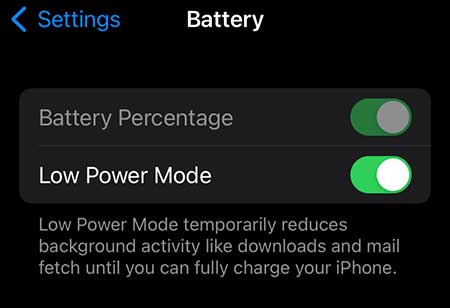
Unfortunately, iOS devices don’t have a setting specifically related to Wi-Fi power saving mode, but they do have a power-saving mode setting called Low Power Mode . This affects the performance overall, so it might be good to turn it off for a better wireless connection.
To do so, we need to go to Settings . Once there, just tap on Battery , and you’ll see the option to toggle Low Power Mode on or off. Turning it on will improve your device’s battery life, but it will negatively affect performance.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi power-saving mode is a great thing when you’re choosing battery life over performance. It’s a feature suitable for smartphones because it provides us a possibility to stay available for longer periods.
However, there’s no point in running Wi-Fi power saving mode on a Windows 10 laptop or PC because these are usually plugged in when we’re using them. So, it’s best to turn them off for these devices.
Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
Turn off WiFi adapter power saving mode
By default, some wireless adapters enable “Power Saving”. This is a “sleep mode”, or rather an energy-saving feature. This means that the adapter will turn off the network connection when inactive. This is not a problem when using Raspberry Pi as a client. Then the WiFi connection is simply reactivated. But if you want to remotely access Raspberry Pi via SSH for example, it may not be accessible. Then it looks like the WiFi adapter is not working. Only the energy saving function is active.
So it is necessary to turn off the power saving function.
For each wireless adapter, switching off the power saving function looks different. As a rule, the energy-saving function is always active. If you have problems reaching Raspberry Pi via the WiFi adapter you should first locate the manufacturer, if you do not already know that. Often, however, one also has to do with noname products.
In the short term, the problem can be solved by staking out the WiFi adapter and plugging it in again. Then it is reinitialized and Raspberry Pi is again accessible via the WiFi. However, this does not help as a permanent solution. So it’s about switching off the energy saving function permanently.
overview
To turn off the power saving mode of a wireless adapter, there are several options that do not all work. It essentially depends on whether the kernel supports the feature for the wireless adapter, or whether you need to choose a product-specific solution.
- Switch off energy-saving mode via the network settings (variant 1)
- Switch off energy-saving mode via the network settings (variant 2)
- Shut down energy-saving mode of a Wi-Fi adapter from Edimax (Realtek chipset)
If the first two variants do not work for the WiFi adapter used, then you should look for a product-specific solution.
Note: Name of the network interfaces
Since Raspbian Stretch, the Ethernet and WiFi network interfaces have different names. So no longer “eth0” and “wlan0”, but “enx …” and “wlx …”. This concerns USB-connected network adapters whose names differ from the designations mentioned here. This means that one must first determine the individual name or change the naming to the old method.
version 1
If there is no product-specific solution, you can try it via the network settings. To do this, open the file with the network settings:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
Enter the following lines or add missing lines:
allow-hotplug wlan0 iface wlan0 inet manual wireless-power off
After saving and closing with Ctrl + O, Return, Ctrl + X all you have to do is reboot.
Note: Unfortunately, this setting does not work with some kernel versions.
version 2
To do this, open the file with the network settings:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
Enter the following lines or add missing lines:
allow-hotplug wlan0 iface wlan0 inet manual post-up iw dev wlan0 set power_save off
This switches off the energy-saving mode due to the condition.
Save, close the file and restart the system.
Solution: Disable energy-saving mode of a WiFi adapter from Edimax (chipset from Realtek)
For this solution to work, the wireless adapter must have a Realtek chipset. In this example RTL8192CU.
Of course, there is the question of whether you have a wireless adapter with this chipset.
If the module “8192cu” is located in one line, then you can create a configuration file for the driver.
sudo nano /etc/modprobe.d/8192cu.conf
Insert the following line into this file:
options 8192cu rtw_power_mgnt = 0 rtw_enusbss = 0
For the shutdown is active, you should restart Raspberry Pi.
Solution: Check power management status
Whether the energy-saving mode of the WiFi adapter in question is actually switched off can only be checked in practice during runtime. But you can at least check whether the setting was adopted.
We install the wireless tools for this.
sudo apt-get install iw wireless tools
The command “iwconfig” informs about the WiFi interfaces.
Here the option “Power Management” should be set to “off”. But that does not mean it really works. Sometimes a configuration change of the drivers is necessary.
An alternative source of information for power management status: