- CentOS/RHEL
- Contents
- Installation
- Notes on EPEL 7
- Special Considerations for Red Hat
- Building from Source
- Releases Other Than 7
- For Release 7
- See Also
- How to Install Wine on RHEL-based Linux Distributions
- On this page
- Installing Wine Using Source Code in RHEL Systems
- Step 1: Installing Dependency Packages
- Step 2: Downloading the Wine Source Code
- Step 3: Extracting Wine Source Code
- Step 4: Compiling Wine from Sources
- Install Wine on Fedora Linux Using Wine Repository
- How to Use Wine to Run Windows Apps & Games
CentOS/RHEL
CentOS is a community-based rebuild of the source published by Red Hat with each release. Consequently, Red Hat itself and other community rebuilds like Scientific Linux should have very similar instructions. In fact, at the very beginning of 2014, Red Hat Inc. announced that they would officially sponsor and collaborate with the CentOS project, much as they do with Fedora.
Rather than sudo, a common convention in Red Hat and related distros has been to acquire super-user rights with su -l, then carry out the necessary actions. The installation and repo-management commands listed here presume you’re in a terminal session as a super-user. However, remember that you should never build wine as root or a super-user, especially on Red Hat-like distros where it can particularly wreak havoc.
Contents
Installation
For those on release 7, be sure to read the next sub-section. As of Mar. 2016, installing wine on CentOS 7 is a bit more involved; read below for the reasons.
For any work with packages, you’ll definitely want to be familiar with your package manager. Up through release 7, the standard package manager has been yum, but with Fedora adopting the leaner, meaner dnf package manager, there’s a good chance this will be increasingly preferred, possibly even the default in release 8.
Since some releases of enterprise linux might not even include a wine package by default, your best bet for finding a fresh package is probably Fedora’s EPEL repo («Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux»). This repo contains updates and extra packages backported from Fedora to more stable Red Hat-based distros. If you want to enable the EPEL repo, all you need to do is install the epel-release meta-package:
yum install epel-release (if using yum) dnf install epel-release (if using dnf)
Then if you want the wine package from the EPEL, it’s as simple as another install command:
yum install wine (yum users) dnf install wine (dnf users)
If your distro does include a wine package by default, you should be able to use the above install command without even enabling the EPEL.
Notes on EPEL 7
At the time of this writing, EPEL 7 still has no 32-bit packages (including wine and its dependencies). There is a 64-bit version of wine, but without the 32-bit libraries needed for WoW64 capabilities, it cannot support any 32-bit Windows apps (the vast majority) and even many 64-bit ones (that still include 32-bit components).
This is primarily because with release 7, Red Hat didn’t have enough customer demand to justify an i386 build. While Red Hat itself still comes with lean multilib and 32-bit support for legacy needs, this is part of Red Hat’s release process, not the packages themselves. Therefore CentOS 7 had to develop its own workflow for building an i386 release, a process that was completed in Oct 2015.
With its i386 release, CentOS has cleared a major hurdle on the way to an EPEL with 32-bit libraries, and now the ball is in the Fedora project’s court (as the maintainers of the EPEL). Once a i386 version of the EPEL becomes available, you should be able to follow the same instructions above to install a fully functional wine package for CentOS 7 and its siblings.
Thankfully, this also means that EPEL 8 shouldn’t suffer from this same problem. In the meantime though, you can keep reading for some hints on getting a recent version of wine from the source code.
Special Considerations for Red Hat
Those with a Red Hat subscription should have access to enhanced help and support, but we wanted to provide some very quick notes on enabling the EPEL for your system. Before installing the epel-release package, you’ll first need to activate some additional repositories.
On release 6 and older, which used the Red Hat Network Classic system for package subscriptions, you need to activate the optional repo with rhn-channel
rhn-channel -a -c rhel-6-server-optional-rpms -u -p
Starting with release 7 and the Subscription Manager system, you’ll need to activate both the optional and extras repos with subscription-manager
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-optional-rpms subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
As for source RPMs signed by Red Hat, there doesn’t seem to be much public-facing documentation. With a subscription, you should be able to login and browse the repos; this post on LWN also has some background.
