- Bluetooth Host Radio Support
- Bluetooth host controllers supported in Windows
- Forcing the Bluetooth stack to load if Windows cannot match the device ID (Windows Vista)
- Ensure in-box support for Bluetooth radios
- Should third-party INF files use the Microsoft-defined class GUID
- Why the Control Panel Bluetooth application is missing
- Why the Bluetooth icon might not appear in the taskbar
- Windows support for Bluetooth radio firmware updates
- Windows support for vendor-specific pass-through commands
- Windows support for vendor-supplied profiles
- Bluetooth profiles and protocols that are enabled by default
- Windows Bluetooth Profiles
- How Group Policy can block Bluetooth radio installation
- How to change the Device ID Profile record published by Windows
- Feedback
- Стек драйверов Bluetooth
Bluetooth Host Radio Support
This topic provides answers to typical questions about Bluetooth Radio support.
Bluetooth host controllers supported in Windows
With Windows, a Bluetooth radio can be packaged as an external dongle or embedded inside a computer but it must be connected to one of the computer’s USB ports. The Bluetooth stack that is included with Windows 7 and Windows Vista does not support Bluetooth radio connections over PCI, I2C, serial, Secure Digital I/O (SDIO), CompactFlash, or PC Card interfaces. In Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, radios connected over alternate transports can be added via a third-party bus driver. Refer to the Extensible Transport sections of the Bluetooth Devices Reference for more information.
Forcing the Bluetooth stack to load if Windows cannot match the device ID (Windows Vista)
A new Bluetooth radio might not match any of the device IDs in the Bluetooth INF (Bth.inf) that is included with Windows. This prevents Windows from loading a Bluetooth stack for the device. IHVs should ensure that their radio works with the native Bluetooth stack in one of the following ways:
- Create an INF for the radio that references Bth.inf. For an example of a vendor-specific INF file for a Bluetooth radio, see Appendix B: An Example of a Vendor-Provided INF File for Use in Windows Vista.
- Store an extended compat ID OS descriptor in the device firmware that specifies an appropriate compatible and subcompatible ID. For information about extended compat ID OS descriptors, see Microsoft OS Descriptors.
- Force the Bluetooth stack to load
The following procedure uses Device Manager to force the Bluetooth stack to load for a new radio:
- Run the Control Panel Device Manager application and identify the Bluetooth radio on the list of devices.
- To run the Update Driver Software Wizard, right-click the Bluetooth radio item and select Update Driver Software.
- Use the wizard to force the Bluetooth stack to install.
Ensure in-box support for Bluetooth radios
IHVs should take the following steps to ensure that their Bluetooth radios have in box support on Windows:
- Ensure that the radio supports the extended compat ID OS feature descriptor. For details, see Microsoft OS Descriptors.
- Obtain Windows Certification Program approval for the Bluetooth radio hardware and the associated INF file. For an example of a vendor-specific INF file for a Bluetooth radio, see Appendix B: An Example of a Vendor-Provided INF File for Use in Windows Vista.
- Use the Partner Center to make the INF file available through Windows Update
It is no longer possible to add radios to the in-box Bth.inf file.
Should third-party INF files use the Microsoft-defined class GUID
IHVs should use the Microsoft-defined class globally unique identifier (GUID) () for Bluetooth devices only in those INF files that reference the in-box Bluetooth INF file (Bth.inf). This means that the device uses the native Windows co installer, services, and notification area icon. IHVs that implement their own Bluetooth stack must create a vendor-specific class GUID and use the WLK test tools to ensure that the stack complies with the unclassified Windows Certification Program.
Why the Control Panel Bluetooth application is missing
The Control Panel Bluetooth application was incorporated into Devices and Printers. Thus, adjusting the Bluetooth radio settings, managing Bluetooth devices, and adding new Bluetooth devices can only be performed from within Devices and Printers.
Why the Bluetooth icon might not appear in the taskbar
If the Bluetooth icon does not appear in the taskbar, it could be due to one or more of the following reasons:
- The Bluetooth radio is turned off.
- The Bluetooth radio is in emulation mode.
- In the Bluetooth Settings dialog, the Show the Bluetooth icon in the notification area check box is not selected.
