- Getting Started with Python Programming and Scripting in Linux – Part 1
- Install Python on Linux
- Install Python IDLE on Linux
- Do Basic Operations with Python on Linux
- A Brief Comment About Object-Oriented Programming
- Illustrating Methods and Properties of Objects: Lists in Python
- How to Run Python Scripts in Linux
- Python scripts
- Working with a Python script
- Writing a sample Python code
- Running the Python script
- Bash-style Python script
- Location of Python interpreter
- Creating a shell script
- Writing a sample shell script
- Running the script
- Final thought
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
Getting Started with Python Programming and Scripting in Linux – Part 1
It has been said (and often required by recruitment agencies) that system administrators need to be proficient in a scripting language. While most of us may be comfortable using Bash (or other Linux shells of our choice) to run command-line scripts, a powerful language such as Python can add several benefits.
To begin with, Python allows us to access the tools of the command-line environment and to make use of Object Oriented Programming features (more on this later in this article).
On top of it, learning Python can boost your career in the fields of creating desktop applications and learning data science.
Being so easy to learn, so vastly used, and having a plethora of ready-to-use modules (external files that contain Python statements), no wonder Python is the preferred language to teach programming to first-year computer science students in the United States.
In this 2-article series, we will review the fundamentals of Python in hopes that you will find it useful as a springboard to get you started with programming and as a quick reference guide afterward.
That said, let’s get started.
Install Python on Linux
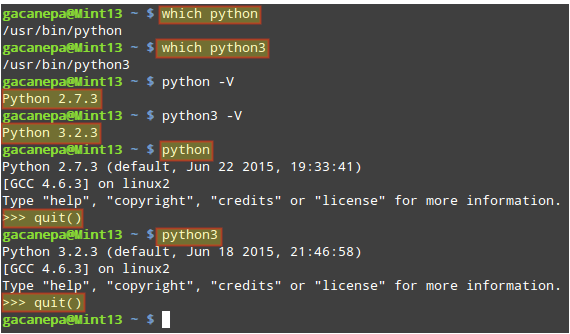
Python versions 2.x and 3.x are usually available in most modern Linux distributions out of the box. You can enter a Python shell by typing python or python3 in your terminal emulator and exit with quit() :
$ which python $ which python3 $ python -v $ python3 -v $ python >>> quit() $ python3 >>> quit()
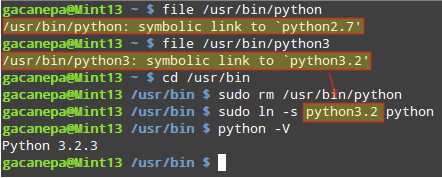
If you want to discard Python 2.x and use 3.x instead when you type python, you can modify the corresponding symbolic links as follows:
$ sudo rm /usr/bin/python $ cd /usr/bin $ ln -s python3.2 python # Choose the Python 3.x binary here
By the way, it is important to note that although versions 2.x are still used, they are not actively maintained. For that reason, you may want to consider switching to 3.x as indicated above. Since there are some syntax differences between 2.x and 3.x, we will focus on the latter in this series.
To install Python 3.x on your respective Linux distributions, run:
$ sudo apt install python3 [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install python3 [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a dev-lang/python [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add python3 [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S python3 [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install python3 [On OpenSUSE]
Install Python IDLE on Linux
Another way you can use Python in Linux is through the IDLE (the Python Integrated Development Environment), a graphical user interface for writing Python code.
$ sudo apt install idle [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install idle [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo apk add idle [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S idle [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install idle [On OpenSUSE]
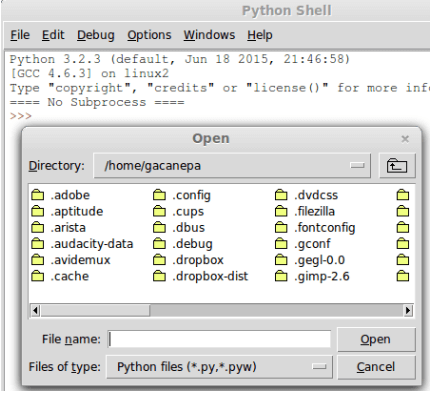
Once installed, you will see the following screen after launching the IDLE. While it resembles the Python shell, you can do more with the IDLE than with the shell.
