- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- License
- joshschmelzle/lswifi
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- Создание сканера Wi-Fi сетей на Python и Scapy
- Создание сканера Wi-Fi сетей на Python и Scapy
- Выбор текстового редактора или IDE
- winwifi
- Installation
- Usage
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
a CLI-centric Wi-Fi scanning tool for Windows
License
joshschmelzle/lswifi
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
lswifi is a CLI-centric Wi-Fi scanning tool for Windows that provides more information about nearby Wi-Fi networks than built-in tools (e.g. netsh show wlan networks ). Examples include Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), showing security AKMs and ciphers, parsing 802.11 feature set, looking at 6 GHz Reduced Neighbor Reports, and more. With capable Wi-Fi adapters, lswifi can detect and show networks in 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands.
Note: The Python Scripts directory must be added to the PATH environment variable.
> python -m pip install lswifi Output nearby Wi-Fi networks:
Output nearby Wi-Fi networks that have a detected signal of -60 dBm or stronger:
Output only networks that match my_ssid (partial match support):
Output verbose information (including Information Elements) for BSSID 00:00:00:00:00:00 (exact match):
Print and add detected AP names column in output:
Print and add detected AP names and QBSS column in output (try adding —mfp or —tpc too!):
Print an alternative table for BSSes which may contain 6 GHz Reduced Neighbor Reports:
Watch event notifications (inc. roaming, connection, scanning, etc.):
options: -h, --help show this help message and exit -version, --version, -V show program's version number and exit -n #, --scans # set how many scans to do before exiting --time # set test in seconds to perform scans for -i #, --interval # seconds between scans -ies [BSSID] print extra information about information elements for a specified BSSID -threshold -82, -t -82 threshold which excludes networks with weak signal strength from results (-82 is default) -all remove threshold filtering which excludes results with weaker signal -g display filter to limit output by 2.4 GHz band -a display filter to limit output by 5 GHz band -six display filter to limit output by 6 GHz band -include SSID display filter to limit results by specified SSIDs (partial matching supported) -exclude SSID display filter to exclude results by specified SSIDs (partial matching supported) -bssid BSSID display filter to limit results by specified BSSIDs (partial matching supported) --ap-names adds an ap name column to output and will cache ap names locally to help provide consistent results --qbss adds station and utilization columns to output using information from AP beacon QBSS IE --tpc adds TPC column to output using information from AP beacon 802.11h --mfp, --pmf adds Protected Management Frame column to output using information from AP beacon RSNE --period adds beacon period column to output using information from AP beacon --uptime, -uptime sort output by access point uptime based on beacon timestamp -rnr, --rnr special mode to create an alternate table based on RNR results --channel-width 20|40|80|160 display filter to limit output by a specified channel width -ethers display ap name column and use ethers files for the names --append-ethers BSSID,APNAME append BSSID and AP name to ethers file for AP names --display-ethers display the list of saved ethers; (BSSID,APNAME) mapping --data-location displays where config items are stored on the local machine -ap print the BSSID of the connected AP -channel print the channel of the connected AP -raw format output as the raw value for other scripts (for -ap and -channel only) --get-interfaces print current Wi-Fi status and information --list-interfaces print a list of available WLAN interfaces --json [JSON] output will be formatted as json --indent 4 JSON output will be formatted with pretty print with provided indent level --csv [CSV] output will be formatted as csv -export [BSSID] export bss and ies bytefiles. default behavior will export all from a scan. to export only one, provide full mac address of the BSSID as argument. -decode BYTEFILE decode a raw .BSS or .IES file --bytes BSSID output debugging bytes for a specified BSSID found in scan results. --watchevents a special mode which watches for notification on a wireless interface such as connection and roaming events --debug increase verbosity in output for debugging Here is how to upgrade lswifi using pip3 when there is a new version available.
