- Как Выполнить команды Linux из Командной строки Windows 10.
- Basic commands for WSL
- Install
- List available Linux distributions
- List installed Linux distributions
- Set WSL version to 1 or 2
- Set default WSL version
- Set default Linux distribution
- Change directory to home
- Run a specific Linux distribution from PowerShell or CMD
- Update WSL
- Check WSL status
- Check WSL version
- Help command
- Run as a specific user
- Change the default user for a distribution
- Shutdown
- Terminate
- Import and export a distribution
- Import a distribution in place
- Unregister or uninstall a Linux distribution
- Mount a disk or device
- Unmount disks
- Deprecated WSL commands
- Feedback
Как Выполнить команды Linux из Командной строки Windows 10.
Как вы знаете, Windows 10 может похвастаться Bash консолью Ubuntu, которая позволяет пользователю получить доступ и запускать приложения Ubuntu Windows 10. Баш предназначен для консольных приложений и услуг и позволяет запускать даже GUI — приложения с помощью небольшой хитрости. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как выполнить команду Linux непосредственно из строки cmd.exe в операционной системе Windows 10.
Можно опустить необходимость в отдельной консоли для Bash на Ubuntu в Windows 10 и запустить конкретную команду или набор команд непосредственно из командной строки. Это стало возможным благодаря реализации подсистеме Windows для Linux (WSL) .
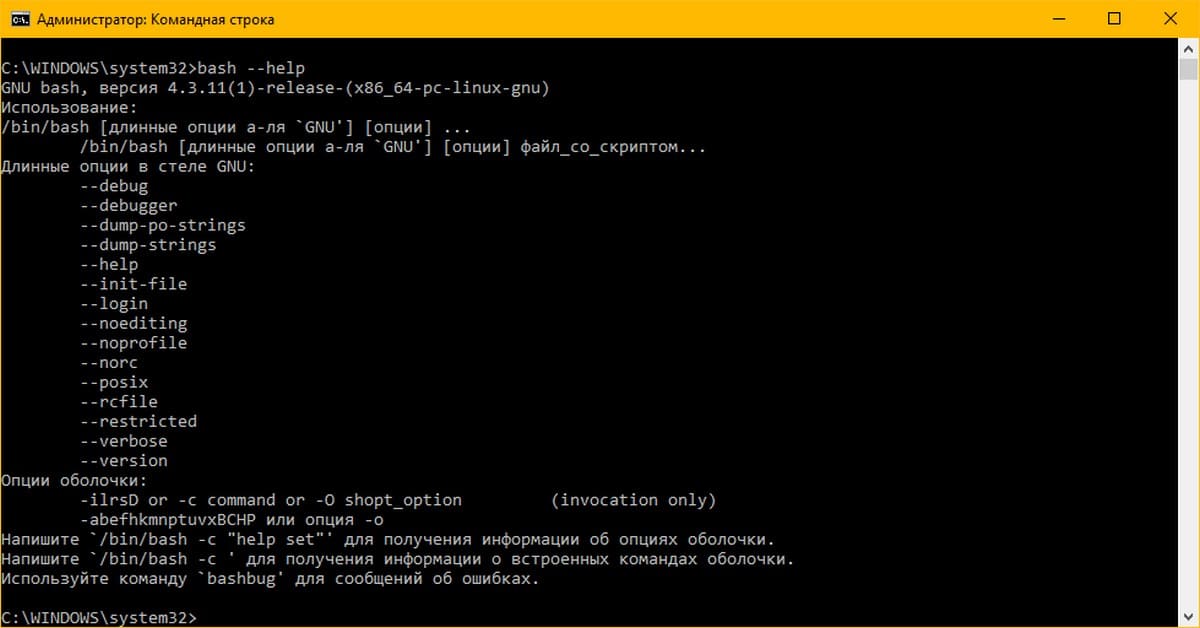
Консоль Баш может быть запущена с помощью следующего файла:
c:\windows\system32\bash.exe
Это приложение консоли, которое поддерживает несколько аргументов командной строки. Вы можете посмотреть их, выполнив команду:
Вывод –help выглядит следующим образом:
Как видно из краткой помощи, вы можете вызвать команду Linux напрямую, используя следующий синтаксис:
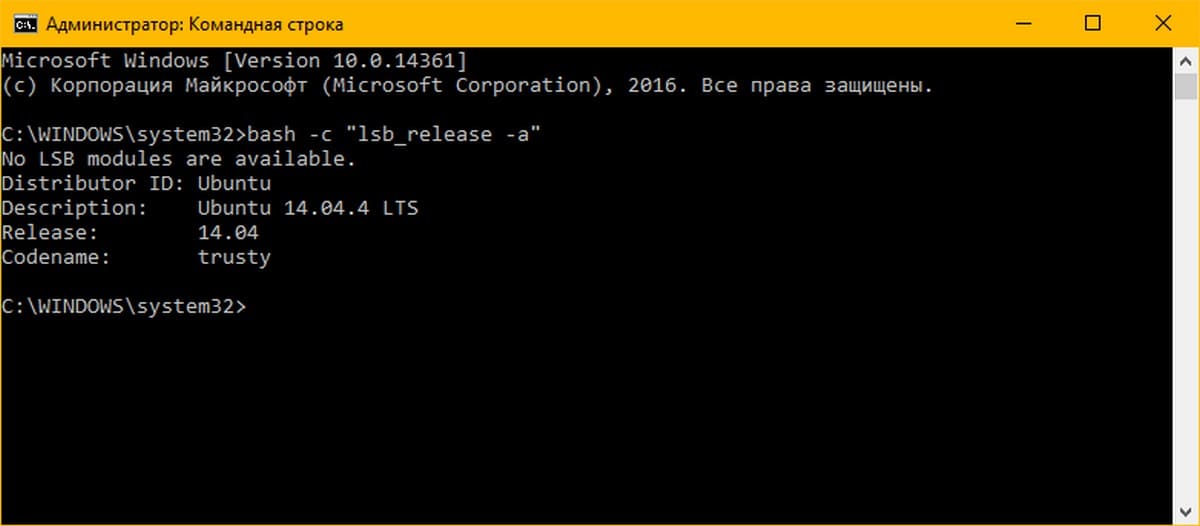
Следующий пример демонстрирует эту способность:
bash -c "lsb_release -a"
Вот некоторые команды Linux которые можно выполнить напрямую из Командной строки Windows 10.
Системная информация
- bash -c «lsb_release -a» — Посмотреть версию Ubuntu
- bash -c «uname -r» — Проверить версию ядра
- bash -c «uname -a» — Посмотреть всю информацию о ядре
- bash -c «arch» — отобразить архитектуру вашего компьютера
- bash -c «cat /proc/cpuinfo» — информация о ЦПУ
- bash -c «cat /proc/meminfo» — проверить использование памяти
- bash -c «df» — информация о использовании дисков