1. open external files easily (File → Open).
2) copy (Ctrl + C) and paste (Ctrl + V) text, 3) find and replace text, 4) show possible completions (a feature known as Intellisense or Autocompletion in other IDEs), 5) change the font type and size, and much more.
On top of this, you can use IDLE to create desktop applications.
Since we will not be developing a desktop application in this 2-article series, feel free to choose between the IDLE and the Python shell to follow the examples.
Do Basic Operations with Python on Linux
As is to be expected, you can perform arithmetic operations (feel free to use as many parentheses as needed to perform all the operations you want!) and manipulate text strings very easily with Python.
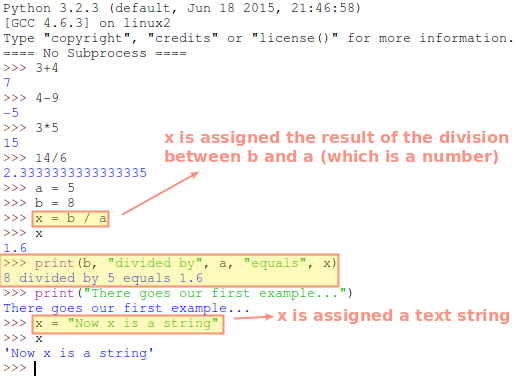
You can also assign the results of operations to variables and display them on the screen. A handy feature in Python is concatenation – just supply the values of variables and/or strings in a comma-delimited list (inside parentheses) to the print function and it will return the sentence composed by the items in the sequence:
>>> a = 5 >>> b = 8 >>> x = b / a >>> x 1.6 >>> print(b, "divided by", a, "equals", x)
Note that you can mix variables of different types (numbers, strings, booleans, etc) and once you have assigned a value to a variable you can change the data type without problems later (for this reason Python is said to be a dynamically typed language).
If you attempt to do this in a statically typed language (such as Java or C#), an error will be thrown.
A Brief Comment About Object-Oriented Programming
In Object Oriented Programming (OOP), all entities in a program are represented as objects and thus they can interact with others. As such, they have properties and most of them can perform actions (known as methods).
For example, let’s suppose we want to create a dog object. Some of the possible properties are color, breed, age, etc, whereas some of the actions a dog can perform are bark(), eat(), sleep(), and many others.
Methods names, as you can see, are followed by a set of parentheses which may (or may not) contain one (or more) arguments (values that are passed to the method).
Let’s illustrate these concepts with one of the basic object types in Python: lists.
Illustrating Methods and Properties of Objects: Lists in Python
A list is an ordered group of items, which do not necessarily have to be all of the same data types. To create an empty list named rockBands, use a pair of square brackets as follows:
To append an item to the end of the list, pass the item to the append() method as follows:
>>> rockBands = [] >>> rockBands.append("The Beatles") >>> rockBands.append("Pink Floyd") >>> rockBands.append("The Rolling Stones") To remove an item from the list, we can pass the specific element to the remove() method, or the position of the element (count starts at zero) in the list to pop() .
In other words, we can use either of the following options to remove “The Beatles” from the list:
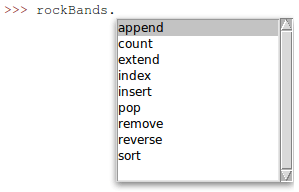
>>> rockBands.remove("The Beatles") or >>> rockBands.pop(0) You can display the list of available methods for an object by pressing Ctrl + Space once you’ve typed the name followed by a dot:
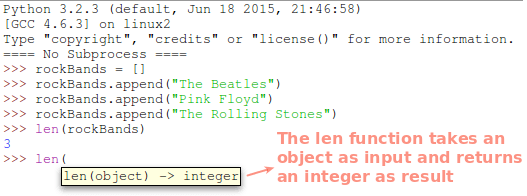
A property of a list object is the number of items it contains. It is actually called length and is invoked by passing the list as an argument to the len built-in function (by the way, the print statement, which we exemplified earlier-, is another Python built-in function).