Windows support for Bluetooth radio firmware updates
Currently, the Bluetooth stack that is included with Windows does not directly support firmware updates. However, for Bluetooth radios connected through a USB port, Windows does support firmware updates in compliance with the USB Device Firmware Update (DFU) specification. IHVs can create a user-mode utility that communicates with their Bluetooth radio over the DFU interface to perform the firmware update and restart the radio.
Windows support for vendor-specific pass-through commands
Windows includes support for vendor-specific pass-through commands. These kernel-mode interfaces are documented in the WDK.
Windows support for vendor-supplied profiles
Windows supports vendor-supplied Bluetooth profiles. The GUIDs for those profiles that have been standardized by the Bluetooth SIG are included in the in box INF file (Bth.inf).
When users pair a Bluetooth device with a computer, the device’s profiles are compared to the profiles that are listed in Bth.inf. If the device profile does not match one of those profiles, users receive a dialog box that asks them to provide appropriate vendor software.
Vendors that want a vendor-specific profile must use their own GUID and reference it in a vendor-specific INF file. This INF file can use Include and Needs directives to reference the appropriate Bth.inf sections and directives. For an example of a vendor-specific INF file, see Appendix B: An Example of a Vendor-Provided INF File for Use in Windows Vista.
Bluetooth profiles and protocols that are enabled by default
The Bluetooth stack included with Windows provides in-box support for only some Bluetooth profiles. Vendors must implement the required services to support any other Bluetooth profiles, much as they do for USB and PCI. Windows can use the Bluetooth profiles that are enabled by default—referred to as supported profiles—to generate physical device objects (PDOs). This enables default loading of the drivers that are required to enable the profile. You can identify the supported profiles in the registry by looking at the SupportedServices and UnsupportedServices values under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Bthport \Parameters key.
The Bthport key is added to the registry only after you install a Bluetooth device.
The following table lists the profiles in Bth.inf that Windows supports.
| Service ID | Description |
|---|---|
| SPP | |
| DUN | |
| HID | |
| HCRP |
Windows Bluetooth Profiles
For a Bluetooth-enabled device or accessory to work with your PC that’s running Windows 10, the device needs to use one of the supported Bluetooth profiles. See the most current list at Supported Bluetooth profiles.
If IHVs do not want Windows to automatically generate a PDO for their device, they can add the service GUID to the list of unsupported services. For examples, see Bth.inf.
How Group Policy can block Bluetooth radio installation
For details on how to use Group Policy to block the installation of Bluetooth radios, see the «Prevent installation of prohibited devices» section of Step-by-Step Guide to Controlling Device Installation and Usage with Group Policy.
Use the following compatible IDs for the Bluetooth radio:
USB\Class_E0 (for USB based radios) MS_BTHX_BTHMINI (for non-USB radios)
This won’t remove Bluetooth driver support if it has already been installed. Also, this policy needs to be applied to the preinstall image.
How to change the Device ID Profile record published by Windows
The Device ID Profile defines an SDP record that can be used to provide identity information to remote devices. Previous and current Windows versions have used the Device ID record published on paired devices to provide device-specific Hardware IDs for generic Bluetooth services.
