- Linux vs. Windows
- Comparison chart
- Multimedia, Gaming, and Productivity Applications
- Threats and Problems
- Cost Comparison
- Market Share and User Base
- History
- References
- Linux vs Windows: Key Difference Between Them
- Types of Files
- General Files
- Directory Files
- Device Files:
- Difference between Windows and Linux Users
- Regular User
- Root User
- Service user
- Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
- Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
- Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
- Linux vs Windows – Difference Between Them
Linux vs. Windows
Both Windows and Linux are Operating systems with their own advantages and differ in functionality and user friendliness.
Comparison chart
Multimedia, Gaming, and Productivity Applications
Both Linux and Windows OS are very rich in multimedia applications, though setting up sound and video options in older versions of Linux can be difficult for some users. The main advantage of Linux is that most of the multimedia applications are freely available, while in the case of Windows, users may have to pay a hefty amount to get the software although many Open Source/Free versions are often available. Moreover, if anyone buys a copy of Windows on a CD-ROM, they do not get any application software with it, other than bundled Microsoft software. But if the same person buys a copy of Linux on a CD-ROM, it typically comes with a lot of free application software, such as Open Office, a complete free Office suite including Spreadsheets, Presentation etc. A new computer with Windows pre-installed may have additional application software but that is totally up to the PC vendor. But, each Linux distribution comes in multiple flavors; the more expensive versions come with more application software.
A major attraction of Windows is the library of games available for purchase. A majority of games support Windows and are released first for the Windows platform. Some of these games can be run on Linux with a compatibility layer like Wine, although Wine is difficult to set up and require different versions of it for various games. Others, and especially more modern games that rely on proprietary delivery systems, copy protection, Windows dependencies, or advanced acceleration features, may fail in Linux environment. Though there are exceptions, such as id Software’s Doom and Quake. When a developer chooses to write graphics code in OpenGL instead of DirectX, Linux ports can become much easier.
The video below features a comparison of Linux-based Ubuntu 12 and Windows 8.

Threats and Problems
Every Windows user has faced security and stability issues. Since Windows is the most widely used OS, hackers, spammers target Windows frequently. Consumer versions of Windows were originally designed for ease-of-use on a single-user PC without a network connection and did not have security features built in. Microsoft releases security patches through its Windows Update service approximately once a month although critical updates are made available at shorter intervals when necessary.
Many times users of Windows OS face the “BLUE SCREEN OF DEATH”, caused by the failure of the system to respond, and eventually the user has to manually restart the PC . This is very frustrating for the user since they may lose valuable data.
On the other hand, Linux is very stable and more secure than Windows. As Linux is community driven, developed through people collaboration and monitored constantly by the developers from every corner of the earth, any new problem raised can be solved within few hours and the necessary patch can be ready at the same time. Also Linux is based on the UNIX architecture which is a multi user OS, so it is much more stable than single user OS Windows.
Cost Comparison
Windows is much more costly in organizational implementation purpose. As Windows Home is a single user OS, so for each PC, the organization needs to purchase a site license copy of Windows, which can be costly. Although, in developing countries and ones with oppressive governments, non-profits can receive a free site license from Microsoft. Where as for the implementation of Linux based solutions the organization only needs to obtain one copy. And as it can be freely distributed, the same copy can be used in all the 50 employees’ workstation. However, setup and support services may need to be purchased on an as-needed basis.
Current prices for some of these products are available on Amazon.com:
Market Share and User Base
According to the market research data of September 2007, on 92.63% of the world’s PCs, Windows is running, while only 0.8% PC users use Linux. The Home users, Multimedia enthusiasts mainly used Windows, where as for serious use, server application, Corporation servers are running on Linux. Irrespective of the GUI, many users find it is very difficult to use Linux as compared to Windows and so the appeal of Linux is very limited to common people. Also for licensing agreement with Microsoft, various PC vendors are entitled to bundle Windows OS with their PC. And for this Windows gain the initial market popularity over Linux. Though these days many PC vendor such as DELL, HP started to give Linux as the preinstalled OS to cut the cost of their PC system.