If you type len followed by opening parentheses in the IDLE, you will see the default syntax of the function:
Now, what about the individual items on the list? Do they have methods and properties as well? The answer is yes. For example, you can convert a string item to uppercase and get the number of characters it contains as follows:
>>> rockBands[0].upper() 'THE BEATLES' >>> len(rockBands[0]) 11
Summary
In this article, we have provided a brief introduction to Python, its command-line shell, and the IDLE, and demonstrated how to perform arithmetic calculations, how to store values in variables, how to print back those values to the screen (either on its own or as part of a concatenation), and explained through a practical example what are the methods and properties of an object.
In the next article, we will discuss control flow with conditionals and loops. We will also demonstrate how to use what we have learned to write a script to help us in our sysadmin tasks.
Does Python sound like something you would like to learn more about? Stay tuned for the second part in this series (where among other things we will combine the bounties of Python and command-line tools in a script), and also consider buying the best udemy python courses to upgrade your knowledge.
As always, you can count on us if you have any questions about this article. Just send us a message using the contact form below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
How to Run Python Scripts in Linux
Python is one of the most popular programming languages of all. It’s an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language that features dynamic semantics. If you’re using Linux, then you’ll come across Python scripts quite frequently.
One of the most basic and crucial things to learn is running a Python script when learning or working with Python. Because Python is an interpreted language, it requires the Python interpreter to execute any Python code. Depending on the type of script, there are a couple of ways you can execute it.
This guide will showcase executing a sample Python script.
Python scripts
Any script is a text file containing the code. The file can then be run using an interpreter. The same goes for any Python script.
Generally, a Python script will have the file extension PY. However, there’s another way of writing a Python script: embedding Python codes into a bash script.
Either way, you need to have the Python package installed in your system. Because it’s a popular programming language, all Linux distros offer pre-built Python binaries directly from the official package servers. Distros like Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Pop! OS etc., comes with Python pre-installed. The package name should be “python” or “python3″ for any other distros”.
Working with a Python script
Creating a sample Python script
For demonstration, let’s make a quick Python script. Open up the terminal and create a file named sample-script.py.
To be able to run the script, it must be marked as an executable file. Mark the file as an executable.
Check the file permission to verify if it worked.
Writing a sample Python code
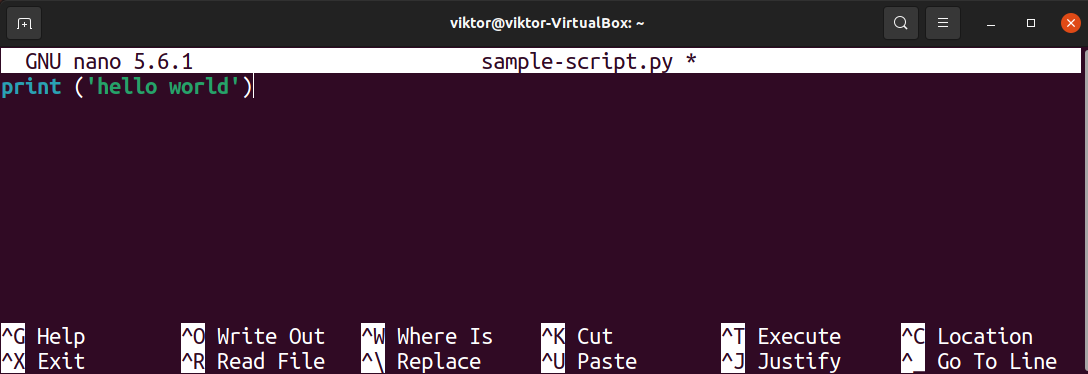
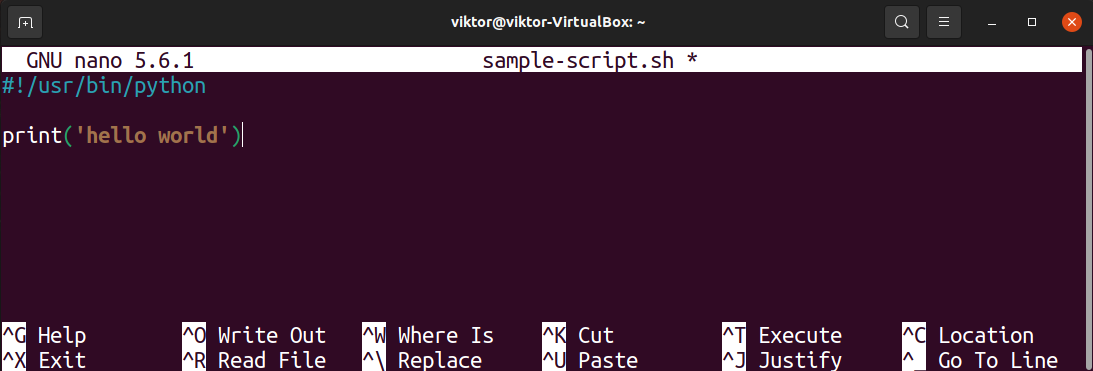
Now, we’re going to put some code in the script. Open up the file in any text editor. For demonstration, I’m going to be using the nano text editor.