Building from Source
Now if you want a bleeding-edge wine release, or you just want to work with the source code, Building Wine from source is probably your best bet. This has a few idiosyncrasies no matter which version of CentOS / Scientific Linux you may be on, which we’ll go over.
One issue with extremely stable distros like CentOS is that your libraries may be older versions than those required by the newest wine release or the tip of the WineHQ git tree. In that case, you may need to debug the build process a little and possibly build newer versions of a library or two from source.
If you do build wine from source, it’s strongly suggested that you don’t install it into your system but rather run it from within the build-directory.
Releases Other Than 7
On releases 5 and 6 (and hopefully 8+) of CentOS, multilib capabilities should make installing the necessary build dependencies a breeze (no chroot needed). you just have to find them first. One approach is the trial-and-error method of simply re-running configure from the wine source code, installing whatever libraries it complains are missing.
Another method is to use a build-dependency tool for your package manager. If that’s yum, you’ll need to install the yum-utils package, while dnf on the other hand needs dnf-plugins-core. One minor annoyance is that if you haven’t used source repos before on CentOS, you’ll also need to enable those in your package manager. Otherwise your builddep tool won’t be able to automatically resolve dependencies.
yum-config-manager --enable epel-source (for yum users) dnf config-manager --set-enabled epel-source (for dnf users)
- For packages actually in CentOS proper. it’s a bit more involved. You’ll essentially need to:
- Get a .repo file for your distro’s source-RPMs
- Copy it into your /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory
- Enable the various repos with a config-manager command like above
For now, CentOS Bug #1646 is probably the best source for what your .repo file should look like and other details. However, we may provide an updated .repo file for further refinement in the future.
Once you do have the source repos enabled, the actual installation should take only a single command:
yum-builddep wine (for yum users) dnf builddep wine (for dnf users)
Anyone that has recently built the latest version of wine from source on CentOS / Scientific Linux / Red Hat is welcome to list all the dependencies here. Then other users can try copying the list and passing it directly to yum or dnf to install any build deps. However, note that these lists are often out-of-date or incomplete, in which case you’ll have to fall back on one of the previous methods.
For Release 7
For the same reasons that a functional wine package in EPEL 7 is still a no-go, it used to be a labyrinth trying to build wine on CentOS 7. The same lack of 32-bit libraries mentioned above is still a potential obstacle. Fortunately, most of the necessary libraries are part of the CentOS base repository, so with the 32-bit release of CentOS 7, only a few extra libraries need to be built manually.
According to user «gcomes» on the CentOS forums, as of Feb. 2016, the only two libraries not provided in the i386 version of CentOS 7 are openal-soft and nss-mdns. You should only need to install the i386 release of CentOS (possibly to a chroot or container) and wine’s dependencies, compile and install these additional two libraries, then build wine from source. You can package the build results as a vanilla 32-bit RPM for your amd64 system.
If you want a WoW64 version, that should be possible too. Just place a completed build directory for 64-bit wine somewhere your 32-bit image can still access, then follow the Shared WoW64 instructions to complete your build.
The multilib capabilities of Red Hat-based distros should theoretically allow installing packages from i386 CentOS into an existing amd64 installation, then building everything without a chroot. However, we have not tested this yet.
See Also
Some Notes for Package Management on Red Hat:
How to Install Wine on RHEL-based Linux Distributions
Wine is an open-source and free application for Linux that enables users to run any windows based software and games on Unix/Linux-like operating system.
Recently, the Wine team proudly announced the stable release of 7.0 and made available for download in source and binary packages for various distributions such as Linux, Windows and Mac.
This release describes a year of development effort and over 9,100 individual changes, which includes a large number of enhancements that are recorded in the release notes below. The main highlights are:
- Most modules converted to PE format.
- Greater theming support, with a bundled theme for a more modern look.
- Largely improved HID stack and joystick support.
- New WoW64 architecture.
- Various bug fixes.
In this article, we will guide you on the simplest way to install the latest release of Wine 7.0 version in RHEL-based distributions such as CentOS Stream, Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux using source code (difficult and only suitable for experts) and on Fedora Linux using official wine repository (easy and recommended for new users).