According to latest IDC report, Windows Server market is gaining popularity over Linux based Server. The annual rate at which Linux is growing in the x86 server space has fallen from around 53 percent in 2003 (45 percent globally), when Windows Server growth was in the mid-20 percent range, to a negative 4 percent growth (less than 10 percent globally) in calendar year 2006, IDC Quarterly Server Tracker figures show. Over the same time period, Windows has continued to report positive annual growth, outpacing the total growth rate in the x 86 markets by more than 4 percent in 2006, indicating that Linux has actually lost market share to Windows Server over this time. Linux servers now represent 12.7 percent of the overall server market while Windows server comprised 38.8 percent of all server revenue in Q1 of 2007. [1]
The main reason is that, while Linux Servers are looking for high performance computing and web serving, but Windows is apparently adopted on a much broader basis.
History
Windows first released as a part of Disk operating System(DOS) in the year of 1985. At that time Apple’s Macintosh was a very popular OS, as it introduced GUI to the world. So to increase the popularity of DOS, Bill Gates’s Microsoft bundled Windows 1 with the DOS at that time. But until Windows 3 which was released in 1990, achieve the success in the GUI based OS market. And with the release of Windows 95, in 1995, Microsoft became a household name in the OS market. From that time on, each Personal Computer comes with Windows OS as the preinstalled OS. The biggest achievement for Windows OS is that it is very user friendly, easy to understand, and it has the versatility to run with almost every different kind of Personal Computers.
Linux is based on the Multiuser OS UNIX, and it can be distributed freely. It is the brainchild of Mr, Linus Torvalds. Typically all underlying source code can be freely modified and used. Linux Kernel was first released for public use in 1991. The biggest achievement for Linux is that it is a multiuser OS and the Security and stability is better than Windows.
References
Linux vs Windows: Key Difference Between Them
When we compare file system in Windows and Linux, in Microsoft Windows, files are stored in folders on different data drives like C: D: E:
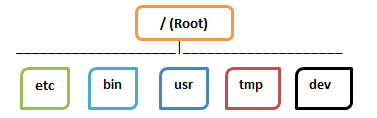
But, in Linux, files are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory.
This root directory can be considered as the start of the file system, and it further branches out various other subdirectories. The root is denoted with a forward slash ‘/’.
A general tree file system on your UNIX may look like this.
Types of Files
In Linux and UNIX, everything is a file. Directories are files, files are files, and devices like Printer, mouse, keyboard etc.are files.
Let’s look into the File types in more detail.
General Files
General Files also called as Ordinary files. They can contain image, video, program or simply text. They can be in ASCII or a Binary format. These are the most commonly used files by Linux Users.
Directory Files
These files are a warehouse for other file types. You can have a directory file within a directory (sub-directory).You can take them as ‘Folders’ found in Windows operating system.
Device Files:
In MS Windows, devices like Printers, CD-ROM, and hard drives are represented as drive letters like G: H:. In Linux, there are represented as files.For example, if the first SATA hard drive had three primary partitions, they would be named and numbered as /dev/sda1, /dev/sda2 and /dev/sda3.
Note: All device files reside in the directory /dev/
All the above file types (including devices) have permissions, which allow a user to read, edit or execute (run) them. This is a powerful Linux/Unix feature. Access restrictions can be applied for different kinds of users, by changing permissions.
Difference between Windows and Linux Users
There are 3 types of users in Linux.
Regular User
A regular user account is created for you when you install Ubuntu on your system. All your files and folders are stored in /home/ which is your home directory. As a regular user, you do not have access to directories of other users.
Root User
Other than your regular account another user account called root is created at the time of installation. The root account is a superuser who can access restricted files, install software and has administrative privileges. Whenever you want to install software, make changes to system files or perform any administrative task on Linux; you need to log in as a root user. Otherwise, for general tasks like playing music and browsing the internet, you can use your regular account.