First check where and if the executable exists:
> where.exe pip3 C:\Users\jsz\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Scripts\pip3.exe C:\Users\jsz\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\Scripts\pip3.exe # OR > where.exe python C:\Users\jsz\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\python.exe C:\Users\jsz\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe C:\Users\jsz\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\python.exe C:\msys64\mingw64\bin\python.exe
Let’s install and upgrade lswifi to the latest version available:
> pip3 install --upgrade lswifi # OR > python -m pip install -U lswifi
Check the version installed:
Looking to install a specific version of lswifi?
python -m pip install lswifi==0.1.33
- What OSes and Python versions are required to run lswifi ?
- Windows 10+ and Python 3.7 are the current minimum versions we’re willing to support (subject to change).
- Windows 11 and capable interface required for 6 GHz support. Don’t have 6 GHz capable interface? Try lswifi -rnr with multi-band 6 GHz APs nearby.
- Can you get add information from radio tap headers?
- Currently there is not a way to get radio tap headers from Native Wifi wlanapi.h.
- Do I need to install lswifi in a virtual environment (venv)?
- Only if you want to. Installing in a venv is optional and not necessary. lswifi currently has zero dependencies outside of the included standard library with Python.
- When I try to run lswifi from my Windows terminal I see an error that says ‘lswifi’ is not recognized as an internal or external command operable program or batch file. ?
- Either lswifi is not installed, or the Python Scripts directory is not in the PATH environment variable.
- To fix ensure the Scripts directory is included in the PATH environment variable and lswifi.exe exists in said folder.
- Here is an example for how to find the Scripts directory (this directory needs to be on the PATH):
> python Python 3.11.0 (main, Oct 24 2022, 18:26:48) [MSC v.1933 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import os,sys >>> os.path.join(sys.prefix, 'Scripts') 'C:\\Users\\jsz\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Python\\Python311\\Scripts'
Want to contribute? Thanks! Please take a few moments to read our contributing notes and check out the authors and credits here.
Создание сканера Wi-Fi сетей на Python и Scapy
Существует множество инструментов для взлома Wi-Fi (802.11), но одно дело использовать уже готовые инструменты, а другое создать свой. Далее покажу, как написать сканер Wi-Fi сетей на Python и Scapy. Наша тулза будет похожа на airmon-ng и Kismet из комплекта aircrack-ng.
Создание сканера Wi-Fi сетей на Python и Scapy
Итак, Scapy написан на Python и может подделывать или декодировать пакеты, отправлять их по сети, захватывать их и сопоставлять запросы и ответы. Он также может выполнять такие задачи, как сканирование, трассировка, зондирование, модульные тесты, атаки и обнаружение сети.
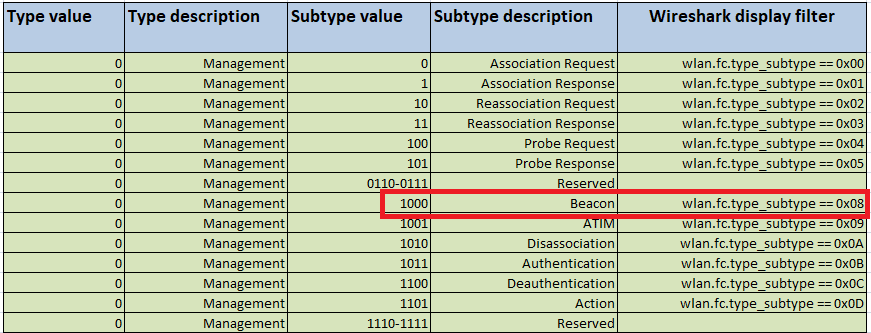
Scapy предоставляет интерфейс к libpcap (той же библиотеке, которую Wireshark использует для захвата и визуализации пакетов) и позволяет захватывать и анализировать пакеты. Он может, например, отфильтровать кадры (frame) точки доступа с типом 0 и подтипом 8.