On this page
Installing Wine Using Source Code in RHEL Systems
Step 1: Installing Dependency Packages
We need to install ‘Development Tools‘ with some core development tools such as GCC, flex, bison, debuggers, etc. this software is must required to compile and build new packages, install them using YUM command.
# yum -y groupinstall 'Development Tools' # yum install gcc libX11-devel freetype-devel zlib-devel libxcb-devel libxslt-devel libgcrypt-devel libxml2-devel gnutls-devel libpng-devel libjpeg-turbo-devel libtiff-devel dbus-devel fontconfig-devel
# dnf -y groupinstall 'Development Tools' # dnf -y install gcc libX11-devel freetype-devel zlib-devel libxcb-devel libxslt-devel libgcrypt-devel libxml2-devel gnutls-devel libpng-devel libjpeg-turbo-devel libtiff-devel dbus-devel fontconfig-devel
Step 2: Downloading the Wine Source Code
Download the source file using wget command under /tmp directory as a normal User.
$ cd /tmp $ wget http://dl.winehq.org/wine/source/7.0/wine-7.0.tar.xz
Step 3: Extracting Wine Source Code
Once the file is downloaded under /tmp directory, use the below tar command to extract it.
$ tar -xvf wine-7.0.tar.xz -C /tmp/
Step 4: Compiling Wine from Sources
It is recommended to compile and build a Wine installer as a normal User. Run the following commands as a normal user.
Note: The installer might take up to 20-30 minutes and in the middle, it will ask you to enter the root password.
---------- On 64-bit Systems ---------- $ cd wine-7.0/ $ ./configure --enable-win64 $ make # make install [Run as root User] ---------- On 32-bit Systems ---------- $ cd wine-7.0/ $ ./configure $ make # make install [Run as root User]
Install Wine on Fedora Linux Using Wine Repository
If you are using the latest version of Fedora Linux, you can install Wine using the official Wine repository as shown.
---------- On Fedora 36 ---------- # dnf config-manager --add-repo https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/fedora/36/winehq.repo # dnf install winehq-stable ---------- On Fedora 35 ---------- # dnf config-manager --add-repo https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/fedora/35/winehq.repo # dnf install winehq-stable
How to Use Wine to Run Windows Apps & Games
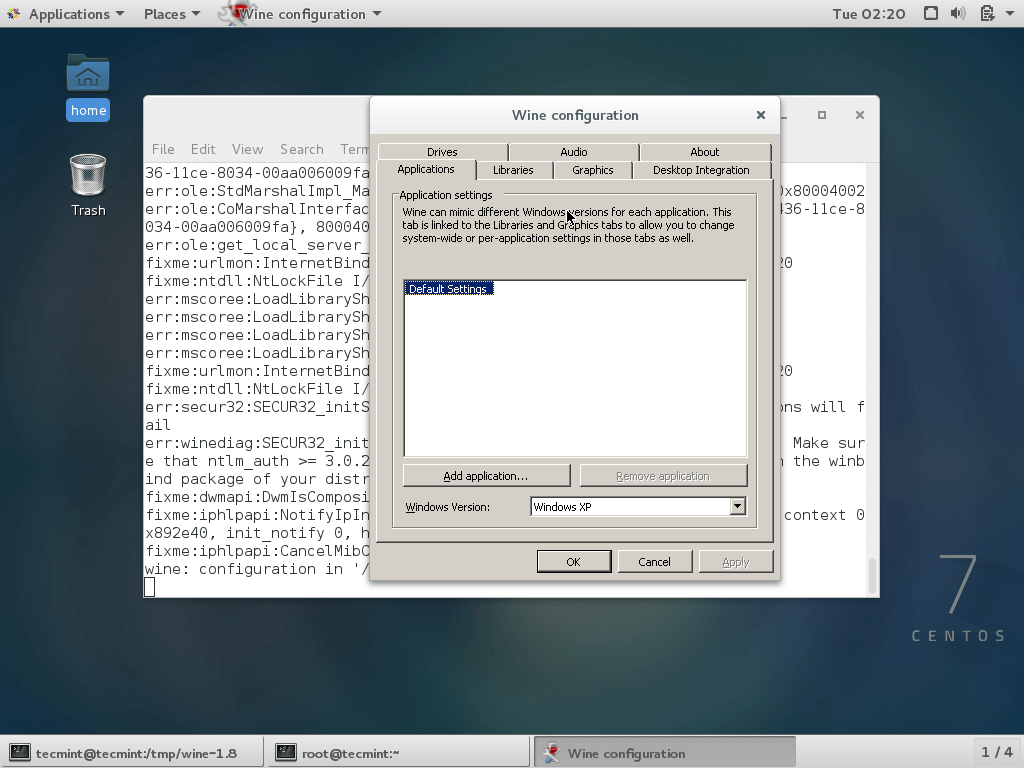
Once the installation completes run the “winecfg” configuration tool from GNOME desktop to see the supported configuration. If you don’t have any of the desktops, you can install it by using the below command as the root user.
