- How To Install Wine 8.0 on Fedora 37/36
- Prerequisite
- Step 1: Configure Wine Repository
- Step 2: Install WineHQ on Fedora
- Step 3: Verify the Installation
- Step 4: Configure Wine
- Step 5: Running .exe file Using Wine
- Conclusion
- How to install Wine 7 on Fedora 35
- What’s new in Wine 7 release
- Benefits of Using Wine
- Related Articles
- Installing Wine on Fedora 35
- 1. Run System Updates
- 2. Install WineHQ repository on fedora 35
- 3. Install Wine 7 on Fedora 35
- Install Wine Stable branch on Fedora 35.
- Install wine Staging branch
- 4. Conclusion
- Wine
- Packages
- Configurations files
- Wine desktop files
- GUI for configuring the Wine registry (winecfg)
- Gui Wine script (winetricks)
- Wine prefix
- Install some basics/utils applications
- Bugs and problems
How To Install Wine 8.0 on Fedora 37/36
Wine is a compatibility layer that allows users to run Windows applications on Linux and other operating systems. WineHQ is the official distributor of the Wine project, which includes the latest stable version of Wine as well as additional features and enhancements.
Before proceeding with the installation, it is important to note that Wine is not an emulator, it does not emulate the Windows operating system. Instead, it provides a compatibility layer that allows Windows applications to run natively on Linux.
In this article, we will show you how to install Wine 8.0 stable release on Fedora Linux..
Prerequisite
You must have a sudo privileged account for the Wine installation on Fedora.
Wine required many development packages. First, we recommend upgrading all system packages using the following commands.
sudo dnf clean allsudo dnf update
Step 1: Configure Wine Repository
The first step in installing WineHQ on Fedora is to add the WineHQ repository to your system. This can be done by running the following commands. First, import the Winehq GPG key into your system.
sudo dnf -y install dnf-plugins-coresudo rpm --import https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
Next, add the Wine package repository to your system.
source /etc/os-releasesudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/fedora/$/winehq.repo
If you are running Fedora 35 or older version repository contains WineHQ 7 and older versions. So if you want to use Wine 8, you need to upgrade Fedora to the latest version.
Step 2: Install WineHQ on Fedora
You have configured the WineHQ yum repository on your Fedora system. The next step is to install WineHQ by running the following command:
sudo dnf install winehq-stable The above command will install a large number of packages as a dependency. The installation may take time as per your network speed. Enjoy a cup of coffee until the installation finishes.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
After finishing the installation process, Use the following command to check the version of wine installed on your system.
Step 4: Configure Wine
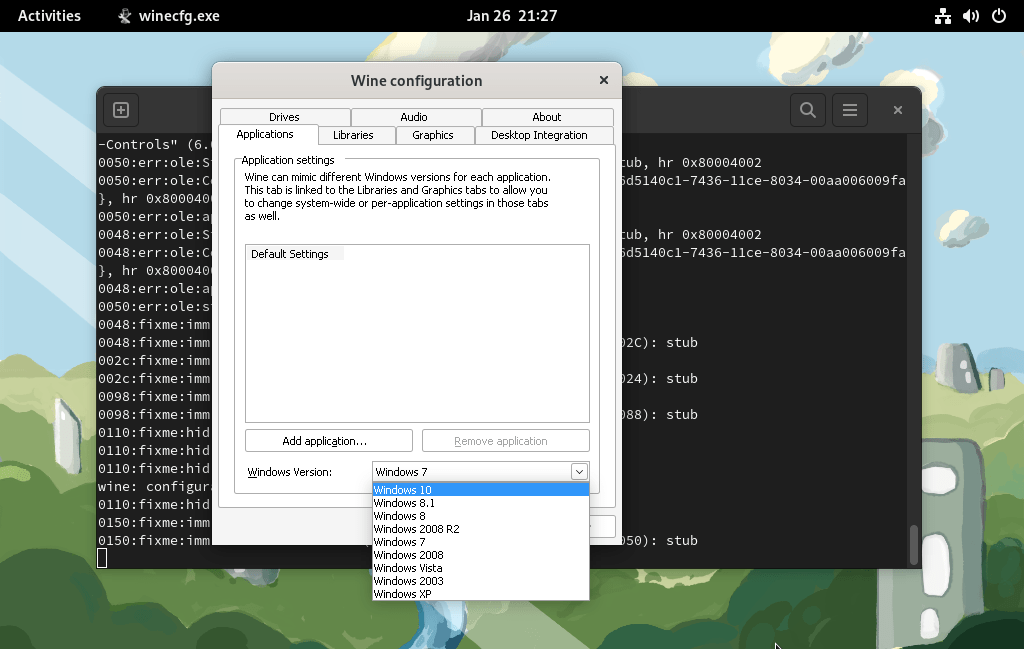
WineHQ is now installed on your system, but it is not yet configured. The next step is to configure Wine by running the following command:
This will open the Wine configuration window, where you can set various options such as the Windows version to emulate and the location of the virtual C drive.