- bash -c «uptime» — время работы с момента включения
- bash -c «uname -a» — Посмотреть информация о ядре
Basic commands for WSL
The WSL commands below are listed in a format supported by PowerShell or Windows Command Prompt. To run these commands from a Bash / Linux distribution command line, you must replace wsl with wsl.exe . For a full list of commands, run wsl —help .
Install
Install WSL and the default Ubuntu distribution of Linux. Learn more. You can also use this command to install additional Linux distributions by running wsl —install . For a valid list of distribution names, run wsl —list —online .
- —distribution : Specify the Linux distribution to install. You can find available distributions by running wsl —list —online .
- —no-launch : Install the Linux distribution but do not launch it automatically.
- —web-download : Install from an online source rather than using the Microsoft Store.
When WSL is not installed options include:
- —inbox : Installs WSL using the Windows component instead of using the Microsoft Store. (WSL updates will be received via Windows updates, rather than pushed out as-available via the store).
- —enable-wsl1 : Enables WSL 1 during the install of the Microsoft Store version of WSL by also enabling the «Windows Subsystem for Linux» optional component.
- —no-distribution : Do not install a distribution when installing WSL.
If you running WSL on Windows 10 or an older version, you may need to include the -d flag with the —install command to specify a distribution: wsl —install -d .
List available Linux distributions
See a list of the Linux distributions available through the online store. This command can also be entered as: wsl -l -o .
List installed Linux distributions
See a list of the Linux distributions installed on your Windows machine, including the state (whether the distribution is running or stopped) and the version of WSL running the distribution (WSL 1 or WSL 2). Comparing WSL 1 and WSL 2. This command can also be entered as: wsl -l -v . Additional options that can be used with the list command include: —all to list all distributions, —running to list only distributions that are currently running, or —quiet to only show distribution names.
Set WSL version to 1 or 2
To designate the version of WSL (1 or 2) that a Linux distribution is running on, replace with the name of the distribution and replace with 1 or 2. Comparing WSL 1 and WSL 2.