Windows also publishes a local Device ID record to identify the Windows device to remote Bluetooth devices. The default values can be adjusted by OEMs to better identify their specific Windows device. These values are defined as in the following table under the HKLM\System\CCS\services\BTHPORT\Parameters registry key:
| ValueName | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIDVendorIDSource | DWORD | 0x01 = Bluetooth SIG namespace 0x02 = USB Forum namespace | 0x01 |
| DIDVendorID | DWORD | OEM specified VendorID | 0x06 – Microsoft Vendor ID |
| DIDProductID | DWORD | OEM specified ProductID | 0x01 – Microsoft Windows |
| DIDVersion | DWORD | OEM specified product version | 0x0800 – Windows 8 |
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
Стек драйверов Bluetooth
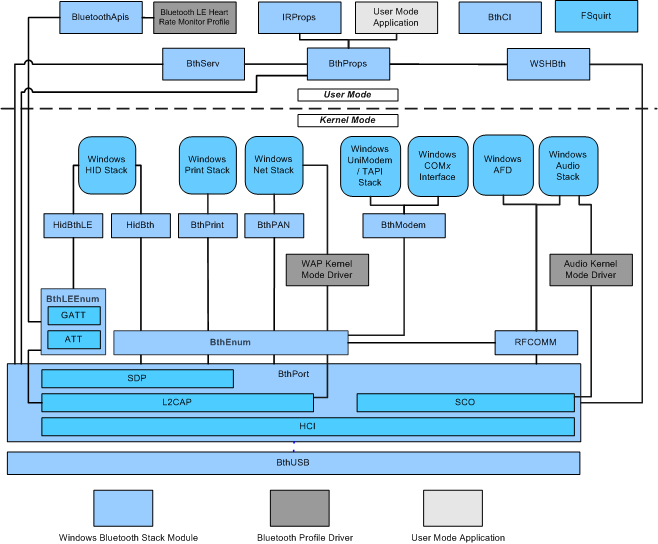
Стек драйверов Bluetooth состоит из основной части поддержки, предоставляемой корпорацией Майкрософт для протокола Bluetooth. С помощью этого стека устройства с поддержкой Bluetooth могут находить друг друга и устанавливать подключения. В таких подключениях устройства могут обмениваться данными и взаимодействовать друг с другом с помощью различных приложений.
На следующем рисунке показаны модули в стеке драйверов Bluetooth, а также возможные настраиваемые драйверы пользовательского режима и режима ядра, не включенные в Windows Vista и более поздних версий. Эти пользовательские драйверы называются драйверами профилей.
- Пользовательский режим
- Приложение в пользовательском режиме — приложение в пользовательском режиме, которое обращается к стеку драйверов Bluetooth через опубликованные API. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Сведения об Bluetooth документации по Windows SDK. Приложения пользовательского режима должны связываться с BthProps.lib, а не с IrProps.lib, чтобы использовать API, такие как BluetoothSetLocalServiceInfo.
- Драйвер режима ядра WAP. Компонент протокола беспроводного приложения (WAP) — это пример драйвера профиля, который взаимодействует между сетевым стеком Windows и BthPort, используя интерфейс L2CAP и, при необходимости, интерфейс SDP, содержащийся в L2CAP. Другие возможные профили включают профиль расширенного распространения аудио (A2DP), профиль удаленного управления аудио-видео (AVRCP), универсальный профиль распространения аудио-видео (GAVDP) и профиль общего доступа к ISDN (CIP).
- Драйвер режима ядра аудио— пример драйвера профиля, который взаимодействует между стеком звука Windows и BthPort, обращаюсь к интерфейсам SCO, содержащимся в последнем. Возможные профили включают профиль Hands Free (HFP), профиль гарнитуры (HSP), профиль беспроводной телефонии (CTP) и профиль intercom (ICP). Этот драйвер профиля входит в состав Windows, начиная с Windows 8.
- Профиль монитора частоты пульса Bluetooth LE — пример драйвера профиля Bluetooth LE, который взаимодействует с API Bluetooth Low Energy (LE).
Примечание BthEnum не создает PDO для служб, которые отображаются в разделе реестра UnsupportedServices , как указано в файле Bth.inf.
- Компонент HCI взаимодействует с локальным радиомодулем с поддержкой Bluetooth через интерфейс хост-контроллера (HCI), определенный в спецификации Bluetooth. Так как все радиомодулы с поддержкой Bluetooth реализуют спецификацию HCI, BthPort может обмениваться данными с любым радиомодулем с поддержкой Bluetooth, независимо от производителя или модели.
- Компонент SCO реализует протокол синхронного Connection-Oriented (SCO). Этот протокол поддерживает создание подключений типа «точка — точка» к удаленному устройству. Клиенты SCO взаимодействуют с интерфейсом SCO, создавая и отправляя блоки запросов Bluetooth (BRB).
- L2CAP реализует протокол управления логическими ссылками и адаптации Bluetooth. Этот протокол поддерживает создание канала без потерь для удаленного устройства. Клиенты L2CAP взаимодействуют с интерфейсом L2CAP, создавая и отправляя блоки запросов Bluetooth (BRB).
- SDP реализует протокол обнаружения служб Bluetooth.