We’ll place a simple program that prints “hello world” on the console screen.
Save the file and close the editor.
Running the Python script
Finally, we can run the script. Call the Python interpreter and pass the location of the file.
Bash-style Python script
So far, we’ve seen the default way of running a Python script. However, there’s an unconventional way of writing and running a Python script as a shell script.
Generally, a shell script contains a list of commands that are interpreted and executed by a shell (bash, zsh, fish shell, etc.). A typical shell script uses shebang to declare the desired interpreter for the script.
We can take this structure to our advantage. We’ll declare the Python interpreter as the desired interpreter for our code. The body of the script will contain the desired Python scripts. Any modern shell will execute the script with the Python interpreter.
The structure will look something like this.
Location of Python interpreter
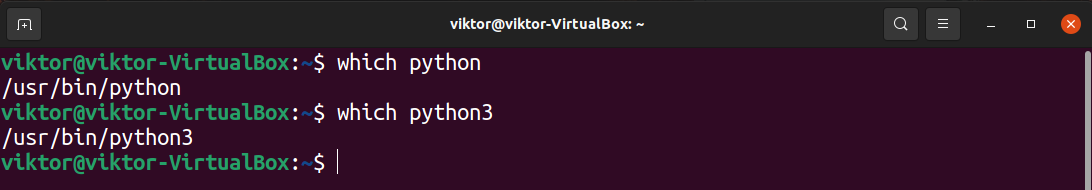
The shebang requires the path of the interpreter. It will tell the shell where to look for the interpreter. Generally, a Python interpreter is available as the command “python” or “python3”. Python 2 is deprecated, so it’s not recommended to use it anymore (except in very specific situations).
To find the location of the Python interpreter, use the which command. It finds the location of the binary of a command.
Creating a shell script
Similar to how we created the Python script, let’s create an empty shell script.
Mark the script as an executable file.
Writing a sample shell script
Open the script file in a text editor.
First, introduce the shebang with the location of the interpreter.
We’ll write a simple Python program that prints “hello world” on the next line.
Save the file and close the editor.
Running the script
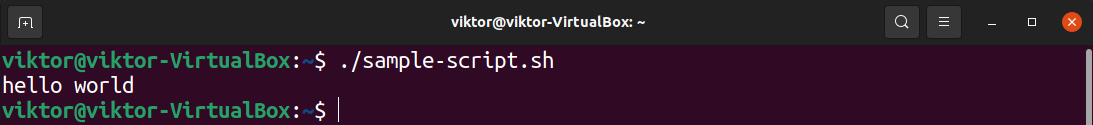
Run the script as you’d run a shell script.
Final thought
It needs to be passed on to the interpreter to run a Python code. Using this principle, we can use various types of scripts to run our Python code. This guide demonstrated running Python scripts directly (filename.py scripts) or indirectly (filename.sh).
In Linux, scripts are generally used to automate certain tasks. If the task needs to be repeated regularly, it can also be automated with the help of crontab. Learn more about using crontab to automate various tasks.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.