Set default WSL version
To set a default version of WSL 1 or WSL 2, replacing with either the number 1 or 2 to represent which version of WSL you would like the installation to default on for new Linux distribution installations. For example, wsl —set-default-version 2 . Comparing WSL 1 and WSL 2.
Set default Linux distribution
To set the default Linux distribution that WSL commands will use to run, replace with the name of your preferred Linux distribution.
Change directory to home
The ~ can be used with wsl to start in the user’s home directory. To jump from any directory back to home from within a WSL command prompt, you can use the command: cd ~ .
Run a specific Linux distribution from PowerShell or CMD
To run a specific Linux distribution with a specific user, replace with the name of your preferred Linux distribution (ie. Debian) and with the name of an existing user (ie. root). If the user doesn’t exist in the WSL distribution, you will receive an error. To print the current user name, use the command whoami .
Update WSL
Update your WSL version to the latest version. Options include:
Check WSL status
See general information about your WSL configuration, such as default distribution type, default distribution, and kernel version.
Check WSL version
Check the version information about WSL and its components.
Help command
See a list of options and commands available with WSL.
Run as a specific user
To run WSL as a specified user, replace with the name of a user that exists in the WSL distribution.
Change the default user for a distribution
Change the default user for your distribution log-in. The user has to already exist inside the distribution in order to become the default user.
For example: ubuntu config —default-user johndoe would change the default user for the Ubuntu distribution to the «johndoe» user.
If you are having trouble figuring out the name of your distribution, use the command wsl -l .
This command will not work for imported distributions, because these distributions do not have an executable launcher. You can instead change the default user for imported distributions using the /etc/wsl.conf file. See the Automount options in the Advanced Settings Configuration doc.
Shutdown
Immediately terminates all running distributions and the WSL 2 lightweight utility virtual machine. This command may be necessary in instances that require you to restart the WSL 2 virtual machine environment, such as changing memory usage limits or making a change to your .wslconfig file.
Terminate
To terminate the specified distribution, or stop it from running, replace with the name of the targeted distribution.
Import and export a distribution
Imports and exports the specified tar file as a new distribution. The filename can be — for standard input. Options include:
- —vhd : Specifies the import/export distribution should be a .vhdx file instead of a tar file
- —version : For import only, specifies whether to import the distribution as a WSL 1 or WSL 2 distribution
Import a distribution in place
Imports the specified .vhdx file as a new distribution. The virtual hard disk must be formatted in the ext4 filesystem type.
Unregister or uninstall a Linux distribution
While Linux distributions can be installed through the Microsoft Store, they can’t be uninstalled through the store.
To unregister and uninstall a WSL distribution:
Replacing with the name of your targeted Linux distribution will unregister that distribution from WSL so it can be reinstalled or cleaned up. Caution: Once unregistered, all data, settings, and software associated with that distribution will be permanently lost. Reinstalling from the store will install a clean copy of the distribution. For example, wsl —unregister Ubuntu would remove Ubuntu from the distributions available in WSL. Running wsl —list will reveal that it is no longer listed.
You can also uninstall the Linux distribution app on your Windows machine just like any other store application. To reinstall, find the distribution in the Microsoft Store and select «Launch».
Mount a disk or device
Attach and mount a physical disk in all WSL2 distributions by replacing with the directory\file path where the disk is located. See Mount a Linux disk in WSL 2. Options include:
- —vhd : Specifies that refers to a virtual hard disk.
- —name : Mount the disk using a custom name for the mountpoint
- —bare : Attach the disk to WSL2, but don’t mount it.
- —type : Filesystem type to use when mounting a disk, if not specified defaults to ext4. This command can also be entered as: wsl —mount -t .You can detect the filesystem type using the command: blkid , for example: blkid .
- —partition : Index number of the partition to mount, if not specified defaults to the whole disk.
- —options : There are some filesystem-specific options that can be included when mounting a disk. For example, ext4 mount options like: wsl —mount -o «data-ordered» or wsl —mount -o «data=writeback . However, only filesystem-specific options are supported at this time. Generic options, such as ro , rw , or noatime , are not supported.
If you’re running a 32-bit process in order to access wsl.exe (a 64-bit tool), you may need to run the command in the following manner: C:\Windows\Sysnative\wsl.exe —command .
Unmount disks
Unmount a disk given at the disk path, if no disk path is given then this command will unmount and detach ALL mounted disks.
Deprecated WSL commands
wslconfig.exe [Argument] [Options] These commands were the original wsl syntax for configuring Linux distributions installed with WSL, but have been replaced with the wsl or wsl.exe command syntax.
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for