Service user
Linux is widely used as a Server Operating System. Services such as Apache, Squid, email, etc. have their own individual service accounts. Having service accounts increases the security of your computer. Linux can allow or deny access to various resources depending on the service.
- You will not see service accounts in Ubuntu Desktop version.
- Regular accounts are called standard accounts in Ubuntu Desktop
In Windows, there are 4 types of user account types.
Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
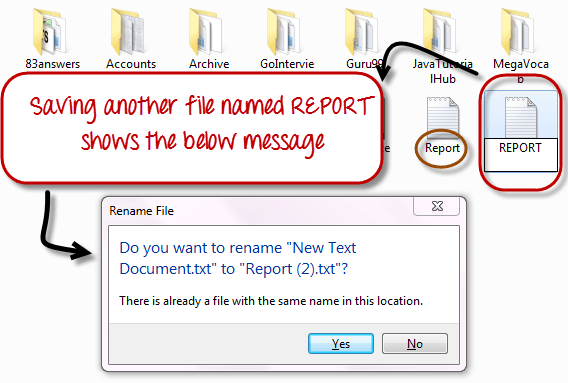
In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder. See below –
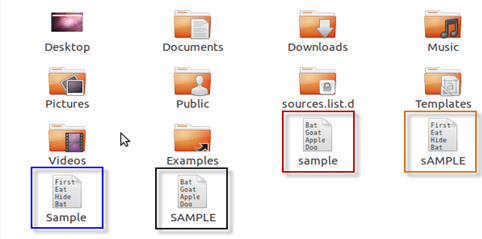
While in Linux, you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory, provided they use different cases.
Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
For every user in Linux, a directory is created as /home/
Consider, a regular user account “Tom”. He can store his personal files and directories in the directory “/home/tom”. He can’t save files outside his user directory and does not have access to directories of other users. For instance, he cannot access directory “/home/jerry” of another user account”Jerry”.
The concept is similar to C:\Documents and Settings in Windows.
When you boot the Linux operating system, your user directory (from the above example /home/tom) is the default working directory. Hence the directory “/home/tom is also called the Home directory which is a misnomer.
The working directory can be changed using some commands which we will learn later.
Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
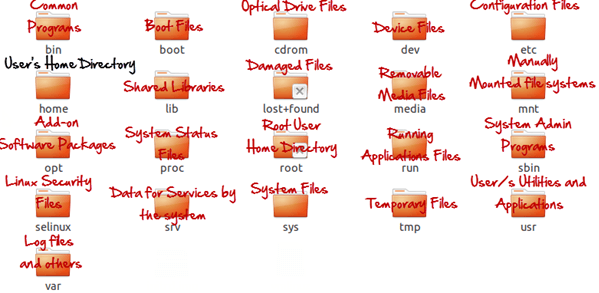
Comparing Windows vs Linux for other directories, in Windows, System and Program files are usually saved in C: drive. But, in Linux, you would find the system and program files in different directories. For example, the boot files are stored in the /boot directory, and program and software files can be found under /bin, device files in /dev. Below are important Linux Directories and a short description of what they contain.
These are most striking differences between Linux and other Operating Systems. There are more variations you will observe when switching to Linux and we will discuss them as we move along in our tutorials.
Linux vs Windows – Difference Between Them
Here is the main difference between Windows and Linux:
| Windows | Linux |
|---|---|
| Windows uses different data drives like C: D: E to stored files and folders. | Unix/Linux uses a tree like a hierarchical file system. |
| Windows has different drives like C: D: E | There are no drives in Linux |
| Hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered as devices | Peripherals like hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are also considered files in Linux/Unix |
| There are 4 types of user account types 1) Administrator, 2) Standard, 3) Child, 4) Guest | There are 3 types of user account types 1) Regular, 2) Root and 3) Service Account |
| Administrator user has all administrative privileges of computers. | Root user is the super user and has all administrative privileges. |
| In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder | Linux file naming convention is case sensitive. Thus, sample and SAMPLE are 2 different files in Linux/Unix operating system. |
| In windows, My Documents is default home directory. | For every user /home/username directory is created which is called his home directory. |