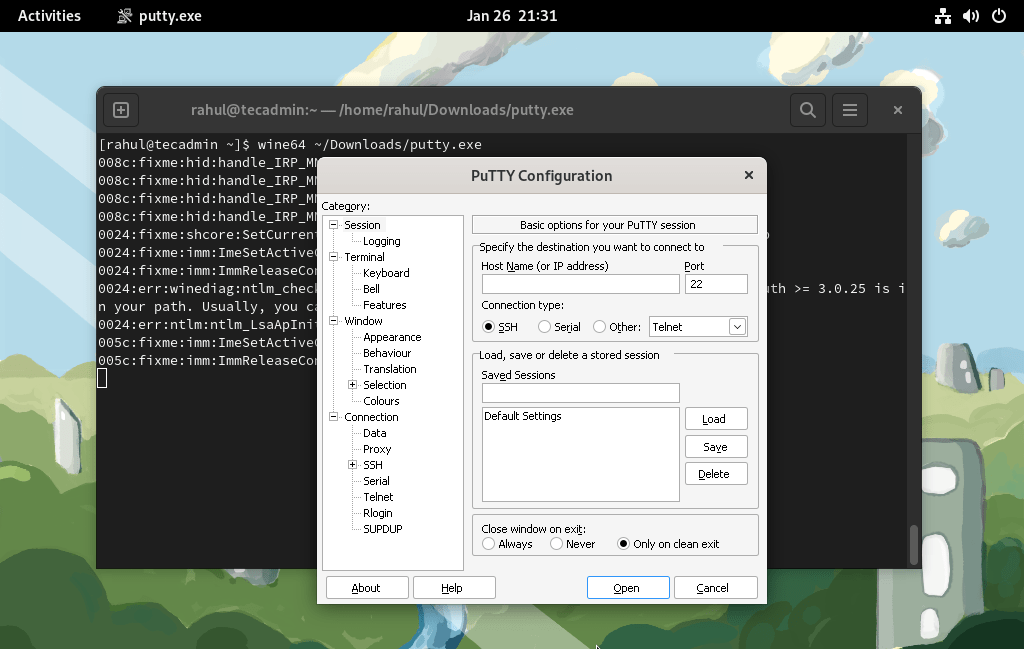
Step 5: Running .exe file Using Wine
For this example, I have downloaded the putty.exe file. Now use the wine utility to run this putty Windows application on your Fedora system.
Conclusion
In this article, we have shown you how to install WineHQ on Fedora Linux. With WineHQ, you can run Windows applications on Linux, making it easy to use your favorite Windows programs on your Linux system.
It’s worth noting that some applications may not work perfectly or may require additional configuration. Some applications may not work at all and compatibility with the new windows versions may not be available. However, you can always check the compatibility of specific applications on the official website of WineHQ.
How to install Wine 7 on Fedora 35
In this tutorial, we are going to install Wine 7 on Fedora 35.
Wine is a compatibility layer capable of running Windows applications on several POSIX-compliant operating systems i.e Linux, macOS, and BSD. Instead of simulating internal Windows logic like a virtual machine or emulator, Wine translates Windows API calls into POSIX calls instantly eliminating the performance and memory penalties of other methods and allowing you to integrate Windows applications in your desktop.
What’s new in Wine 7 release
- Reimplimentation of winMM joystick driver
- All unix libraries converted to the syscall-based libraries
Benefits of Using Wine
- Unix has made it possible to write powerful scripts, Wine makes it possible to call windows applications from scripts that can also laverage Unix environment.
- Wine makes it possible to access Windows applications remotely.
- Wine makes it possible to use thin clients i.e install Wine and you will easily connect to windows applications using x-terminal.
- Wine is open-source so you can easily extend to suite your needs.
- Wine can be used to make existing windows applications available on the web by using VNC and its Java/HTML5 client.
Related Articles
Installing Wine on Fedora 35
1. Run System Updates
To begin with we need to update our repositories to make them up to date. Open your terminal and type the following command;
When updates are complete, move ahead to install WineHQ packages.
2. Install WineHQ repository on fedora 35
Add the following WineHQ repository to Fedora 35. This will enable us to run wine with ease on our Fedora 35 workstation/server.
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/fedora/35/winehq.repoSample output will look like this;
Output Adding repo from: https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/fedora/35/winehq.repo3. Install Wine 7 on Fedora 35
We can now begin installing Wine 7 after completing the addition of the WineHQ repository to our system. We are going to install the Wine development branch. Run the following command on your terminal.
$ sudo dnf install winehq-develYou will see the following output.
Output Installing: winehq-devel x86_64 1:7.0.rc2-1.1 WineHQ 76 k Installing dependencies: SDL2 i686 2.0.18-2.fc35 updates 632 k SDL2 x86_64 2.0.18-2.fc35 updates 602 k alsa-lib i686 1.2.6.1-3.fc35 updates 529 k alsa-lib x86_64 1.2.6.1-3.fc35 updates 497 k avahi-libs i686 0.8-14.fc35 fedora 72 k avahi-libs x86_64 0.8-14.fc35 fedora 68 k bzip2-libs i686 1.0.8-9.fc35 fedora 40 k cairo i686 1.17.4-4.fc35 fedora 716 k cairo x86_64 1.17.4-4.fc35 fedora 664 kTo allow installation to continue press Y and enter command.