Этот кадр включает в себя различную информацию:
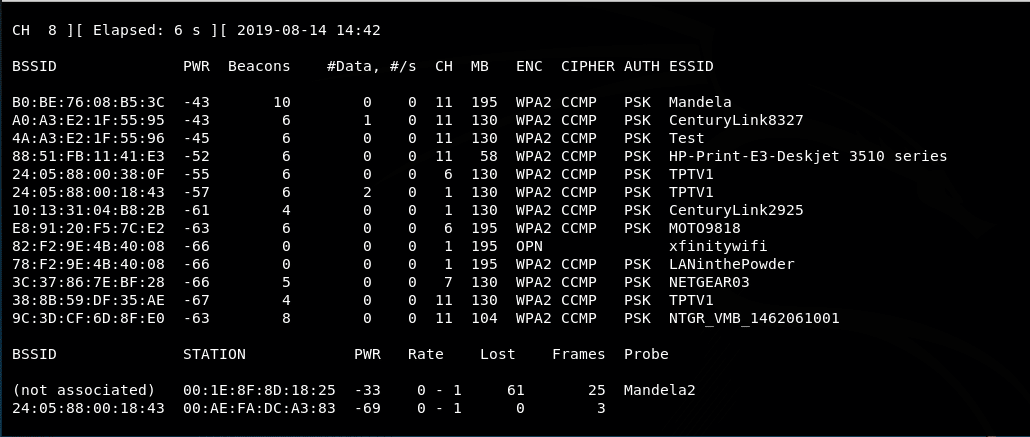
Если мы сможем получить эти кадры и проанализировать эту информацию, мы сможем создать сканер, который действует аналогично kismet или airodump-ng.
Для простоты в этом первом скрипте мы создадим сканер WiFi, который захватывает и отображает только канал, BSSID, шифрование и SSID.
Выбор текстового редактора или IDE
Для написания скриптов понадобится текстовый редактор. Подойдет любой текстовый редактор, такой как Leafpad, Vim, Gedit, Vi, Kate и т. д. Если вы умеете создавать скрипты с помощью IDE PyCharm, еще лучше.
В моем случае будет использоваться Kate — простой текстовый редактор с некоторыми возможностями IDE, полезными для Python, такими как проверка отступов и синтаксис. Если он у вас не установлен, вы можете установить его из репозитория Kali Linux:
winwifi
A Wi-Fi CLI tool for Windows. It allows you to scan Wi-Fi Access Points without being an admin to disable and enable the Wi-Fi interface.
Check pipx for installing as a standalone executable utility.
Installation
Usage
wifi 0.0.5 A Windows Wi-Fi CLI Usage: wifi [SWITCHES] [SUBCOMMAND [SWITCHES]] args. Meta-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits Subcommands: connect Connect to a specific access point; see 'wifi connect --help' for more info connected Show the current connected Wi-Fi SSID; see 'wifi connected --help' for more info disconnect Disconnect from a Wi-Fi access point; see 'wifi disconnect --help' for more info forget Remove speicifc access points from the historical list; see 'wifi forget --help' for more info history List the historical Wi-Fi access points; see 'wifi history --help' for more info scan Scan and list nearby Wi-Fi access points; see 'wifi scan --help' for more info wifi connect 0.0.5 Connect to a specific access point Usage: wifi connect [SWITCHES] ssid [passwd=''] Hidden-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits Switches --oneshot Do not remember the connection wifi connected 0.0.5 Show the current connected Wi-Fi SSID Usage: wifi connected [SWITCHES] Hidden-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits wifi disconnect 0.0.5 Disconnect from a Wi-Fi access point Usage: wifi disconnect [SWITCHES] Hidden-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits wifi forget 0.0.5 Remove speicifc access points from the historical list Usage: wifi forget [SWITCHES] ssids. Hidden-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits wifi history 0.0.5 List the historical Wi-Fi access points Usage: wifi history [SWITCHES] Hidden-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits wifi scan 0.0.5 Scan and list nearby Wi-Fi access points Usage: wifi scan [SWITCHES] Hidden-switches -h, --help Prints this help message and quits --help-all Print help messages of all subcommands and quit -v, --version Prints the program's version and quits Switches --refresh Force to refresh the Wi-Fi AP list