# dnf groupinstall workstation OR # yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop"
Once the X Window System installed, run the command as a normal user to see wine configuration.
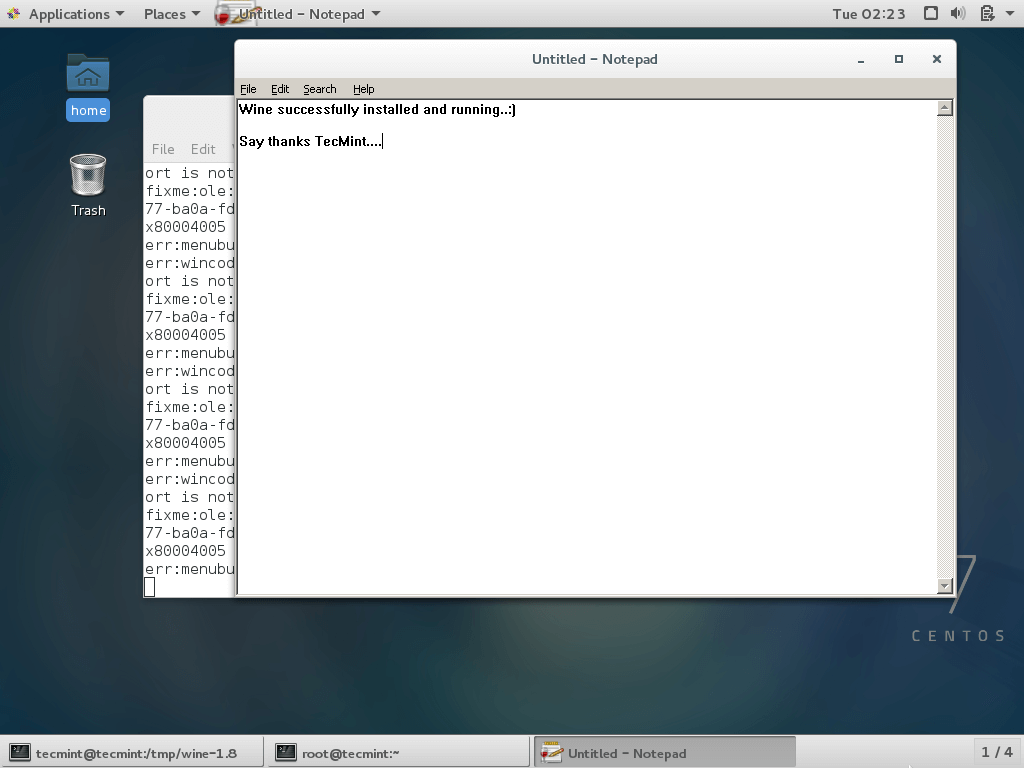
To run the Wine, you must specify the full path to the executable program or program name as shown in the example below.
--------- On 32-bit Systems --------- $ wine notepad $ wine c:\\windows\\notepad.exe
--------- On 64-bit Systems --------- $ wine64 notepad $ wine64 c:\\windows\\notepad.exe
Wine is not perfect, because while using wine we see so many programs crashes. I think the wine team will soon fix all bugs in their upcoming version meanwhile do share your comments using our below form.