This command will install WineHQ development version and its many dependent packages.
Press Y again to allow WineHQ key to be added also. It will look like this;
Output $ WineHQ packages 114 kB/s | 3.1 kB 00:00 Importing GPG key 0xF987672F: Userid : "WineHQ packages [email protected]>" Fingerprint: D43F 6401 4536 9C51 D786 DDEA 76F1 A20F F987 672F From : https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key Is this ok [y/N]: y Key imported successfully Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded.Lastly, we can check the version of installed Wine on Fedora 35 with the following command;
I also want to show you how to install both stable and staging branches
Install Wine Stable branch on Fedora 35.
This is the recommended install because it has passed all tests. To install this branch run the following command on your command line;
$ sudo dnf install winehq-stableInstall wine Staging branch
To install this staging branch, use the following command.
$ sudo dnf install winehq-staging Now that we have completed the installation of Wine, we need to run the Wine program in order to start using it. To run the program on our terminal type the following;
4. Conclusion
Congratulations we have successfully installed Wine on our Fedora 35 Linux. If you faced any issues please feel free to contact us for assistance. Or you can consult WineHQ documentation.
Wine
Wine is an open source implementation of the Windows API on top of X and OpenGL.
Wine emulates the Windows runtime environment by translating Windows system calls into POSIX-compliant system calls, recreating the directory structure of Windows systems, and providing alternative implementations of Windows system libraries, system services through wineserver.
Packages
Fedora’s Wine packages are split up to allow for smaller installations. The wine meta package will bring with it the most important components of Wine. Expert users may want to pick specific components from the list here. The current versions of the Wine packages can also be seen on the Fedora packages application.
Configurations files
The default wine configuration files is stored in your $HOME directory:
Wine desktop files
Wine respects the XDG Base Directory Specification. $XDG_DATA_HOME defines the base directory relative to which user-specific data files should be stored. If $XDG_DATA_HOME is either not set or empty, it defaults to $HOME/.local/share .
Wine stores its desktop files in $XDG_DATA_HOME/applications/wine .
GUI for configuring the Wine registry (winecfg)
winecfg is a GUI configuration tool for Wine, designed to make life a little easier than editing the registry.
This utility is provide by the wine-common package. It allows you to:
- set the Windows version
- change the default libraries (DLLs) Wine loads
- modify graphics settings
- modify desktop integration related settings
- modify drive mappings
- change sound/audio settings
| Some applications do not work with the default Windows version which Wine offers. E.g.: Amazon Kindle Desktop Edition. |
Gui Wine script (winetricks)
Winetricks is a helper script to download and install various redistributable runtime libraries needed to run some programs in Wine. These may include replacements for components of Wine using closed source libraries.
sudo dnf install winetricksIt can download and install applications and libraries needed to run some programs in Wine, e.g., Adobe Digital Edition.
Wine prefix
A Wine prefix is a folder that contains all of the Wine configurations as well as all of the Windows pieces that Wine uses for compatibility, including libraries and a registry.
Some applications need a 32 or 64 wine prefix, this can be done in the following way:
WINEPREFIX="$HOME/" WINEARCH=winxx wine winebootTo use a wine prefix created before:
Install some basics/utils applications
How to install the follow applications under wine?
- use winetricks as descibed before and select install application in the menu «What you do you want to do?»
- in «Which package(s) would you like to install?» select adobe_diged4
- download from → Amazon Kindle
- install it
- use winecfg to change the default windows version so is 7 to a higher version
Bugs and problems
Before reporting bugs against Wine please make sure your system is fully up to date.
Also check if a newer version is available in the updates-testing repository.
dnf --enablerepo=updates-testing update wine
If you are using the proprietary graphics drivers please remove them from your system and try again, as they are known to cause problems.
When debugging Wine, your goal is to determine if the issue is one of code functionality or packaging in Fedora.
Check the Wine Application Database to see if your application is supported, or if there are known issues that match yours. Anything that falls into this category is a bug in upstream code functionality.
The next step is to see if the problem persists with a clean ~/.wine folder. To try this without losing your old configuration:
Afterwards try to trigger the bug again. Your original wine folder can be restored with:
rm -fr ~/.wine; mv ~/.wine-save ~/.wine
If your application still does not work but has been working in a previous version of wine it is probably a regression. Consider filling a bug in the upstream Wine-staging bug tracking system.
If you really think that your bug is Fedora-related, file a bug against the Wine component in Fedora’s bug tracking system.
All Fedora Documentation content available under CC BY-SA 4.0 or, when specifically noted, under another accepted free and open content license.
Last build: 2023-07-13 04:50:22 UTC | Last content update: 2022-10-03